java8学习笔记-Stream流
JDK1.8新增了Stream类,从而把函数式编程的风格引入到Java语言中,Stream类的API提供了强大的功能,使用Stream后,可以写出更加强大,更加简洁的代码
首先,Stream流有一些特性:
- Stream流不是一种数据结构,不保存数据,它只是在原数据集上定义了一组操作。
- 这些操作是惰性的,即每当访问到流中的一个元素,才会在此元素上执行这一系列操作。
- Stream不保存数据,故每个Stream流只能使用一次。
关于应用在Stream流上的操作,可以分成两种:Intermediate(中间操作)和Terminal(终止操作)。中间操作的返回结果都是Stream,故可以多个中间操作叠加;终止操作用于返回我们最终需要的数据,只能有一个终止操作。至于哪些方法是中间操作,哪些方法是终止操作,我们一会儿再说。
使用Stream流,可以清楚地知道我们要对一个数据集做何种操作,可读性强。而且可以很轻松地获取并行化Stream流,不用自己编写多线程代码,可以让我们更加专注于业务逻辑。
默认情况下,从有序集合、生成器、迭代器产生的流或者通过调用Stream.sorted产生的流都是有序流,有序流在并行处理时会在处理完成之后恢复原顺序。unordered()方法可以解除有序流的顺序限制,更好地发挥并行处理的性能优势,例如distinct将保存任意一个唯一元素而不是第一个,limit将保留任意n个元素而不是前n个。
流的常用生成方法
Collection接口的stream()或parallelStream()方法
parallelStream()是并行方法,parallelStream()不一定比stream()快(需要开启线程,线程竞争),而且parallelStream()是线程不安全的,所以使用parallelStream()要综合考量,测试百万数据的List<String> 的System.out.println(),stream()依旧比parallelStream()要快
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();Random random = new Random();for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {list.add(random.nextInt());}Instant start = Instant.now();
// list.stream().forEach(System.out::print); //193毫秒list.parallelStream().forEach(System.out::print);//275毫秒Instant end = Instant.now();System.out.println("");System.out.println("_______________________________________________________________________");System.out.println("end:" + end.toEpochMilli());System.out.println("start:" + start.toEpochMilli());System.out.println("time:" + (end.toEpochMilli() - start.toEpochMilli()));静态的Stream.of()、Stream.empty()方法
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList();Random random = new Random();for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {list.add(random.nextInt());}Instant start = Instant.now();
// Stream.of(list).forEach(System.out::println); //71毫秒Stream.empty().forEach(System.out::println);//37毫秒
// list.stream().forEach(System.out::print); //193毫秒
// list.parallelStream().forEach(System.out::print);//275毫秒Instant end = Instant.now();System.out.println("");System.out.println("_______________________________________________________________________");System.out.println("end:" + end.toEpochMilli());System.out.println("start:" + start.toEpochMilli());System.out.println("time:" + (end.toEpochMilli() - start.toEpochMilli()));Arrays.stream(array, from, to)
包前不包后
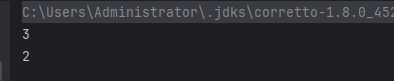
int[] arr = {1, 3, 2, 4, 55, 64, 98, 23};Arrays.stream(arr, 1, 3).forEach(System.out::println);
流的常用Intermediate方法(中间操作)
filter(Predicate) 将结果为false的元素过滤掉
int[] arr = {1, 3, 2, 4, 55, 64, 98, 23};//过滤单数保留双数Arrays.stream(arr).filter(item->(item & 1) == 0).forEach(System.out::println);map(fun) 转换元素的值,可以用方法引元或者lambda表达式
int[] arr = {1, 3, 2, 4, 55, 64, 98, 23};//filter过滤单数保留双数//map将剩余元素除以2Arrays.stream(arr).filter(item->(item & 1) == 0).map(item -> item / 2).forEach(System.out::println);flatMap(fun) 若元素是流,将流摊平为正常元素,再进行元素转换
简单点描述就是嵌套的集合扁平化
比如集合里面包含集合/数组
List<List<String>> list = Arrays.asList(Arrays.asList("A", "B"),Arrays.asList("C", "D"),Arrays.asList("E", "E"));// 使用 flatMap 扁平化列表List<String> collect = list.stream().flatMap(List::stream).collect(Collectors.toList());System.out.println(collect); //[A, B, C, D, E, E]或者集合里面本身没有集合/数组但是可以操作(字符串切割)变成集合/数组
List<Person> list = Arrays.asList(new Person("张三", "1,2,3"),new Person("李四", "2,3"),new Person("王五", "2,4"));Set<Object> collect = list.stream().flatMap(person -> Arrays.stream(person.getHobbies().split(","))).collect(Collectors.toSet());System.out.println(collect);limit(n) 保留前n个元素 常配合排序使用
int[] arr = {1, 3, 2, 4, 55, 64, 98, 23};Arrays.stream(arr).limit(2).forEach(System.out::print); //13skip(n) 跳过前n个元素
int[] arr = {1, 3, 2, 4, 55, 64, 98, 23};Arrays.stream(arr).skip(6).forEach(System.out::print); //9823distinct() 剔除重复元素
int[] arr = {1, 2, 2, 4, 2};Arrays.stream(arr).distinct().forEach(System.out::print); //124sorted() ,sorted(Comparator) 将Comparable元素的流排序
int[] arr = {1, 2, 2, 4, 2};Arrays.stream(arr).sorted().forEach(System.out::print); //12224
List<Person> list = Arrays.asList(new Person("张三", 18,"2,3"),new Person("李四", 14,"2,3"),new Person("王五", 21,"2,4"));//根据年龄排序 reversed()倒序操作list.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getAge).reversed()).forEach(System.out::println);peek(fun) 流不变,但会把每个元素传入fun执行,可以用作调试
可以理解为没有返回结果的forEach()
List<Person> list = Arrays.asList(new Person("张三", 18,"2,3"),new Person("李四", 14,"2,3"),new Person("王五", 21,"2,4"));//根据年龄排序 reversed()倒序操作list.stream().sorted(Comparator.comparing(Person::getAge).reversed()).peek(item->{item.setAge(item.getAge() + 1);}).peek(item->{item.setAge(item.getAge() + 1);}).peek(item->{item.setAge(item.getAge() + 1);}).forEach(System.out::println);结果:
Person(name=王五, age=24, hobbies=2,4)
Person(name=张三, age=21, hobbies=2,3)
Person(name=李四, age=17, hobbies=2,3)流的Terminal方法(终结操作)
max(Comparator)
min(Comparator)
count()
findFirst() 返回第一个元素
findAny() 返回任意元素
anyMatch(Predicate) ,allMatch(Predicate) ,noneMatch(Predicate)
anyMatch(Predicate)任意元素匹配时返回true
所有元素匹配时返回true
没有元素匹配时返回true
