【C#补全计划】委托
一、委托的概念
1. 委托使函数(方法)的容器
2. 可以理解为表示函数(方法)的变量类型
3. 用来存储、传递函数(方法)
4. 委托的本质是一个类,用来定义函数(方法)的类型(返回值和参数的类型)
5. 不同的函数(方法)必须对应各自“格式”一致的委托
二、委托的语法
1. 关键字:delegate
2. 语法:访问修饰符 delegate 返回值 委托名(参数列表);
3. 位置:声明在namespace或class中(在namespace中更常用)
4. 不写访问修饰符默认为public,在其他命名空间也能使用。若使用private则不能在其他命名空间使用
三、创建自定义委托
using System;namespace Delegate
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){}}// 声明一个存储无参无返回值函数的容器:这里只定义了规则,并没有使用public delegate void MyDelegate();// 声明一个存储有参无返回值函数的容器public delegate void MyDelegate2(int a, int b);// 声明一个存储无参有返回值函数的容器public delegate int MyDelegate3();// 声明一个存储有参有返回值函数的容器public delegate int MyDelegate4(int a, int b);
}
四、使用委托
1. 委托常用在:
(1)作为类的成员
(2)作为函数的参数
2. 代码
using System;namespace Delegate
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){// 委托的初始化MyDelegate md1 = new MyDelegate(fun);// 第二种方式MyDelegate md2 = fun;// 委托的使用md1.Invoke();// 第二种方式md2();Console.WriteLine("---------------------");Test t = new Test();t.testFun(fun, atk); // 传递方法}static void fun(){Console.WriteLine("调用fun()");}static void atk(int atk, int def){Console.WriteLine("造成" + (atk - def) + "点伤害");}}// 声明一个存储无参无返回值函数的容器:这里只定义了规则,并没有使用public delegate void MyDelegate();// 声明一个存储有参无返回值函数的容器public delegate void MyDelegate2(int a, int b);// 声明一个存储无参有返回值函数的容器public delegate int MyDelegate3();// 声明一个存储有参有返回值函数的容器public delegate int MyDelegate4(int a, int b);class Test{private MyDelegate fun1;private MyDelegate2 fun2;public void testFun(MyDelegate f1, MyDelegate2 f2){int atk = 3; // 假设这是攻击力int def = 1; // 假设这是防御力// 先处理一些别的逻辑 当这些逻辑处理完了 再执行传入的函数atk *= 2; // 攻击力翻倍def += 2; // 防御力加2f1();f2(atk, def);}}
}
运行结果如下:
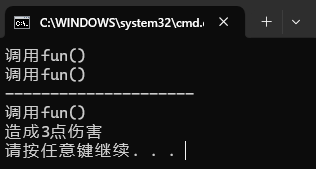
五、多播委托
1. 概念:委托变量可以存储多个函数
2. 代码:
using System;namespace Delegate
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){// 委托的初始化MyDelegate md1 = new MyDelegate(fun);// 第二种方式MyDelegate md2 = fun;// 委托的使用md1.Invoke();// 第二种方式md2();Console.WriteLine("---------------------");Test t = new Test();t.testFun(fun, atk); // 传递方法Console.WriteLine("---------------------");// 多播委托MyDelegate md3 = fun;md3();Console.WriteLine("添加2个函数后:");md3 += fun; // += 向委托md3中添加函数md3 += fun2;md3();Console.WriteLine("删除1个fun()后:");md3 -= fun; // -= 在委托md3中移除函数md3();md3 = null; // 清空委托}static void fun(){Console.WriteLine("调用fun()");}static void fun2(){Console.WriteLine("调用fun2()");}static void atk(int atk, int def){Console.WriteLine("造成" + (atk - def) + "点伤害");}}// 声明一个存储无参无返回值函数的容器:这里只定义了规则,并没有使用public delegate void MyDelegate();// 声明一个存储有参无返回值函数的容器public delegate void MyDelegate2(int a, int b);// 声明一个存储无参有返回值函数的容器public delegate int MyDelegate3();// 声明一个存储有参有返回值函数的容器public delegate int MyDelegate4(int a, int b);class Test{private MyDelegate fun1;private MyDelegate2 fun2;public void testFun(MyDelegate f1, MyDelegate2 f2){int atk = 3; // 假设这是攻击力int def = 1; // 假设这是防御力// 先处理一些别的逻辑 当这些逻辑处理完了 再执行传入的函数atk *= 2; // 攻击力翻倍def += 2; // 防御力加2f1();f2(atk, def);}}
}
运行结果如下:
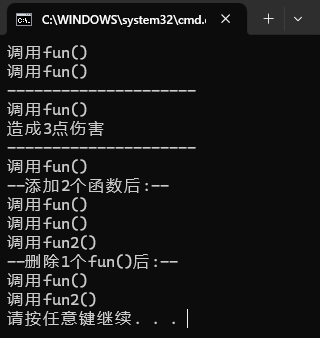
六、系统定义的委托
1. 前提:引用System命名空间
2. Action:无返回值的委托
3. Func:有返回值的委托
4. 代码:
using System;namespace Delegate
{class Program{static void Main(string[] args){// 委托的初始化MyDelegate md1 = new MyDelegate(fun);// 第二种方式MyDelegate md2 = fun;// 委托的使用md1.Invoke();// 第二种方式md2();Console.WriteLine("---------------------");Test t = new Test();t.testFun(fun, atk); // 传递方法Console.WriteLine("---------------------");// 多播委托MyDelegate md3 = fun;md3();Console.WriteLine("--添加2个函数后:--");md3 += fun; // += 向委托md3中添加函数md3 += fun2;md3();Console.WriteLine("--删除1个fun()后:--");md3 -= fun; // -= 在委托md3中移除函数md3();md3 = null; // 清空委托Console.WriteLine("---------------------");// 使用系统定义的委托// Action:无返回值的委托Action a = fun; // 无参无返回值a();Action<int, int> a2 = atk; // 有参无返回值a2(3, 2);// Func:有返回值的委托Func<int> f1 = fun3; // 无参有返回值int x = f1();Func<int, int, string> f2 = fun4; // 有参有返回值,最后一个泛型为返回值string s = f2(0, 0);}static void fun(){Console.WriteLine("调用fun()");}static void fun2(){Console.WriteLine("调用fun2()");}static int fun3(){Console.WriteLine("调用fun3()");return 0;}static string fun4(int a, int b){Console.WriteLine("调用fun4()");return "";}static void atk(int atk, int def){Console.WriteLine("造成" + (atk - def) + "点伤害");}}// 声明一个存储无参无返回值函数的容器:这里只定义了规则,并没有使用public delegate void MyDelegate();// 声明一个存储有参无返回值函数的容器public delegate void MyDelegate2(int a, int b);// 声明一个存储无参有返回值函数的容器public delegate int MyDelegate3();// 声明一个存储有参有返回值函数的容器public delegate int MyDelegate4(int a, int b);class Test{private MyDelegate fun1;private MyDelegate2 fun2;public void testFun(MyDelegate f1, MyDelegate2 f2){int atk = 3; // 假设这是攻击力int def = 1; // 假设这是防御力// 先处理一些别的逻辑 当这些逻辑处理完了 再执行传入的函数atk *= 2; // 攻击力翻倍def += 2; // 防御力加2f1();f2(atk, def);}}
}
今天的学习就到这里了。感谢阅读。
再见!
