JavaScript手录07-数组
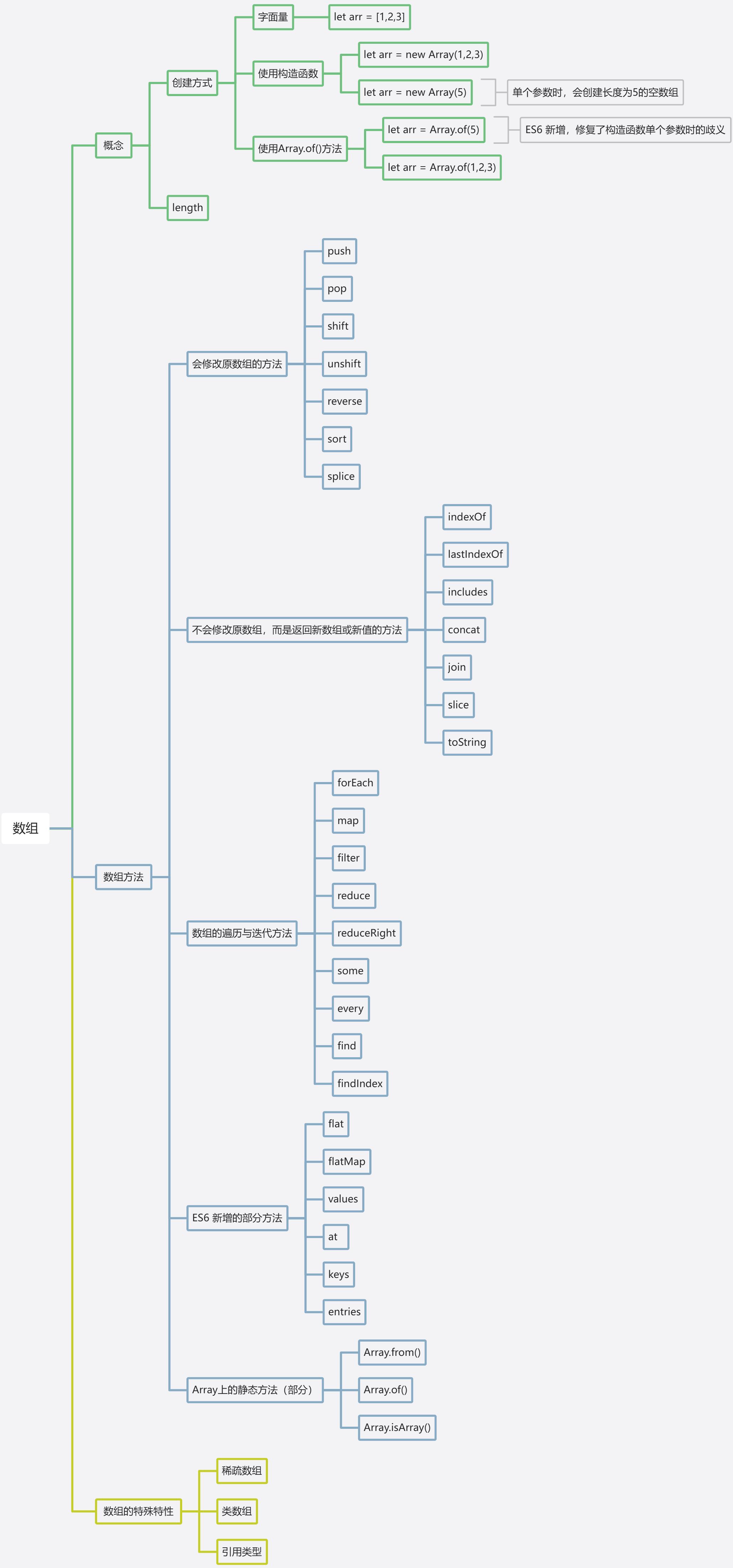
数组是 JavaScript 中最常用的数据结构之一,用于存储有序的集合数据。它具有灵活、易用的特点,支持多种操作方法。以下是 JavaScript 数组的核心知识:
一、数组的基本概念
数组是**有序的元素集合**,元素可以是任意数据类型(数字、字符串、对象、甚至其他数组等),并且长度可以动态变化。
1. 数组的创建方式
// 1. 数组字面量(最常用)
const arr1 = [1, 2, 3];
const arr2 = ['a', true, { name: '张三' }, [4, 5]]; // 元素类型不限// 2. 构造函数 Array()
const arr3 = new Array(1, 2, 3); // 等价于 [1,2,3]
const arr4 = new Array(5); // 创建长度为5的空数组(元素为 undefined)// 3. Array.of()(ES6+,解决 new Array 单参数的歧义)
const arr5 = Array.of(5); // [5](直接将参数作为元素)
const arr6 = Array.of(1, 2, 3); // [1,2,3]
2. 数组的索引与长度
- 索引:数组元素的位置编号,从
0开始(负数和非整数索引会被当作对象属性处理,不计算在数组长度内)。 - 长度(length):数组的
length属性表示元素个数,可读写(修改length可截断或扩展数组)。
const arr = [10, 20, 30];
console.log(arr[0]); // 10(访问索引0的元素)
console.log(arr.length); // 3(长度为3)// 修改 length 截断数组
arr.length = 2;
console.log(arr); // [10, 20]// 修改 length 扩展数组(新增元素为 undefined)
arr.length = 4;
console.log(arr); // [10, 20, undefined, undefined]
二、数组的常用方法
数组提供了大量内置方法,按功能可分为修改原数组和返回新数组两类。以及数组的遍历/迭代方法与ES6+ 新增的一些实用方法。
修改原数组的方法(会改变原数组)【7个】
以下这些方法会直接修改调用它们的数组本身,返回值通常与修改结果相关。
push(…elements)
push(...elements) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 向数组末尾添加一个或多个元素 |
| 参数 | ...elements(要添加的元素) |
| 返回值 | 添加元素后数组的新长度 |
示例:
// push()方法
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5]
let len = arr.push(5,6)
console.log(arr);
console.log(len);
pop()
pop() | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 删除数组的最后一个元素 |
| 参数 | 无 |
| 返回值 | 被删除的元素;如果数组为空,则返回undefined |
示例:
// pop()方法
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5]
console.log(arr.length); // 5
let popItem = arr.pop()
console.log(arr); // [1,2,3,4]
console.log(popItem); // 5
console.log(arr.length); // 4
unshift(…elements)
unshift(...elements) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 向数组开头添加一个或多个元素 |
| 参数 | ...elements(要添加的元素) |
| 返回值 | 添加元素后数组的新长度 |
示例:
// unshift()方法
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5]
console.log(arr.length); // 5
let len = arr.unshift(-1,0)
console.log(arr); // [-1,0,1,2,3,4,5]
console.log(len); // 7
shift()
shift() | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 删除数组的第一个元素 |
| 参数 | 无 |
| 返回值 | 被删除的元素;如果数组为空,则返回undefined |
示例:
// shift()方法
let arr = [1,2,3]
let shiftItem = arr.shift()
console.log(arr); // [2,3]
console.log(shiftItem); // 1
splice(start[, deleteCount[, …items]])
