嵌入式学习笔记——day25
- 标准i/o操作
- 缓冲区
- 文件i/o操作
一、标准i/o操作
1.fwrite:size_t fread(void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream);
(1)功能:从指定的stream流对象中获取nmemeb个大小为size字节的数据块到ptr所在的本地内存中。
(2)参数:
1)ptr 要存储数据的本地内存一般是数组或者结构体指针
2)size 单个数据块的元数据大小。最小单元的大小
3)nmemb 要获取的数据块的个数,拷贝的数据块个数。
4)stream 要获取数据的源文件流对象,如果是stdin表示从键盘获取数据,如果是fp文件则表示从普通文件获取。
5)返回值:成功 小于等于nemeb的整数,表示获取的数据长度,失败 小于0,结尾 0;
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct{
char name[10];
int age;
char add[50];
}PER;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
FILE *fp = fopen("01.txt", "w");
PER per;
strcpy(per.name, "zhhangsan");
per.age = 20;
strcpy(per.add, "jiabeidasha");
fwrite(&per, sizeof(PER), 1, fp);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
2.fread:size_t fwrite(const void *ptr, size_t size,size_t nmemb, FILE *stream);
(1)功能:从ptr所在本地内存中取出nmemb个大小为size的数据块写入到stream流对应的文件流对象中。
(2)参数:
1)ptr 要写的数据块地址,一般是数组或者结构体指针
2)size 要写的数据块元数据大小,单位是字节
3)nmemb 要写的数据块的个数
4)stream 要写的目标文件流对象。如果是stdout则表示数据会写到终端屏幕显示,如果是fp的普通文件则会写入到文件中。
5)返回值:成功 小于等于nmemb 的个数。失败 <0
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <strings.h>
typedef struct{
char name[10];
int age;
char add[50];
}PER;
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
FILE *fp = fopen("01.txt", "r");
if(NULL == fp)
{
fprintf(stderr,"fopen error");
return 1;
}
PER per;
bzero(&per, sizeof(PER));
size_t vel = fread(&per, sizeof(PER), 2, fp);
if(vel>0)
{
printf("%lu %s %d %s\n",vel,per.name,per.age,per.add);
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
2
3. fseek:int fseek(FILE *stream, long offset, int whence);
(1)功能:将stream流文件中的文件指针从whence位置开始,偏移offset字节的长度。
(2)参数:
1)stream 要移动文件指针的目标文件流对象。
注意:不支持设备文件,一般用于普通文件。
2)offset 要在文件内偏移的距离,单位字节。如果值为整数,则向文件末尾偏, 如果值为负数,则向文件开头偏移
3)whence 偏移的起始位置,由系统定义的三个宏开始。
SEEK_SET 文件的开头位置
SEEK_CUR 文件的当前位置
SEEK_END 文件的末尾位置
(3)返回值:成功: 返回 0,失败: -1;
(4)注意:如果从文件的指定位置向后偏移过程中已经超过了文件的当前末尾位置,则会自动以'\0'来填充文件内容,从而形成一种被称为"空洞文件" 的特殊文件。
4. ftell: long ftell(FILE *stream);rewind(fp);
(1)功能:获取当前文件流指针的具体位置,一般以文件开头到当前指针的字节数为返回值。
(2)参数:
1)stream 要返回指针距离的文件流对象
2)返回值:成功 获取到的距离长度,单位是字节失败 -1;
5. rewind: rewind(fp);
(1)等效于:fseek(stream,0L,SEEK_SET);
(2)功能:移到文件开头位置
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
FILE *fp = fopen("01.txt", "r");
if(NULL ==fp)
{
fprintf(stderr, "fopen error");
return 1;
}
fseek(fp, 0, SEEK_END);
long size = ftell(fp);
printf("size : %ld\n",size);
rewind(fp);
char buf[1024] = {0};
fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), fp);
printf("%s",buf);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
6. /a.out运行(FILE*类型)
(1)stdin->标准输入(终端,关联键盘),scanf,gets,......
1)与scanf区别:如果接受字符串,stdin接受可以有空格,结束标识是\n,并且\n也被接收,scanf如果接收空格则表示接收字符串完毕,如果是回车\n去缓冲区了。
(2)swtdout->标准输出,常规类信息(终端,关联屏幕),printf
(3)stderr->标准错误输出,错误类信息,比普通类信息优先级高(终端,关联屏幕)
二、缓冲区
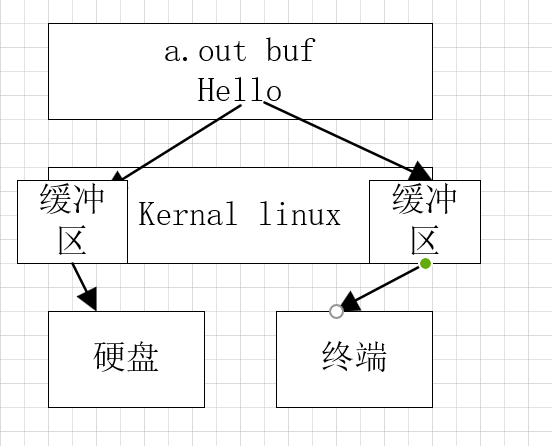
1.内核和硬件设备速度不匹配,为了匹配速度创造的机制。本质是队列。
2.行缓冲
(1)缓冲区大小1k,terminal,主要用于人机交互stdout,缓存区满或者遇到\n刷新,行缓存多是关于终端的一些操作.
(2)刷新条件:
1)遇到\n刷新
2)缓存区满刷新
3)程序结束刷新
4)fflush刷新 fflush(stdout); FILE*fp stdin stdout stderr
3.全缓冲
(1)缓冲区大小4k,主要用于文件的读写,缓存区满刷新缓存区,对普通文件进行标准IO操作,建立的缓存一般为全缓存,一般用于写操作。
的缓存一般为全缓存。
(2)刷新条件:
1)缓存区满刷新
2)程序结束刷新
3)fflush来刷新 fflush(fp);
4.无缓冲

