《Java 程序设计》第 8 章 - Java 常用核心类详解
引言
在 Java 编程世界中,核心类库是构建一切应用的基础。第 8 章将带大家深入学习 Java 中最常用的核心类,这些类贯穿于日常开发的方方面面。掌握这些核心类的使用技巧,能让我们的代码更简洁、高效、易维护。本章将从 Object 类讲起,逐步介绍 Math 类、基本类型包装类以及日期时间 API,每个知识点都配有完整可运行的代码示例,帮助大家快速上手。
8.1 Object:终极父类
在 Java 中,所有类都直接或间接继承自 Object 类,它是 Java 类层次结构的根。Object 类定义了所有对象都具备的基本方法,掌握这些方法是理解 Java 面向对象特性的基础。
类图(Object 类核心方法)
@startuml
class Object {+ toString(): String+ equals(Object): boolean+ hashCode(): int+ clone(): Object+ finalize(): void+ getClass(): Class<?>+ notify(): void+ notifyAll(): void+ wait(): void+ wait(long): void+ wait(long, int): void
}
@enduml

8.1.1 toString () 方法

作用:返回对象的字符串表示形式,默认实现为 类名@哈希码的十六进制。
使用场景:打印对象、日志输出等需要对象文字描述的场景。
最佳实践:自定义类建议重写 toString (),返回对象的关键属性信息。
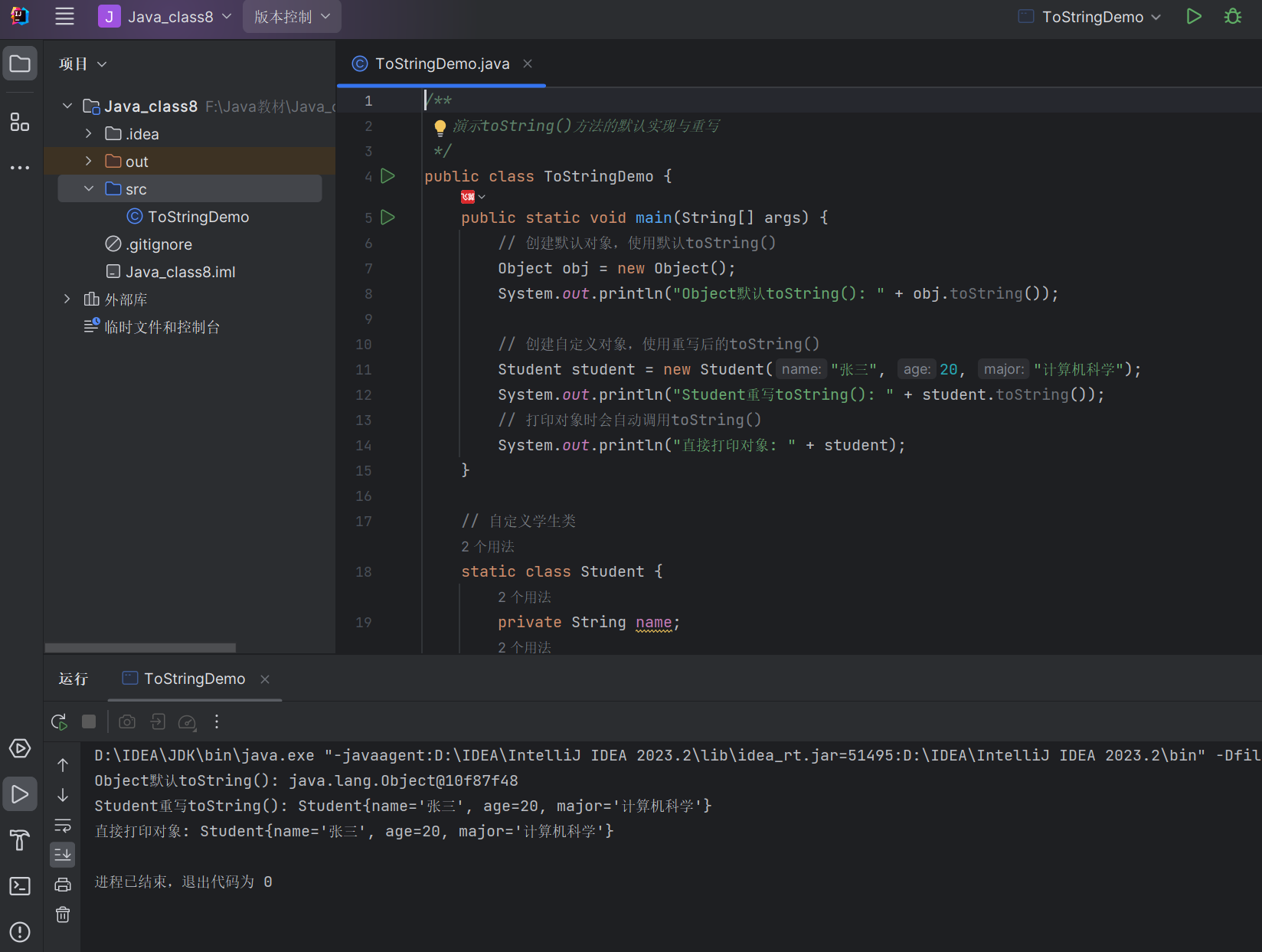
代码示例:toString () 方法使用与重写
/*** 演示toString()方法的默认实现与重写*/
public class ToStringDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 创建默认对象,使用默认toString()Object obj = new Object();System.out.println("Object默认toString(): " + obj.toString());// 创建自定义对象,使用重写后的toString()Student student = new Student("张三", 20, "计算机科学");System.out.println("Student重写toString(): " + student.toString());// 打印对象时会自动调用toString()System.out.println("直接打印对象: " + student);}// 自定义学生类static class Student {private String name;private int age;private String major;public Student(String name, int age, String major) {this.name = name;this.age = age;this.major = major;}// 重写toString()方法,返回对象的关键信息@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Student{name='" + name + "', age=" + age + ", major='" + major + "'}";}}
}
运行结果:
8.1.2 equals () 方法

作用:判断两个对象是否 "相等",默认实现为 this == obj(比较内存地址)。
与 == 的区别:
==对于基本类型比较值,对于引用类型比较内存地址- equals () 默认比较内存地址,重写后可自定义 "相等" 逻辑(如比较属性值)
重写原则:
- 自反性:
x.equals(x)应返回 true - 对称性:
x.equals(y)与y.equals(x)结果一致 - 传递性:若
x.equals(y)和y.equals(z)为 true,则x.equals(z)也为 true - 一致性:多次调用结果应一致
- 非空性:
x.equals(null)应返回 false
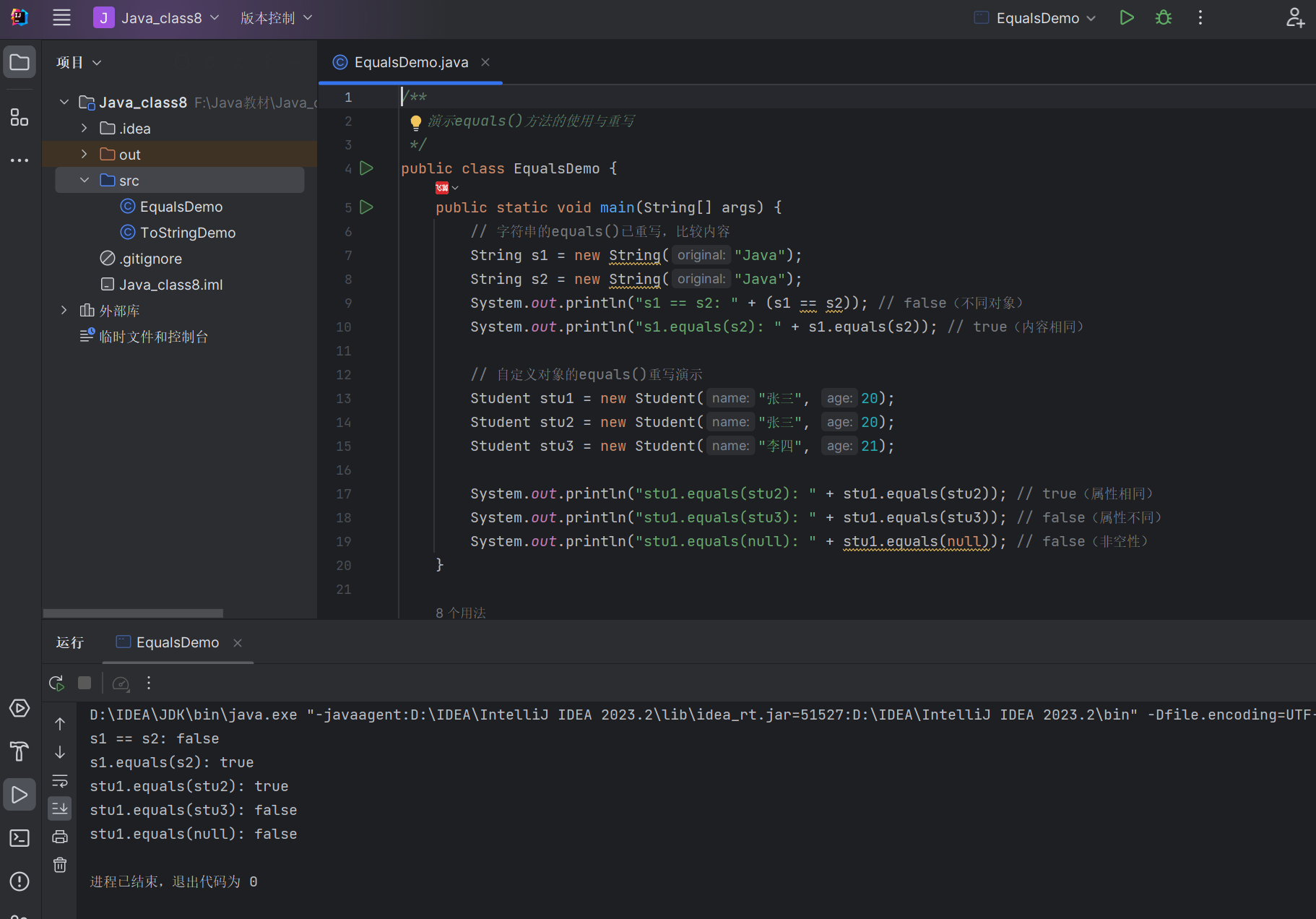
代码示例:equals () 方法重写与使用
/*** 演示equals()方法的使用与重写*/
public class EqualsDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 字符串的equals()已重写,比较内容String s1 = new String("Java");String s2 = new String("Java");System.out.println("s1 == s2: " + (s1 == s2)); // false(不同对象)System.out.println("s1.equals(s2): " + s1.equals(s2)); // true(内容相同)// 自定义对象的equals()重写演示Student stu1 = new Student("张三", 20);Student stu2 = new Student("张三", 20);Student stu3 = new Student("李四", 21);System.out.println("stu1.equals(stu2): " + stu1.equals(stu2)); // true(属性相同)System.out.println("stu1.equals(stu3): " + stu1.equals(stu3)); // false(属性不同)System.out.println("stu1.equals(null): " + stu1.equals(null)); // false(非空性)}static class Student {private String name;private int age;public Student(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}// 重写equals(),当姓名和年龄都相同时认为相等@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {// 1. 自反性检查:地址相同直接返回trueif (this == o) return true;// 2. 非空性和类型检查if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;// 3. 转换类型并比较属性Student student = (Student) o;return age == student.age && name.equals(student.name);}}
}
运行结果:
8.1.3 hashCode () 方法
作用:返回对象的哈希码值,主要用于哈希表(如 HashMap、HashSet)中快速定位对象。
与 equals () 的关系:
- 若
x.equals(y)为 true,则x.hashCode()必须等于y.hashCode() - 若
x.hashCode()不等,则x.equals(y)一定为 false - 若
x.hashCode()相等,x.equals(y)不一定为 true(哈希冲突)
重写建议:当重写 equals () 时,必须同时重写 hashCode (),确保相等的对象有相同的哈希码。
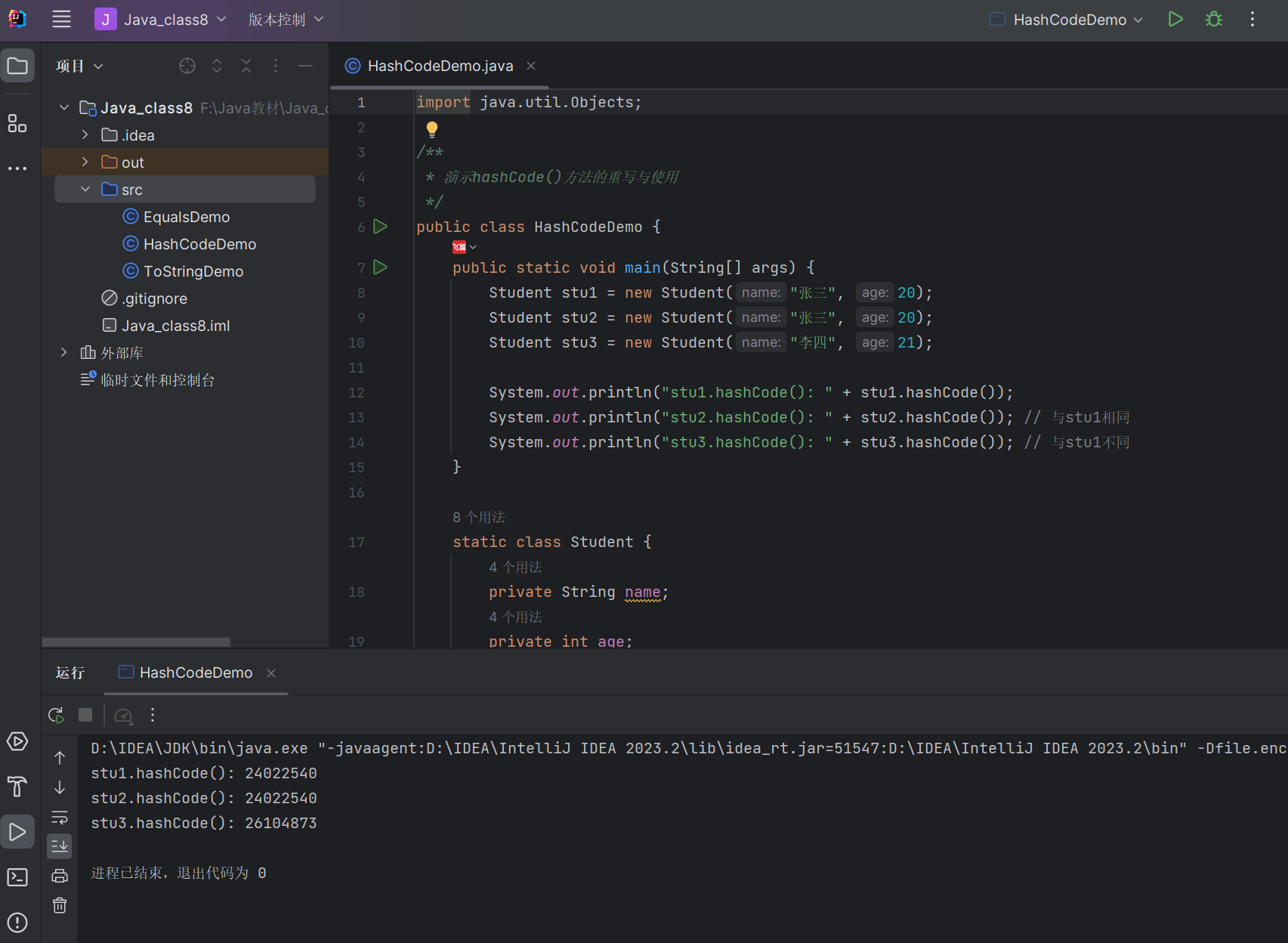
代码示例:hashCode () 方法重写
import java.util.Objects;/*** 演示hashCode()方法的重写与使用*/
public class HashCodeDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {Student stu1 = new Student("张三", 20);Student stu2 = new Student("张三", 20);Student stu3 = new Student("李四", 21);System.out.println("stu1.hashCode(): " + stu1.hashCode());System.out.println("stu2.hashCode(): " + stu2.hashCode()); // 与stu1相同System.out.println("stu3.hashCode(): " + stu3.hashCode()); // 与stu1不同}static class Student {private String name;private int age;public Student(String name, int age) {this.name = name;this.age = age;}// 重写equals()@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;Student student = (Student) o;return age == student.age && Objects.equals(name, student.name);}// 重写hashCode(),基于name和age计算哈希码@Overridepublic int hashCode() {// Objects.hash()会自动处理null值return Objects.hash(name, age);}}
