[笔记]几起风电结构失效案例与简单分析
1.韩国风电421事故
原始资料:紧急!大型风力发电机组倒塌事故


1.1 事故关键信息
- 2018年后投产的4兆瓦以上机组,基础结构安全系数平均降低22%。首尔大学朴志勋教授团队通过数字孪生技术模拟发现,当偏航系统误差超过0.47度时,塔筒根部应力峰值可达设计值的180%,与该风机七次偏航故障记录形成印证。
- 离事故现场3公里的云阳里村,76岁村民李顺子指着墙面的裂纹说:"这些铁塔立起来后,山间的风都带着呜咽。"村民自发组织的声波检测显示,16赫兹的低频震动与德国《职业健康》期刊记载的"风电综合症"诱发阈值完全吻合。尽管运营商承诺安装隔音屏障,但多数老人仍坚持每晚服用安神药剂。
- 西门子歌美飒技术总监在事故说明会上透露,全球132台同型机组中,11号机的发电效率持续低于平均值19%。卫星遥感图像显示,该机组所在山脊三年间累计沉降4.9厘米,远超环评预测的2厘米阈值。值得关注的是,项目施工方为追赶工期,省略了地质雷达扫描工序,这一细节在事故后被匿名举报者曝光。
- 2023年全国风电事故中,72%集中于单机容量4兆瓦以上的新锐机型。这与国际可再生能源机构《超大型风机安全白皮书》的警示形成呼应——塔筒高度突破80米后,湍流激振效应呈几何级数增长。
- 在华城山事故现场,来自慕尼黑再保险公司的风险评估师正使用三维激光扫描仪重建倒塌过程。初步数据显示,基础环法兰螺栓在断裂前承受的应力仅为设计载荷的58%,这个矛盾数值让调查团队陷入困惑。参与勘查的德国工程师穆勒指出:"这就像万吨巨轮在平静港湾突然解体,必然存在多重诱因的叠加效应。"
1.2 关键信息
- 偏航系统迎风桨叶调节会极大影响塔筒应力,特别是根部应力?(Todo)
- 低频振动与系统固有震荡频率的关系
- 同地点,发电效率偏低的机组可能异常预警
- 地质沉降
- 4M瓦机型,80米后的激振效应几乎级数增长(???)
- 问题不在法兰和连接件。
2.美国2022年的风电事故白皮书
原始文档:envista-whitepaper-common-wind-turbine-failures.pdf
2.2 关键信息
- Wind Turbine Generators (WTGs)
- Between lost Power Purchase Agreement (PPA) revenue and Federal Wind Production Tax Credits, a WTG that is out of service may cost a producer a significant amount of revenue each week. 事故的数量是周级别的。。。
- the number of incidents will inevitably increase.
- 白皮书的主要内容:In this whitepaper, we outline the common failure modes associated with WTGs, from electrical and mechanical failures to structural disasters and trending cyber risks, as a background for carriers and other professionals that work with this industry.
- 失效原因
- Electrical Incidents
- critical components, such as bus bar systems, sensors and other crucial electrical systems. WTGs often operate in harsh environments.
- arc flashes =>fires
- the second main failure sources.(blades is the first one)
- 失效根因:lightning strikes, electrical malfunction, mechanical failure and maintenance errors.
- Mechanical Incidents
- sophisticated mechanical systems to operate, any of which present risks for failure and fire(风力机各部件的成本分析-与风速的相关性标志着该器件的失效风险与载荷的关系)
- WTGs are vulnerable to fatigue, issues with overspeed, vibration, resonance and frequency 疲劳损伤:由:超载、振动、声源性故障、频率引发
- Quality Assurance and Quality Control (QA/QC) measures are not properly reviewed and assessed, including reviewing if the work did in fact take place, serious risk for failure and safety concerns are likely to arise.
- Structural Failures
- tower collapse 、 blade fracture
- high-wind or weather-related events
- Overstress, strain in the tower, and stress to the blades
- experienced engineers and experts must be deployed on scene to evaluate the failure and determine potential causes and what, if any, mitigation measures may be taken.
- Cyber Incidents
- According to the U.S. Department of Homeland Security3, the energy sector, specifically renewables, will be a significant target for hackers in the coming years. Wind farms are extremely vulnerable to hackers due to the lackluster physical security, outdated and decentralized communication systems, protocols and operational technologies (OT), as well as an overall lack of training on cyber preparedness.(这就是国标SAC/TC50专门对控制与侦测系统进行指导性设计的原因?)
- It is imperative that the insurance industry becomes familiar with the apparent cyber risks and mitigation strategies, including identifying and appointing experienced cyber security professionals should the worst occur.(国外为啥这类白皮书层出不穷是因为,会有投资,保险,公共安全,审计,等多个利益相关方,所有的信息,肯定会做到更大程度的公开透明)
- 意义,可以用来借鉴的文本:U.S. wind power capacity continues to grow at impressive levels. As WTG installations continue to increase nationwide and the market simultaneously begins to mature, the occurrence and severity of incidents involving WTGs will also increase. Following any loss or incident involving wind turbine equipment, it is crucial that experienced engineers and experts be consulted immediately. Therefore, it is helpful to have a team of reputable, electrical, materials, mechanical, and structural engineers pre-vetted so that these kinds of incidents can be responded to quickly and efficiently.