splice(start, [, deleteCount[, ...items]]) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 从指定位置删除、添加或者替换元素(最灵活的修改方法) |
| 参数 | + start:起始索引(可以为负数,如果为负数则从末尾开始计算;)+ deleteCount (可选):要删除的元素数量(如果为 0 则不删除元素)+ ...items (可选):要添加到数组的元素,从start位置开始插入 |
| 返回值 | 被删除的元素组成的新数组;如果没有删除元素,则返回空数组。 |
示例:
// splice(start,deleteCount,...items)方法
// 删除元素
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5]
let delArr = arr.splice(2,2)
console.log(arr);
console.log(delArr);
// 添加元素
arr.splice(2,0,...delArr)
console.log(arr);
// 替换元素
arr.splice(2,2,-3,-4)
console.log(arr);
// 从末尾删除元素
arr.splice(-3,3)
console.log(arr);
reverse()
reverse() | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 反转数组元素的顺序 |
| 参数 | 无 |
| 返回值 | 反转后的新数组 |
示例:
// reverse()方法
let arr = [1,2,3]
console.log(arr.reverse()); // [3,2,1]
sort([compareFunction])
sort([compareFunction]) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 对数组元素进行排序(默认按照字符串Unicode编码排序) |
| 参数 | + compareFunction (可选):自定义排序规则的函数,格式为(a, b) => { ... }+ 如果返回值<0:则 a 排在 b 前面 + 如果返回值=0:则 a 和 b 位置不变 + 如果返回值>0:则 b 排在 a 前面 |
| 返回值 | 排序后的新数组 |
示例:
// sort([compareFunction])方法
// 默认排序
let arr = ['a', 'c', 'b', 'e', 'd']
// console.log(arr.sort());
// 升序
let numArr = [3,6,78,9,6,10]
numArr.sort((a,b) => { return a-b })
console.log(numArr);
// 降序
let numArr2 = [3,6,7,9,6,10]
numArr2.sort((a,b) => { return b-a })
console.log(numArr2);
不修改原数组的方法(返回新结果,原数组不变)【7个】
以下这些方法不会修改原数组,而是返回新的数组、字符串或者其他值。
concat(…arrays)
concat(...arrays) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 合并两个或多个数组(或值),返回合并后的新数组 |
| 参数 | ...arrays(要合并的数组或值,可以是单个元素,也可以是数组) |
| 返回值 | 合并后的新数组 |
示例:
// concat()方法
let arr = [1,2,3]
let arr2 = [3,4,5]
let item = 6
let newArr = arr.concat(arr2,item)
console.log(newArr);
slice(start,[,end])
slice(start,[,end]) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 从数组中提取子数组,从start到end前一位;左开右闭;不包括end |
| 参数 | + start:起始索引,可为负数;如果为负数,则从末尾计算。(按照数组索引从0开始计算)+ end(可选):结束索引,默认到数组末尾;如果为负数,则从末尾计算。 |
| 返回值 | 返回提取到的新数组,原数组不变 |
示例:
// slice方法
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5]
let newArr = arr.slice(2, -1)
console.log(newArr); // [3,4]
join([separator])
join([separator])(separator意为分隔符) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 将数组元素拼接为字符串(默认用英文逗号分隔) |
| 参数 | separator(可选)分隔符(默认为英文逗号) |
| 返回值 | 拼接后的字符串 |
示例:
// join()方法
let arr = ['h','e','l','l','o','!']