}
运行结果:
8.1.4 clone () 方法
作用:创建并返回对象的副本,实现对象的复制。
使用条件:
- 类必须实现
Cloneable接口(标记接口,无方法) - 重写 clone () 方法(通常调用
super.clone()) - 若有引用类型属性,需考虑深拷贝
浅拷贝 vs 深拷贝:
- 浅拷贝:基本类型属性复制值,引用类型属性复制地址(共享对象)
- 深拷贝:所有属性都复制新对象,完全独立
代码示例:对象克隆(浅拷贝与深拷贝)
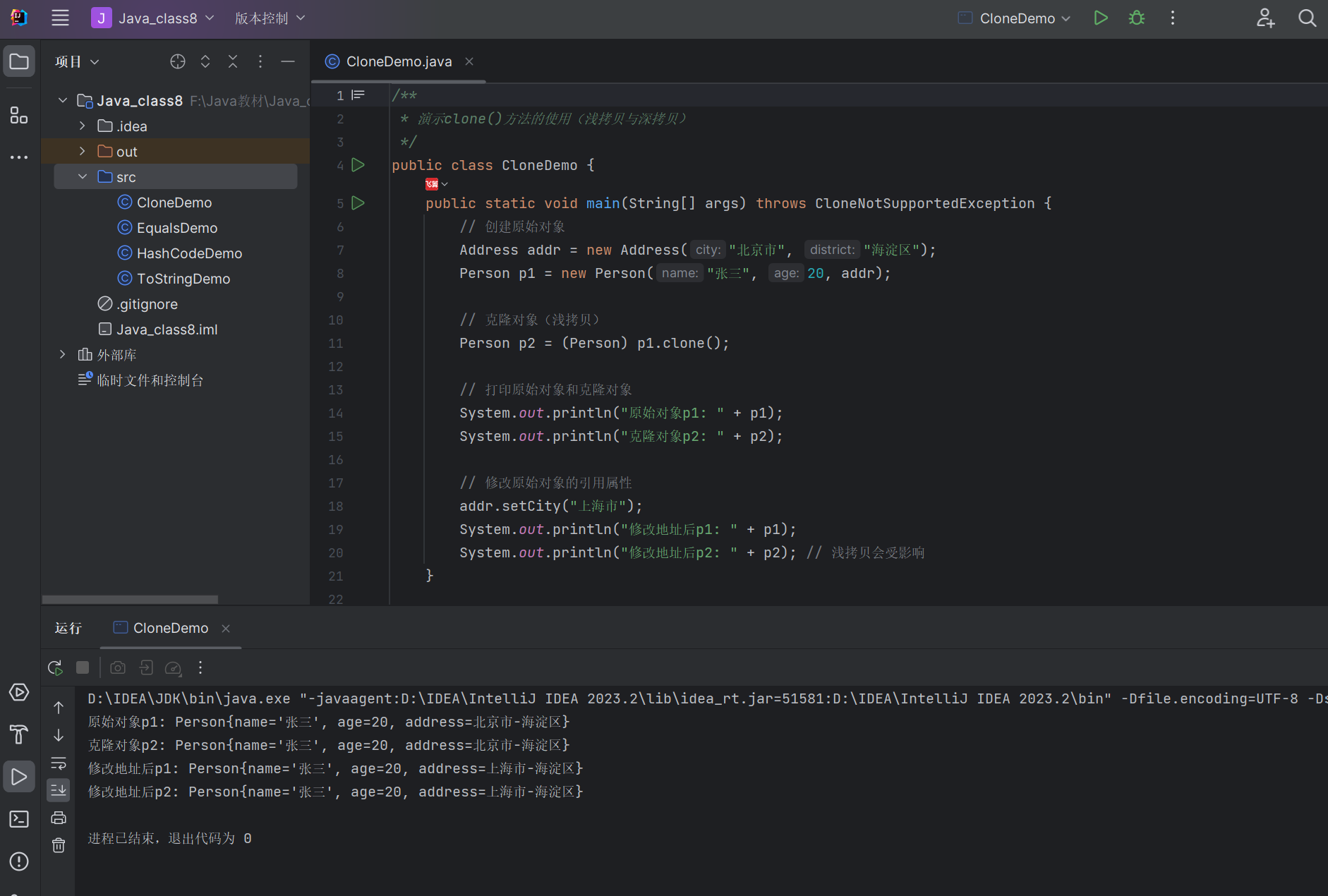
/*** 演示clone()方法的使用(浅拷贝与深拷贝)*/
public class CloneDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws CloneNotSupportedException {// 创建原始对象Address addr = new Address("北京市", "海淀区");Person p1 = new Person("张三", 20, addr);// 克隆对象(浅拷贝)Person p2 = (Person) p1.clone();// 打印原始对象和克隆对象System.out.println("原始对象p1: " + p1);System.out.println("克隆对象p2: " + p2);// 修改原始对象的引用属性addr.setCity("上海市");System.out.println("修改地址后p1: " + p1);System.out.println("修改地址后p2: " + p2); // 浅拷贝会受影响}// 地址类(引用类型)static class Address {private String city;private String district;public Address(String city, String district) {this.city = city;this.district = district;}public void setCity(String city) {this.city = city;}@Overridepublic String toString() {return city + "-" + district;}}// 人员类(实现Cloneable接口)static class Person implements Cloneable {private String name;private int age;private Address address; // 引用类型属性public Person(String name, int age, Address address) {this.name = name;this.age = age;this.address = address;}// 重写clone()方法(浅拷贝)@Overrideprotected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {// 调用父类clone()实现浅拷贝return super.clone();}@Overridepublic String toString() {return "Person{name='" + name + "', age=" + age + ", address=" + address + "}";}}
}
运行结果:
深拷贝实现:修改 Person 类的 clone () 方法,对引用类型属性也进行克隆:
// 深拷贝实现
@Override
protected Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {// 1. 先浅拷贝基本类型Person clone = (Person) super.clone();// 2. 对引用类型属性单独克隆clone.address = new Address(address.city, address.district);return clone;
}
8.1.5 finalize () 方法
作用:垃圾回收器回收对象前调用,用于释放资源(如文件句柄、网络连接)。
特点:
- 执行时间不确定(垃圾回收时机不确定)
- 不推荐依赖此方法释放资源(建议用 try-with-resources)
- Java 9 后已标记为过时(@Deprecated)
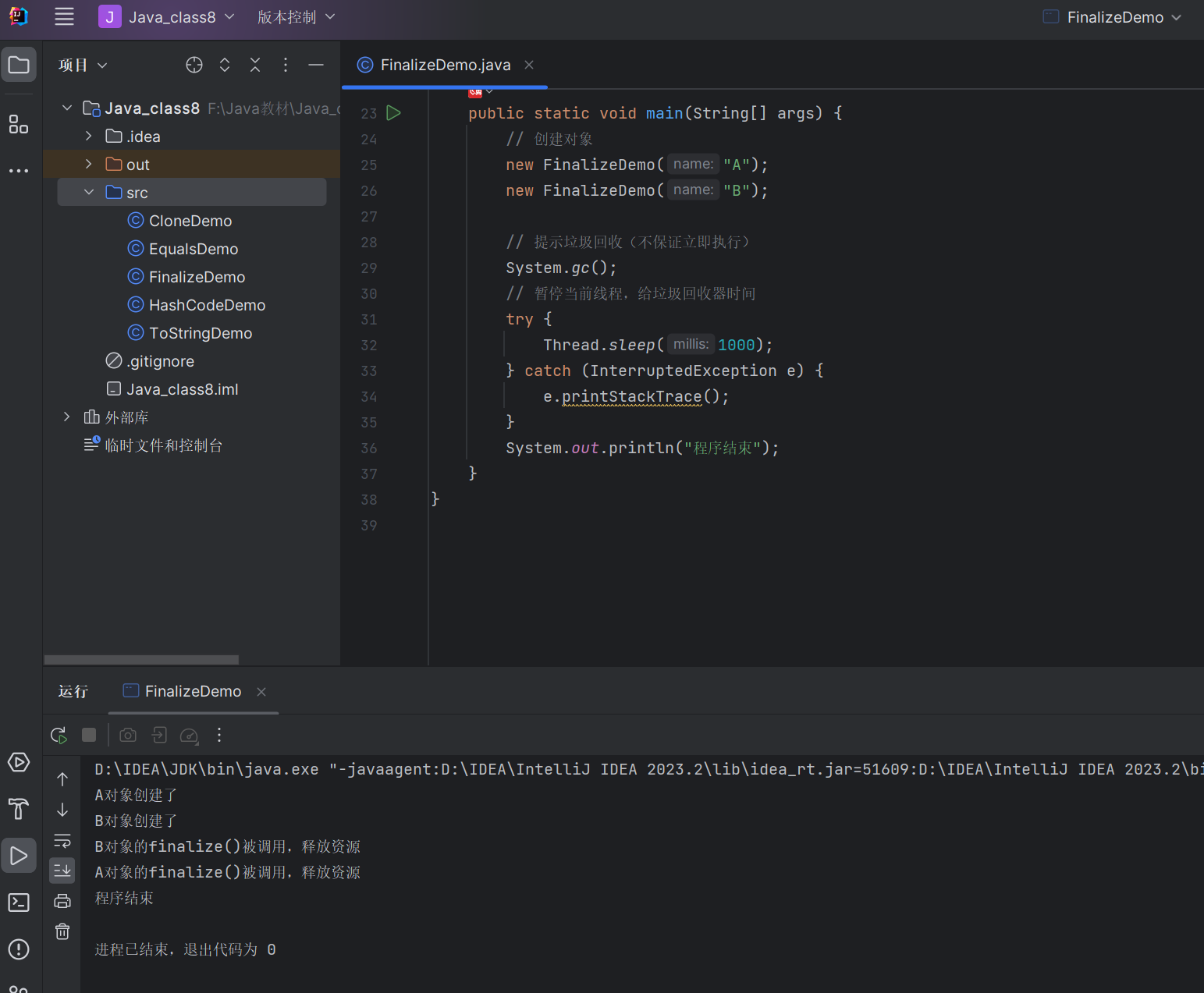
代码示例:finalize () 方法演示
/*** 演示finalize()方法的使用(仅作了解,实际开发不推荐)*/
public class FinalizeDemo {private String name;public FinalizeDemo(String name) {this.name = name;System.out.println(name + "对象创建了");}// 重写finalize()方法@Overrideprotected void finalize() throws Throwable {try {System.out.println(name + "对象的finalize()被调用,释放资源");} finally {// 调用父类的finalize()super.finalize();}}public static void main(String[] args) {// 创建对象new FinalizeDemo("A");new FinalizeDemo("B");// 提示垃圾回收(不保证立即执行)System.gc();// 暂停当前线程,给垃圾回收器时间try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println("程序结束");}
}
运行结果:
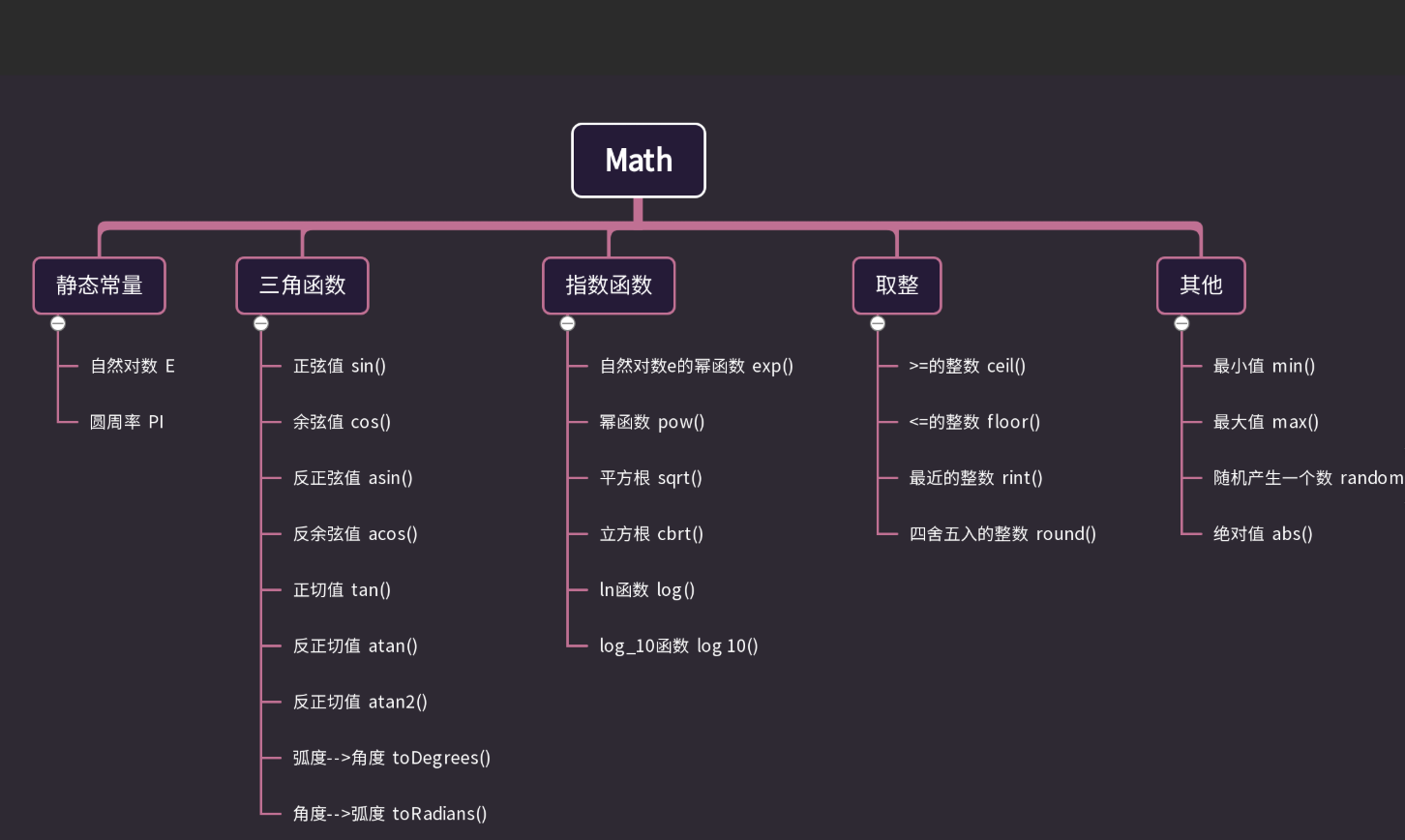
8.2 Math 类
Math 类是 Java 提供的数学工具类,包含大量静态方法,用于基本数学运算。
常用方法分类
| 类别 | 常用方法 | 功能描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 绝对值 | abs(int/double) | 计算绝对值 |
| 最值 | max(a,b), min(a,b) | 计算最大值 / 最小值 |
| 三角函数 | sin(), cos(), tan(), toRadians() | 三角函数计算(弧度制) |
| 指数对数 | pow(a,b), sqrt(), log(), exp() | 幂运算、平方根、对数 |
| 取整 | ceil(), floor(), round() | 向上取整、向下取整、四舍五入 |
| 随机数 | random() | 生成 [0.0,1.0) 的随机数 |
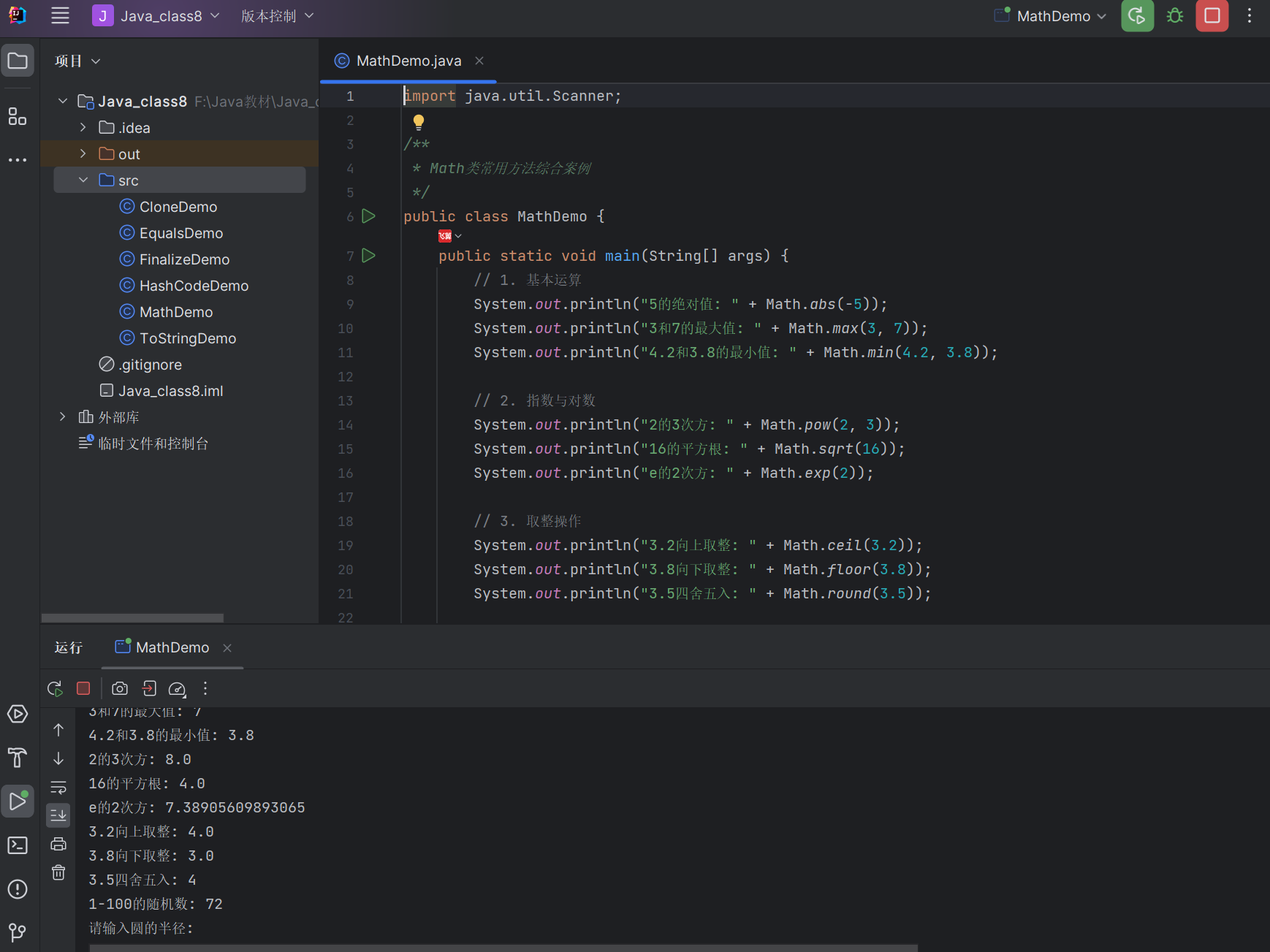
代码示例:Math 类常用方法综合案例
import java.util.Scanner;/*** Math类常用方法综合案例*/
