Java 学习笔记(基础篇8)
1. 综合练习:学生信息管理系统
设计一个学生信息管理系统,要求使用数组存储学生对象,并实现学生信息的添加和删除功能。具体需求如下:
① 定义Student类,包含以下属性:
id(int 类型,唯一标识)name(String 类型,姓名)age(int 类型,年龄)- 提供带参构造方法和相应的 getter 方法
② 实现学生信息管理功能(在StudentTest类中):
(1) 初始化一个长度为 3 的Student类型数组
(2) 添加 3 个初始学生对象到数组中
(3) 尝试添加第 4 个学生对象,要求:
- 添加前需检查 id 是否重复(若重复则提示 "当前 id 重复,请修改 id 后再进行添加")
- 若数组已满则进行扩容(新数组长度 = 原数组长度 + 1)
- 尝试删除 id 为 4 的学生对象,要求:
- 先查找该 id 在数组中的索引位置
- 若存在则删除该学生,若不存在则提示 "当前 id 不存在,删除失败"
③ 实现必要的工具方法:
- 判断数组中是否包含指定 id 的学生(
contains方法) - 计算数组中非 null 元素的个数(
getCount方法) - 数组扩容(
createNewArr方法) - 查找指定 id 在数组中的索引(
getIndex方法) - 打印数组中所有非 null 的学生信息(
printArr方法)
public class StudentTest {public static void main(String[] args) {Student[] arr = new Student[3];Student stu1 = new Student(1,"张三",23);Student stu2 = new Student(2,"李四",24);Student stu3 = new Student(3,"王五",25);arr[0] = stu1;arr[1] = stu2;arr[2] = stu3;Student stu4 = new Student(4,"赵六",26);boolean flag = contains(arr, stu4.getId());if (flag){System.out.println("当前id重复,请修改id后再进行添加");} else{int count = getCount(arr);if (count == arr.length){Student[] newArr = createNewArr(arr);newArr[count] = stu4;} else{arr[count] = stu4;}}int index = getIndex(arr,4);if (index >= 0){arr[index] = null;printArr(arr);} else{System.out.println("当前id不存在,删除失败");}}public static int getIndex(Student[] arr, int id){for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){Student stu = arr[i];if (stu != null){int sid = stu.getId();if (id == sid){return i;}}}return -1; //不太理解}public static void printArr(Student[] arr){for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {Student stu = arr[i];if (stu != null){System.out.println(stu.getId() + "," + stu.getName() + "," + stu.getAge());}}}public static Student[] createNewArr(Student[] arr){ //不太理解Student[] newArr = new Student[arr.length + 1];for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {newArr[i] = arr[i];}return newArr;}public static int getCount(Student[] arr){int count = 0;for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {if (arr[i] != null){count++;}}return count;}public static boolean contains(Student[] arr, int id){for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {Student stu = arr[i];if (stu != null){ //不太理解int sid = stu.getId();if(sid == id){return true;}}}return false;}
}关键逻辑:
① 数组扩容:Java 数组长度一旦创建不可修改,当数组存满元素后,需通过创建新数组实现 “扩容”。
public static Student[] createNewArr(Student[] arr) {// 1. 创建长度比原数组多1的新数组Student[] newArr = new Student[arr.length + 1];// 2. 复制原数组元素到新数组for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {newArr[i] = arr[i];}// 3. 返回扩容后的新数组return newArr;
}(1) 关键点 1:
- 新数组长度 = 原数组长度 + 1,确保有空间容纳新元素。
- 通过循环复制原数组元素,保证数据不丢失。
- 扩容后需使用新数组继续操作(原数组已无法存储新元素)。
(2) 关键点 2 :
Q1:为什么需要形参?
A1:形参 Student[] arr 的作用是:告诉方法 “要对哪个数组进行扩容”。如果没有这个形参,方法就不知道要操作哪个数组,无法实现 “通用的扩容功能”。
Q2:形参和 main 中的 arr 是同一个吗?