let str = arr.join('-')
console.log(str);
indexOf(searchElement[, formIndex])
indexOf(searchElement[,formIndex]) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 从前往后查找元素中数组中的第一个索引 |
| 参数 | + searchElement:要查找的元素+ formIndex(可选):起始查找索引(默认为0) |
| 返回值 | 如果查找到目标元素,则返回索引;否则,返回-1 注:查找采用 ===比较,无法识别NaN``[NaN].indexOf(NaN) => -1 |
示例:
// indexOf(searchElement[,formIndex])
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5]
let index = arr.indexOf(5)
let index2 = arr.indexOf(NaN)
console.log(index); // 4
console.log(index2); // -1
lastIndexOf(searchElement[,formIndex])
lastIndexOf(searchElement[,formIndex]) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 从后往前查找目标元素中数组中的最后一个索引 |
| 参数 | + searchElement:要查找的元素+ formIndex(可选):起始查找索引,默认为数组末尾 |
| 返回值 | 如果查找到目标元素,则返回索引;否则,返回-1 |
示例:
// lastIndexOf(searchElement[,formIndex])
let arr = [1,2,3,4,4,4,5]
let index = arr.lastIndexOf(4)
console.log(index); // 5
includes(searchElement[,formIndex])
includex(searchElement[,formIndex]) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 判断数组是否包含某个元素 |
| 参数 | + searchElement:要查找的元素+ formIndex(可选):起始查找索引(默认为0) |
| 返回值 | 如果数组中包含目标元素,则返回true;否则,返回false优势:可以识别 NaN``[NaN].includes(NaN) => true |
示例:
// includes(searchElement[, formIndex])
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5,'a','c','d',NaN]
let index = arr.includes(3)
let index2 = arr.includes('a')
let index3 = arr.includes(NaN)
console.log(index) // true
console.log(index2) // true
console.log(index3) // true
toString()
toString() | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 将数组转为字符串(等价于join(),默认逗号分隔) |
| 参数 | 无 |
| 返回值 | 目标数组转换成的字符串 |
示例:
// toString() 方法
let arr = ['h','e','l','l','o']
let str = arr.toString()
console.log(str) // 'h,e,l,l,o'
数组的遍历/迭代方法(对数组中的每个元素进行操作)【9个】
这类方法用于遍历数组,通过回调函数处理数组中的每个元素。一般会返回新数组或者新值,不修改原数组。(除非在回调函数中主动修改了原数组)
forEach(callback[, thisArg])
forEach(callback[, thisArg]) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 遍历数组,对每个元素执行回调函数(无返回值) |
| 参数 | + callback:回调函数,格式为(currentValue,index,array) => {...}- currentValue:当前元素- index:当前元素的索引- array:原数组+ thisArg(可选):回调函数中this的指向 |
| 返回值 | 无 |
| 特点 | + 无法通过return或者break中断循环(除非抛出异常)+ 不修改原数组,除非中回调中主动修改 |
示例:
// forEach()方法let arr = [1,2,3,4,5]arr.forEach((item, index) => {console.log(item + '-' + index);})
map(callback[, thisArg])
map(callback[, thisArg]) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 遍历数组,对数组中的每个元素执行回调函数 |
| 参数 | + callback:回调函数,格式为(currentValue,index,array) => {...}- currentValue:当前元素- index:当前元素的索引- array:原数组+ thisArg(可选):回调函数中this的指向 |
| 返回值 | 新数组,长度与原数组相同,新数组的元素为回调函数返回值 |
示例:
// map(callback[, thisArg])
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5]
let newArr = arr.map((item, index) => item + 1)
console.log(newArr); // [2,3,4,5,6]
filter(callback[, thisArg])
filter(callback[, thisArg]) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 遍历数组,筛选出符合条件的元素组成新数组 |
| 参数 | + callback:回调函数,格式为(currentValue,index,array) => {...}- currentValue:当前元素- index:当前元素的索引- array:原数组+ thisArg(可选):回调函数中this的指向 |
| 返回值 | 筛选后的新数组(可能为空) |
示例:
// filter(callback[, thisArg])
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5]
let newArr = arr.filter((item, index) => item > 2)
console.log(newArr); // [3,4,5]
let newArr2 = arr.filter(item => item > 10)
console.log(newArr2); // []
find(callback[,thisArg])【ES6新增】
find(callback[,thisArg]) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 遍历数组,返回第一个符合条件的元素【ES6新增】 |
| 参数 | + callback:回调函数,格式为(currentValue,index,array) => {...}- currentValue:当前元素- index:当前元素的索引- array:原数组+ thisArg(可选):回调函数中this的指向 |
| 返回值 | 找到符合条件的第一个元素则返回该元素,否则返回undefined |
示例:
// find(callback[, thisArg])
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5]
let item = arr.find(item => item > 3)
console.log(item); // 4
findIndex(callback[,thisArg])
findIndex(callback[,thisArg]) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 遍历数组,返回第一个符合条件的元素的索引【ES6新增】 |
| 参数 | + callback:回调函数,格式为(currentValue,index,array) => {...}- currentValue:当前元素- index:当前元素的索引- array:原数组+ thisArg(可选):回调函数中this的指向 |
| 返回值 | 如果查找到符合条件的第一个元素,则返回索引;否则,返回-1 |
示例:
// findIndex(callback[,thisArg])
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5]
let index = arr.findIndex(item => item > 2)
console.log(index);
some(callback[,thisArg])