public class MathDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. 基本运算System.out.println("5的绝对值: " + Math.abs(-5));System.out.println("3和7的最大值: " + Math.max(3, 7));System.out.println("4.2和3.8的最小值: " + Math.min(4.2, 3.8));// 2. 指数与对数System.out.println("2的3次方: " + Math.pow(2, 3));System.out.println("16的平方根: " + Math.sqrt(16));System.out.println("e的2次方: " + Math.exp(2));// 3. 取整操作System.out.println("3.2向上取整: " + Math.ceil(3.2));System.out.println("3.8向下取整: " + Math.floor(3.8));System.out.println("3.5四舍五入: " + Math.round(3.5));// 4. 随机数应用:生成1-100的随机整数int randomNum = (int) (Math.random() * 100) + 1;System.out.println("1-100的随机数: " + randomNum);// 5. 综合案例:计算圆的面积和周长Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.print("请输入圆的半径: ");double radius = scanner.nextDouble();double area = Math.PI * Math.pow(radius, 2); // 面积=πr²double circumference = 2 * Math.PI * radius; // 周长=2πrSystem.out.printf("半径为%.2f的圆,面积: %.2f,周长: %.2f%n", radius, area, circumference);scanner.close();}
}
运行结果:
8.3 基本类型包装类
Java 为 8 种基本类型提供了对应的包装类,用于将基本类型转为对象,便于在泛型、集合等场景中使用。
包装类对应关系
| 基本类型 | 包装类 | 父类 |
|---|---|---|
| byte | Byte | Number |
| short | Short | Number |
| int | Integer | Number |
| long | Long | Number |
| float | Float | Number |
| double | Double | Number |
| char | Character | Object |
| boolean | Boolean | Object |
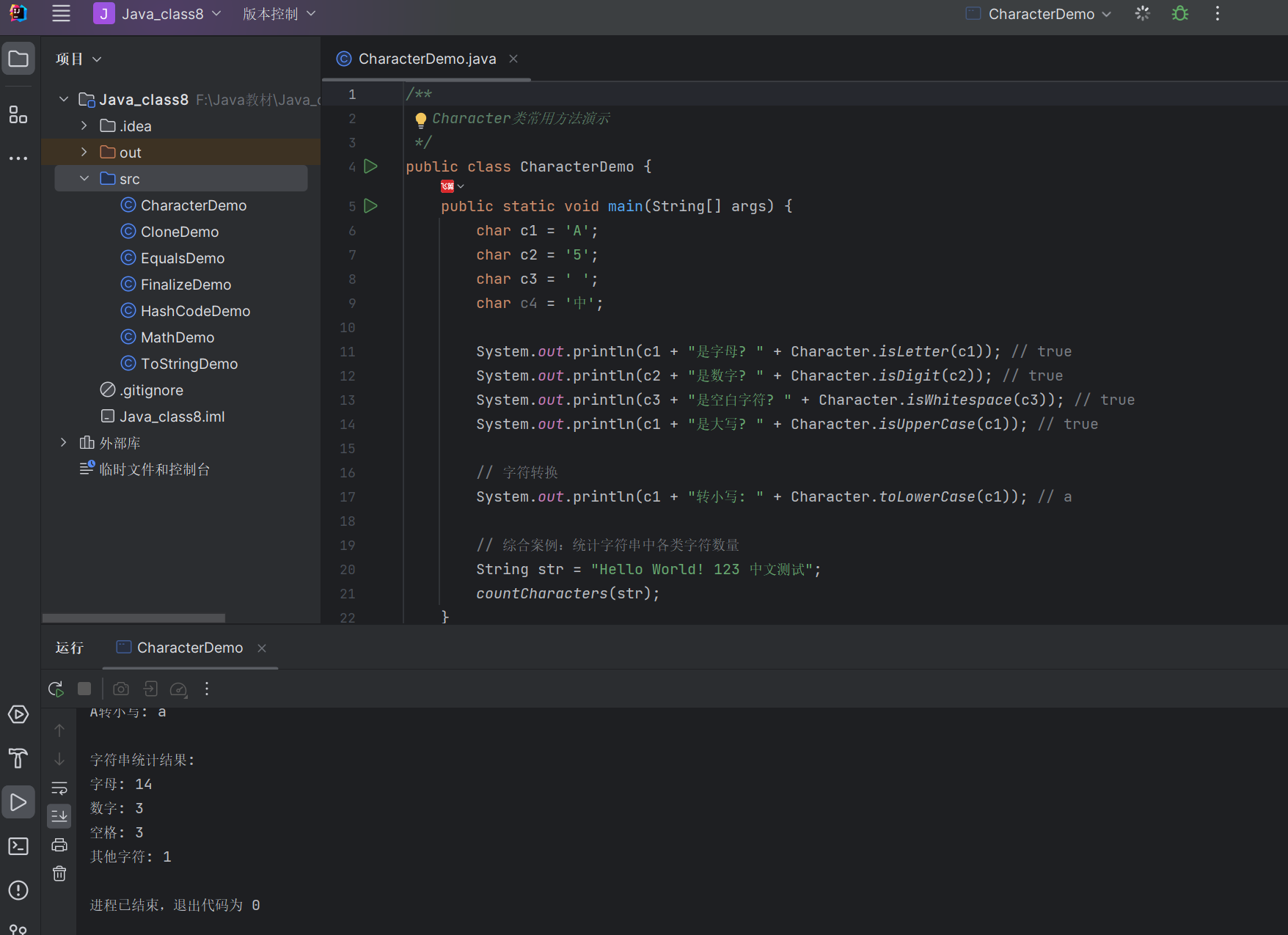
8.3.1 Character 类
Character 类用于操作单个字符,提供字符判断和转换的静态方法。
常用方法
isLetter(char):是否为字母isDigit(char):是否为数字isWhitespace(char):是否为空白字符isUpperCase(char)/isLowerCase(char):是否为大小写toUpperCase(char)/toLowerCase(char):转换大小写
代码示例:Character 类使用
/*** Character类常用方法演示*/
public class CharacterDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {char c1 = 'A';char c2 = '5';char c3 = ' ';char c4 = '中';System.out.println(c1 + "是字母? " + Character.isLetter(c1)); // trueSystem.out.println(c2 + "是数字? " + Character.isDigit(c2)); // trueSystem.out.println(c3 + "是空白字符? " + Character.isWhitespace(c3)); // trueSystem.out.println(c1 + "是大写? " + Character.isUpperCase(c1)); // true// 字符转换System.out.println(c1 + "转小写: " + Character.toLowerCase(c1)); // a// 综合案例:统计字符串中各类字符数量String str = "Hello World! 123 中文测试";countCharacters(str);}// 统计字符串中字母、数字、空格和其他字符的数量public static void countCharacters(String str) {int letterCount = 0; // 字母数量int digitCount = 0; // 数字数量int spaceCount = 0; // 空格数量int otherCount = 0; // 其他字符数量for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {char c = str.charAt(i);if (Character.isLetter(c)) {letterCount++;} else if (Character.isDigit(c)) {digitCount++;} else if (Character.isWhitespace(c)) {spaceCount++;} else {otherCount++;}}System.out.println("\n字符串统计结果:");System.out.println("字母: " + letterCount);System.out.println("数字: " + digitCount);System.out.println("空格: " + spaceCount);System.out.println("其他字符: " + otherCount);}
}
运行结果:
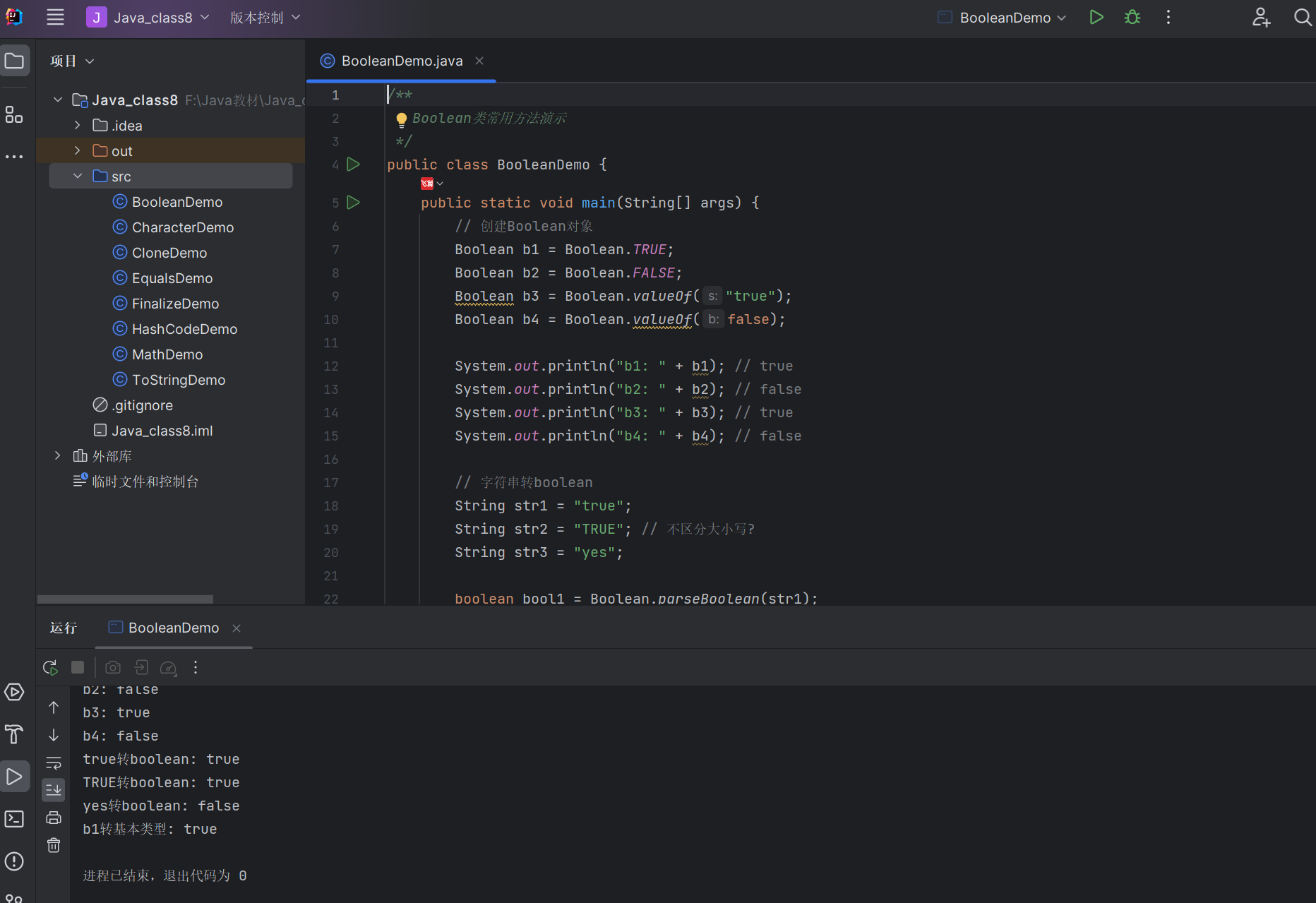
8.3.2 Boolean 类
Boolean 类是 boolean 的包装类,提供了 boolean 与 String 的转换方法。
常用方法
parseBoolean(String):将字符串转为 boolean("true" 返回 true,其他返回 false)valueOf(boolean)/valueOf(String):返回 Boolean 对象booleanValue():将 Boolean 对象转为 boolean 基本类型
代码示例:Boolean 类使用
/*** Boolean类常用方法演示*/
public class BooleanDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 创建Boolean对象Boolean b1 = Boolean.TRUE;Boolean b2 = Boolean.FALSE;Boolean b3 = Boolean.valueOf("true");Boolean b4 = Boolean.valueOf(false);System.out.println("b1: " + b1); // trueSystem.out.println("b2: " + b2); // falseSystem.out.println("b3: " + b3); // trueSystem.out.println("b4: " + b4); // false// 字符串转booleanString str1 = "true";String str2 = "TRUE"; // 不区分大小写?String str3 = "yes";boolean bool1 = Boolean.parseBoolean(str1);boolean bool2 = Boolean.parseBoolean(str2); // 注意:仅"true"(忽略大小写? 不,严格小写"true"才返回true)boolean bool3 = Boolean.parseBoolean(str3);System.out.println(str1 + "转boolean: " + bool1); // trueSystem.out.println(str2 + "转boolean: " + bool2); // false(必须严格小写"true")System.out.println(str3 + "转boolean: " + bool3); // false// 对象转基本类型boolean primitive = b1.booleanValue();System.out.println("b1转基本类型: " + primitive); // true}
}
运行结果:
8.3.3 创建数值类对象
数值类(Integer、Double 等)继承自 Number 类,提供多种创建对象的方式。
代码示例:数值类对象创建
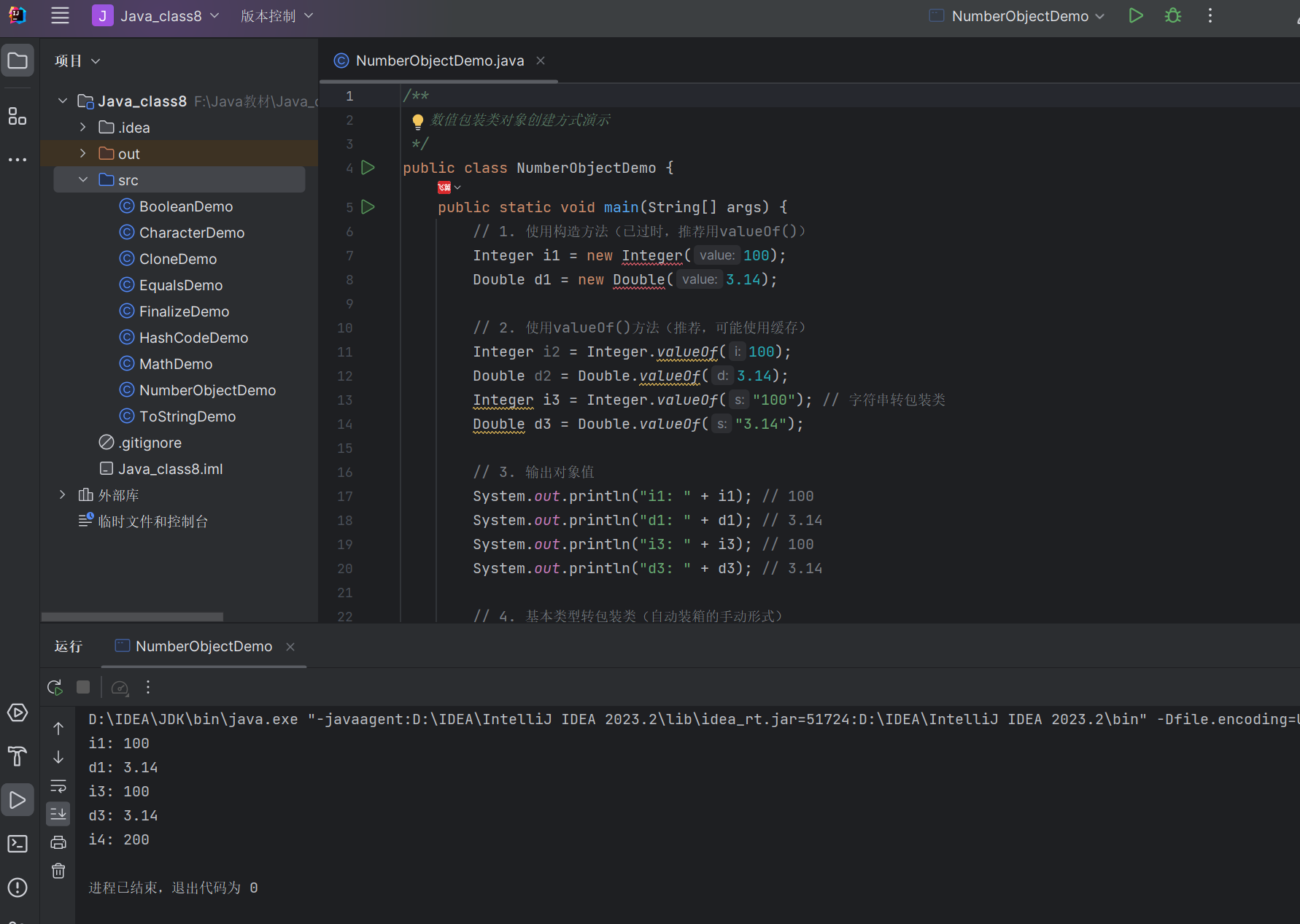
/*** 数值包装类对象创建方式演示*/
