C# 入门教程(四)委托详解
文章目录
- 1、什么是委托
- 2、委托的声明(自定义委托)
- 3、委托的使用
- 3.1 实例:把方法当作参数传给另一个方法
- 3.2 注意:难精通+易使用+功能强大东西,一旦被滥用则后果非常严重
- 4、委托的高级使用
- 4.1 多播(multicast)委托
- 4.2隐式异步调用
- 1. 同步与异步的简介
- 2.同步调用与异步调用的对比
- 3. 隐式多线程 vs 显式多线程
1、什么是委托
在 C#里,委托属于引用类型,其作用是封装和引用一个或多个方法。可以把它想象成一种类型安全的函数指针,不过它比函数指针更强大,因为它支持多播(也就是可以引用多个方法)。委托经常会在事件处理、回调函数以及异步编程中被用到。
-
委托(delegate)是函数指针的"升级版"
- 实例:C/C++中的函数指针
#include <stdio.h>// 函数:加法 int add(int a, int b) {return a + b; }// 函数:减法 int subtract(int a, int b) {return a - b; }int main() {// 声明一个函数指针int (*operation)(int, int);// 让函数指针指向add函数operation = add;printf("加法结果: %d\n", operation(5, 3)); // 输出8// 让函数指针指向subtract函数operation = subtract;printf("减法结果: %d\n", operation(5, 3)); // 输出2return 0; } -
一切皆地址
- 变量(数据)是以某个地址为起点的一段内存中所存储的值
- 函数(算法)是以某个地址为起点的一段内存中所存储的一组机器语言指令
-
直接调用与间接调用
- 直接调用:通过
函数名来调用函数,CPU通过函数名直接获得函数所在地址并开始执行→返回 - 间接调用:通过
函数指针来调用函数,CPU通过读取函数指针存储的值获得函数所在地址并开始执行→返回
- 直接调用:通过
-
Java中没有与委托相对应的功能实体
-
委托的简单使用
- Action委托
- Func委托
namespace DelegateExample {class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Calculatator calculatator = new Calculatator();//无参数委托Action act = new Action(calculatator.Report);//打印出来的都是一样的act();act.Invoke();calculatator.Report();//带参数的委托Func<int, int, int> func = new Func<int, int, int>(calculatator.Add);int a = 13;int b = 10;int z = func.Invoke(a, b);Console.WriteLine(z);Func<int, int, int> func2 = new Func<int, int, int>(calculatator.Sub);int z1 = func2.Invoke(a, b);Console.WriteLine(z1);}}class Calculatator{public void Report(){Console.WriteLine("I have 3 Methods");}public int Add(int x, int y){return x + y;}public int Sub(int x, int y){return x - y;}} }
2、委托的声明(自定义委托)
- 委托是一种类(class),类是数据类型所以委托也是一种数据类型
- 它的声名方式与一般的类不同,主要是为了照顾可读性和C/C++传统
- 注意声明委托的位置
- 避免写错地方结果声明成嵌套类型
- 委托与所封装的方法必需类型兼容

返回值的数据类型一致- 参数列表在
个数和数据类型上一致(参数名不需要一样)
namespace DelegateExample
{public delegate int Calc(int x, int y);class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Calculatator calculatator = new Calculatator();Calc calc1 = new Calc(calculatator.Add);Calc calc2 = new Calc(calculatator.Sub);Calc calc3 = new Calc(calculatator.mul);Calc calc4 = new Calc(calculatator.Div);int a = 10;int b = 5;int c = calc1.Invoke(a, b);Console.WriteLine(c);int c1 = calc2.Invoke(a, b);Console.WriteLine(c1);int c2 = calc3.Invoke(a, b);Console.WriteLine(c2);int c3 = calc4.Invoke(a, b);Console.WriteLine(c3);}}class Calculatator{public int Add(int x, int y){return x + y;}public int Sub(int x, int y){return x - y;}public int mul(int x, int y){return x * y;}public int Div(int x, int y){return x / y;}}
}3、委托的使用
3.1 实例:把方法当作参数传给另一个方法
- 正确使用1:模板方法,“借用”指定的外部方法来产生结果相当于“填空题”常位于代码中部委托有返回值
namespace DelegateExample
