Flink Stream API核心概念继承体系
Flink核心概念继承体系详解
概述
Flink的架构设计基于清晰的继承体系,每个核心抽象都有其完整的类层次结构。本文档将深入分析DataStream、Function、Transformation和StreamOperator四大核心抽象的继承关系,结合源码理解其设计理念和实现机制。
1. DataStream继承体系
1.1 DataStream类层次结构
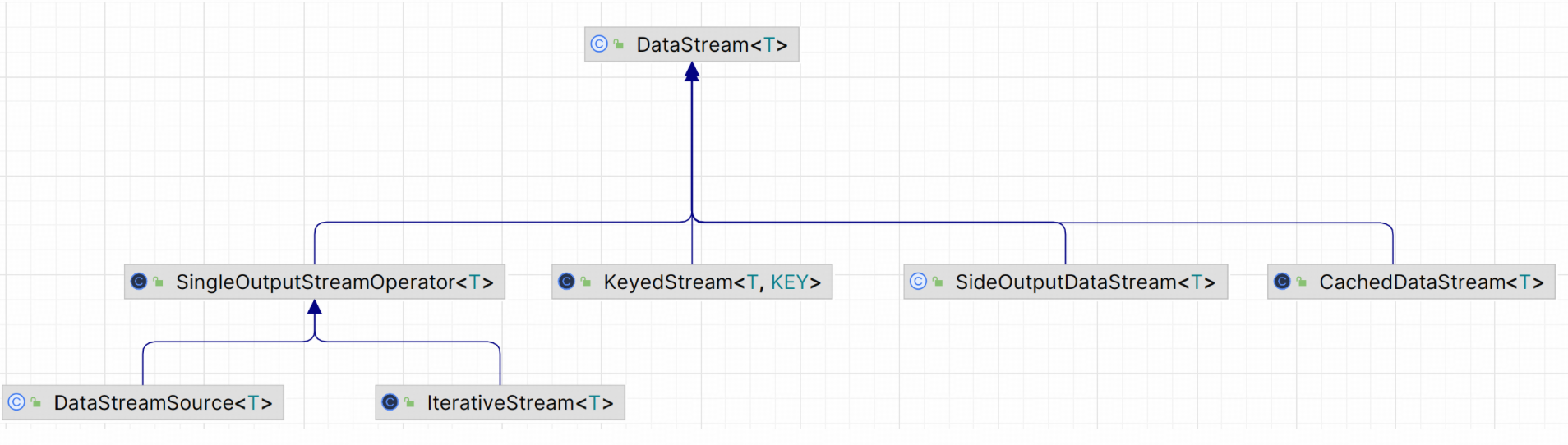
1.2 DataStream核心属性分析
public class DataStream<T> {/** 每个DataStream都包含一个Transformation,表示数据处理逻辑 */protected final Transformation<T> transformation;/** 执行环境引用,用于添加transformation到执行图 */protected final StreamExecutionEnvironment environment;protected DataStream(StreamExecutionEnvironment environment, Transformation<T> transformation) {this.environment = requireNonNull(environment, "Execution Environment must not be null.");this.transformation = requireNonNull(transformation, "Stream Transformation must not be null.");}
}
1.3 主要子类特点
SingleOutputStreamOperator:
- 最常用的DataStream子类
- 支持设置算子名称、UID、并行度等属性
- 大部分转换操作返回此类型
KeyedStream:
- 通过keyBy()操作产生
- 支持窗口操作和有状态计算
- 继承DataStream但提供键控流特有的API
SideOutputDataStream:
- 侧输出流,通过getSideOutput()产生
- 用于从主流中分离特定数据
2. Function继承体系
2.1 Function层次分类
Function按照功能丰富程度分为三个层次:
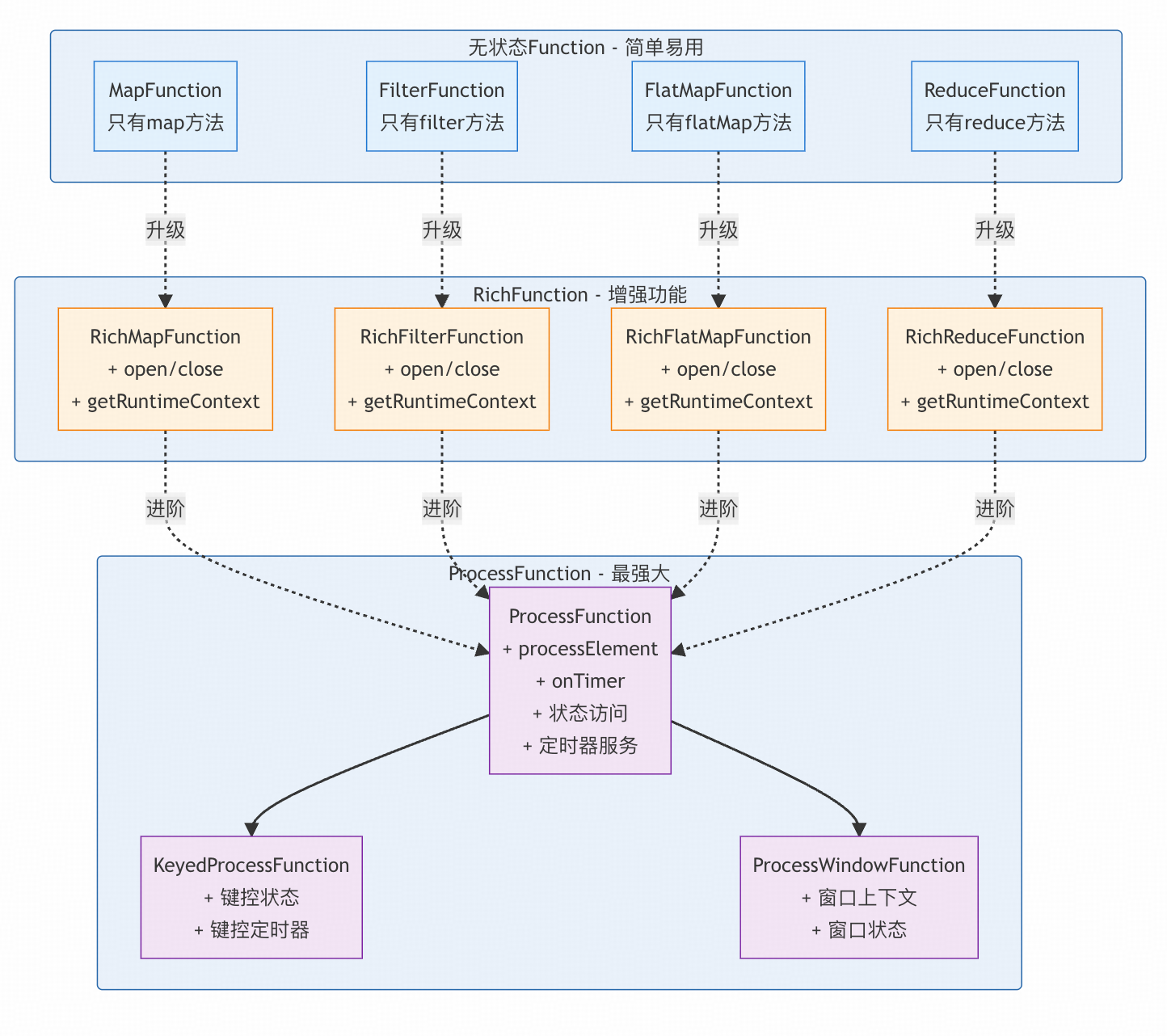
2.2 Function层次详解
2.2.1 无状态Function
- 特点:最简单,只包含数据转换逻辑
- 限制:无法访问Flink状态和运行时上下文
- 使用场景:简单的数据转换操作
// 示例:简单的MapFunction
public class UpperCaseMapper implements MapFunction<String, String> {@Overridepublic String map(String value) throws Exception {return value.toUpperCase();}
}
2.2.2 RichFunction
