PAT 1087 All Roads Lead to Rome

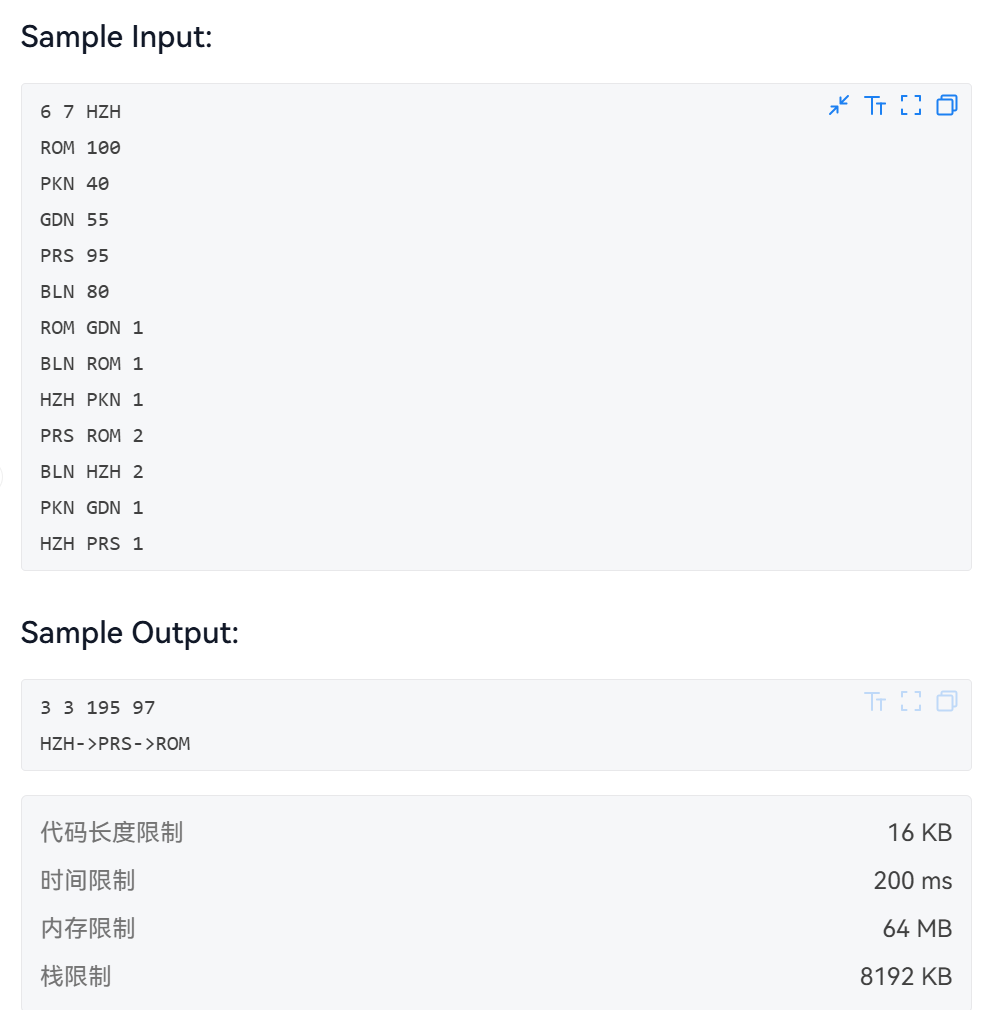
题目大意为:有N个城市(N个点),K个边,起始点的所有的点都有一个幸福值,现在让我们求从开始城市到ROM这座城市的最小花费(也就是最短距离)在最小花费的基础上,保证沿途经过城市的幸福值总和最大,在幸福值最大的基础上找平均幸福值最大的路径。
很明显涉及最短距离,用dijkstra算法来实现,保证沿途经过城市的幸福值总和最大涉及保存最优路径,当有多条最短路径的时候,要找其幸福值最大的路径,因此涉及DFS
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <limits.h>
#include <queue>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
// 123456789
// 105
//
int N;
int K;
string startcity;
struct node
{int cost;int happness;string name;
}city[205];
struct edge
{int w;int to;int next;
}e[40005];
int head[205];
int cut;
unordered_map<string,int> mp;
void add(int x,int y,int w)
{e[cut].w=w;e[cut].to=y;e[cut].next=head[x];head[x]=cut;cut++;
}
int dist[205];
bool flag[205];
typedef pair<int,int> pii;
priority_queue<pii,vector<pii>,greater<pii> >q;
vector<int> path[205];void dijkstra(int s)
{for(int i=0;i<=N;i++){dist[i]=INT_MAX;}dist[s]=0;q.push({dist[s],s});while(!q.empty()){pii z=q.top();q.pop();int u=z.second;if(flag[u]==0){flag[u]=1;for(int i=head[u];i!=-1;i=e[i].next){int v=e[i].to;if(flag[v]==0&&dist[v]>dist[u]+e[i].w){dist[v]=dist[u]+e[i].w;path[v].clear();path[v].push_back(u);q.push({dist[v],v});}else if(dist[v]==dist[u]+e[i].w){path[v].push_back(u);}}}else{continue;}}}
int ans;
vector<int> anspath;
vector<int> temppath;
int anshappness;
int ansavge;
void dfs(int end,int temphappness)
{if(end==0){ans++;if(temphappness>anshappness){anshappness=temphappness;anspath=temppath;}else if(temphappness==anshappness){double temp=(double)temphappness/(temppath.size()-1);double end=(double)anshappness/(anspath.size()-1);if(temp>end){anspath=temppath;}}return ;}else{for(int i=0;i<path[end].size();i++){temppath.push_back(path[end][i]);dfs(path[end][i],temphappness+city[path[end][i]].happness);temppath.pop_back();}}
}
int main()
{//ios::sync_with_stdio(0),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(cin>>N;cin>>K;cin>>startcity;int cnt=0;mp[startcity]=cnt;city[0].name=startcity; for(int i=1;i<=N-1;i++){cin>>city[i].name>>city[i].happness;cnt++;mp[city[i].name]=cnt;}memset(head,-1,sizeof(head));for(int i=0;i<K;i++){string tempx;cin>>tempx;int x;x=mp[tempx];int y;string tempy;cin>>tempy;y=mp[tempy];int w;cin>>w;add(x,y,w);add(y,x,w);}dijkstra(mp[startcity]);//保存从startcity到ROM的所有路径temppath.push_back(mp["ROM"]);int temphappness=0; dfs(mp["ROM"],temphappness+city[mp["ROM"]].happness);cout<<ans<<" ";cout<<dist[mp["ROM"]]<<" ";cout<<anshappness<<" ";double ansavgeend=(double)anshappness/(anspath.size()-1);cout<<(int)ansavgeend;cout<<endl;for(int i=anspath.size()-1;i>=0;i--){if(i==0){cout<<city[anspath[i]].name;}else{cout<<city[anspath[i]].name<<"->";}}return 0;}
我们用vector path[205];保存每一个顶点的最近前缀,在跑dijkstra的过程中可以存储所有的最近前缀。
然后用DFS从终点开始一个个的遍历每一个点,一直到起始点结束,这样就走完了所有的可能的最短路径,在dfs的过程可以找到最优的路径(最小花费(也就是最短距离)在最小花费的基础上,保证沿途经过城市的幸福值总和最大,在幸福值最大的基础上找平均幸福值最大的路径。)
总结:dijkstra+dfs
PAT有一道题是类似的:
PAT 1018 Public Bike Management
思路差不多,我对找所有的符合条件的路径这里掌握不熟。