some(callback[,thisArg]) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 判断数组中是否至少有一个符合条件的元素 |
| 参数 | + callback:回调函数,格式为(currentValue,index,array) => {...}- currentValue:当前元素- index:当前元素的索引- array:原数组+ thisArg(可选):回调函数中this的指向 |
| 返回值 | <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">true</font> 或 <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">false</font>(一旦找到符合条件的元素,立即停止遍历)。 |
示例:
// some(callback[,thisArg])
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5]
let res = arr.some(item => item > 4)
console.log(res); // true
every(callback[,thisArg])
every(callback[,thisArg]) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 判断数组中是否所有元素都符合条件 |
| 参数 | + callback:回调函数,格式为(currentValue,index,array) => {...}- currentValue:当前元素- index:当前元素的索引- array:原数组+ thisArg(可选):回调函数中this的指向 |
| 返回值 | <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">true</font> 或 <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">false</font>(一旦找到不符合条件的元素,立即停止遍历)。 |
示例:
// every(callback[,thisArg])
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5]
let res = arr.every(item => item > 0)
console.log(res); // true
reduce(callback[, initialValue])
reduce(callback[, initialValue]) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 对数组元素从左到右累计计算,返回累计结果。(非常灵活) |
| 参数 | + callback:累计函数,格式为(accumulator,currentValue,index,array) => {...}- accumulator:累计器(上一次回调的返回值,或者初始值)- currentValue:当前元素- index:当前元素的索引- array:原数组+ initialValue(可选):初始值;如果不提供,则默认使用数组第一个元素作为初始值,从第二个元素开始遍历。 |
| 返回值 | 最终的累计结果 |
示例:
// reduce(callback[,initialValue])
// 求和let arr1 = [1,2,3,4,5]let sum = arr1.reduce((acc,item)=>acc+item,0)console.log(sum);
// 求最大值let arr2 = [1,2,3,4,5]let max = arr2.reduce((max,item)=>max>item?max:item)console.log(max);
// 求最小值let arr3 = [1,2,3,4,5]let min = arr3.reduce((min,item)=>min<item?min:item)console.log(min);
// 去重let arr4 = [1,2,2,3,3,3,4,4,4,4,5,5,5,5,6]let resArr = arr4.reduce((res, item) => {if(!res.includes(item)){res.push(item)}return res}, [])console.log(resArr);
reduceRight(callback[,intialValue])
reduceRight(callback[,intialValue]) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 与reduce类似,但从右往左遍历数组 |
| 参数 | + callback:累计函数,格式为(accumulator,currentValue,index,array) => {...}- accumulator:累计器(上一次回调的返回值,或者初始值)- currentValue:当前元素- index:当前元素的索引- array:原数组+ initialValue(可选):初始值;如果不提供,则默认使用数组第一个元素作为初始值,从第二个元素开始遍历。 |
| 返回值 | 最终的累计结果 |
示例:
// every(callback[,thisArg])
let arr = [1,2,3,4,5]
let res = arr.every(item => item > 0)
console.log(res); // true
ES6+ 新增方法(较新的实用方法)
flat(depth)
flat(depth) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 将嵌套数组“扁平化”(展开深层数组) |
| 参数 | depth(可选)扁平化的深度,默认为1(Infinity表示无限深度,完全扁平化) |
| 返回值 | 扁平化后的新数组,不修改原数组 |
示例:
const arr = [1, [2, [3, [4]]]];console.log(arr.flat()); // [1, 2, [3, [4]]](深度1)
console.log(arr.flat(2)); // [1, 2, 3, [4]](深度2)
console.log(arr.flat(Infinity)); // [1, 2, 3, 4](无限深度,完全扁平化)
flatMap(callback[,thisArg])
flatMap(callback[,thisArg]) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 先对数组执行 <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">map</font> 操作,再对结果执行 <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">flat(depth=1)</font>(等价于 <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">map(...).flat(1)</font>)。比 <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">map</font> 后再 <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">flat</font> 更高效。 |
| 参数 | + callback:回调函数,格式为(currentValue,index,array) => {...}- currentValue:当前元素- index:当前元素的索引- array:原数组+ thisArg(可选):回调函数中this的指向 |
| 返回值 | 操作完成后的新数组 |
示例:
const arr = ["hello world", "good morning"];
// 先split成数组,再扁平化(depth=1)
const words = arr.flatMap(str => str.split(" "));
console.log(words); // ["hello", "world", "good", "morning"]
// 等价于:arr.map(str => str.split(" ")).flat(1)
entries()、keys()、values()
#### <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">entries()</font>、<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">keys()</font>、<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">values()</font> | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 返回数组的 迭代器对象(可用于 <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">for...of</font> 循环) |
| 简介 | + <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">entries()</font>:返回 <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">[索引, 元素]</font> 形式的迭代器;+ <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">keys()</font>:返回索引的迭代器;+ <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">values()</font>:返回元素的迭代器。 |
