[ Spring 框架 ] 框架搭建和属性赋值
目录
1. Spring定义:
(1). IOC( Inversion of Control):
(2). AOP (Aspect Oriented Programming):
(3)一站式:
2. spring搭建:
(1). 创建一个Maven项目
(2). 导入核心 jar包
(3). 编写 spring 配置文件
(4). 编写实体类,并生成set方法
(5). 在resource中加入spring核心依赖
(6)获取对象,测试spring
3. xml配置方式属性赋值
4. 注解方式实现属性赋值
(1). 开启注解扫描
(2). 注解自己所创建的对象
5. spring注解标签分类
(1). 生成对象的注解
(2). 属性注入的注解
1. Spring定义:
Spring是一个 轻量级 (核心功能的jar比较小,运行占的资源少),IOC 和 AOP 的 一站式的Java开发框架
官网地址: Spring | Home
(1). IOC( Inversion of Control):
控制反转,是一种编程思想,将对象的管理(创建 初始化 存储 销毁 添加额外的功能...)统一交给spring框架
正控:若要使用某个对象,需要自己去负责对象的创建
反控:若要使用某个对象,只需要从Spring框架中获取需要使用的对象,不关心对象的创建过程,而是把创建对象的控制权反转给了 Spring 框架.
以前开发时,在哪需要对象,我们就在哪里new一个对象 ; 而现在,由于IOC容器(spring框架)负责对象的实例化、对象的初始化,对象和对象之间依赖关系、 对象的销毁、对外提供对象的查找等操作,即对象的整个生命周期都是由容器来控制. 我们就把创建对象都交给spring框架完成,自己不new对象,需要使用对象时,直接从spring框架中获取 .
(2). AOP (Aspect Oriented Programming):
面向切面编程 ,是一种编程思想(是面向对象的补充) 可以使用代理对象,在不修改源代码的情况下,为目标方法添加额外的功能
(3)一站式:
涉及数据访问层,web层层,可以对项目中的对象进行管理,还提供AOP功能,便于功能的扩展,对后端的项目统一管理
spring项目体系结构:
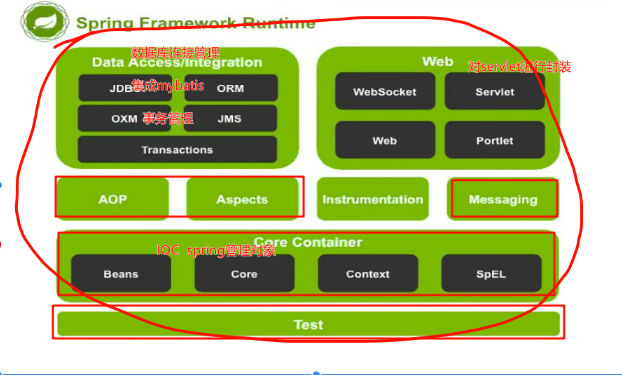
2. spring搭建:
(1). 创建一个Maven项目
(2). 导入核心 jar包
<!-- spring-context -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
(3). 编写 spring 配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user" class="com.ff.spring.model.User"> </bean>
</beans>
(4). 编写实体类 Dao接口 和 Service
例如
package com.ffyc.spring.model;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;public class Student {private int no;private String name ;public Student(){System.out.println("这是无参的构造方法");}public int getNo() {return no;}public void setNo(int no) {this.no = no;}public String getName() {return name;}public void setName(String name) {this.name = name;}
}
(5). 在resource中加入spring核心依赖
<bean id="student" class="com.ffyc.spring.model.Student"></bean>
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.ffyc.spring.dao.StudentDao"></bean>
<bean id="studentService" class="com.ffyc.spring.service.StudentService">
例如:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"><!--1.配置: 在spring中配置我们的类,把我们的类交给spring管理--><bean id="student" class="com.ffyc.spring.model.Student" scope="prototype"></bean><!--生成对象的作用域: spring框架默认创建一个对象(scope="singleton"),例如dao service对象.如果需要创建多个对象时,需要添加配置scope="prototype" 例如模型类student --><bean id="studentDao" class="com.ffyc.spring.dao.StudentDao"></bean><bean id="studentService" class="com.ffyc.spring.service.StudentService"><!--创建对象,并为属性注入值--><!--方法一:用set方法为属性赋值(推荐)--><property name="studentDao" ref="studentDao"></property><property name="student" ref="student"></property><!--方法二: 用构造方法赋值 --><!-- <constructor-arg name="studentDao" ref="studentDao"></constructor-arg>--></bean></beans>(6)测试spring
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");
StudentService studentService =applicationContext.getBean("studentService",StudentService.class);
例如:
package com.ffyc.spring.test;import com.ffyc.spring.model.Student;
import com.ffyc.spring.service.StudentService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;public class Test1 {public static void main(String[] args) {/*之前如何使用对象: 在哪需要,就在哪new对现在如果使用对象: 把我们的类配置给spring框架,当spring框架启动时就会为我们创建对象,需要时从spring框架里直接获取就行*///启动spring框架,获取配置文件 现在获取对象ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("application.xml");Student student1 = applicationContext.getBean("student", Student.class);Student student2 = applicationContext.getBean("student", Student.class);System.out.println(student1);System.out.println(student2);StudentService studentService =applicationContext.getBean("studentService",StudentService.class);}
}
3. xml配置方式属性赋值
1. 定义:
指Spring 创建对象的过程中,将对象依赖属性(简单值 集合 对象)通过配置设置给该对象
实现 IOC 需要 DI 做支持, 也可以简单理解为在创建对象时,为对象的属性赋值方式有两种:
(1). 通过set和get方法对属性赋值
(2). 通过构造方法为属性赋值
package com.ffyc.spring.service;import com.ffyc.spring.dao.StudentDao;