(1)0k 主要用于出错处理信息的输出 stderr 不对数据缓存直接刷新。
printf();==>>stdout (对于排查错误难度变大)
fprintf(strerr,"fopen error %s",filename);(无视其他,直接输出)。
(2)界面交互 出错处理,使用gdb查看,FILE结构体,或使用写入数据测试缓冲区。
(3)缓冲区的大小是可以设置。
三、文件i/o操作
1.与标准io的区别:
(1)标准io属于c库中,(c库还包含string系列函数、math系列函数、大小写转换等等;文件io一般对设备文件操作,也可以对普通文件操作
(2)文件io没有缓冲区(对于文本文件但是硬件上有缓冲区),标准io有缓冲区;
(3)文件io操作对象不是流,而是文件描述符FILE*


- 注意:c库封装了系统调用,c库更通用可以跨平台,系统调用只适用liunx;

2. 文件IO的定义
操作系统为了方便用户使用系统功能而对外提供的一组系统函数。称之为 系统调用 其中有个文件IO;一般都是对设备文件操作,当然也可以对普通文件进行操作。
注:一个基于Linux内核的没有缓存的IO机制
3.文件IO的特性
(1) 没有缓存区
(2)操作对象不在是流,而是文件描述符
(3)文件描述符:很小的非负的整数 int 0-1023
(4)内核每打开一个文件就会获得一个文件 描述符
注:每个程序在启动的时候操作系统默认为其打开
三个描述符与流对象匹配:
0 ==>STDIN_FILENO (宏)=== stdin
1 ==>STDOUT_FILENO == stdout
2 ==>STDERR_FILENO == stderr
4.相关函数
1.open
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int a = 12312;
int fd = open("1.txt", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0666);
if (-1 == fd)
{
fprintf(stderr, "open error\n");
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
2.write
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<string.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd = open("1.txt", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0666);
if (-1 == fd)
{
fprintf(stderr, "open error\n");
return 1;
}
char buf[1024]="hello";
size_t ret= write(fd, buf, strlen(buf));
printf("write ret :%ld\n",ret);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
3.read
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd = open("1.txt", O_RDONLY);
if (-1 == fd)
{
fprintf(stderr, "open error\n");
return 1;
}
char buf[1024] = {0};
ssize_t ret=read(fd, buf, sizeof(buf));
printf("readret:%ld %s\n",ret,buf);
close(fd);
return 0;
}
注:一些小命令
1.file +文件名 产看文件类型 data默认为二进制文

2. stat +文件名 查看文件大小

3.去除换行
PER per;
memset(&per,0,sizeof(per));
bzero(&per, sizeof(per));
4. - 作者 组里的人 其他人


5. umask 延码 与文件创建相关 权限 相减