public class NumberObjectDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. 使用构造方法(已过时,推荐用valueOf())Integer i1 = new Integer(100);Double d1 = new Double(3.14);// 2. 使用valueOf()方法(推荐,可能使用缓存)Integer i2 = Integer.valueOf(100);Double d2 = Double.valueOf(3.14);Integer i3 = Integer.valueOf("100"); // 字符串转包装类Double d3 = Double.valueOf("3.14");// 3. 输出对象值System.out.println("i1: " + i1); // 100System.out.println("d1: " + d1); // 3.14System.out.println("i3: " + i3); // 100System.out.println("d3: " + d3); // 3.14// 4. 基本类型转包装类(自动装箱的手动形式)int num = 200;Integer i4 = Integer.valueOf(num);System.out.println("i4: " + i4); // 200}
}
8.3.4 数值类的常量
数值类定义了表示取值范围和特殊值的常量。
代码示例:数值类常量使用
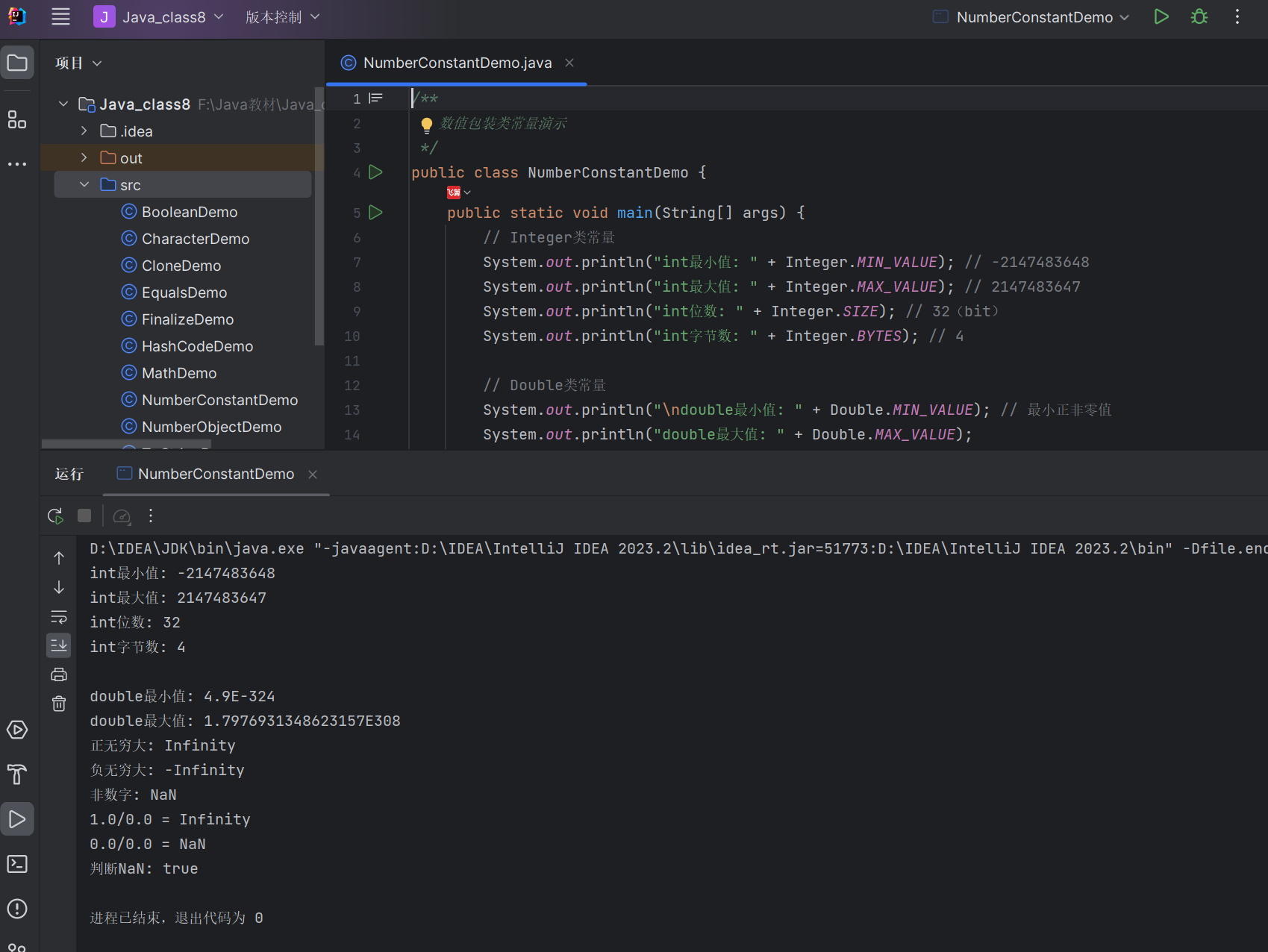
/*** 数值包装类常量演示*/
public class NumberConstantDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// Integer类常量System.out.println("int最小值: " + Integer.MIN_VALUE); // -2147483648System.out.println("int最大值: " + Integer.MAX_VALUE); // 2147483647System.out.println("int位数: " + Integer.SIZE); // 32(bit)System.out.println("int字节数: " + Integer.BYTES); // 4// Double类常量System.out.println("\ndouble最小值: " + Double.MIN_VALUE); // 最小正非零值System.out.println("double最大值: " + Double.MAX_VALUE);System.out.println("正无穷大: " + Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY);System.out.println("负无穷大: " + Double.NEGATIVE_INFINITY);System.out.println("非数字: " + Double.NaN);// 演示无穷大和NaNdouble inf = 1.0 / 0.0;double nan = 0.0 / 0.0;System.out.println("1.0/0.0 = " + inf); // InfinitySystem.out.println("0.0/0.0 = " + nan); // NaNSystem.out.println("判断NaN: " + Double.isNaN(nan)); // true}
}
运行结果:
8.3.5 自动装箱与自动拆箱
- 自动装箱:基本类型自动转为包装类对象(如
int → Integer) - 自动拆箱:包装类对象自动转为基本类型(如
Integer → int)
代码示例:自动装箱与拆箱
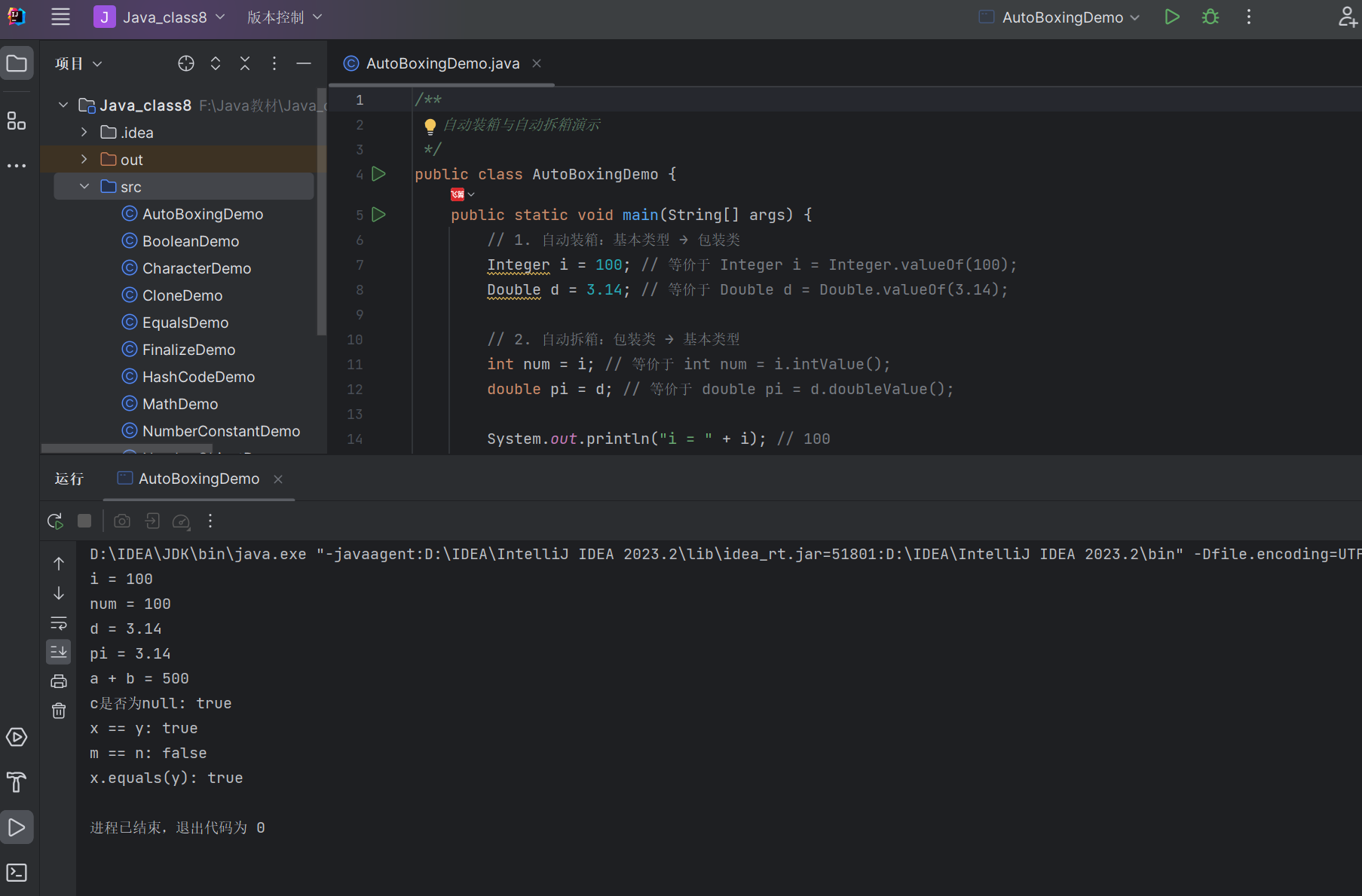
/*** 自动装箱与自动拆箱演示*/
public class AutoBoxingDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. 自动装箱:基本类型 → 包装类Integer i = 100; // 等价于 Integer i = Integer.valueOf(100);Double d = 3.14; // 等价于 Double d = Double.valueOf(3.14);// 2. 自动拆箱:包装类 → 基本类型int num = i; // 等价于 int num = i.intValue();double pi = d; // 等价于 double pi = d.doubleValue();System.out.println("i = " + i); // 100System.out.println("num = " + num); // 100System.out.println("d = " + d); // 3.14System.out.println("pi = " + pi); // 3.14// 3. 集合中的自动装箱java.util.List<Integer> list = new java.util.ArrayList<>();list.add(1); // 自动装箱:int → Integerlist.add(2);list.add(3);// 4. 运算中的自动拆箱Integer a = 200;Integer b = 300;int sum = a + b; // 自动拆箱为int后计算System.out.println("a + b = " + sum); // 500// 5. 注意:包装类可能为null,拆箱时需避免NullPointerExceptionInteger c = null;// int error = c; // 运行时抛出NullPointerExceptionSystem.out.println("c是否为null: " + (c == null)); // true// 6. Integer缓存机制(-128~127之间的值会缓存)Integer x = 127;Integer y = 127;Integer m = 128;Integer n = 128;System.out.println("x == y: " + (x == y)); // true(缓存命中)System.out.println("m == n: " + (m == n)); // false(超出缓存范围)System.out.println("x.equals(y): " + x.equals(y)); // true(值比较)}
}
运行结果:
8.3.6 字符串转换为基本类型
包装类提供了parseXxx(String)方法,将字符串转为对应的基本类型。
代码示例:字符串转基本类型
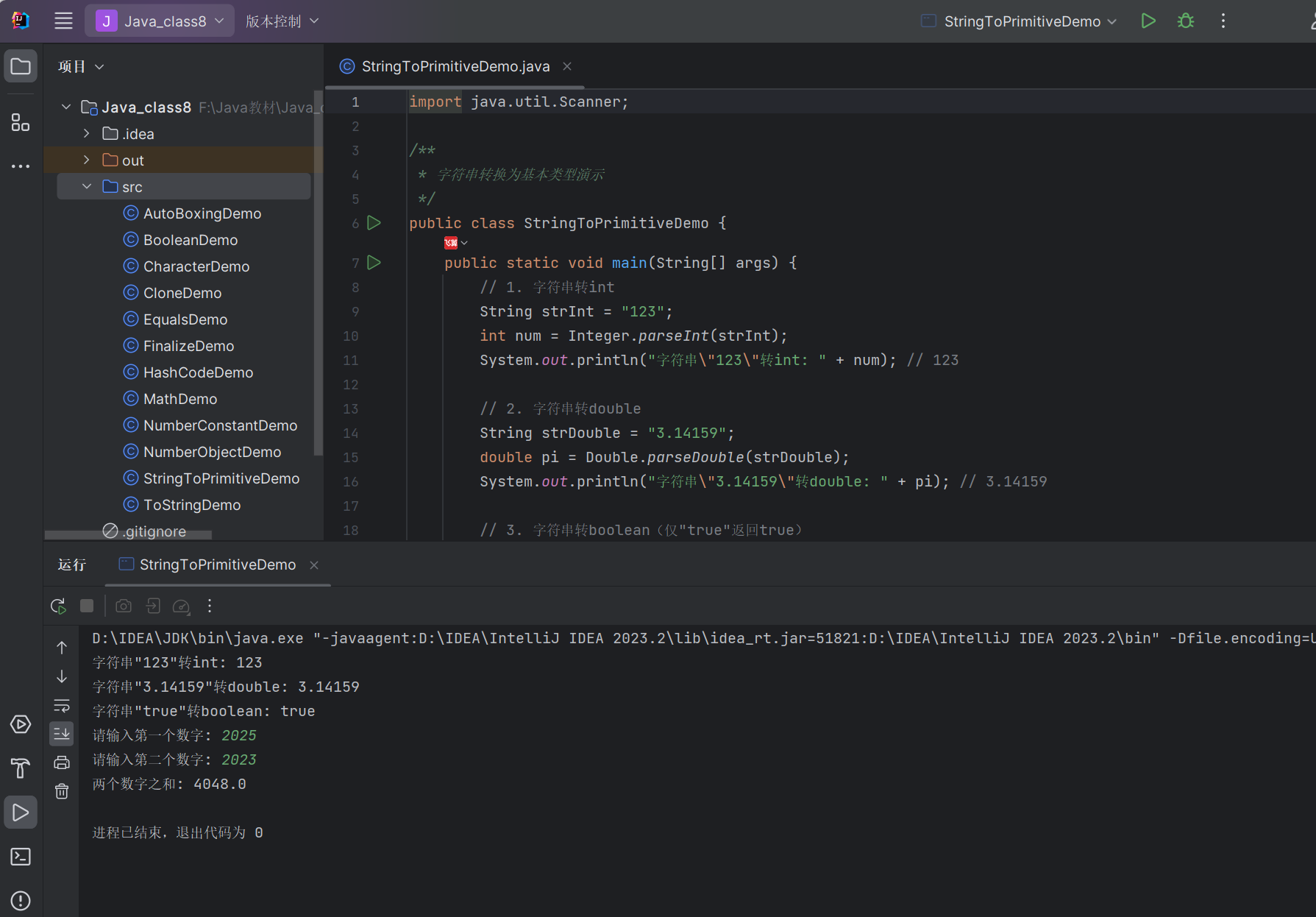
import java.util.Scanner;/*** 字符串转换为基本类型演示*/
public class StringToPrimitiveDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. 字符串转intString strInt = "123";int num = Integer.parseInt(strInt);System.out.println("字符串\"123\"转int: " + num); // 123// 2. 字符串转doubleString strDouble = "3.14159";double pi = Double.parseDouble(strDouble);System.out.println("字符串\"3.14159\"转double: " + pi); // 3.14159// 3. 字符串转boolean(仅"true"返回true)String strBool = "true";boolean flag = Boolean.parseBoolean(strBool);System.out.println("字符串\"true\"转boolean: " + flag); // true// 4. 综合案例:计算用户输入的数字之和Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);System.out.print("请输入第一个数字: ");String input1 = scanner.nextLine();System.out.print("请输入第二个数字: ");String input2 = scanner.nextLine();try {// 字符串转数字double num1 = Double.parseDouble(input1);double num2 = Double.parseDouble(input2);double sum = num1 + num2;System.out.println("两个数字之和: " + sum);} catch (NumberFormatException e) {System.out.println("输入格式错误,无法转换为数字!");}scanner.close();}
}
运行结果:
8.3.7 BigInteger 和 BigDecimal 类