示例:
const arr = ["a", "b"];// entries()
for (const [index, value] of arr.entries()) {console.log(index, value); // 0 "a";1 "b"
}// keys()
for (const key of arr.keys()) {console.log(key); // 0;1
}// values()
for (const value of arr.values()) {console.log(value); // "a";"b"
}
at(index)
at(index) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 根据索引获取数组元素(支持 负索引,ES2022 新增)。 |
| 参数 | <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">index</font>:索引(正数从左数,负数从右数,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">-1</font> 表示最后一个元素)。 |
| 返回值 | <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">index</font>对应的数组元素,类似于<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">arr[index]</font>,但支持负数索引。注:比 <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">arr[index]</font> 更简洁地支持负索引(<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">arr[-1]</font> 不生效,而 <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">arr.at(-1)</font> 可行)。 |
示例:
const arr = [10, 20, 30];
console.log(arr.at(1)); // 20(同arr[1])
console.log(arr.at(-1)); // 30(最后一个元素,等价于arr[arr.length-1])
console.log(arr.at(-2)); // 20(倒数第二个元素)
数组的静态方法(Array构造函数上的方法)
Array.isArray(value)
Array.isArray(value) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 判断一个值是否为数组(比 <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">typeof</font> 更可靠,<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">typeof []</font> 返回 <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">object</font>)。 |
| 参数 | value:要执行判断的目标 |
| 返回值 | <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">true</font> 或 <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">false</font>。 |
示例:
console.log(Array.isArray([])); // true
console.log(Array.isArray({})); // false
console.log(Array.isArray("array")); // false
Array.from(arrayLike[, mapFn[, thisArg]])
Array.from(arrayLike[, mapFn[, thisArg]]) | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 将 类数组对象(如 <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">arguments</font>、DOM 集合)或 可迭代对象(如 <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">Set</font>、<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">Map</font>)转为真正的数组。 |
| 参数 | + <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">arrayLike</font>:类数组或可迭代对象;+ <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mapFn</font>(可选):类似 <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">map</font> 的回调函数,对每个元素处理后再返回;+ <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">thisArg</font>(可选):<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">mapFn</font> 中 <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">this</font> 的指向。 |
| 返回值 | 转化完成后的新数组 |
示例:
// 类数组转数组
const arrayLike = { 0: "a", 1: "b", length: 2 };
const arr = Array.from(arrayLike);
console.log(arr); // ["a", "b"]// 带mapFn:转数组的同时处理元素
const nums = Array.from([1, 2, 3], x => x * 2);
console.log(nums); // [2, 4, 6]
Array.of(…elements)
#### <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">Array.of(...elements)</font> | |
|---|---|
| 功能 | 创建一个包含指定元素的数组(解决 <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">new Array()</font> 的怪异行为:<font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">new Array(3)</font> 创建长度为 3 的空数组,而 <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">Array.of(3)</font> 创建 <font style="color:rgb(0, 0, 0);">[3]</font>)。 |
示例:
console.log(Array.of(1, 2, 3)); // [1, 2, 3]
console.log(Array.of(5)); // [5](对比new Array(5) → 长度5的空数组)
三、数组的特殊特性
- 稀疏数组:包含空元素的数组(索引不连续)。
const arr = [1, , 3]; // 索引1为空
console.log(arr.length); // 3(长度仍为3)
console.log(arr[1]); // undefined
- 数组与类数组:类数组(如
arguments、DOM 集合)具有length和索引,但没有数组方法,可通过Array.from()转换为数组。
const likeArr = { 0: 'a', 1: 'b', length: 2 };
const arr = Array.from(likeArr); // 转换为 ['a', 'b']
- 数组的引用类型特性:数组是引用类型,赋值和传递时操作的是引用地址。
const arr1 = [1, 2];
const arr2 = arr1; // 引用赋值
arr2.push(3);
console.log(arr1); // [1, 2, 3](原数组被修改)
练习
