list类的常用接口实现及迭代器
目录
1. list类的介绍
2.list类的常用接口
2.1 list类的常用构造
2.2 list类对象的容量操作
2.3 list迭代器
2.4 list类的常用操作
3.list的模拟实现
1. list类的介绍
list代表的是双向链表,常见的有创建,增,删,改几个接口(功能),对于list类来说,复杂的是它的迭代器,本章则会讲解list类的常见接口实现以及list类的简单实现。
2.list类的常用接口
2.1 list类的常用构造
| 构造函数 | 接口说明 |
| list(size_t n,const T& val=T())(注:T代表模版) | 构造n个val值的元素 |
| list() | 默认构造 |
| list(const list<T>& x) | 拷贝构造 |
| list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last) | 利用迭代器区间构造list |
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{list<int> l1;//默认构造list<int> l2(l1);//拷贝构造list<int> l3(10, 1);//构造n个val值string s("123456");list<int> l4(s.begin(), s.end());//利用迭代器区间构造return 0;
}2.2 list类对象的容量操作
| 函数名称 | 接口说明 |
| empty | 判断list是否为空,是返回true,否则返回false |
| size | 返回list中有效节点个数 |
2.3 list迭代器
| 函数名称 | 接口说明 |
| begin+end | begin返回第一个元素的迭代器 end返回最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器 |
| rbegin+rend | rbegin返回最后一个元素的迭代器 rend返回第一个元素前一个位置的迭代器 |
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{list<int> l(10, 1);//构造n个val值for (auto e : l){cout << e << " ";}return 0;
}2.4 list类的常用操作
| 函数名称 | 接口说明 |
| front | 返回list的第一个节点值的引用 |
| back | 返回list的最后一个节点值的引用 |
| push_front | 在list首元素前插入值为val的元素 |
| pop_front | 删除list第一个元素 |
| push_back | 在list尾部插入值为val的元素 |
| pop_back | 删除list最后一个元素 |
| insert | 在list的pos位置中插入值为val的值 |
| erase | 删除list的pos位置的数据 |
| swap | 交换两个list中的元素 |
| clear | 清空list中的有效元素 |
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
void Print(const list<int>& l)
{list<int>::const_iterator it = l.begin();while (it != l.end()){cout << *it << " ";++it;}cout << endl;}
int main()
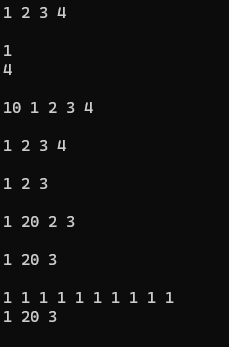
{list<int> l1;l1.push_back(1);l1.push_back(2);l1.push_back(3);l1.push_back(4);Print(l1);//打印cout << endl;int a = l1.front();cout << a << endl;cout << l1.back() << endl;cout << endl;l1.push_front(10);Print(l1);cout << endl;l1.pop_front();Print(l1);cout << endl;l1.pop_back();Print(l1);cout << endl;list<int>::iterator it = l1.begin();++it;l1.insert(it, 20);Print(l1);cout << endl;l1.erase(it);Print(l1);cout << endl;list<int> l2(10, 1);l1.swap(l2);Print(l1);Print(l2);cout << endl;l1.clear();Print(l1);return 0;
}
3.list的模拟实现
3.1 list的基本结构
list的基本结构由三个类组成,一个是自己本身,一个是list的每个节点,最后就是有关迭代器的类,由于list中的底层结构是不连续的,因此不能用原本指针去访问,要对list的指针进行一个封装
namespace chuxin
{template<class T>struct list_node//链表的节点{T _data;list_node<T>* _prev;list_node<T>* _next;};template<class T>struct list_iterator//迭代器{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T> Self;Node* _node;};template<class T>//链表class list{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:typedef list_iterator<T> iterator;private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};
}3.2 list的构造及析构
对于list来说,三个类都需要构造,但是,析构只有list就够了
namespace chuxin
{template<class T>struct list_node//链表的节点{T _data;list_node<T>* _prev;list_node<T>* _next;list_node(const T& data = T())//构造:_data(data), _prev(nullptr), _next(nullptr){}};template<class T>struct list_iterator//迭代器{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T> Self;Node* _node;list_iterator(Node* node)//构造:_node(node){}};template<class T>//链表class list{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:typedef list_iterator<T> iterator;list()//默认构造{_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}list(const list<T>& lt)//拷贝构造{empty();for (auto& e : lt){push_back(e);}}~list()//析构{clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};
}3.3 迭代器
迭代器要进行的操作有++,--,比较,以及使用数据
template<class T>struct list_iterator//迭代器{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T> Self;Node* _node;list_iterator(Node* node)//构造:_node(node){}T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}Self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}bool operator!=(const Self& s)const{return s._node != _node;}bool operator==(const Self& s)const{return s._node == _node;}};对于list的迭代器,还要重载一个—>,由于list内每个节点内的数据可能是一个结构体,这时候虽然还能用 . 作用符访问,但是较复杂。
struct AA
{int _a1 = 1;int _a2 = 1;
};
void test_list1()
{list<int> lt;list<AA> lta;lta.push_back(AA());lta.push_back(AA());lta.push_back(AA());lta.push_back(AA());list<AA>::iterator ita = lta.begin();while (ita != lta.end()){//cout << (*ita)._a1 << ":" << (*ita)._a2 << endl;// 特殊处理,本来应该是两个->才合理,为了可读性,省略了一个->cout << ita->_a1 << ":" << ita->_a2 << endl;cout << ita.operator->()->_a1 << ":" << ita.operator->()->_a2 << endl;++ita;}cout << endl;
} template<class T>struct list_iterator//迭代器{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T> Self;Node* _node;list_iterator(Node* node)//构造:_node(node){}T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}T* operator->(){return &_node->_data;}Self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}bool operator!=(const Self& s)const{return s._node != _node;}bool operator==(const Self& s)const{return s._node == _node;}};对于迭代器,还要实现一个const的版本,如果要实现一个const的版本,发现两个类的结构大多相似,这时候就可以利用模版