import com.ffyc.spring.model.Student;public class StudentService {StudentDao studentDao;Student student;/* //方法二: 通过构造方法为属性赋值public StudentService(StudentDao studentDao, Student student) {this.studentDao = studentDao;this.student = student;}*/public void save(){/*StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDao();Student student = new Student();studentDao.*/studentDao.saveStudent(student);}//方法二: 通过set和get方法对属性赋值public StudentDao getStudentDao() {return studentDao;}public void setStudentDao(StudentDao studentDao) {this.studentDao = studentDao;}public Student getStudent() {return student;}public void setStudent(Student student) {this.student = student;}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"><!--1.配置: 在spring中配置我们的类,把我们的类交给spring管理--><bean id="student" class="com.ffyc.spring.model.Student" scope="prototype"></bean><!--生成对象的作用域: spring框架默认创建一个对象(scope="singleton"),例如dao service对象.如果需要创建多个对象时,需要添加配置scope="prototype" 例如模型类student --><bean id="studentDao" class="com.ffyc.spring.dao.StudentDao"></bean><bean id="studentService" class="com.ffyc.spring.service.StudentService"><!--创建对象,并为属性注入值--><!--方法一:用set方法为属性赋值(推荐)--><property name="studentDao" ref="studentDao"></property><property name="student" ref="student"></property><!--方法二: 用构造方法赋值 --><!-- <constructor-arg name="studentDao" ref="studentDao"></constructor-arg>--></bean></beans>注意: spring 生成对象的作用域 scope ="singleton / prototype"
singleton(默认): 在 Spring中只存在一个对象(bean) ,每次拿取都是同一个.
prototype : 相当于getBean()的时候都会创建一个新的对象
4. 注解方式实现属性赋值
(1). 开启注解扫描
<context:component-scan base-package="包名"> </context:component-scan>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"><!--配置 spring对哪个包下的类进行扫描--><context:component-scan base-package="com.ffyc.spring"> </context:component-scan></beans>(2). 注解自己所创建的对象
@Component (value=“user”)等同于 <bean id=“user” class=“”></bean>
@Service
@Repository
以上注解都可以实现创建对象功能,为了后续扩展功能,在不同的层使用不同的注解标记@Scope(value=“prototype”) 原型@Scope(value=“ singleton ”) 单例
package com.ffyc.spring.model;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;@Component //等价于配置注解 <bean id="student" class="com.ffyc.spring.model.Student" scope="prototype"></bean>
@Scope(value = "prototype")
public class Student {private int no;private String name ;public Student(){System.out.println("这是无参的构造方法");}
}
package com.ffyc.spring.dao;import com.ffyc.spring.model.Student;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;@Repository(value = "studentDao")
public class StudentDao {public void saveStudent(Student student){System.out.println("保存学生");}
}
package com.ffyc.spring.service;import com.ffyc.spring.dao.StudentDao;
import com.ffyc.spring.model.Student;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;//service服务层 进行事务管理 数据访问...
@Service
public class StudentService {@Autowired//相当于<property name="studentDao" ref="studentDao"></property>StudentDao studentDao;@AutowiredStudent student;/* //方法二: 通过构造方法为属性赋值public StudentService(StudentDao studentDao, Student student) {this.studentDao = studentDao;this.student = student;}*/public void save(){/*StudentDao studentDao = new StudentDao();Student student = new Student();studentDao.*/studentDao.saveStudent(student);}//方法二: 通过set和get方法对属性赋值public StudentDao getStudentDao() {return studentDao;}public void setStudentDao(StudentDao studentDao) {this.studentDao = studentDao;}public Student getStudent() {return student;}public void setStudent(Student student) {this.student = student;}
}
@Autowired: 是spring框架中提供的注解标签,默认要求注入的对象必须存在,如果不存在,会报错 可以根据属性 类型 或者 对象名字(value="名字")去spring框架中查找对象
@Resource: 是Java中提供的注解标签 同样要求注入的对象也必须存在,如果不存在,会报错
可以根据属性 类型 或者 对象名字(value="名字")去spring框架中查找对象
5. spring注解标签分类
(1). 生成对象的注解
@Component
@Service
@Repository
(2). 属性注入的注解
@Autowired
@Qualifier (value = "studao") 通过对象名查找
@Resource