练习1:栈/队列模拟(<font style="background-color:#FBDE28;">push</font>、<font style="background-color:#FBDE28;">pop</font>、<font style="background-color:#FBDE28;">shift</font>、<font style="background-color:#FBDE28;">unshift</font>)
目标:用数组模拟栈(后进先出)和队列(先进先出)的操作。
- 栈:用
push(入栈)和pop(出栈)实现,如[1,2,3]入栈4后为[1,2,3,4],出栈后为[1,2,3]。 - 队列:用
push(入队)和shift(出队)实现,如[1,2,3]入队4后为[1,2,3,4],出队后为[2,3,4]。
任务:
- 创建一个空数组
stack,依次入栈10、20、30,再出栈一次,打印最终数组。 - 创建一个空数组
queue,依次入队'a'、'b'、'c',再出队一次,打印最终数组。
练习2:数组截取与合并(<font style="background-color:#FBDE28;">slice</font>、<font style="background-color:#FBDE28;">concat</font>)
目标:用 slice 截取子数组,用 concat 合并数组(均不修改原数组)。
任务:
已知数组 const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]:
- 用
slice截取索引1到4(不含4)的子数组,结果应为[2,3]。 - 用
concat将子数组与[6,7]合并,结果应为[2,3,6,7]。
练习3:数组转换(<font style="background-color:#FBDE28;">map</font>)
目标:用 map 将数组按规则转换(返回新数组,长度不变)。
任务:
- 将数字数组
[1, 2, 3, 4]转换为每个元素的平方组成的数组,结果[1,4,9,16]。 - 将对象数组
[{name: '张三', age: 18}, {name: '李四', age: 20}]转换为仅包含姓名的数组,结果['张三', '李四']。
练习4:数组筛选(<font style="background-color:#FBDE28;">filter</font>)
目标:用 filter 筛选出符合条件的元素(返回新数组,长度可能减少)。
任务:
- 从
[5, 2, 9, 1, 5, 6]中筛选出大于5的元素,结果[9,6]。 - 从对象数组
[{id: 1, done: true}, {id: 2, done: false}, {id: 3, done: true}]中筛选出done为true的对象,结果[{id:1,...}, {id:3,...}]。
练习5:数组判断(<font style="background-color:#FBDE28;">some</font>、<font style="background-color:#FBDE28;">every</font>)
目标:用 some 和 every 判断数组元素是否符合条件。
任务:
- 判断
[2,4,6,7]中是否有奇数(some),结果应为true(7是奇数)。 - 判断
[2,4,6,7]中是否全是偶数(every),结果应为false。 - 判断对象数组
[{score: 60}, {score: 80}, {score: 90}]中是否所有分数都 ≥60(every),结果true。
练习6:数组聚合(<font style="background-color:#FBDE28;">reduce</font>)
目标:用 reduce 实现数组的求和、求平均值、去重等聚合操作。
任务:
- 求
[1,2,3,4,5]的总和,结果15。 - 求
[1,2,3,4,5]的平均值,结果3。 - 对
[1,2,2,3,3,3]去重,结果[1,2,3]。 - 将对象数组
[{name: 'a', count: 2}, {name: 'b', count: 3}]中count累加,结果5。
练习7:数组排序(<font style="background-color:#FBDE28;">sort</font>)
目标:用 sort 对数组进行排序,掌握自定义排序规则。
任务:
- 对
[3,1,4,2]进行升序排序,结果[1,2,3,4]。 - 对
[3,1,4,2]进行降序排序,结果[4,3,2,1]。 - 对对象数组
[{name: '张三', age: 20}, {name: '李四', age: 18}]按age升序排序,结果[李四(18), 张三(20)]。
练习8:数组扁平化(<font style="background-color:#FBDE28;">flat</font>、<font style="background-color:#FBDE28;">flatMap</font>)
目标:用 flat 或 flatMap 处理嵌套数组。
任务:
- 将
[1, [2, [3, [4]]]]完全扁平化,结果[1,2,3,4](用flat(Infinity))。 - 对
['hello world', 'good morning']先按空格拆分(split),再扁平化,结果['hello','world','good','morning'](用flatMap)。
练习9:数组查找(<font style="background-color:#FBDE28;">indexOf</font>、<font style="background-color:#FBDE28;">find</font>、<font style="background-color:#FBDE28;">findIndex</font>)
目标:用查找方法定位数组元素。
任务:
- 在
[10,20,30,20]中找到20第一次出现的索引(indexOf),结果1。 - 在对象数组
[{id:1, name:'a'}, {id:2, name:'b'}]中找到id=2的对象(find),结果{id:2, name:'b'}。 - 在
[5,10,15,20]中找到第一个大于12的元素的索引(findIndex),结果2(元素15)。
练习10:综合练习(多方法组合)
目标:组合使用多种方法处理复杂场景。
任务:
现有数组 const data = [ { name: '张三', score: 85, subject: '数学' }, { name: '张三', score: 90, subject: '语文' }, { name: '李四', score: 75, subject: '数学' }, { name: '李四', score: 80, subject: '语文' } ],完成以下操作:
- 筛选出数学成绩 ≥80 的记录(
filter),结果应为[{name: '张三', score:85, ...}]。 - 提取所有学生的语文成绩,组成
[{name: '张三', score:90}, ...](filter+map)。 - 计算每个学生的平均分(
reduce分组聚合),结果[{name: '张三', avg:87.5}, {name: '李四', avg:77.5}]。
练习参考答案
练习1:栈/队列模拟(push、pop、shift、unshift)
// 1. 栈模拟(后进先出)
let stack = [];
stack.push(10); // 入栈:[10]
stack.push(20); // 入栈:[10, 20]
stack.push(30); // 入栈:[10, 20, 30]
stack.pop(); // 出栈:移除30,stack变为 [10, 20]
console.log("栈结果:", stack); // [10, 20]// 2. 队列模拟(先进先出)
let queue = [];
queue.push('a'); // 入队:['a']
queue.push('b'); // 入队:['a', 'b']
queue.push('c'); // 入队:['a', 'b', 'c']
queue.shift(); // 出队:移除'a',queue变为 ['b', 'c']
console.log("队列结果:", queue); // ['b', 'c']
练习2:数组截取与合并(slice、concat)
const arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];// 1. 截取索引1到4(不含4)的子数组
const subArr = arr.slice(1, 3); // 从索引1开始,到索引3前结束(即1和2)
console.log("截取结果:", subArr); // [2, 3]// 2. 合并子数组与[6,7]
const mergedArr = subArr.concat([6, 7]);
console.log("合并结果:", mergedArr); // [2, 3, 6, 7]
练习3:数组转换(map)
// 1. 数字数组转平方数组
const nums = [1, 2, 3, 4];
const squared = nums.map(num => num **2);
console.log("平方结果:", squared); // [1, 4, 9, 16]// 2. 对象数组提取姓名
const users = [{ name: '张三', age: 18 },{ name: '李四', age: 20 }
];
const names = users.map(user => user.name);
console.log("姓名数组:", names); // ['张三', '李四']
练习4:数组筛选(filter)
// 1. 筛选大于5的元素