- BigInteger:用于任意精度的整数运算
- BigDecimal:用于任意精度的小数运算(解决 float/double 的精度问题)
代码示例:高精度计算
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.math.RoundingMode;/*** BigInteger和BigDecimal类演示*/
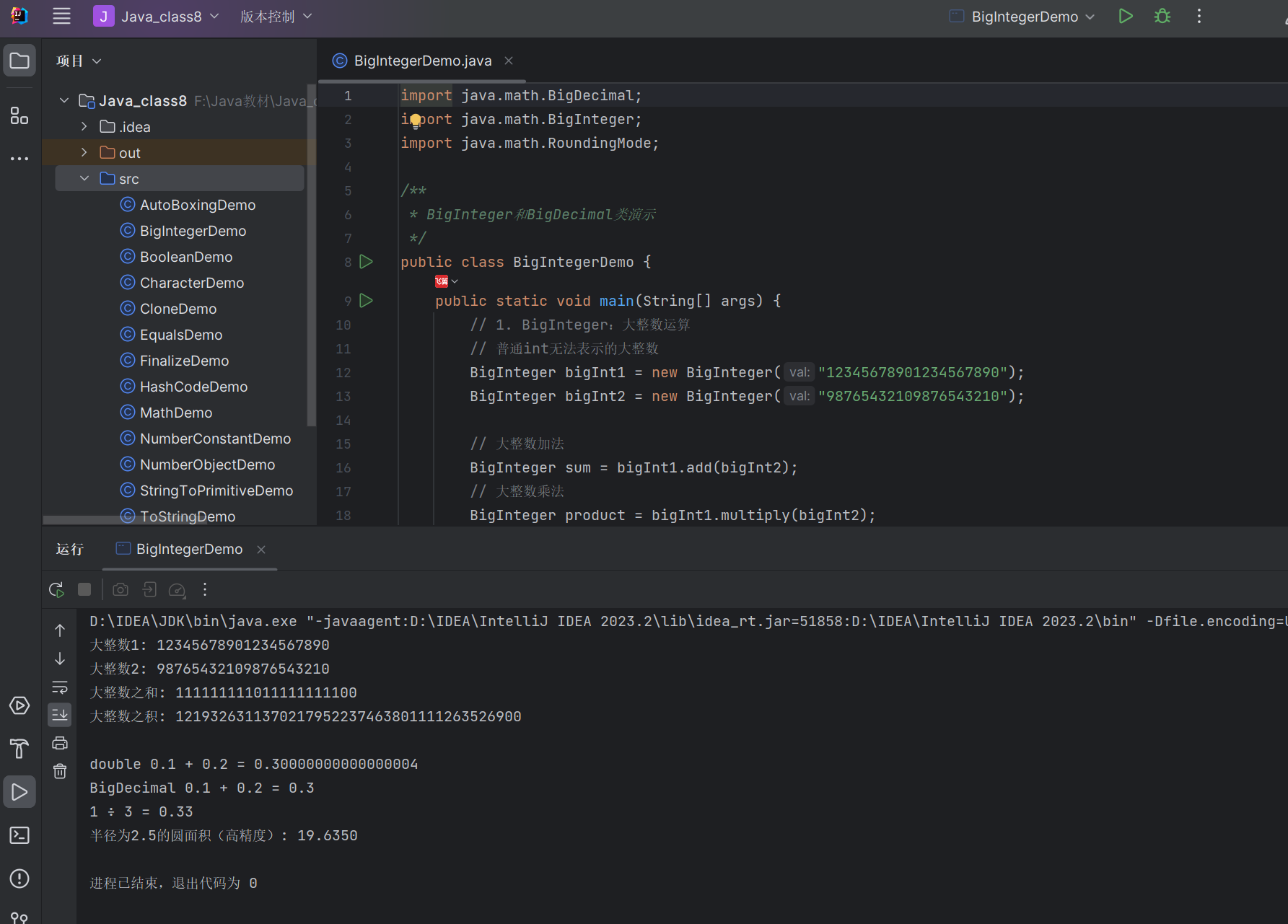
public class BigIntegerDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. BigInteger:大整数运算// 普通int无法表示的大整数BigInteger bigInt1 = new BigInteger("12345678901234567890");BigInteger bigInt2 = new BigInteger("98765432109876543210");// 大整数加法BigInteger sum = bigInt1.add(bigInt2);// 大整数乘法BigInteger product = bigInt1.multiply(bigInt2);System.out.println("大整数1: " + bigInt1);System.out.println("大整数2: " + bigInt2);System.out.println("大整数之和: " + sum);System.out.println("大整数之积: " + product);// 2. BigDecimal:高精度小数运算(解决double精度问题)// 问题:double运算有精度误差double d1 = 0.1;double d2 = 0.2;System.out.println("\ndouble 0.1 + 0.2 = " + (d1 + d2)); // 0.30000000000000004(误差)// 使用BigDecimal解决精度问题BigDecimal bd1 = new BigDecimal("0.1"); // 注意:用字符串构造,避免double本身的误差BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal("0.2");BigDecimal bdSum = bd1.add(bd2);System.out.println("BigDecimal 0.1 + 0.2 = " + bdSum); // 0.3// 3. BigDecimal除法(需指定保留位数和舍入模式)BigDecimal dividend = new BigDecimal("1");BigDecimal divisor = new BigDecimal("3");// 保留2位小数,四舍五入BigDecimal result = dividend.divide(divisor, 2, RoundingMode.HALF_UP);System.out.println("1 ÷ 3 = " + result); // 0.33// 4. 综合案例:计算圆的面积(高精度)BigDecimal radius = new BigDecimal("2.5");BigDecimal pi = new BigDecimal("3.14159265358979323846");BigDecimal area = pi.multiply(radius.pow(2)); // 面积=πr²// 保留4位小数area = area.setScale(4, RoundingMode.HALF_UP);System.out.println("半径为2.5的圆面积(高精度): " + area); // 19.6349}
}
运行结果:
8.4 日期 - 时间 API

Java 8 引入了新的日期 - 时间 API(java.time 包),解决了旧 API(Date、Calendar)的线程不安全、设计混乱等问题。
新日期时间 API 核心类关系图
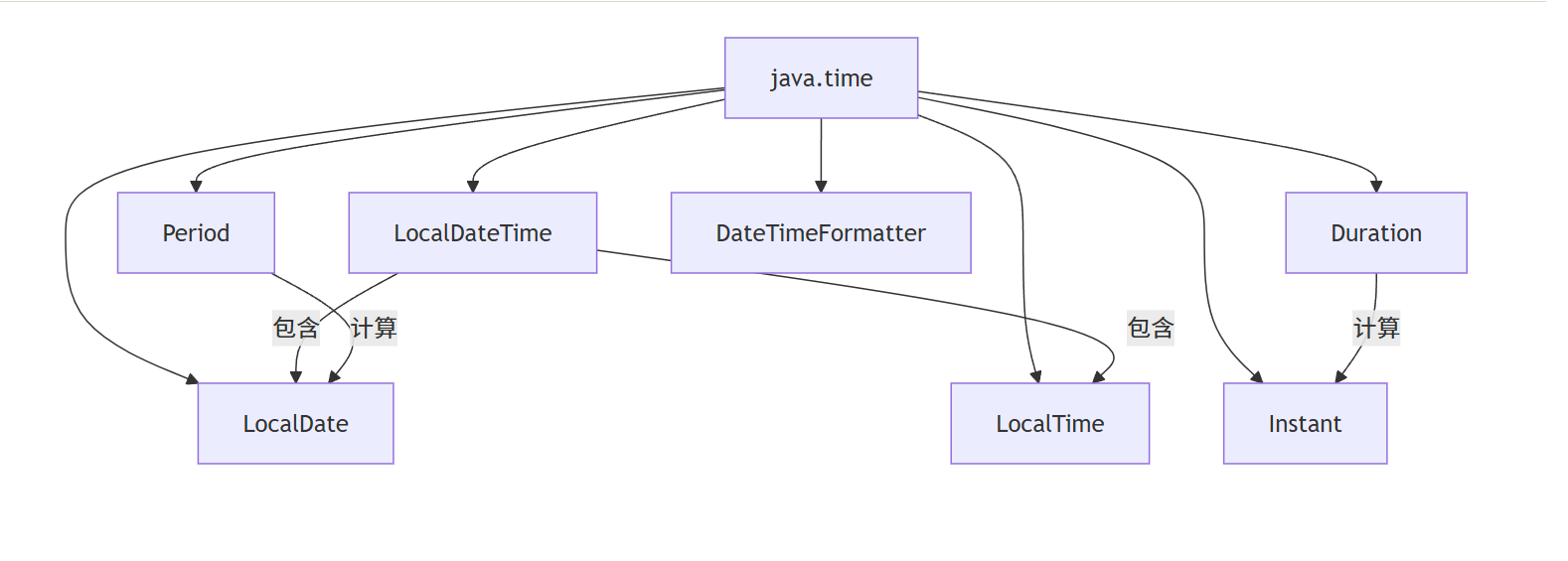
8.4.1 本地日期类 LocalDate
LocalDate 表示不含时间的日期(年 - 月 - 日),不可变且线程安全。
常用方法
now():获取当前日期of(int year, int month, int dayOfMonth):创建指定日期plusDays(long)/minusDays(long):增减天数getYear()/getMonthValue()/getDayOfMonth():获取年 / 月 / 日isLeapYear():判断是否闰年
代码示例:LocalDate 使用
import java.time.LocalDate;/*** LocalDate类常用方法演示*/
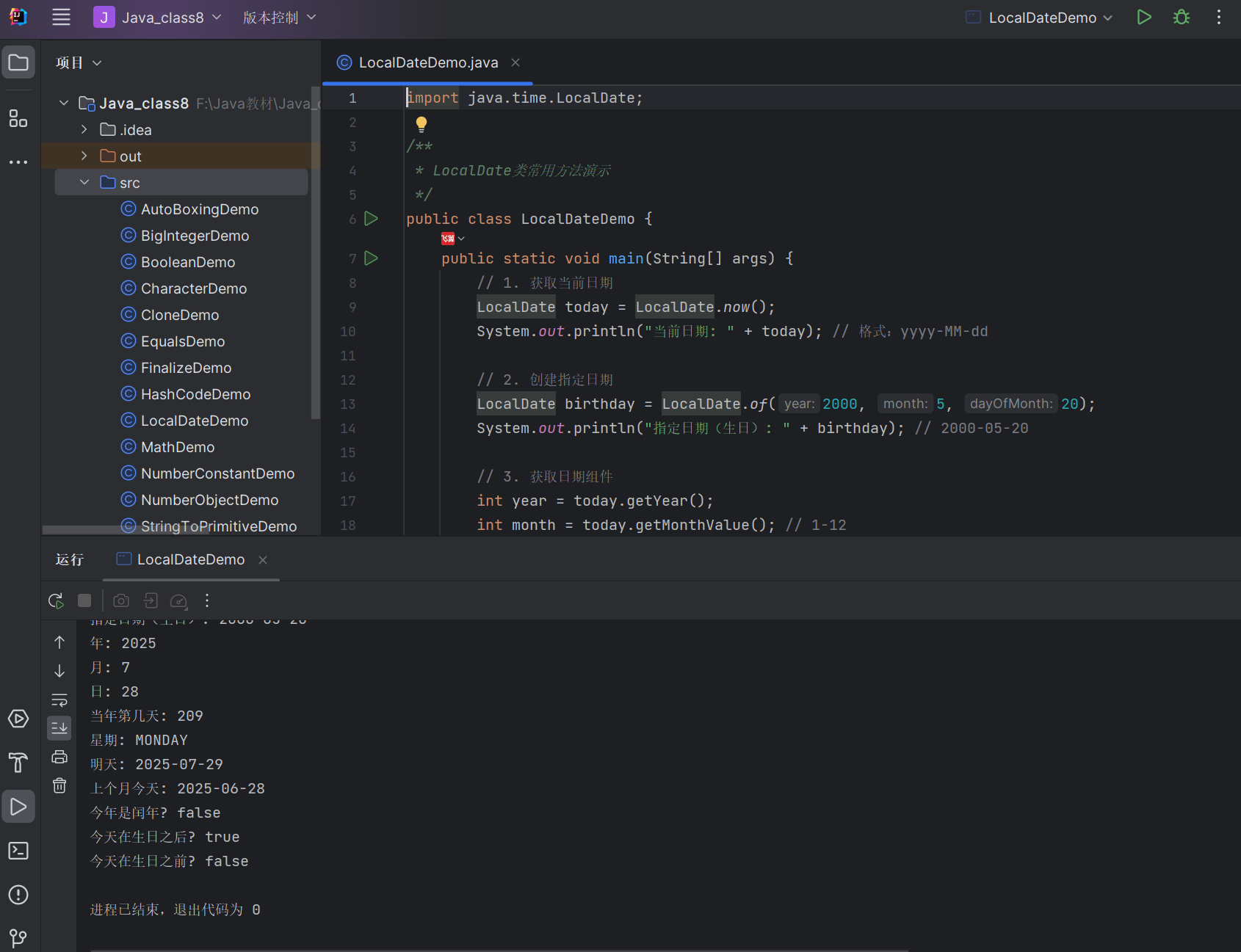
public class LocalDateDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. 获取当前日期LocalDate today = LocalDate.now();System.out.println("当前日期: " + today); // 格式:yyyy-MM-dd// 2. 创建指定日期LocalDate birthday = LocalDate.of(2000, 5, 20);System.out.println("指定日期(生日): " + birthday); // 2000-05-20// 3. 获取日期组件int year = today.getYear();int month = today.getMonthValue(); // 1-12int day = today.getDayOfMonth();int dayOfYear = today.getDayOfYear(); // 当年的第几天String weekday = today.getDayOfWeek().name(); // 星期几(英文)System.out.println("年: " + year);System.out.println("月: " + month);System.out.println("日: " + day);System.out.println("当年第几天: " + dayOfYear);System.out.println("星期: " + weekday);// 4. 日期加减LocalDate tomorrow = today.plusDays(1);LocalDate lastMonth = today.minusMonths(1);System.out.println("明天: " + tomorrow);System.out.println("上个月今天: " + lastMonth);// 5. 判断闰年boolean isLeap = today.isLeapYear();System.out.println("今年是闰年? " + isLeap);// 6. 日期比较boolean isAfter = today.isAfter(birthday);boolean isBefore = today.isBefore(birthday);System.out.println("今天在生日之后? " + isAfter); // trueSystem.out.println("今天在生日之前? " + isBefore); // false}
}
运行结果(因当前日期不同而变化):
8.4.2 本地时间类 LocalTime
LocalTime 表示不含日期的时间(时:分: 秒。纳秒),不可变且线程安全。
常用方法
now():获取当前时间of(int hour, int minute, int second):创建指定时间plusHours()/minusMinutes():增减时 / 分 / 秒getHour()/getMinute()/getSecond():获取时分秒
代码示例:LocalTime 使用
import java.time.LocalTime;/*** LocalTime类常用方法演示*/
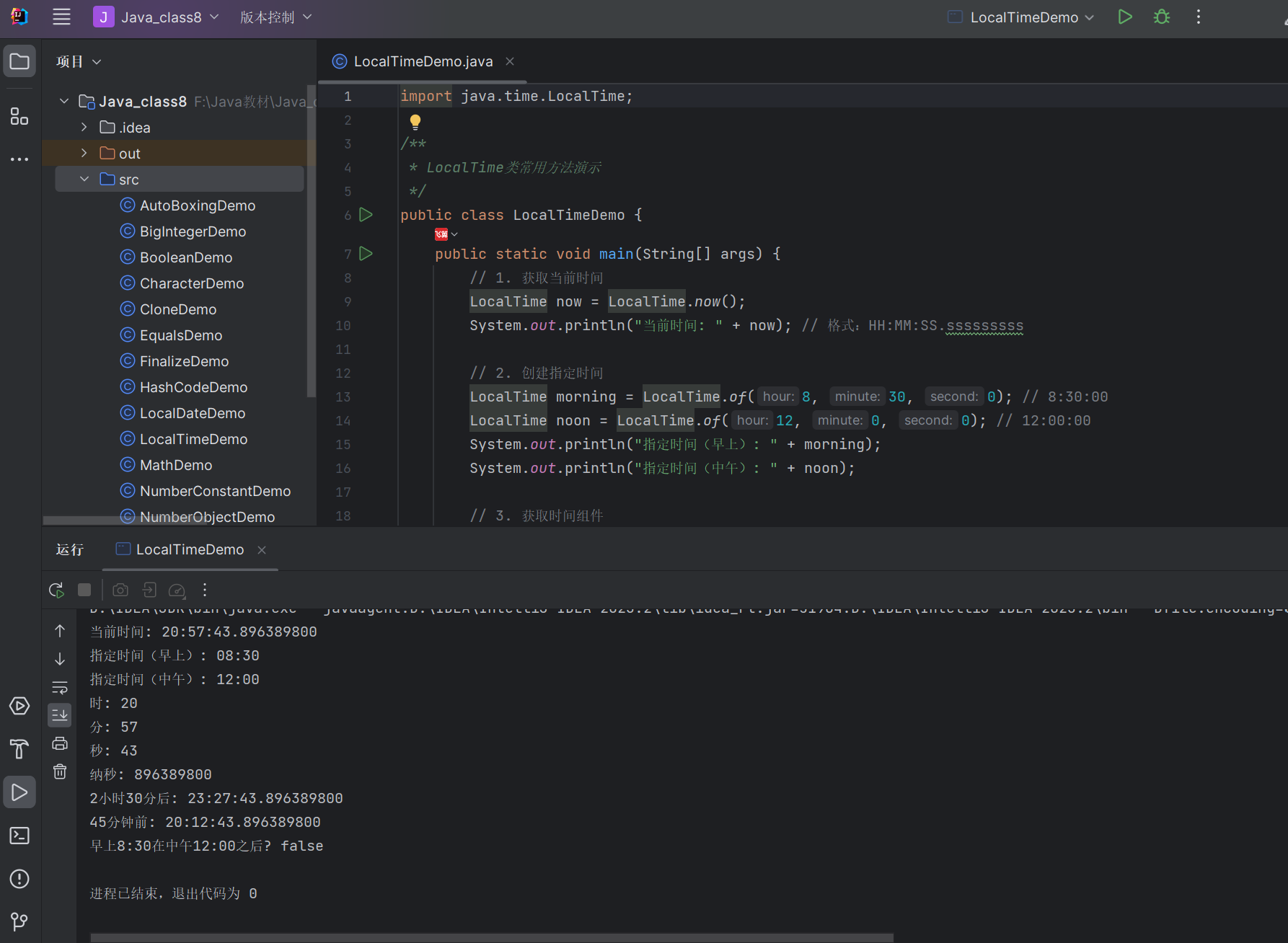