{public delegate int Calc(int x, int y);class Program{static void Main(string[] args){ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory();WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();Func<Product> func1 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakePizza);Func<Product> func2 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakeCare);Box box1 = wrapFactory.WarpProduct(func1);Box box2 = wrapFactory.WarpProduct(func2);Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);}}class Product{public string Name { get; set; }}class Box{public Product Product { get; set; }}class WrapFactory(){public Box WarpProduct(Func<Product> getProduct){Box box = new Box();Product product = getProduct.Invoke();box.Product = product;return box;}}class ProductFactory(){public Product MakePizza(){Product product = new Product();product.Name = "pizza";return product;}public Product MakeCare(){Product product = new Product();product.Name = "care";return product;}}
}- 正确使用2:回调(callback)方法,调用指定的外部方法相当于”流水线”常位于代码末尾委托无返回值
namespace DelegateExample
{public delegate int Calc(int x, int y);class Program{static void Main(string[] args){ProductFactory productFactory = new ProductFactory();WrapFactory wrapFactory = new WrapFactory();Func<Product> func1 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakePizza);Func<Product> func2 = new Func<Product>(productFactory.MakeCare);// 实例化一个日志类,进行价格大于50的时候,打印相关日志Logger logger = new Logger();Action<Product> Log = new Action<Product>(logger.Log);Box box1 = wrapFactory.WarpProduct(func1, Log);Box box2 = wrapFactory.WarpProduct(func2, Log);Console.WriteLine(box1.Product.Name);Console.WriteLine(box2.Product.Name);}}class Logger{public void Log(Product product){Console.WriteLine("产品名:{0},价格:{1},创建于:{2}", product.Name, product.Price, DateTime.UtcNow);}}class Product{public string Name { get; set; }public decimal Price { get; set; }}class Box{public Product Product { get; set; }}class WrapFactory(){public Box WarpProduct(Func<Product> getProduct, Action<Product> LogCallback){Box box = new Box();Product product = getProduct.Invoke();if (product.Price > 50){LogCallback.Invoke(product);}box.Product = product;return box;}}class ProductFactory(){public Product MakePizza(){Product product = new Product();product.Name = "pizza";product.Price = 10;return product;}public Product MakeCare(){Product product = new Product();product.Name = "care";product.Price = 100;return product;}}}3.2 注意:难精通+易使用+功能强大东西,一旦被滥用则后果非常严重
- 缺点1:这是一种方法级别的紧耦合,现实工作中要慎之又慎
- 缺点2:使可读性下降、debug的难度增加
- 缺点3:把委托回调、异步调用和多线程纠缠在一起,会让代码变得难以阅读和维护
- 缺点4:委托使用不当有可能造成内存泄漏和程序性能下降
4、委托的高级使用
4.1 多播(multicast)委托
多播委托(Multicast Delegate) 是一种特殊的委托类型,它可以同时引用多个方法,当委托被调用时,会依次执行所有被引用的方法。这一特性使得多播委托成为实现事件机制、回调链等场景的核心基础。
多播委托通过将多个方法组合成一个可调用的实体,实现了 “一次调用,多方响应” 的效果,是 C# 中实现事件、回调等功能的核心机制。
namespace DelegateExample
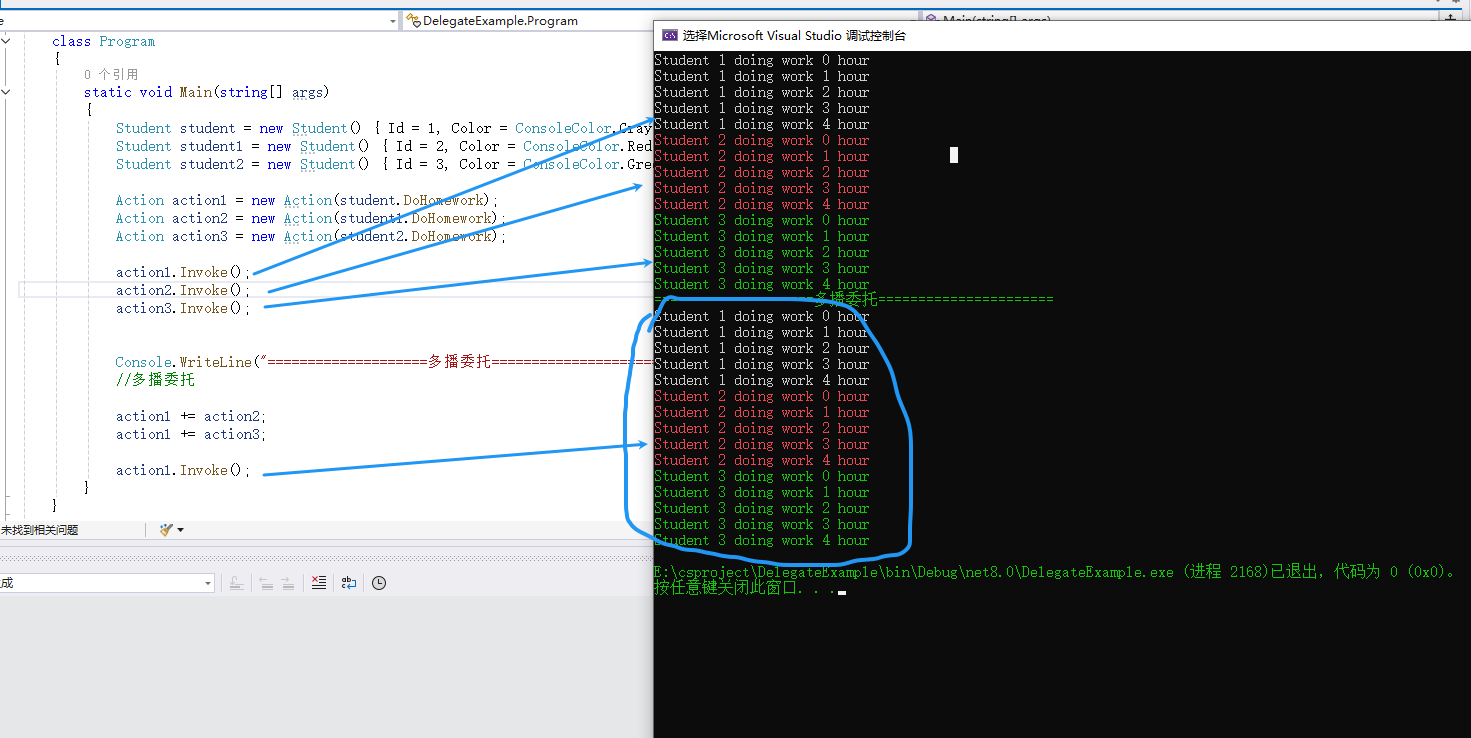