RichFunction在无状态Function基础上增加了两方面功能:
public abstract class AbstractUdfStreamOperator<OUT, F extends Function>extends AbstractStreamOperator<OUT> {/** 用户函数,在setup()方法中会设置RuntimeContext */protected final F userFunction;@Overridepublic void setup(StreamTask<?, ?> containingTask, StreamConfig config, Output<StreamRecord<OUT>> output) {super.setup(containingTask, config, output);// 为用户函数注入RuntimeContext,使其能访问状态等功能FunctionUtils.setFunctionRuntimeContext(userFunction, getRuntimeContext());}
}
增强功能:
- 生命周期管理:open()和close()方法
- 运行时上下文:getRuntimeContext()访问状态、度量等
// 示例:RichMapFunction
public class StatefulMapper extends RichMapFunction<String, String> {private ValueState<Integer> countState;@Overridepublic void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {// 初始化状态ValueStateDescriptor<Integer> descriptor = new ValueStateDescriptor<>("count", Integer.class);countState = getRuntimeContext().getState(descriptor);}@Overridepublic String map(String value) throws Exception {Integer count = countState.value();if (count == null) count = 0;countState.update(count + 1);return value + "_" + count;}
}
2.2.3 ProcessFunction
ProcessFunction是最强大的Function,提供三个核心构建块:
- 事件处理:processElement()方法
- 状态访问:通过RuntimeContext
- 定时器服务:事件时间和处理时间定时器
// 示例:KeyedProcessFunction
