无锁队列的设计与实现
什么是无锁队列?
有锁队列:有所队列通过互斥锁或其他同步机制的保证线程安全,因为存在对临界变量的加锁和解锁,所以可能会发生阻塞,因此属于阻塞队列。
无所队列:无所队列通过原子操作来实现线程安全,因为不需要加锁,因此属于非阻塞队列。
为什么需要无锁队列?
锁的局限性:
1.加锁不当时,发生死锁
2.在高并发的环境中,锁竞争激烈,加锁失败导致频繁阻塞或线程切换,造成吞吐量下降
无锁和无等待的区别
无锁:无锁至少一个线程成功,其他可能需要重试,无锁依赖CAS等原子操作
无等待:无等待所有线程都会成功,不会发生重试,无等待依赖exchange等原子操作
volatile关键字
1.防止编译器对代码优化
2.确保内存可见性(保证读写的数据最新)
内存屏障 std::atomic_thread_fence
一行代码可能会产生多条cpu指令,而cpu为了优化性能可能对指令进行重排这在多线程环境中可能会发生错误(即无法保证顺序性),通过内存屏障可以防止指令重排(顺序性),同时也保证内存的可见性。
伪共享问题
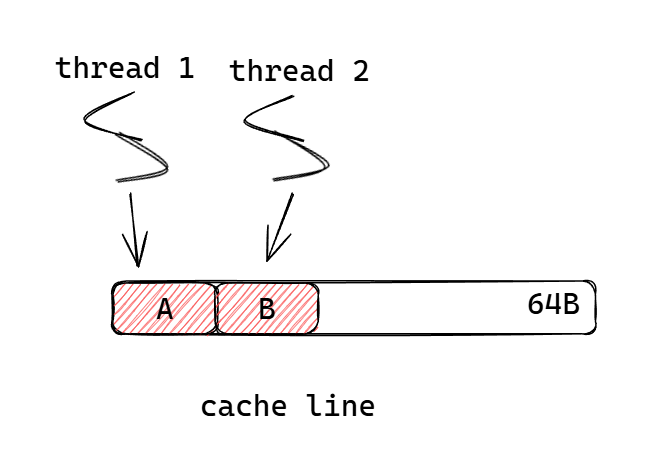
cpu通过多级缓存解决cpu数据处理速度与数据读取速度不匹配的问题,并基于写回策略来实现缓存于主存之间的数据同步,同时使用总线嗅探机制来保证不同核心之间的缓存同步,而cpu的缓存是以缓存行为单位缓存数据的,比如上图的AB就是在同一个缓存行中,任一线程对A或B进行修改时,由于缓存一致性协议,都会将该缓存行标记为脏,如果其他核心需要读取的数据在对应缓存行中,即使对应数据没有发生改变,依旧需要进行缓存同步,频繁的缓存同步会导致性能的下降。
解决:通过内存对齐将A和B放在不同的缓存行。
SPSC(单生产者单消费者)无锁队列实现
SPSC无锁队列基于ringbuffer实现,为了避免取余的耗时操作,要求ringbuffer大小为2的指数幂大小。
#pragma once// SPSC
#include <atomic>
#include <cstddef>
#include <type_traits>template<typename T, std::size_t Capacity>
class RingBuffer
{
public:static_assert(Capacity && !(Capacity & (Capacity - 1)), "Capacity must be power of 2");RingBuffer() : read_(0), write_(0) {}~RingBuffer() {//调用析构函数时,必定不会存在其他线程对read_或write_进行修改,因此可以直接用releaxed内存序std::size_t r = read_.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);std::size_t w = write_.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);while (r != w) {reinterpret_cast<T *>(&buffer_[r])->~T();r = (r + 1) & (Capacity - 1);}}// 这里使用万能引用和完美转发,支持左值和右值template<typename U>bool Push(U && value) {//对于write_,只有一个生产者线程对其进行修改,当该生产者线程读取write_时,必然可以直接从缓存中读取到最新值const std::size_t w = write_.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);//使用位与代替取余操作,提高性能const std::size_t next_w = (w + 1) & (Capacity - 1);// 检查缓冲区是否满,需要读取最新的read_,因此使用acquire内存序if (next_w == read_.load(std::memory_order_acquire)) {return false;}//在对应未初始化内存上构造元素对象new (&buffer_[w]) T(std::forward<U>(value));//写write_使用release内存序,因为消费者线程需要通过最新的write_判断是否为空write_.store(next_w, std::memory_order_release);return true;}bool Pop(T & value) {const std::size_t r = read_.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);// 检查缓冲区是否空if (r == write_.load(std::memory_order_acquire)) {return false;}// 取出元素并析构value = std::move(*reinterpret_cast<T *>(&buffer_[r]));reinterpret_cast<T *>(&buffer_[r])->~T();read_.store((r + 1) & (Capacity - 1), std::memory_order_release);return true;}std::size_t Size() const {//调用size函数时,可能有消费者线程和生产者线程调用pop或push,因此需要使用acquire内存序const std::size_t r = read_.load(std::memory_order_acquire);const std::size_t w = write_.load(std::memory_order_acquire);return (w >= r) ? (w - r) : (Capacity - r + w);}private://为了避免伪共享问题,通过alignas(64),使每个数据都与64对齐alignas(64) std::atomic<std::size_t> read_;alignas(64) std::atomic<std::size_t> write_;//通过std::aligned_storage_t申请一块alignas(64) std::aligned_storage_t<sizeof(T), alignof(T)> buffer_[Capacity]; // 支持 pod 和 非 pod 类型
};
MPSC(多生产者单消费者)无锁队列实现
#include <atomic>
#include <utility>template<typename T>
class MPSCQueueNonIntrusive
{