{public delegate int Calc(int x, int y);class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student student = new Student() { Id = 1, Color = ConsoleColor.Gray };Student student1 = new Student() { Id = 2, Color = ConsoleColor.Red };Student student2 = new Student() { Id = 3, Color = ConsoleColor.Green };Action action1 = new Action(student.DoHomework);Action action2 = new Action(student1.DoHomework);Action action3 = new Action(student2.DoHomework);Console.WriteLine("====================单播委托======================");action1.Invoke();action2.Invoke();action3.Invoke();Console.WriteLine("====================多播委托======================");//多播委托action1 += action2;action1 += action3;action1.Invoke();}}class Student{public int Id { get; set; }public ConsoleColor Color { get; set; }public void DoHomework(){for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){Console.ForegroundColor = this.Color;Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing work {1} hour", this.Id, i);}}}
}打印结果,多个单播委托和多播委托打印结果一致;
4.2隐式异步调用
1. 同步与异步的简介
- 中英文的语言差异
- 同步:你做完了我(在你的基础上)接着做
- 异步:咱们两个同时做(相当于汉语中的“同步进行”)
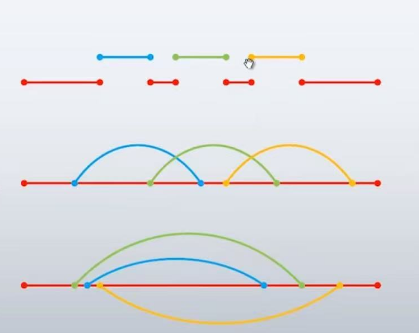
2.同步调用与异步调用的对比
- 每一个运行的程序是一个进程(process)
- 每个进程可以有一个或者多个线程(thread )
- 同步调用是在同一线程内异步调用的底层机理是多线程。
- 串行同步单线程,并行异步多线程
3. 隐式多线程 vs 显式多线程
- 直接同步调用:使用方法名
- 间接同步调用:使用单播/多播委托的Invoke方法
namespace DelegateExample
{public delegate int Calc(int x, int y);class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student student = new Student() { Id = 1, Color = ConsoleColor.Gray };Student student1 = new Student() { Id = 2, Color = ConsoleColor.Red };Student student2 = new Student() { Id = 3, Color = ConsoleColor.Green };//直接调用student.DoHomework();student1.DoHomework();student2.DoHomework();//单播委托间接调用Action action1 = new Action(student.DoHomework);Action action2 = new Action(student1.DoHomework);Action action3 = new Action(student2.DoHomework);action1.Invoke();action2.Invoke();action3.Invoke();//多播委托间接调用action1 += action2;action1 += action3;action1.Invoke();for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;Console.WriteLine("Main thread {0}", i);}}}class Student{public int Id { get; set; }public ConsoleColor Color { get; set; }public void DoHomework(){for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){Console.ForegroundColor = this.Color;Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing work {1} hour", this.Id, i);}}}
}
打印结果均相同

- 隐式异步调用:使用委托的BeginInvoke
namespace DelegateExample