template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>struct list_iterator//迭代器{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> Self;Node* _node;list_iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}Self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}bool operator!=(const Self& s)const{return s._node != _node;}bool operator==(const Self& s)const{return s._node == _node;}};template<class T>//链表class list{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:typedef list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;typedef list_iterator<T,const T&,const T*> const_iterator;list(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}list(const list<T>& lt){empty();for (auto& e : lt){push_back(e);}}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}private:Node* _head;size_t _size;
};
此时利用三个模版参数就可以实现简洁化
3.4 赋值,clear,size,begin,end,front,back,empty
这几个较简单,不做叙述
template<class T>//链表class list{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:typedef list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;typedef list_iterator<T,const T&,const T*> const_iterator;list(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}list(const list<T>& lt){empty();for (auto& e : lt){push_back(e);}}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}void clear(){auto it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}}// lt1 = lt3void swap(list<T>& lt){std::swap(_head, lt._head);std::swap(_size, lt._size);}list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt){swap(lt);return *this;}iterator begin(){return _head->_next;}iterator end(){return _head;}const_iterator begin() const{return _head->_next;}const_iterator end() const{return _head;}size_t size() const{return _size;}T& front(){return _head->_next->_data;}T& back(){return _head->_prev->_data;}bool empty() const{return _size == 0;}private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};3.5 insert,erase,push_back,push_front,pop_back,pop_front
对于这些增删查改,可以进行一些复用,insert,erase,这里的插入,删除和链表完全相似,也不做详细叙述
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node(x);prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_next = cur;newnode->_prev = prev;cur->_prev = newnode;++_size;return newnode;}void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* prev = pos._node->_prev;Node* next = pos._node->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete pos._node;--_size;return next;}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}void pop_back(){iterator it = end();--it;erase(it);}3.5 总代码
List.h
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
namespace chuxin
{template<class T>struct list_node//链表的节点{T _data;list_node<T>* _prev;list_node<T>* _next;list_node(const T& data = T()):_data(data), _prev(nullptr), _next(nullptr){}};template<class T,class Ref,class Ptr>struct list_iterator//迭代器{typedef list_node<T> Node;typedef list_iterator<T,Ref,Ptr> Self;Node* _node;list_iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}Self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}bool operator!=(const Self& s)const{return s._node != _node;}bool operator==(const Self& s)const{return s._node == _node;}};template<class T>//链表class list{typedef list_node<T> Node;public:typedef list_iterator<T,T&,T*> iterator;typedef list_iterator<T,const T&,const T*> const_iterator;list(){_head = new Node;_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;_size = 0;}list(const list<T>& lt){empty();for (auto& e : lt){push_back(e);}}~list(){clear();delete _head;_head = nullptr;}void clear(){auto it = begin();while (it != end()){it = erase(it);}}// lt1 = lt3void swap(list<T>& lt){std::swap(_head, lt._head);std::swap(_size, lt._size);}list<T>& operator=(list<T> lt){swap(lt);return *this;}iterator begin(){return _head->_next;}iterator end(){return _head;}const_iterator begin() const{return _head->_next;}const_iterator end() const{return _head;}iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* prev = cur->_prev;Node* newnode = new Node(x);prev->_next = newnode;newnode->_next = cur;newnode->_prev = prev;cur->_prev = newnode;++_size;return newnode;}void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);}void push_front(const T& x){insert(begin(), x);}iterator erase(iterator pos){assert(pos != end());Node* prev = pos._node->_prev;Node* next = pos._node->_next;prev->_next = next;next->_prev = prev;delete pos._node;--_size;return next;}void pop_front(){erase(begin());}void pop_back(){iterator it = end();--it;erase(it);}size_t size() const{return _size;}T& front(){return _head->_next->_data;}T& back(){return _head->_prev->_data;}bool empty() const{return _size == 0;}private:Node* _head;size_t _size;};
}