IPC 进程间通信 interprocess communicate
三大类:
1、古老的通信方式
无名管道 有名管道 信号
2、IPC对象通信 systemvBSD suse fedora kernel.org
消息队列(用的相对少,这里不讨论)
共享内存
信号量集
3、socket通信
网络通信
线程信号,posix sem_init
特列:古老的通信方式中信号是唯一的异步通信
所有的通信方式中共享内存是唯一的最高效
管道==》无名管道、有名管道
无名管道 ===》pipe ==》只能给有亲缘关系进程通信
有名管道===》fifo==》可以给任意单机进程通信
无名管道
1、管道是半双工的工作模式
2、所有的管道都是特殊的文件不支持定位操作。Iseek->>fd fseek->>FILE*
3、管道是特殊文件,读写使用文件IO。fgets,fread,fgetc,(这个有缓冲区)
open,read,write,close(首选)
1,读端存在,一直向管道中去写,超过64k,写会阻塞。
2.写端是存在的,读管道,如果管道为空的话,读会阻塞。
3.管道破裂,,读端关闭,写管道。
4.read0,写端关闭,如果管道没有内容,read;
使用框架:
创建管道==》读写管道==》关闭管道
1、无名管道===》管道的特例===>pipe函数
特性:
1.1亲缘关系进程使用
1.2 有固定的读写端
流程:
创建并打开管道:pipe函数
#include <unistd.h>
int pipe(int pipefd[2]);
功能:创建并打开一个无名管道
参数:pipefd[0]==>无名管道的固定读端读堵塞:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{int fd[2]={0};int ret = pipe(fd);if(-1==ret){perror("pipe");return 1;}pid_t pid =fork();if(pid>0){close(fd[0]);char buf[]="hello,child";sleep(3);write(fd[1], buf,sizeof(buf)+1);}else if(pid==0){close(fd[1]);char buf[50]={0};read(fd[0], buf, sizeof(buf));printf("child,buf :%s\n",buf);}else{perror("fork");return 1;}return 0;
}写堵塞:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{int fd[2]={0};// create pipe + open pipe int ret = pipe(fd);if(-1 == ret){perror("pipe");return 1;}pid_t pid = fork();if(pid>0){//write fd close(fd[0]);char buf[1024]={0};memset(buf,'a',sizeof(buf));int i = 0 ;for(i=0;i<65;i++){write(fd[1],buf,sizeof(buf));printf("i is %d\n",i);}}else if(0==pid){// read onlyclose(fd[1]);sleep(5);char buf[50]={0};read(fd[0],buf,sizeof(buf));printf("child ,buf:%s\n",buf);}else {perror("fork");return 1;}return 0;
}注意:管道的创建必须在fork之前
有名管道
有名管道===》fifo==》有文件名称的管道。 文件系统中可见
框架:
创建有名管道==》打开有名管道==》读写管道==》关闭管道==》卸载有名管道
有名管道的打开,会堵塞。
1.创建:mkfifo
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
remove0;int mkfifo(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
功能:在指定的pathname路径+名称下创建一个权限为mode的有名管道文件。
参数:pathname要创建的有名管道路径+名称mode 8进制文件权限。
返回值:成功0失败-1;2.打开有名管道 open
注意:该函数使用的时候要注意打开方式,
因为管道是半双工模式,所有打开方式直接决定
当前进程的读写方式。
一般只有如下方式:
int fd-read = open("./fifo",O_RDONLY); ==>fd 是固定读端
int fd-write = open("./fifo",O_WRONLY); ==>fd 是固定写端
不能是O_RDWR方式打开文件。
不能有O_CREAT选项,因为创建管道有指定的mkfifo函数3、管道的读写:文件IO
读: read(fd-read,buff,sizeof(buff);
写 : write(fd-write,buff,sizeof(buff);4、关闭管道:
close(fd)
5、卸载管道:remove()
int unlink(const char *pathname);
功能:将指定的pathname管道文件卸载,同时
从文件系统中删除。
参数:ptahtname 要卸载的有名管道
返回值:成功0
失败-1;进程间通信===》信号通信
应用:异步通信(时间随机)。中断(被更高优先级的进程打断,等其工作完之后再回到本程序)。
1~64;32应用编程。
信号处理,忽略9和19.