const numbers = [5, 2, 9, 1, 5, 6];
const greaterThan5 = numbers.filter(num => num > 5);
console.log("大于5的元素:", greaterThan5); // [9, 6]// 2. 筛选done为true的对象
const tasks = [{ id: 1, done: true },{ id: 2, done: false },{ id: 3, done: true }
];
const completedTasks = tasks.filter(task => task.done);
console.log("已完成任务:", completedTasks); // [{id:1,...}, {id:3,...}]
练习5:数组判断(some、every)
const numbers = [2, 4, 6, 7];// 1. 判断是否有奇数(some)
const hasOdd = numbers.some(num => num % 2 !== 0);
console.log("是否有奇数:", hasOdd); // true(7是奇数)// 2. 判断是否全是偶数(every)
const allEven = numbers.every(num => num % 2 === 0);
console.log("是否全是偶数:", allEven); // false// 3. 判断所有分数是否≥60
const scores = [{ score: 60 }, { score: 80 }, { score: 90 }];
const allPass = scores.every(item => item.score >= 60);
console.log("是否全部及格:", allPass); // true
练习6:数组聚合(reduce)
// 1. 求和
const sum = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].reduce((acc, cur) => acc + cur, 0);
console.log("总和:", sum); // 15// 2. 求平均值
const avg = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5].reduce((acc, cur, _, arr) => {acc += cur;// 最后一次迭代时计算平均值return _ === arr.length - 1 ? acc / arr.length : acc;
}, 0);
console.log("平均值:", avg); // 3// 3. 数组去重
const unique = [1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3].reduce((acc, cur) => {if (!acc.includes(cur)) acc.push(cur);return acc;
}, []);
console.log("去重结果:", unique); // [1, 2, 3]// 4. 累加count属性
const items = [{ name: 'a', count: 2 },{ name: 'b', count: 3 }
];
const totalCount = items.reduce((acc, item) => acc + item.count, 0);
console.log("总count:", totalCount); // 5
练习7:数组排序(sort)
// 1. 升序排序
const arr1 = [3, 1, 4, 2];
arr1.sort((a, b) => a - b);
console.log("升序结果:", arr1); // [1, 2, 3, 4]// 2. 降序排序
const arr2 = [3, 1, 4, 2];
arr2.sort((a, b) => b - a);
console.log("降序结果:", arr2); // [4, 3, 2, 1]// 3. 按age升序排序对象数组
const people = [{ name: '张三', age: 20 },{ name: '李四', age: 18 }
];
people.sort((a, b) => a.age - b.age);
console.log("按年龄排序:", people); // [李四(18), 张三(20)]
练习8:数组扁平化(flat、flatMap)
// 1. 完全扁平化嵌套数组
const nestedArr = [1, [2, [3, [4]]]];
const flatArr = nestedArr.flat(Infinity); // 无限深度
console.log("完全扁平化:", flatArr); // [1, 2, 3, 4]// 2. flatMap处理字符串数组
const strs = ['hello world', 'good morning'];
const words = strs.flatMap(str => str.split(' '));
console.log("拆分并扁平化:", words); // ['hello','world','good','morning']
练习9:数组查找(indexOf、find、findIndex)
// 1. indexOf查找元素第一次出现的索引
const nums = [10, 20, 30, 20];
const firstIndex = nums.indexOf(20);
console.log("20第一次出现的索引:", firstIndex); // 1// 2. find查找id=2的对象
const objs = [{ id: 1, name: 'a' },{ id: 2, name: 'b' }
];
const foundObj = objs.find(obj => obj.id === 2);
console.log("找到的对象:", foundObj); // {id:2, name:'b'}// 3. findIndex查找第一个大于12的元素索引
const values = [5, 10, 15, 20];
const targetIndex = values.findIndex(val => val > 12);
console.log("大于12的元素索引:", targetIndex); // 2(元素15)
练习10:综合练习(多方法组合)
const data = [{ name: '张三', score: 85, subject: '数学' },{ name: '张三', score: 90, subject: '语文' },{ name: '李四', score: 75, subject: '数学' },{ name: '李四', score: 80, subject: '语文' }
];// 1. 筛选出数学成绩≥80的记录
const mathPass = data.filter(item => item.subject === '数学' && item.score >= 80);
console.log("数学及格的记录:", mathPass);
// [{name: '张三', score:85, subject:'数学'}]// 2. 提取所有学生的语文成绩
const chineseScores = data.filter(item => item.subject === '语文').map(item => ({ name: item.name, score: item.score }));
console.log("语文成绩:", chineseScores);
// [{name: '张三', score:90}, {name: '李四', score:80}]// 3. 计算每个学生的平均分
const avgScores = data// 先按姓名分组.reduce((acc, item) => {const student = acc.find(s => s.name === item.name);if (student) {student.scores.push(item.score);} else {acc.push({ name: item.name, scores: [item.score] });}return acc;}, [])// 再计算平均分.map(student => ({name: student.name,avg: student.scores.reduce((sum, s) => sum + s, 0) / student.scores.length}));
console.log("学生平均分:", avgScores);
// [{name: '张三', avg:87.5}, {name: '李四', avg:77.5}]
拓展 数组实际应用场景
1. 数据筛选与格式化(电商商品列表处理)
场景:从接口返回的商品列表中,筛选出“在售且价格低于100元”的商品,并格式化展示字段。
// 接口返回的原始数据
const products = [{ id: 1, name: "T恤", price: 89, status: "onSale", category: "服装" },{ id: 2, name: "运动鞋", price: 199, status: "onSale", category: "鞋类" },{ id: 3, name: "袜子", price: 19, status: "onSale", category: "服装" },{ id: 4, name: "背包", price: 299, status: "outOfStock", category: "配饰" },