public class LocalTimeDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. 获取当前时间LocalTime now = LocalTime.now();System.out.println("当前时间: " + now); // 格式:HH:MM:SS.sssssssss// 2. 创建指定时间LocalTime morning = LocalTime.of(8, 30, 0); // 8:30:00LocalTime noon = LocalTime.of(12, 0, 0); // 12:00:00System.out.println("指定时间(早上): " + morning);System.out.println("指定时间(中午): " + noon);// 3. 获取时间组件int hour = now.getHour(); // 24小时制int minute = now.getMinute();int second = now.getSecond();int nano = now.getNano(); // 纳秒System.out.println("时: " + hour);System.out.println("分: " + minute);System.out.println("秒: " + second);System.out.println("纳秒: " + nano);// 4. 时间加减LocalTime later = now.plusHours(2).plusMinutes(30);LocalTime earlier = now.minusMinutes(45);System.out.println("2小时30分后: " + later);System.out.println("45分钟前: " + earlier);// 5. 时间比较boolean isMorningLater = morning.isAfter(noon);System.out.println("早上8:30在中午12:00之后? " + isMorningLater); // false}
}
运行结果:
8.4.3 本地日期时间类 LocalDateTime
LocalDateTime 是 LocalDate 和 LocalTime 的组合,表示完整的日期和时间,是最常用的日期时间类。
常用方法
now():获取当前日期时间of(...):创建指定日期时间toLocalDate()/toLocalTime():拆分日期和时间- 继承 LocalDate 和 LocalTime 的所有方法
代码示例:LocalDateTime 使用
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalDate; // 添加LocalDate导入
import java.time.LocalTime; // 添加LocalTime导入/*** LocalDateTime类常用方法演示*/
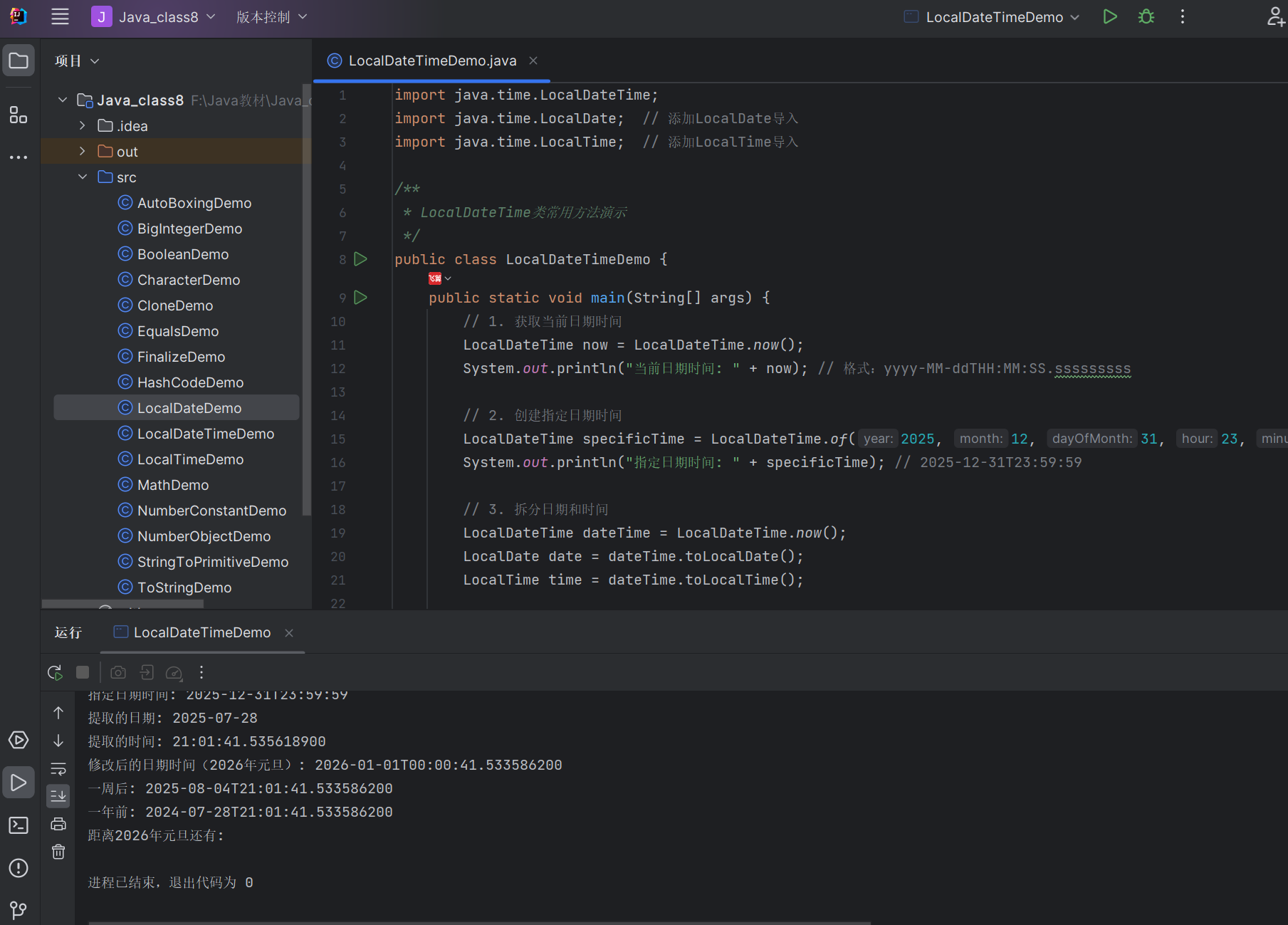
public class LocalDateTimeDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. 获取当前日期时间LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();System.out.println("当前日期时间: " + now); // 格式:yyyy-MM-ddTHH:MM:SS.sssssssss// 2. 创建指定日期时间LocalDateTime specificTime = LocalDateTime.of(2025, 12, 31, 23, 59, 59);System.out.println("指定日期时间: " + specificTime); // 2025-12-31T23:59:59// 3. 拆分日期和时间LocalDateTime dateTime = LocalDateTime.now();LocalDate date = dateTime.toLocalDate();LocalTime time = dateTime.toLocalTime();System.out.println("提取的日期: " + date);System.out.println("提取的时间: " + time);// 4. 修改日期时间LocalDateTime modified = now.withYear(2026) // 修改年份.withMonth(1) // 修改月份.withDayOfMonth(1) // 修改日期.withHour(0) // 修改小时.withMinute(0); // 修改分钟System.out.println("修改后的日期时间(2026年元旦): " + modified);// 5. 日期时间加减LocalDateTime nextWeek = now.plusWeeks(1);LocalDateTime lastYear = now.minusYears(1);System.out.println("一周后: " + nextWeek);System.out.println("一年前: " + lastYear);// 6. 综合案例:计算距离新年还有多久LocalDateTime newYear = LocalDateTime.of(2026, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0);System.out.println("距离2026年元旦还有: ");}
}
运行结果:
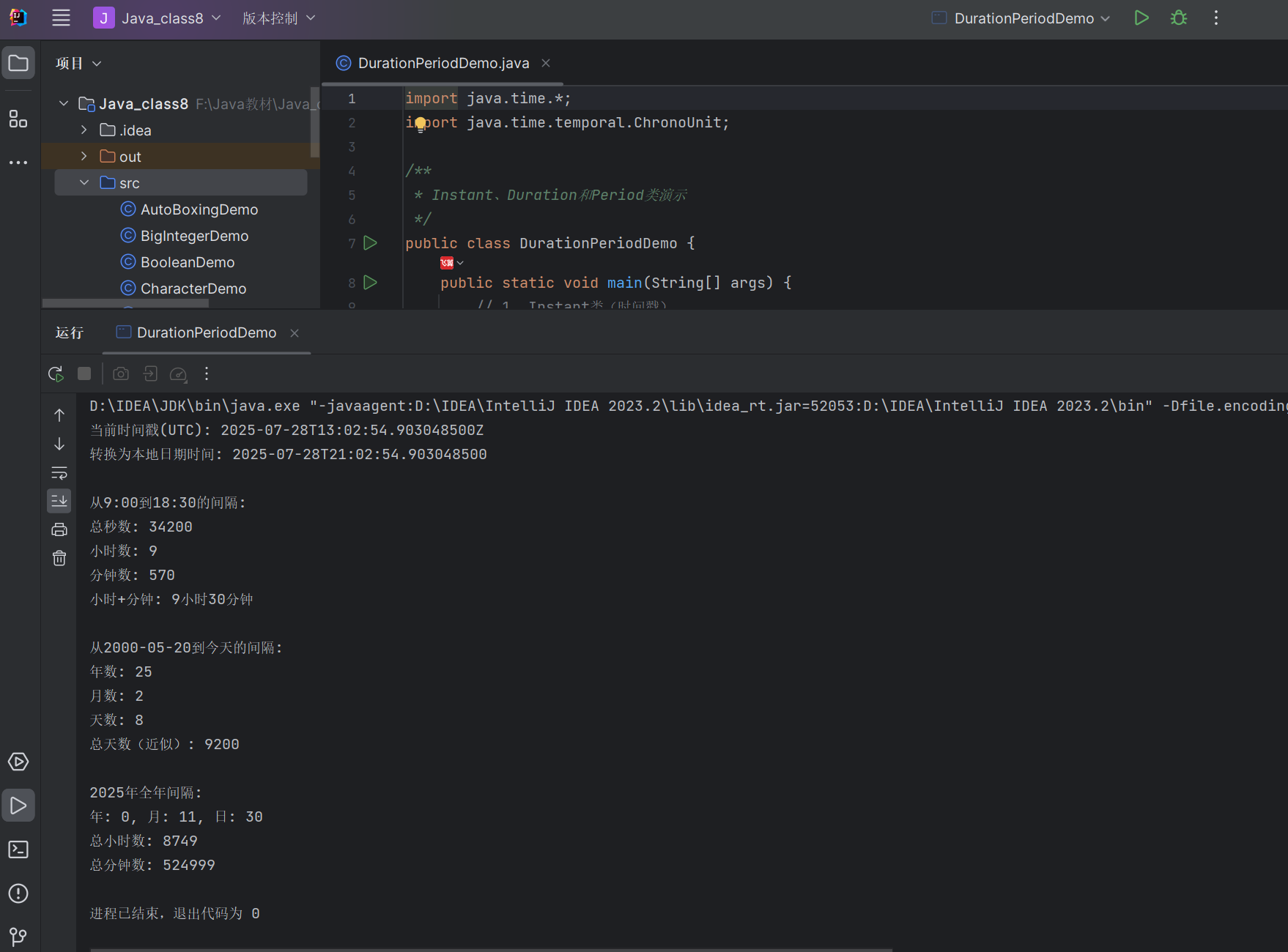
8.4.4 Instant 类、Duration 类和 Period 类
- Instant:表示时间戳(UTC 时区的瞬间),类似旧 API 的 Date
- Duration:计算两个时间(LocalTime、LocalDateTime、Instant)之间的间隔(时分秒)
- Period:计算两个日期(LocalDate)之间的间隔(年月日)
代码示例:时间间隔计算
import java.time.*;
import java.time.temporal.ChronoUnit;/*** Instant、Duration和Period类演示*/
public class DurationPeriodDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. Instant类(时间戳)Instant nowInstant = Instant.now();System.out.println("当前时间戳(UTC): " + nowInstant); // 格式:yyyy-MM-ddTHH:MM:SS.sssssssssZ// 转换为本地日期时间(需指定时区)LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.ofInstant(nowInstant, ZoneId.systemDefault());System.out.println("转换为本地日期时间: " + localDateTime);// 2. Duration类(计算时间间隔)LocalTime time1 = LocalTime.of(9, 0, 0); // 9:00LocalTime time2 = LocalTime.of(18, 30, 0); // 18:30Duration duration = Duration.between(time1, time2);System.out.println("\n从9:00到18:30的间隔:");System.out.println("总秒数: " + duration.getSeconds());System.out.println("小时数: " + duration.toHours());System.out.println("分钟数: " + duration.toMinutes());System.out.println("小时+分钟: " + duration.toHours() + "小时" + duration.toMinutes()%60 + "分钟");// 3. Period类(计算日期间隔)LocalDate date1 = LocalDate.of(2000, 5, 20); // 生日LocalDate date2 = LocalDate.now(); // 今天Period period = Period.between(date1, date2);System.out.println("\n从2000-05-20到今天的间隔:");System.out.println("年数: " + period.getYears());System.out.println("月数: " + period.getMonths());System.out.println("天数: " + period.getDays());System.out.println("总天数(近似): " + ChronoUnit.DAYS.between(date1, date2));// 4. 综合案例:计算两个日期时间的完整间隔LocalDateTime start = LocalDateTime.of(2025, 1, 1, 10, 0, 0);LocalDateTime end = LocalDateTime.of(2025, 12, 31, 23, 59, 59);Duration timeDiff = Duration.between(start, end);Period dateDiff = Period.between(start.toLocalDate(), end.toLocalDate());System.out.println("\n2025年全年间隔:");System.out.println("年: " + dateDiff.getYears() + ", 月: " + dateDiff.getMonths() + ", 日: " + dateDiff.getDays());System.out.println("总小时数: " + timeDiff.toHours());System.out.println("总分钟数: " + timeDiff.toMinutes());}