A2:不是同一个对象,但它们可以指向同一个数组。
- 形参
arr:是createNewArr方法的局部变量,作用域仅限这个方法内部。 main中的arr:是main方法的局部变量,作用域仅限main方法。
② 空元素安全处理:stu != null 判断:数组中未赋值的位置默认值为 null,直接调用 null 对象的方法会触发 空指针异常
public static boolean contains(Student[] arr, int id) {for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {Student stu = arr[i];// 关键判断:仅处理非空元素if (stu != null) { int sid = stu.getId(); // 若stu为null,此行会报错if (sid == id) {return true;}}}return false;
}- 过滤数组中的空位置(
null),只对已存储有效对象的位置进行操作。 - 是避免空指针异常的核心防御性代码。
③ 目标元素查找标记:return -1:查找元素时,需明确区分 “找到” 和 “未找到” 两种情况。数组索引为非负整数(0,1,2...),需用特殊值表示 “未找到”。
public static int getIndex(Student[] arr, int id) {for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {Student stu = arr[i];if (stu != null && stu.getId() == id) {return i; // 找到目标,返回索引(非负整数)}}return -1; // 未找到目标,返回-1
}- 当循环遍历完整个数组,始终没有找到
id匹配的学生时,方法返回-1,明确告诉调用者:“数组中没有这个 id 的学生”,这是编程中约定俗成的写法。
④ if (count == arr.length) 的逻辑意义:这句话的意思是:判断 “已存储的元素数量” 是否等于 “数组总长度”,即数组是否已经存满了。
如果成立(
count == arr.length):
