【递归、搜索与回溯算法】专题一 递归
文章目录
- 0.理解递归、搜索与回溯
- 1.面试题 08.06.汉诺塔问题
- 1.1 题目
- 1.2 思路
- 1.3 代码
- 2. 合并两个有序链表
- 2.1 题目
- 2.2 思路
- 2.3 代码
- 3.反转链表
- 3.1 题目
- 3.2 思路
- 3.3 代码
- 4.两两交换链表中的节点
- 4.1 题目
- 4.2 思路
- 4.3 代码
- 5. Pow(x, n) - 快速幂
- 5.1 题目
- 5.2 思路
- 5.3 代码
0.理解递归、搜索与回溯



1.面试题 08.06.汉诺塔问题
1.1 题目
题目链接

1.2 思路



1.3 代码
class Solution {
public:void hanota(vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b, vector<int>& c) {dfs(a, b, c, a.size());}void dfs(vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b, vector<int>& c, int n){if(n == 1){c.push_back(a.back());a.pop_back();return;}dfs(a, c, b, n - 1);c.push_back(a.back());a.pop_back();dfs(b, a, c, n - 1);}
};
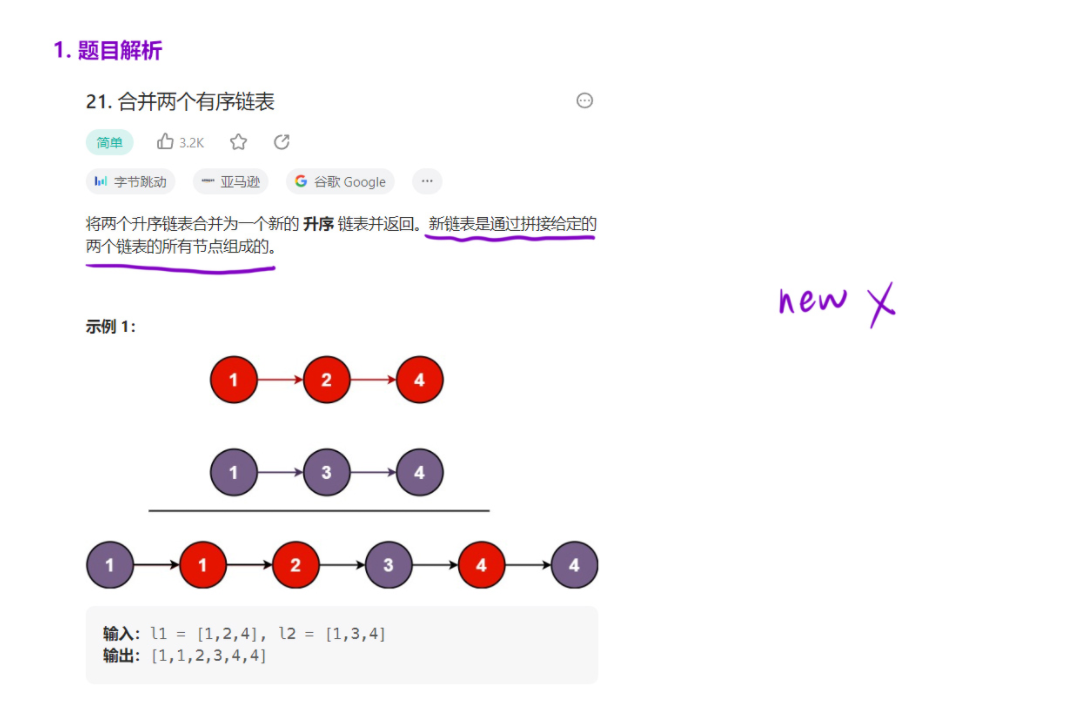
2. 合并两个有序链表
2.1 题目
题目链接