public class TimeoutProcessFunction extends KeyedProcessFunction<String, String, String> {@Overridepublic void processElement(String value, Context ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {// 处理事件out.collect("Processed: " + value);// 注册定时器ctx.timerService().registerEventTimeTimer(ctx.timestamp() + 60000);}@Overridepublic void onTimer(long timestamp, OnTimerContext ctx, Collector<String> out) throws Exception {// 定时器触发时的处理逻辑out.collect("Timer fired at: " + timestamp);}
}
3. Transformation继承体系
3.1 Transformation分类
Transformation分为物理和虚拟两大类:
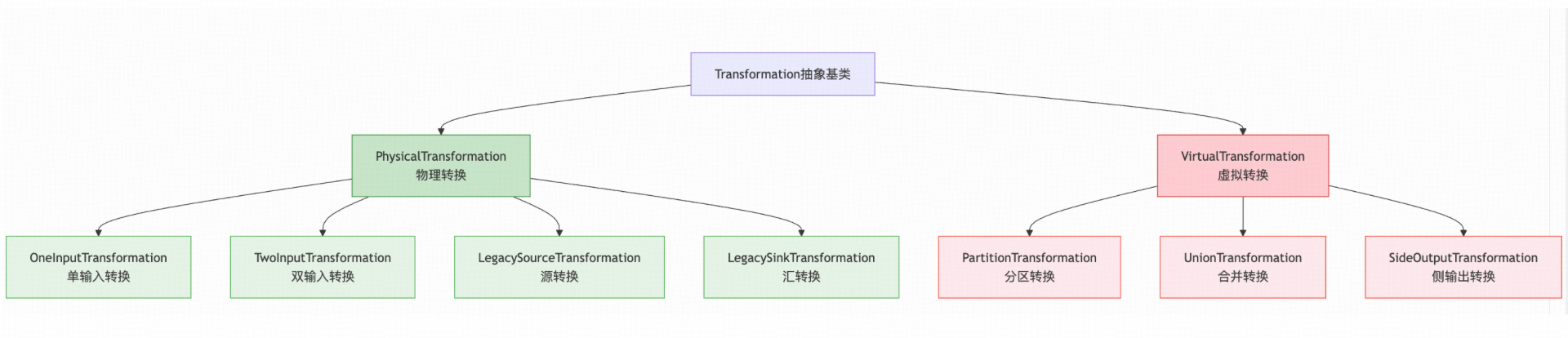
3.2 物理vs虚拟Transformation
物理Transformation(包含实际算子逻辑):
- 会转换为实际运行的StreamOperator
- 包含StreamOperatorFactory
- 会被添加到Environment的transformations列表
虚拟Transformation(不包含算子逻辑):
- 不会转换为实际算子
- 只包含元数据信息(如分区策略)
- 不会被添加到transformations列表
4. StreamOperator继承体系
4.1 StreamOperator层次结构
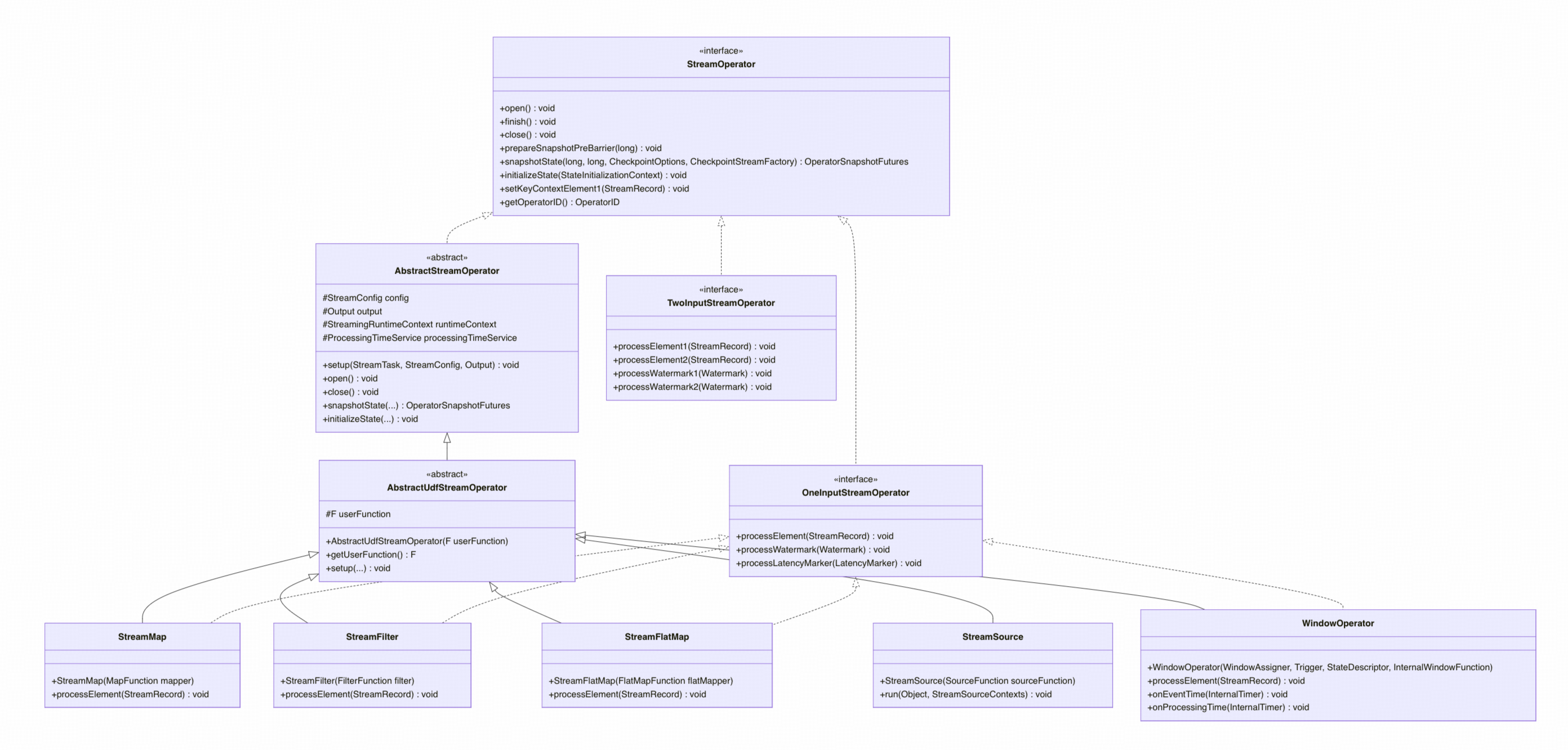
4.2 StreamOperator接口分析
StreamOperator是所有算子的顶层接口,定义了算子的基本生命周期:
public interface StreamOperator<OUT> extends CheckpointListener, KeyContext, Serializable {// 生命周期方法void open() throws Exception; // 初始化void finish() throws Exception; // 数据处理完成void close() throws Exception; // 资源清理// 检查点相关方法void prepareSnapshotPreBarrier(long checkpointId) throws Exception;OperatorSnapshotFutures snapshotState(long checkpointId, long timestamp,CheckpointOptions checkpointOptions,CheckpointStreamFactory storageLocation) throws Exception;void initializeState(StateInitializationContext context) throws Exception;// 键上下文管理void setKeyContextElement1(StreamRecord<?> record) throws Exception;void setKeyContextElement2(StreamRecord<?> record) throws Exception;// 算子标识OperatorID getOperatorID();