说明数组中已经没有空位置了(所有位置都存了学生对象),此时直接添加新元素会 “装不下”,必须先扩容。如果不成立(
count < arr.length):
说明数组还有空位置(length比实际存储的count大),可以直接把新元素添加到数组的count索引位置(因为数组的前count个位置已经存满,第count个位置正好是空的)。
2. String 类
(1) String 构造方法:
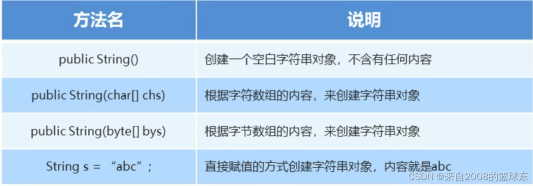
package com.mochu.project1;public class StringDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 推荐用法String name = "末初";System.out.println(name);// 几乎不用String s1 = new String();System.out.println(s1);// 几乎不用String s2 = new String("末初");System.out.println(s2);char[] chars = {'a', 'b', 'c'};String s3 = new String(chars);System.out.println(s3);byte[] bytes = {97, 98, 99, 100};String s4 = new String(bytes);System.out.println(s4);}
}
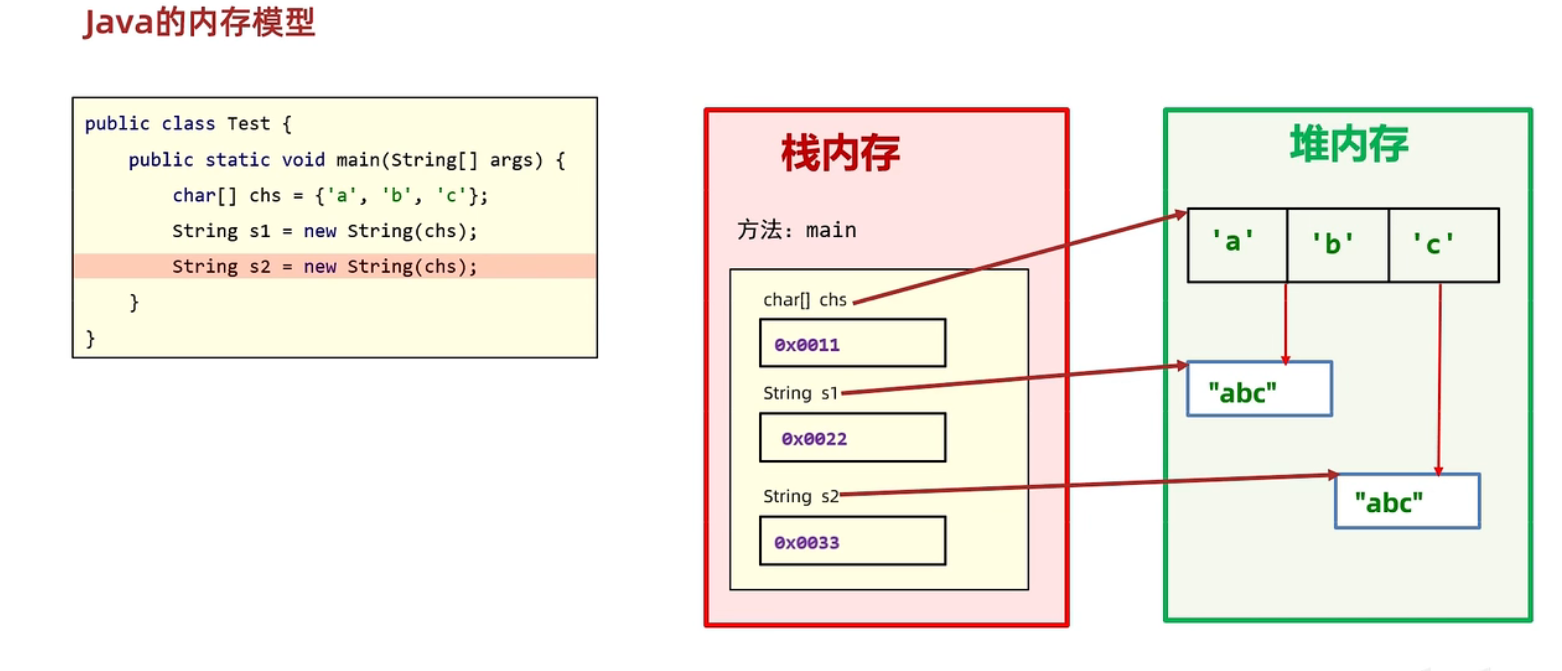
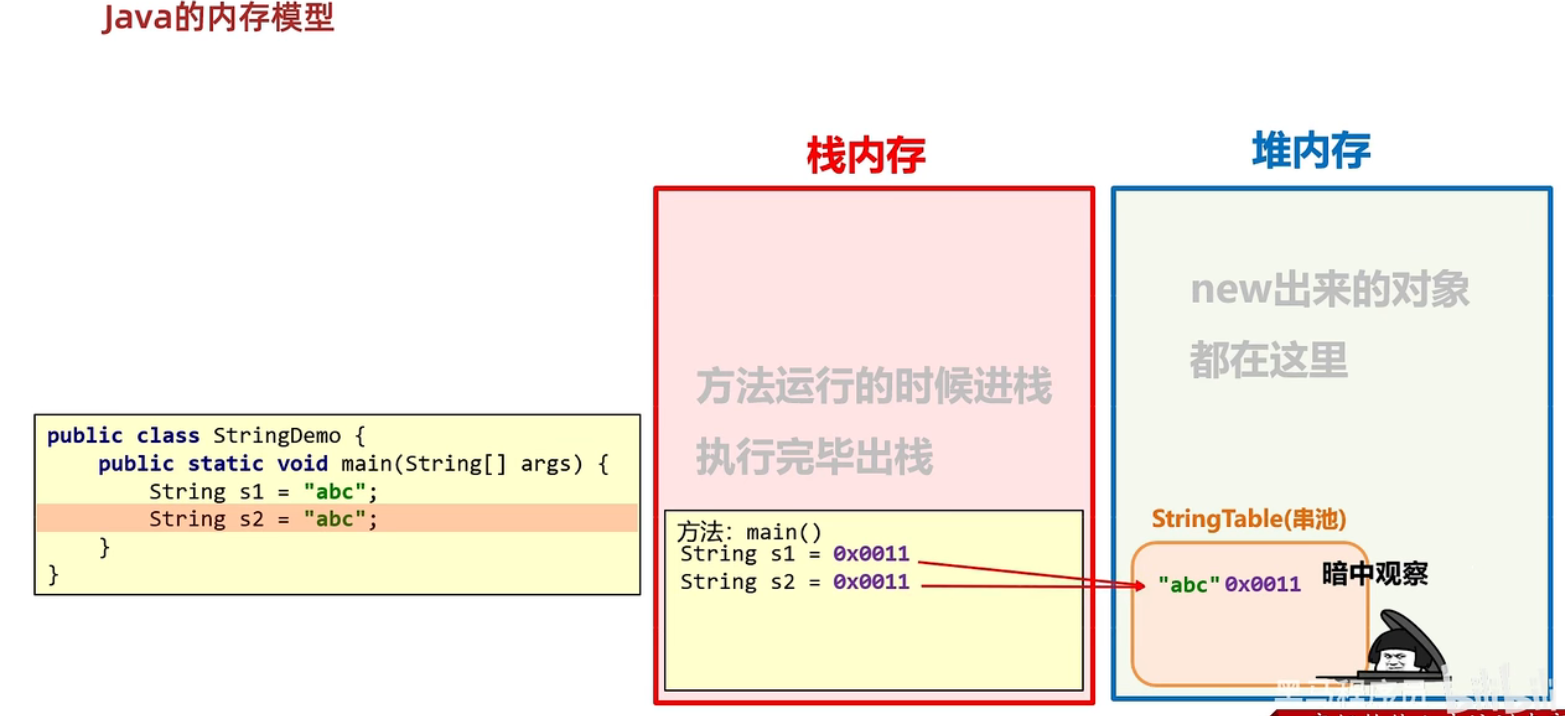
(2) 构造和直接赋值方式创建对象区别:
- 通过 new 创建的字符串对象,每一次 new 都会申请一个内存空间,虽然内容相同,但是地址值不同
- 以直接赋值方式给出的字符串,只要字符序列相同(顺序和大小写),无论在程序代码中出现几次,JVM 都只会建立一个 String 对象,并在字符串池中维护
(3) 字符串的比较
① == 号的作用
- 比较基本数据类型:比较的是具体的值
- 比较引用数据类型:比较的是对象地址值
② equals 方法的作用
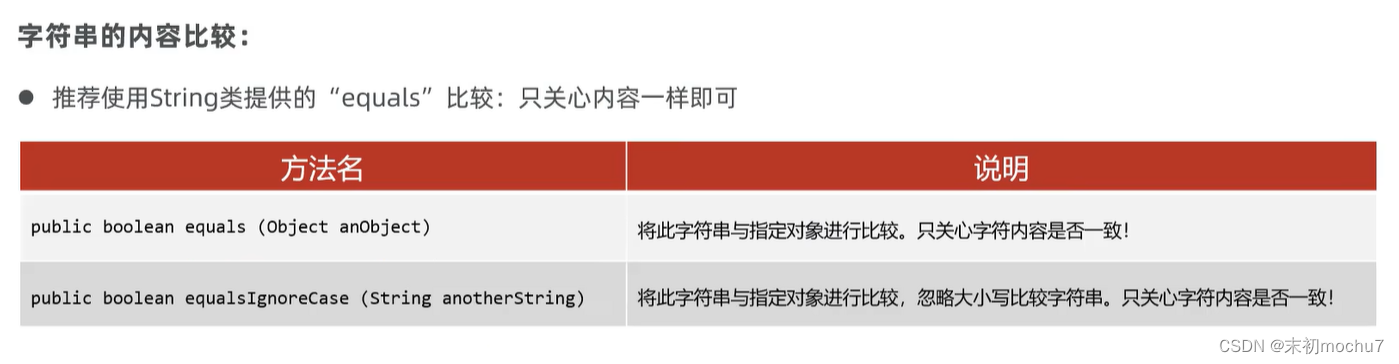