2.2 思路


2.3 代码
class Solution {
public:ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2) {if(l1 == nullptr) return l2;if(l2 == nullptr) return l1;if(l1->val < l2->val){l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next, l2);return l1;}else{l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2->next);return l2;}}
};
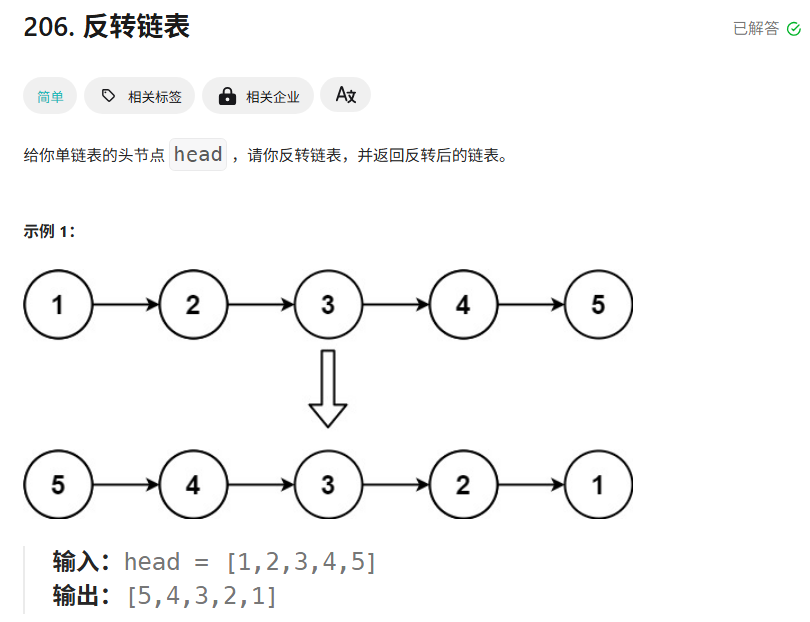
3.反转链表
3.1 题目
题目链接


3.2 思路


3.3 代码
class Solution {
public:ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head;ListNode* newHead = reverseList(head->next);head->next->next = head;head->next = nullptr;return newHead;}
};
4.两两交换链表中的节点
4.1 题目
题目链接


4.2 思路


4.3 代码
老方法-迭代
class Solution {
public:ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head;ListNode* newhead = new ListNode(0);newhead->next = head;ListNode* prev = newhead, * cur = head, * next = head->next, * nnext = next->next;while(cur && next){// 交换节点prev->next = next;next->next = cur;cur->next = nnext;// 移动prev、cur、next、nnextprev = cur;cur = nnext;if(cur) next = cur->next;if(next) nnext = next->next;}prev = newhead->next;delete newhead;return prev;}
};
新方法-递归
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* struct ListNode {* int val;* ListNode *next;* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}* };*/
class Solution {
public:ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head) {if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head;ListNode* tmp = swapPairs(head->next->next);ListNode* newhead = head->next;head->next->next = head;head->next = tmp;return newhead;}
};
5. Pow(x, n) - 快速幂
5.1 题目
题目链接

5.2 思路



5.3 代码
方法一
class Solution {
public:double myPow(double x, int N) {double ret = 1;long long int n = N;// 如果 n 是负数,将其转换为正数(即取绝对值),并将底数 x 变为 1/xif(n < 0){n = -n;x = 1/x;}while(n){// 检查 n 的最低位是否为 1(通过 n & 1 判断)。如果是 1,则将当前的 x 乘到 ret 中。这是因为当前位对应的幂需要被累乘到结果中。if(n & 1)ret *= x;// 将 x 平方(即 x *= x),相当于将指数翻倍。// 将 n 右移一位(即 n >>= 1),相当于去掉当前最低位,处理下一位。x *= x;n >>= 1;}return ret;}
};
方法二 - 递归
class Solution {
public:double myPow(double x, int n) {// -2^31 <= n <= 2^31// 当n是负的很大的数时,会越界,所以需要将N强转成long longreturn n > 0 ? Pow(x, n) : Pow(1/x, - (long long)n); }double Pow(double x, int n){if(n == 0) return 1.0;double tmp = Pow(x, n/2);return n % 2 == 0 ? tmp * tmp : tmp * tmp * x;}
};