}
4.3 AbstractStreamOperator实现分析
AbstractStreamOperator提供了StreamOperator接口的默认实现:
核心功能:
- 生命周期管理:实现了open、close等方法
- 状态管理:提供检查点和状态恢复功能
- 运行时上下文:管理RuntimeContext和相关服务
- 度量和监控:集成度量系统
关键属性:
public abstract class AbstractStreamOperator<OUT> implements StreamOperator<OUT> {/** 算子配置信息 */protected StreamConfig config;/** 输出收集器,用于发送数据到下游 */protected Output<StreamRecord<OUT>> output;/** 运行时上下文,提供状态、度量等服务 */protected StreamingRuntimeContext runtimeContext;/** 处理时间服务 */protected ProcessingTimeService processingTimeService;/** 状态后端,用于状态存储 */protected AbstractKeyedStateBackend<?> keyedStateBackend;
}
4.4 AbstractUdfStreamOperator分析
AbstractUdfStreamOperator是用户函数算子的基类:
public abstract class AbstractUdfStreamOperator<OUT, F extends Function>extends AbstractStreamOperator<OUT> {/** 用户函数,这是用户业务逻辑的载体 */protected final F userFunction;public AbstractUdfStreamOperator(F userFunction) {this.userFunction = requireNonNull(userFunction);checkUdfCheckpointingPreconditions();}@Overridepublic void setup(StreamTask<?, ?> containingTask, StreamConfig config, Output<StreamRecord<OUT>> output) {super.setup(containingTask, config, output);// 关键:为用户函数注入RuntimeContextFunctionUtils.setFunctionRuntimeContext(userFunction, getRuntimeContext());}@Overridepublic void open() throws Exception {super.open();// 调用用户函数的open方法FunctionUtils.openFunction(userFunction, new Configuration());}