{public delegate int Calc(int x, int y);class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student student = new Student() { Id = 1, Color = ConsoleColor.Gray };Student student1 = new Student() { Id = 2, Color = ConsoleColor.Red };Student student2 = new Student() { Id = 3, Color = ConsoleColor.Green };Action action1 = new Action(student.DoHomework);Action action2 = new Action(student1.DoHomework);Action action3 = new Action(student2.DoHomework);//.NET 5 及更高版本Action.BeginInvoke 受到了限制action1.BeginInvoke(null, null);action2.BeginInvoke(null, null);action3.BeginInvoke(null, null);for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;Console.WriteLine("Main thread {0}", i);}}}class Student{public int Id { get; set; }public ConsoleColor Color { get; set; }public void DoHomework(){for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){Console.ForegroundColor = this.Color;Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing work {1} hour", this.Id, i);}}}
}- 显式导步调用:使用Thread
using System.Threading;namespace DelegateExample
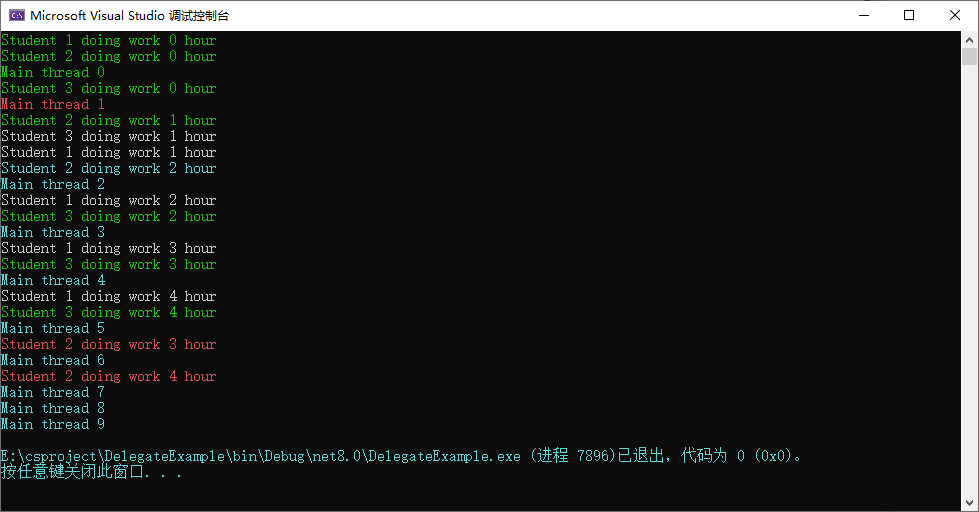
{public delegate int Calc(int x, int y);class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student student = new Student() { Id = 1, Color = ConsoleColor.Gray };Student student1 = new Student() { Id = 2, Color = ConsoleColor.Red };Student student2 = new Student() { Id = 3, Color = ConsoleColor.Green };Thread thread1 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(student.DoHomework));Thread thread2 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(student1.DoHomework));Thread thread3 = new Thread(new ThreadStart(student2.DoHomework));thread1.Start();thread2.Start();thread3.Start();for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;Console.WriteLine("Main thread {0}", i);}}}class Student{public int Id { get; set; }public ConsoleColor Color { get; set; }public void DoHomework(){for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){Console.ForegroundColor = this.Color;Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing work {1} hour", this.Id, i);}}}
}打印结果:异步调用
- Task 异步调用
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;namespace DelegateExample
{public delegate int Calc(int x, int y);class Program{static void Main(string[] args){Student student = new Student() { Id = 1, Color = ConsoleColor.Gray };Student student1 = new Student() { Id = 2, Color = ConsoleColor.Red };Student student2 = new Student() { Id = 3, Color = ConsoleColor.Green };Task task1 = new Task(student.DoHomework);Task task2 = new Task(student1.DoHomework);Task task3 = new Task(student2.DoHomework);task1.Start();task2.Start();task3.Start();for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++){Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Cyan;Console.WriteLine("Main thread {0}", i);}}}class Student{public int Id { get; set; }public ConsoleColor Color { get; set; }public void DoHomework(){for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++){Console.ForegroundColor = this.Color;Console.WriteLine("Student {0} doing work {1} hour", this.Id, i);}}}
}