}
运行结果:
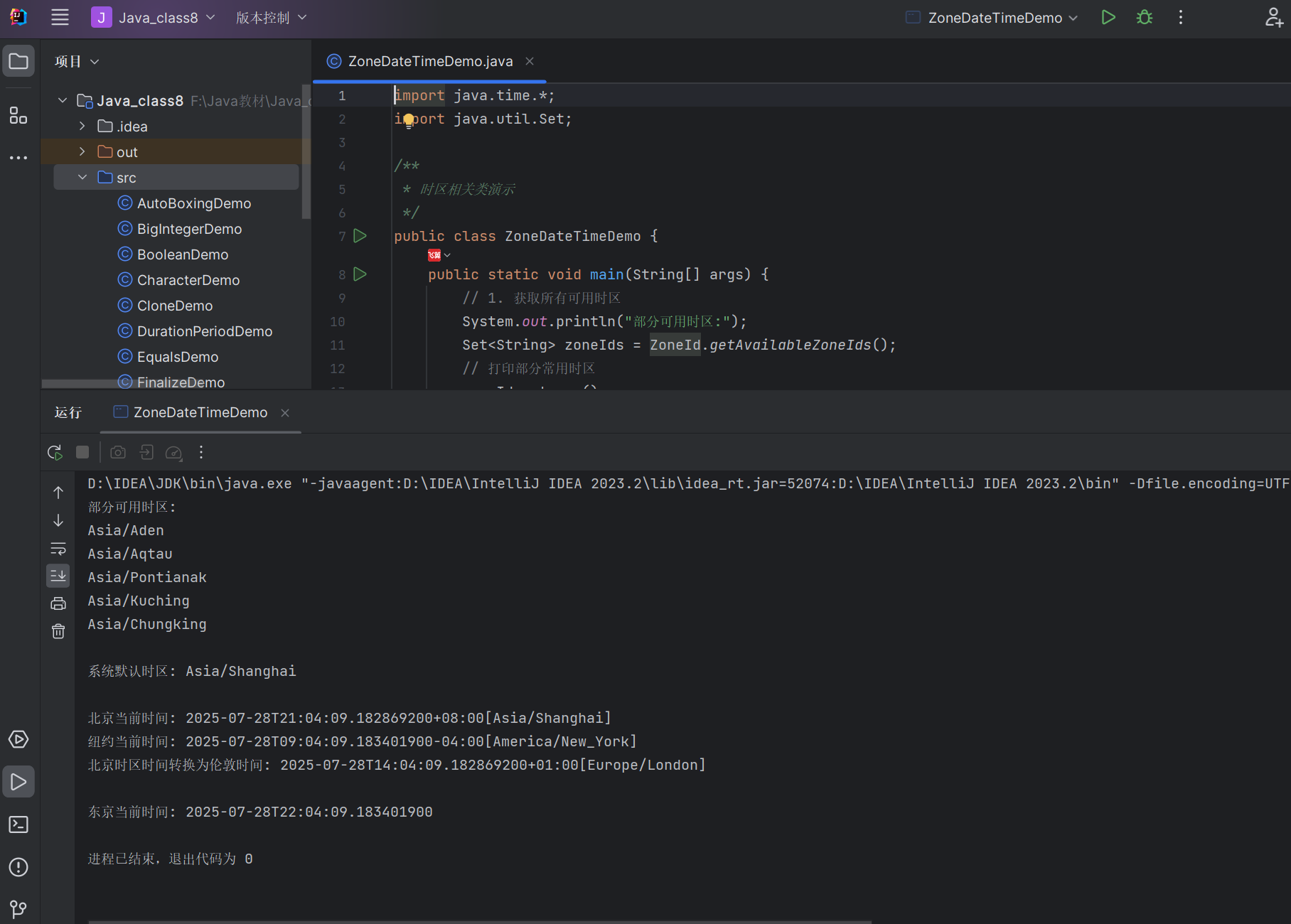
8.4.5 其他常用类
- ZoneId/ZoneOffset:表示时区
- ZonedDateTime:带时区的日期时间
- Clock:时钟,用于获取当前时间(可指定时区)
代码示例:时区相关类使用
import java.time.*;
import java.util.Set;/*** 时区相关类演示*/
public class ZoneDateTimeDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. 获取所有可用时区System.out.println("部分可用时区:");Set<String> zoneIds = ZoneId.getAvailableZoneIds();// 打印部分常用时区zoneIds.stream().filter(zone -> zone.contains("Asia") || zone.contains("UTC")).limit(5).forEach(System.out::println);// 2. 获取系统默认时区ZoneId defaultZone = ZoneId.systemDefault();System.out.println("\n系统默认时区: " + defaultZone);// 3. ZonedDateTime:带时区的日期时间ZonedDateTime beijingTime = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("Asia/Shanghai"));ZonedDateTime newYorkTime = ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneId.of("America/New_York"));System.out.println("\n北京当前时间: " + beijingTime);System.out.println("纽约当前时间: " + newYorkTime);// 4. 时区转换ZonedDateTime converted = beijingTime.withZoneSameInstant(ZoneId.of("Europe/London"));System.out.println("北京时区时间转换为伦敦时间: " + converted);// 5. Clock类使用Clock clock = Clock.system(ZoneId.of("Asia/Tokyo"));LocalDateTime tokyoTime = LocalDateTime.now(clock);System.out.println("\n东京当前时间: " + tokyoTime);}
}
运行结果:
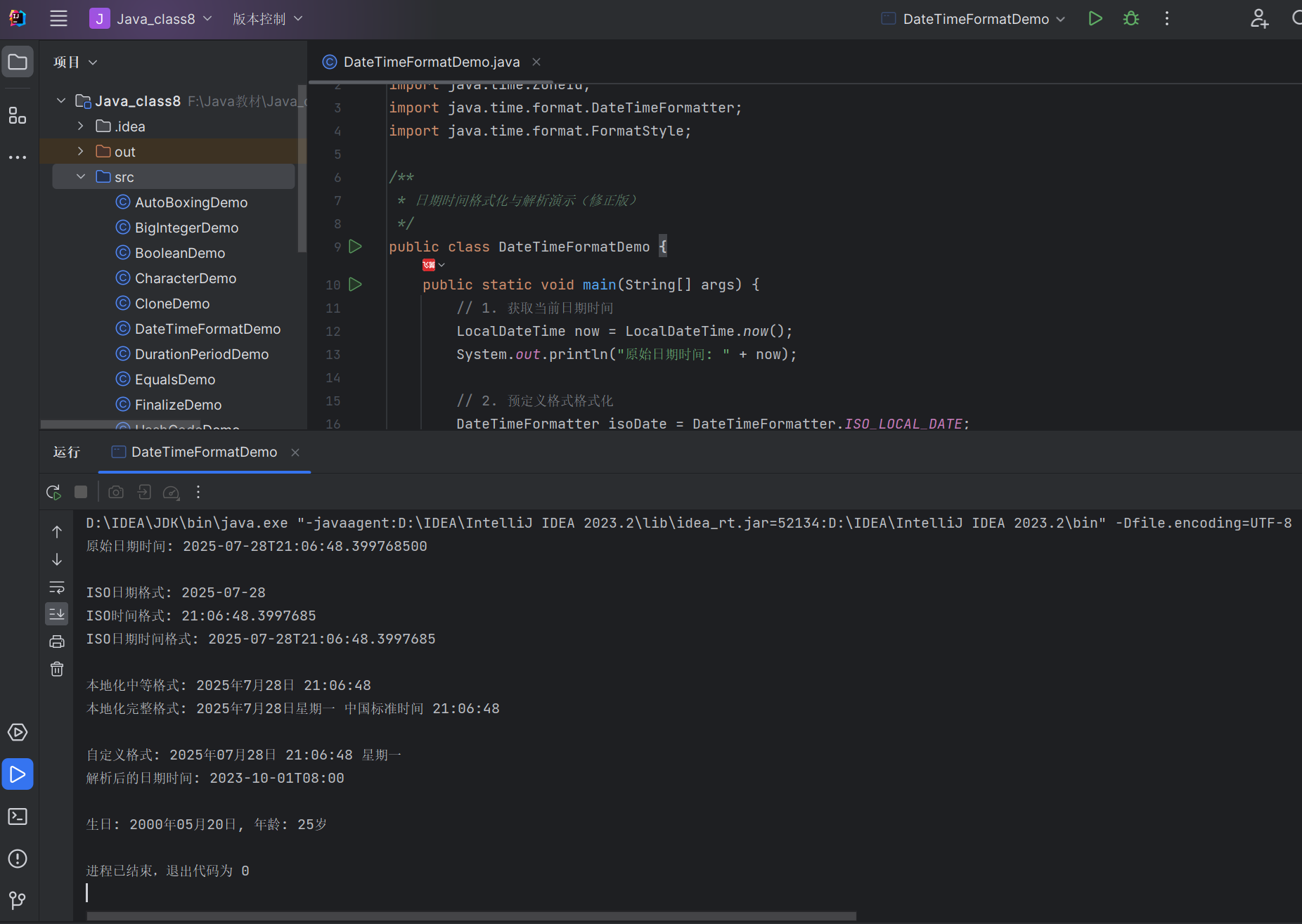
8.4.6 日期时间解析和格式化
使用DateTimeFormatter类对日期时间进行格式化(对象→字符串)和解析(字符串→对象)。
常用预定义格式
ISO_LOCAL_DATE:yyyy-MM-ddISO_LOCAL_TIME:HH:mm:ssISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME:yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ssofPattern(String):自定义格式(如 "yyyy 年 MM 月 dd 日 HH:mm:ss")
代码示例:日期时间格式化与解析
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.time.format.FormatStyle;/*** 日期时间格式化与解析演示(修正版)*/
public class DateTimeFormatDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. 获取当前日期时间LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();System.out.println("原始日期时间: " + now);// 2. 预定义格式格式化DateTimeFormatter isoDate = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE;DateTimeFormatter isoTime = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_TIME;DateTimeFormatter isoDateTime = DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME;System.out.println("\nISO日期格式: " + now.format(isoDate)); // yyyy-MM-ddSystem.out.println("ISO时间格式: " + now.format(isoTime)); // HH:mm:ss.sssssssssSystem.out.println("ISO日期时间格式: " + now.format(isoDateTime)); // yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ss.sssssssss// 3. 本地化格式(修正:FULL格式需要时区,使用ZonedDateTime或指定时区)DateTimeFormatter mediumFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.MEDIUM);// 解决FULL格式问题:为格式化器指定时区DateTimeFormatter fullFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofLocalizedDateTime(FormatStyle.FULL).withZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()); // 添加系统默认时区System.out.println("\n本地化中等格式: " + now.format(mediumFormatter)); // 2025-7-28 21:05:39// 使用带时区的格式化器处理LocalDateTimeSystem.out.println("本地化完整格式: " + fullFormatter.format(now)); // 包含时区信息的完整格式// 4. 自定义格式(常用模式字母:y-年, M-月, d-日, H-24时, m-分, s-秒, a-上午/下午)DateTimeFormatter customFormatter = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss EEEE");String formatted = now.format(customFormatter);System.out.println("\n自定义格式: " + formatted); // 2025年07月28日 21:05:30 星期一// 5. 字符串解析为日期时间(必须与格式完全匹配)String dateTimeStr = "2023年10月01日 08:00:00 星期日";LocalDateTime parsedDateTime = LocalDateTime.parse(dateTimeStr, customFormatter);System.out.println("解析后的日期时间: " + parsedDateTime);// 6. 综合案例:格式化生日并计算年龄String birthdayStr = "2000-05-20";// 解析生日字符串LocalDateTime birthday = LocalDateTime.parse(birthdayStr + "T00:00:00", isoDateTime);// 格式化生日String birthdayFormatted = birthday.format(DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日"));// 计算年龄int age = LocalDateTime.now().getYear() - birthday.getYear();System.out.println("\n生日: " + birthdayFormatted + ", 年龄: " + age + "岁");}