public:MPSCQueueNonIntrusive() : _head(new Node()), _tail(_head.load(std::memory_order_relaxed)){Node* front = _head.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);front->Next.store(nullptr, std::memory_order_relaxed);}~MPSCQueueNonIntrusive(){T* output;while (Dequeue(output))delete output;Node* front = _head.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);delete front;}//多生产者线程,需要考虑其他线程的影响void Enqueue(T* input){Node* node = new Node(input);//对head进行原子交换操作,因为需要对最新值进行修改,以此采用memory_order_acq_rel内存序Node* prevHead = _head.exchange(node, std::memory_order_acq_rel);prevHead->Next.store(node, std::memory_order_release);}//单消费者线程,无需考虑其他线程的影响bool Dequeue(T*& result){//只有一个消费线程会对tail进行修改,因此消费者线程可以采用relaxed内存序读取Node* tail = _tail.load(std::memory_order_relaxed);//生产者线程可能会对tail->Next进行修改,因此需要采用acquire内存序Node* next = tail->Next.load(std::memory_order_acquire);if (!next)return false;result = next->Data;_tail.store(next, std::memory_order_release);delete tail;return true;}private:struct Node{Node() = default;explicit Node(T* data) : Data(data){Next.store(nullptr, std::memory_order_relaxed);}T* Data;std::atomic<Node*> Next;};std::atomic<Node*> _head;std::atomic<Node*> _tail;MPSCQueueNonIntrusive(MPSCQueueNonIntrusive const&) = delete;MPSCQueueNonIntrusive& operator=(MPSCQueueNonIntrusive const&) = delete;
};DPDK源码解析
数据结构
struct rte_ring {char name[RTE_RING_NAMESIZE]; /**< Name of the ring. */int flags; /**< Flags supplied at creation. *//** Ring producer status. */struct prod {uint32_t watermark; /**< Maximum items before EDQUOT. */uint32_t sp_enqueue; /**< True, if single producer. */uint32_t size; /**< Size of ring. */uint32_t mask; /**< Mask (size-1) of ring. */volatile uint32_t head; /**< Producer head. */volatile uint32_t tail; /**< Producer tail. */} prod __rte_cache_aligned;/** Ring consumer status. */struct cons {uint32_t sc_dequeue; /**< True, if single consumer. */uint32_t size; /**< Size of the ring. */uint32_t mask; /**< Mask (size-1) of ring. */volatile uint32_t head; /**< Consumer head. */volatile uint32_t tail; /**< Consumer tail. */
#ifdef RTE_RING_SPLIT_PROD_CONS} cons __rte_cache_aligned;
#else} cons;
#endif#ifdef RTE_LIBRTE_RING_DEBUGstruct rte_ring_debug_stats stats[RTE_MAX_LCORE];
#endifvoid * ring[0] __rte_cache_aligned; /**< Memory space of ring starts here.* not volatile so need to be careful* about compiler re-ordering */
};prod和cons通过__rte_cache_aligned将内存地址对齐到64的倍数,prod和cons中存在head和tail两个标记,都使用了volatile关键字,即保证了一致性,下面看head和tail如何在多生产者和多消费者环境下发挥作用。
多生产者入队函数:__rte_ring_mp_do_enqueue
__rte_ring_mp_do_enqueue实现了可以同时有多个生产者线程进行数据的入队操作,并依据入队的前后顺序保证了入队数据对消费者线程的可见性。
/*** @internal Enqueue several objects on the ring (multi-producers safe).** This function uses a "compare and set" instruction to move the* producer index atomically.** @param r* A pointer to the ring structure.* @param obj_table* A pointer to a table of void * pointers (objects).* @param n* The number of objects to add in the ring from the obj_table.* @param behavior* RTE_RING_QUEUE_FIXED: Enqueue a fixed number of items from a ring* RTE_RING_QUEUE_VARIABLE: Enqueue as many items a possible from ring* @return* Depend on the behavior value* if behavior = RTE_RING_QUEUE_FIXED* - 0: Success; objects enqueue.* - -EDQUOT: Quota exceeded. The objects have been enqueued, but the* high water mark is exceeded.* - -ENOBUFS: Not enough room in the ring to enqueue, no object is enqueued.* if behavior = RTE_RING_QUEUE_VARIABLE* - n: Actual number of objects enqueued.*/
static inline int __attribute__((always_inline))