共享内存
IPC对象操作通用框架:
Ox ftok
key值 ==>申请 ==》读写 ==》关闭 ==》卸载
key值:===》唯一键值
创建方式有三种:
1、IPC_PRIVATE固定的私有键值,其值等于 OxO,一般用于有亲缘关系的进程间使用。
2、ftok(创建临时键值。
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
"/etc"!
key_t ftok(const char *pathname, int proj_id);
功能:通过该函数可以将pathname指定的路径用来以
proj_id生成唯一的临时键值。
参数:pathname 路径+名称===》任意文件,只要不会
被删除重建即可。
proj_id 整形的数字,一般用ASCll码的单字符
表示与参数1的运算。
返回值:成功返回唯一键值
失败-1;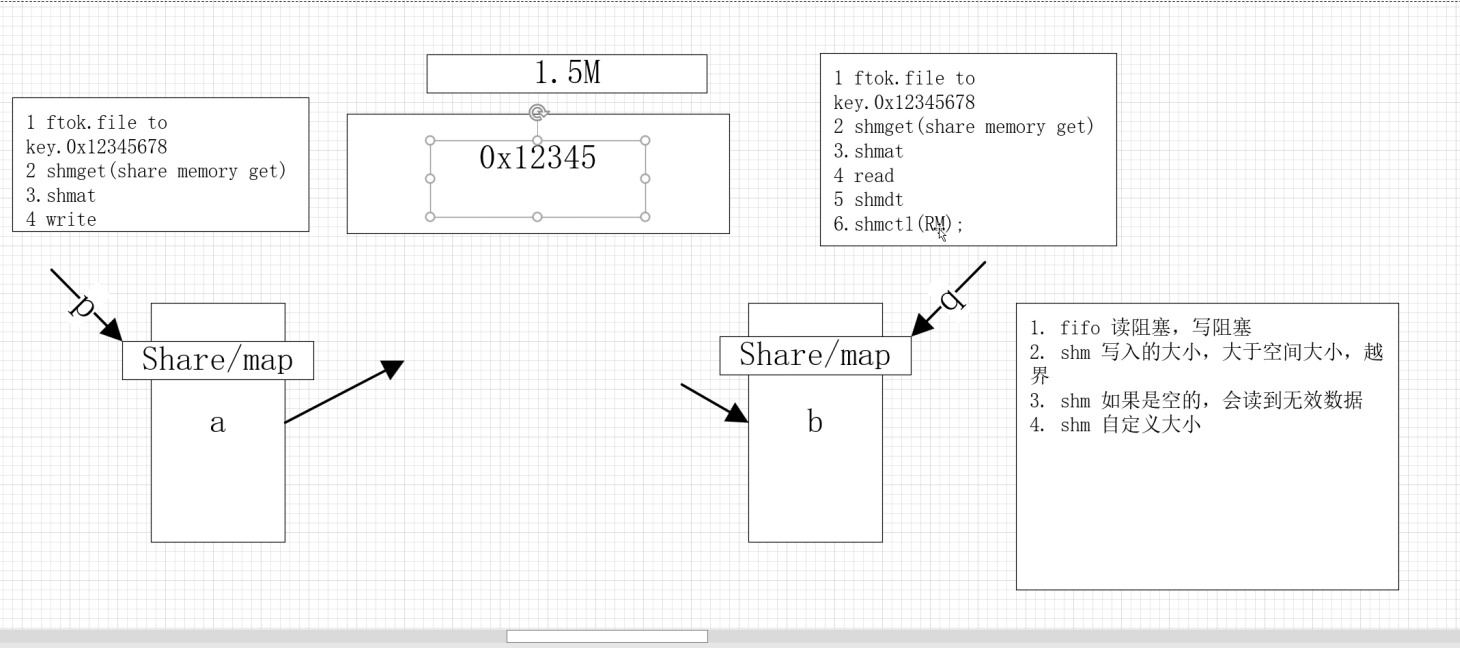
ipcs :进程间通信命令显示
ipcrm:进程间通信的删除
eg:
写:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{key_t key = ftok("./", '!');if (-1 == key){perror("ftok");return 1;}printf("key is 0x%x\n", key);int shmid = shmget(key, 4096, IPC_CREAT | 0666);if (-1 == shmid){perror("shmid");return 1;}void *p = shmat(shmid, NULL, !SHM_RDONLY);if ((void *)-1 == p){perror("shmat");return 1;}char buf[] = "hello,this is shm test";// strcpy(p,buf);memcpy(p, buf, strlen(buf));shmdt(p);return 0;
}读:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/ipc.h>
#include <sys/shm.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{key_t key = ftok("./", '!');if (-1 == key){perror("ftok");return 1;}printf("key is 0x%x\n", key);int shmid = shmget(key, 4096, IPC_CREAT | 0666);if (-1 == shmid){perror("shmid");return 1;}void *p = shmat(shmid, NULL, !SHM_RDONLY);if ((void *)-1 == p){perror("shmat");return 1;}char buf[4096] = {0};// strcpy(p,buf);memcpy(buf, p, sizeof(buf));printf("buf %s\n", buf);shmdt(p);// shmctl(shmid, IPC_RMID, NULL);return 0;
}