}运行结果:
8.5 小结
本章介绍了 Java 中最常用的核心类,这些类是 Java 编程的基础,在日常开发中频繁使用:
Object 类:所有类的父类,重点掌握
toString()、equals()、hashCode()的重写原则,理解浅拷贝与深拷贝的区别。Math 类:提供丰富的数学运算方法,注意
random()生成随机数的使用场景。基本类型包装类:
- 掌握自动装箱与拆箱的机制及注意事项(如 Integer 缓存)
- 字符串与基本类型的转换方法(
parseXxx()) - 高精度计算使用
BigInteger和BigDecimal
日期 - 时间 API(Java 8+):
- 核心类:
LocalDate、LocalTime、LocalDateTime - 时间间隔计算:
Duration(时间)和Period(日期) - 格式化与解析:
DateTimeFormatter自定义格式
- 核心类:
这些核心类极大简化了 Java 编程,提高了代码的可读性和安全性,建议多动手练习加深理解。
编程练习
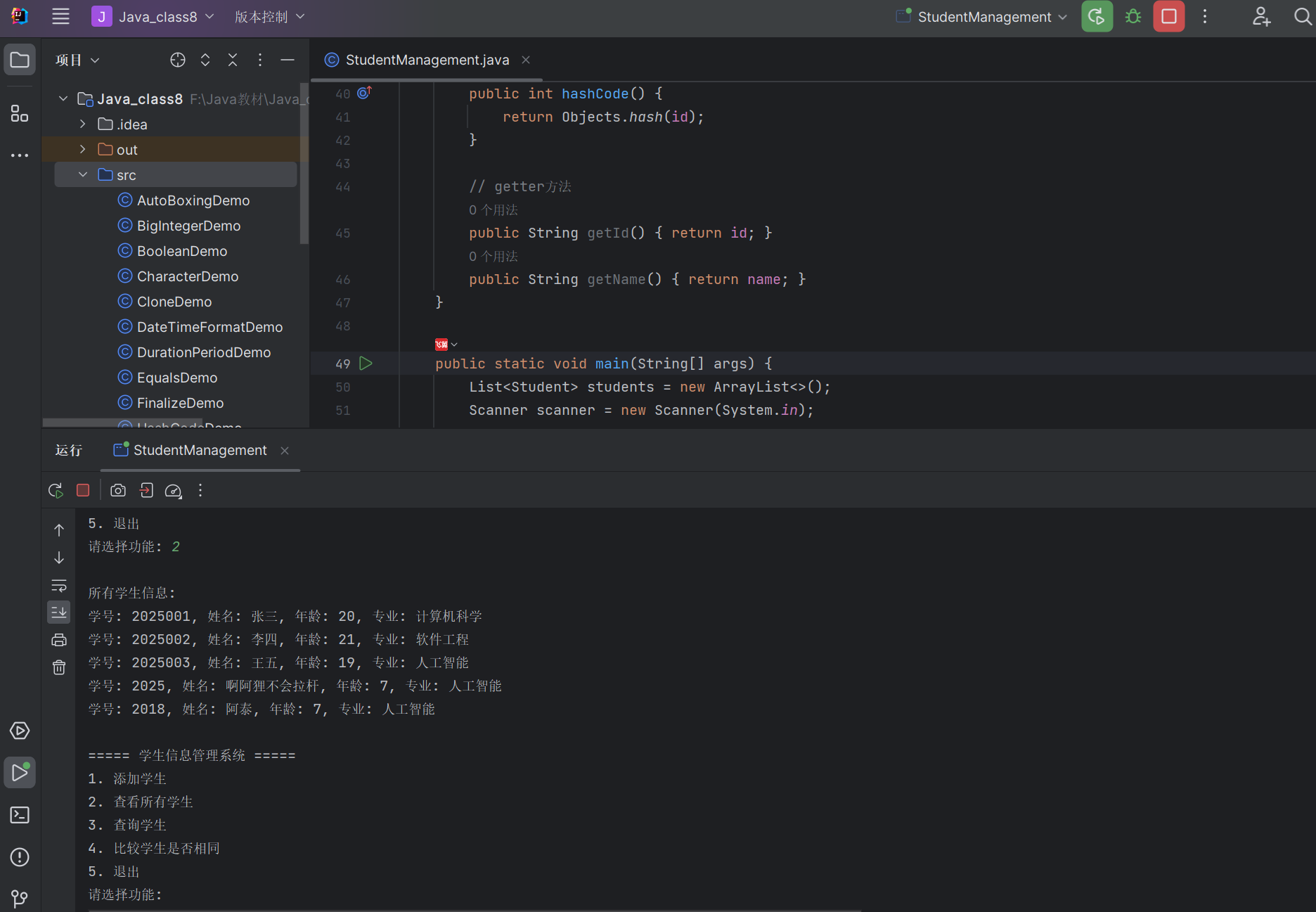
练习 1:学生信息管理系统(Object 类应用)
需求:设计 Student 类,重写 toString ()、equals ()、hashCode () 方法,实现学生信息的添加、查询和比较。
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Scanner;/*** 练习1:学生信息管理系统*/
public class StudentManagement {static class Student {private String id; // 学号(唯一标识)private String name; // 姓名private int age; // 年龄private String major; // 专业public Student(String id, String name, int age, String major) {this.id = id;this.name = name;this.age = age;this.major = major;}// 重写toString()显示学生信息@Overridepublic String toString() {return "学号: " + id + ", 姓名: " + name + ", 年龄: " + age + ", 专业: " + major;}// 重写equals():学号相同则认为是同一个学生@Overridepublic boolean equals(Object o) {if (this == o) return true;if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;Student student = (Student) o;return Objects.equals(id, student.id);}// 重写hashCode():基于学号计算@Overridepublic int hashCode() {return Objects.hash(id);}// getter方法public String getId() { return id; }public String getName() { return name; }}public static void main(String[] args) {List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);// 添加示例学生students.add(new Student("2025001", "张三", 20, "计算机科学"));students.add(new Student("2025002", "李四", 21, "软件工程"));students.add(new Student("2025003", "王五", 19, "人工智能"));while (true) {System.out.println("\n===== 学生信息管理系统 =====");System.out.println("1. 添加学生");System.out.println("2. 查看所有学生");System.out.println("3. 查询学生");System.out.println("4. 比较学生是否相同");System.out.println("5. 退出");System.out.print("请选择功能: ");int choice = scanner.nextInt();scanner.nextLine(); // 消费换行符switch (choice) {case 1:// 添加学生System.out.print("请输入学号: ");String id = scanner.nextLine();System.out.print("请输入姓名: ");String name = scanner.nextLine();System.out.print("请输入年龄: ");int age = scanner.nextInt();scanner.nextLine(); // 消费换行符System.out.print("请输入专业: ");String major = scanner.nextLine();Student newStudent = new Student(id, name, age, major);// 检查学号是否已存在if (students.contains(newStudent)) {System.out.println("学号已存在,添加失败!");} else {students.add(newStudent);System.out.println("添加成功!");}break;case 2:// 查看所有学生System.out.println("\n所有学生信息:");if (students.isEmpty()) {System.out.println("暂无学生信息");} else {for (Student s : students) {System.out.println(s);}}break;case 3:// 查询学生System.out.print("请输入要查询的学号: ");String queryId = scanner.nextLine();Student queryStudent = new Student(queryId, "", 0, "");boolean found = false;for (Student s : students) {if (s.equals(queryStudent)) {System.out.println("找到学生: " + s);found = true;break;}}if (!found) {System.out.println("未找到学号为" + queryId + "的学生");}break;case 4:// 比较学生是否相同System.out.print("请输入第一个学生的学号: ");String id1 = scanner.nextLine();System.out.print("请输入第二个学生的学号: ");String id2 = scanner.nextLine();Student s1 = new Student(id1, "", 0, "");Student s2 = new Student(id2, "", 0, "");boolean isSame = students.contains(s1) && students.contains(s2) && s1.equals(s2);System.out.println("两个学生是否为同一个人? " + isSame);break;case 5:// 退出System.out.println("程序退出");scanner.close();return;default:System.out.println("无效选择,请重新输入");}}}
}