__rte_ring_mp_do_enqueue(struct rte_ring *r, void * const *obj_table,unsigned n, enum rte_ring_queue_behavior behavior)
{uint32_t prod_head, prod_next;uint32_t cons_tail, free_entries;const unsigned max = n;int success;unsigned i;uint32_t mask = r->prod.mask;int ret;/* move prod.head atomically */do {/* Reset n to the initial burst count */n = max;prod_head = r->prod.head;cons_tail = r->cons.tail;/* The subtraction is done between two unsigned 32bits value* (the result is always modulo 32 bits even if we have* prod_head > cons_tail). So 'free_entries' is always between 0* and size(ring)-1. */free_entries = (mask + cons_tail - prod_head);/* check that we have enough room in ring */if (unlikely(n > free_entries)) {if (behavior == RTE_RING_QUEUE_FIXED) {__RING_STAT_ADD(r, enq_fail, n);return -ENOBUFS;}else {/* No free entry available */if (unlikely(free_entries == 0)) {__RING_STAT_ADD(r, enq_fail, n);return 0;}n = free_entries;}}prod_next = prod_head + n;success = rte_atomic32_cmpset(&r->prod.head, prod_head,prod_next);} while (unlikely(success == 0));/* write entries in ring */ENQUEUE_PTRS();COMPILER_BARRIER();/* if we exceed the watermark */if (unlikely(((mask + 1) - free_entries + n) > r->prod.watermark)) {ret = (behavior == RTE_RING_QUEUE_FIXED) ? -EDQUOT :(int)(n | RTE_RING_QUOT_EXCEED);__RING_STAT_ADD(r, enq_quota, n);}else {ret = (behavior == RTE_RING_QUEUE_FIXED) ? 0 : n;__RING_STAT_ADD(r, enq_success, n);}/** If there are other enqueues in progress that preceeded us,* we need to wait for them to complete*/while (unlikely(r->prod.tail != prod_head))rte_pause();r->prod.tail = prod_next;return ret;
}最开始生产者的head与tail都指向同一个位置。
每个线程通过对生产者head的CAS操作抢占剩余空间中的槽位。
基于抢占到的槽位,生产者线程进行数据写入。
数据写入完成之后,基于生产者tail来保证数据的可见性,即先写入的数据先见到,每个线程依据获取空闲槽位的先后顺序依次更新tail指针,具体来说每个线程更新生产者的tail指针时,需要先等待tail指针与当前线程获取的head相同,以此来保证只有前面槽位的数据已经更新完成时,才能更新当前的槽位的数据。
多消费者出队函数:__rte_ring_mc_do_dequeue
__rte_ring_mc_do_dequeue实现了多消费者线程同时从队列中取数据,并依据取数据的前后顺序,保证了生产者线程对于剩余槽位的可见性。
static inline int __attribute__((always_inline))
__rte_ring_mc_do_dequeue(struct rte_ring *r, void **obj_table,unsigned n, enum rte_ring_queue_behavior behavior)
{uint32_t cons_head, prod_tail;uint32_t cons_next, entries;const unsigned max = n;int success;unsigned i;uint32_t mask = r->prod.mask;/* move cons.head atomically */do {/* Restore n as it may change every loop */n = max;cons_head = r->cons.head;prod_tail = r->prod.tail;/* The subtraction is done between two unsigned 32bits value* (the result is always modulo 32 bits even if we have* cons_head > prod_tail). So 'entries' is always between 0* and size(ring)-1. */entries = (prod_tail - cons_head);/* Set the actual entries for dequeue */if (n > entries) {if (behavior == RTE_RING_QUEUE_FIXED) {__RING_STAT_ADD(r, deq_fail, n);return -ENOENT;}else {if (unlikely(entries == 0)){__RING_STAT_ADD(r, deq_fail, n);return 0;}n = entries;}}cons_next = cons_head + n;success = rte_atomic32_cmpset(&r->cons.head, cons_head,cons_next);} while (unlikely(success == 0));/* copy in table */DEQUEUE_PTRS();COMPILER_BARRIER();/** If there are other dequeues in progress that preceded us,* we need to wait for them to complete*/while (unlikely(r->cons.tail != cons_head))rte_pause();__RING_STAT_ADD(r, deq_success, n);r->cons.tail = cons_next;return behavior == RTE_RING_QUEUE_FIXED ? 0 : n;
}最开始消费者的head与tail都指向同一个位置。
每个线程通过对消费者head的CAS操作抢占队列中的包含数据的槽位。
基于抢占到的槽位,消费者线程进行数据读取。
数据读取完成之后,基于消费者tail来保证空闲空间的可见性,即先读取的空间先被生产者线程看到,具体来说每个消费者线程更新消费者的tail指针时,需要先等待tail指针与当前线程获取的head相同,以此来保证前面数据已经读取完成时,才更新当前线程。
以上对生产者和消费者的tail指针的更新都没有使用原子操作,这是因为当变量的地址为4的整数倍时,对该变量操作即为原子操作,而volatile保证了变量对其他线程的可见性。
https://github.com/0voice