];// 处理逻辑:筛选 + 格式化
const filteredProducts = products.filter(item => item.status === "onSale" && item.price < 100) // 筛选在售且低价商品.map(item => ({// 只保留需要的字段并格式化productId: item.id,productName: item.name,salePrice: `¥${item.price.toFixed(2)}`, // 价格格式化category: item.category}));console.log(filteredProducts);
// 输出:
// [
// { productId: 1, productName: "T恤", salePrice: "¥89.00", category: "服装" },
// { productId: 3, productName: "袜子", salePrice: "¥19.00", category: "服装" }
// ]
2. 数组聚合与统计(用户订单分析)
场景:统计用户订单中各状态的数量,并计算总消费金额。
// 订单数据
const orders = [{ id: 1, userId: 101, amount: 89, status: "paid" },{ id: 2, userId: 101, amount: 159, status: "paid" },{ id: 3, userId: 101, amount: 49, status: "cancelled" },{ id: 4, userId: 101, amount: 299, status: "pending" },
];// 聚合统计:用reduce一次性完成多维度计算
const orderStats = orders.reduce((acc, order) => {// 1. 累计总消费金额(只算已支付)if (order.status === "paid") {acc.totalPaid += order.amount;}// 2. 统计各状态数量if (acc.statusCount[order.status]) {acc.statusCount[order.status]++;} else {acc.statusCount[order.status] = 1;}return acc;},{ totalPaid: 0, statusCount: {} } // 初始值
);console.log(orderStats);
// 输出:
// {
// totalPaid: 248, // 89 + 159
// statusCount: { paid: 2, cancelled: 1, pending: 1 }
// }
3. 数组去重与合并(用户标签管理)
场景:合并两个用户标签数组,并去除重复标签,同时按字母排序。
// 已有标签和新标签
const existingTags = ["前端", "JavaScript", "React"];
const newTags = ["React", "Vue", "前端", "TypeScript"];// 合并、去重、排序
const uniqueTags = [...new Set([...existingTags, ...newTags])] // 合并+去重.sort((a, b) => a.localeCompare(b)); // 按中文拼音排序console.log(uniqueTags);
// 输出:["JavaScript", "React", "TypeScript", "Vue", "前端"]
4. 嵌套数组处理(多级评论数据扁平化)
场景:将嵌套的评论数据(含子评论)扁平化为一维数组,方便渲染。
// 嵌套评论数据
const comments = [{id: 1,content: "主评论1",replies: [{ id: 11, content: "子评论1-1" },{ id: 12, content: "子评论1-2" }]},{id: 2,content: "主评论2",replies: []}
];// 扁平化:用reduce递归处理嵌套结构
const flattenComments = comments.reduce((acc, comment) => {// 先推入当前主评论acc.push({ id: comment.id, content: comment.content, isReply: false });// 再处理子评论(递归)if (comment.replies.length > 0) {const replyComments = comment.replies.map(reply => ({...reply,isReply: true}));acc.push(...flattenComments(replyComments)); // 递归扁平化}return acc;
}, []);console.log(flattenComments);
// 输出:
// [
// { id: 1, content: "主评论1", isReply: false },
// { id: 11, content: "子评论1-1", isReply: true },
// { id: 12, content: "子评论1-2", isReply: true },
// { id: 2, content: "主评论2", isReply: false }
// ]
5. 条件查询与分组(学生成绩管理)
场景:将学生成绩按科目分组,并筛选出每科平均分≥80的科目。
// 学生成绩数据
const scores = [{ subject: "数学", name: "张三", score: 85 },{ subject: "数学", name: "李四", score: 92 },{ subject: "语文", name: "张三", score: 78 },{ subject: "语文", name: "李四", score: 88 },{ subject: "英语", name: "张三", score: 90 },{ subject: "英语", name: "李四", score: 85 },
];// 按科目分组并计算平均分
const subjectGroups = scores.reduce((acc, item) => {// 按科目分组if (!acc[item.subject]) {acc[item.subject] = [];}acc[item.subject].push(item.score);return acc;
}, {});// 筛选出平均分≥80的科目
const qualifiedSubjects = Object.entries(subjectGroups).map(([subject, scores]) => {const avg = scores.reduce((sum, s) => sum + s, 0) / scores.length;return { subject, avg: avg.toFixed(1) };}).filter(item => item.avg >= 80);console.log(qualifiedSubjects);
// 输出:
// [
// { subject: "数学", avg: "88.5" },
// { subject: "英语", avg: "87.5" }
// ]
6. 数组操作防抖(搜索联想优化)
场景:用户输入搜索关键词时,防抖处理并过滤匹配的选项。
// 所有可选关键词
const allKeywords = ["JavaScript", "Java", "Python", "TypeScript", "PHP"];// 防抖函数(复用之前的实现)
function debounce(fn, delay = 300) {let timer;return (...args) => {clearTimeout(timer);timer = setTimeout(() => fn.apply(this, args), delay);};
}// 搜索输入处理
const searchInput = document.getElementById("searchInput");
searchInput.addEventListener("input",debounce((e) => {const keyword = e.target.value.trim().toLowerCase();if (!keyword) {console.log("请输入关键词");return;}// 筛选匹配的关键词(不区分大小写)const matched = allKeywords.filter(item => item.toLowerCase().includes(keyword));console.log("匹配结果:", matched);})
);
总结
实际项目中,数组方法的价值体现在:
- 链式调用:
filter+map+sort等组合,高效处理数据流水线。 - 聚合能力:
reduce几乎能完成所有复杂聚合(分组、统计、转换等)。 - 简洁性:替代冗长的
for循环,代码可读性更高。
根据具体场景选择合适的方法组合,能显著提升开发效率。例如:
- 筛选数据用
filter,转换数据用map,两者常链式使用。 - 复杂统计用
reduce,分组操作是其典型应用。 - 处理嵌套结构时,
flat(浅嵌套)或递归+reduce(深嵌套)更高效。