}
核心职责:
- 用户函数管理:持有并管理用户函数
- 上下文注入:为用户函数提供RuntimeContext
- 生命周期转发:将算子生命周期事件转发给用户函数
4.5 具体算子实现示例
4.5.1 StreamMap实现
public class StreamMap<IN, OUT> extends AbstractUdfStreamOperator<OUT, MapFunction<IN, OUT>>implements OneInputStreamOperator<IN, OUT> {public StreamMap(MapFunction<IN, OUT> mapper) {super(mapper);chainingStrategy = ChainingStrategy.ALWAYS;}@Overridepublic void processElement(StreamRecord<IN> element) throws Exception {// 调用用户函数进行数据转换output.collect(element.replace(userFunction.map(element.getValue())));}
}
4.5.2 输入接口的作用
OneInputStreamOperator:
- 定义单输入算子的数据处理接口
- 核心方法:processElement()处理数据元素
TwoInputStreamOperator:
- 定义双输入算子的数据处理接口
- 核心方法:processElement1()和processElement2()
4.6 继承关系速记
StreamOperator的继承关系遵循以下规律:
- 顶层接口:StreamOperator定义基本契约
- 通用基类:绝大部分算子基于AbstractStreamOperator实现
- 用户函数算子:需要用户函数的算子继承AbstractUdfStreamOperator
- 输入接口:
- 单输入算子实现OneInputStreamOperator
- 双输入算子实现TwoInputStreamOperator
5. 继承体系设计原则
5.1 分层设计原则
- 接口定义契约:顶层接口定义基本行为规范
- 抽象类提供实现:中间抽象类提供通用功能实现
- 具体类专门化:底层具体类实现特定功能
5.2 职责分离原则
- 用户层:DataStream和Function面向用户,提供易用API
- 内核层:Transformation和Operator面向内核,提供执行能力
- 执行层:StreamTask负责算子的实际执行
5.3 扩展性原则
- 开放封闭:对扩展开放,对修改封闭
- 组合优于继承:通过组合用户函数实现功能扩展
- 接口隔离:不同类型的算子实现不同的接口
💡 IDE快捷键小提示
在IDE中快速查看继承关系:
- Ctrl+H:查看类型层次结构
- Ctrl+N:快速打开类
- Ctrl+点击:跳转到定义
返回目录
Flink 源码系列