3. 综合练习
(1) 题目:字符串字符类型统计
请编写一个 Java 程序,实现对输入字符串中不同类型字符的统计功能。具体要求如下:
程序需要接收用户输入的一个字符串,统计该字符串中:
- 大写字母(A-Z)的个数
- 小写字母(a-z)的个数
- 数字字符(0-9)的个数
分别输出上述三种类型字符的统计结果,每种结果占一行
public class test5 {public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.println("请输入一个字符串");String str = sc.next();int bigCount = 0;int smallCount = 0;int numberCount = 0;for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {char c = str.charAt(i);if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') {smallCount++;} else if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z') {bigCount++;} else if (c >= '0' && c <= '9') { //不太理解numberCount++;}}System.out.println(bigCount);System.out.println(smallCount);System.out.println(numberCount);}
}
关键逻辑:
① 为什么 c >= '0' && c <= '9' 能判断数字字符?
- 在计算机中,所有字符都有对应的ASCII 码值(一个整数)。当你用
c >= '0'比较时,Java 会自动将字符转换为对应的 ASCII 码值进行比较。 - 因此:
c >= '0' && c <= '9'等价于c的ASCII码 >= 48 且 <= 57,这正好是所有数字字符(0-9)的范围。 - 如果写成
c >= 0 && c <= 9是错误的,因为字符'0'的 ASCII 码是 48,远大于整数 0,这样永远无法判断出数字字符。