- Electrical Incidents
2.3 文献引用
1. https://www.awea.org/wind-101/basics-of-wind-energy/wind-facts-at-aglance
2.https://www.imperial.ac.uk/news/153886/fires-major-cause-wind-farm-failure/
3. https://www,dnvgl.com/article/why-windfarms-need-to-step-up-cyber-security-128082
3.美国风电联合会的风力发电机维护手册
3.1 SCADA和CMMS系统
这里的记录似乎不是技术性的,而是管理性的,一种质量保证。
- Beyond SCADA storage, many owner/operators have also implemented computerized maintenance management systems (CMMS) for their work orders.(chap2.5)
- trend analysis, detailed parts tracking, and root cause analysis.
- turbine, BOP, and plant performance, especially over the life of the equipment and wind plant.
- Well-written work orders can provide a goldmine of information
- the affected component would be chosen from a standard breakdown of the turbine, e.g. taxonomy, metadata framework, or equipment breakdown workflow.
- In order to conduct real root-cause analysis, it is also useful to capture a brief description of the failure mechanism and/or the ex ternal event that caused the downtime or maintenance, e.g. cur tailment, chipped gear tooth, dirty oil, etc.
- or relevant event types, the source of parts is also a useful piece of information. This includes parts acquired through non-standard methods, e.g. swapped from another turbine, purchased outside the supply system, machined on site, etc. Identifying the source of parts allows for more accurate cost calculations and will allow more advanced CMMS towards parts and inventory tracking.
- equipment status include online, offline/ fault, planned maintenance, unplanned maintenance, degraded, etc.
- V. A. Peters, P. S. Veers, and A. Ogilvie, “Wind Energy Computerized Maintenance Management System (CMMS): Data Collection Recommenda tions for Reliability Analysis,” Sandia, Albuquerque, NM, USA, SAND2009 4184, 2009.
-
3.1.1 风机监测的项目列表
这里的CBM condition based maintenance 大概率是个和time-schdule based maintenance对照的概念,其实就是预发行维护。要主动监测并发现问题。
801 总章节是一个中国人写的,似乎:
Committee Chair: Junda Zhu, NRG Systems(location)
Principal Author: Junda Zhu, NRG Systems(company)

3.1.1.1 风机叶片失效监测
RP 821 Wind Turbine Blade Condition Monitoring
这是一则:recommended practice (RP),由:AWEA Opera tions and Maintenance (O&M) Committee.
编制人员:
- Bruce Hamilton, Navigant Consulting
- Jim Turnbull, SKF
- David Clark, Bachmann(主作)
There are six major failure modes that can be monitored by a blade condition monitoring system.
3.1.1.1.1个可能失效原因的样例:
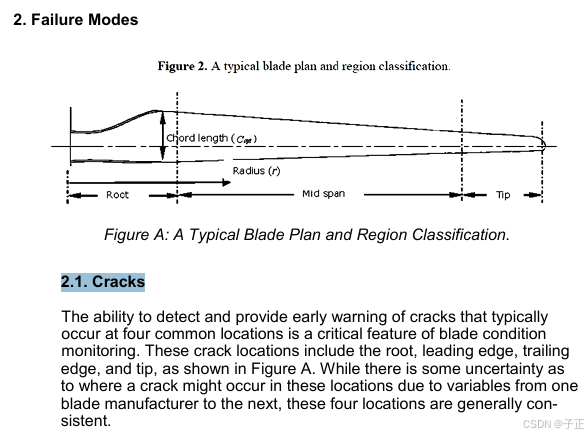
3.1.1.1.2 技术手段 - 要点
没有完全做笔记,这部分可以。
- Fiber Optic.........fast, high-resolution strain data from structures,They are light weight and would not affect performance. However, they are also difficult to install outside of initial blade manufacture, expensive, and do not detect all failure modes. This is likely why fiber optic technology has had limited success and adoption in the wind industry
- Laser Reference.....这个挺有用。用激光测距来测量某些关键指标。
- P. J. Schubel and R. J. Crossley, “Wind Turbine Blade Design,” Energies, vol. 5, no. 9, pp. 3425-3449, Sept. 2012. 这是叶片设计相关的一份参考资料。
- As a note to system designers and integrators, the perfect wind turbine blade condition monitoring system would have the following features:
- The ability to detect all 6 common failure modes
- Robust sensors
- The ability to provide blade and blade position identification
- The ability to provide sensor identification
- A cost-effective method for either retrofit to existing turbines or instal lation at original manufacture
- Wireless and self-powered sensors to facilitate installation and data collection
3.1.1.2 机舱部分失效监测
这本书似乎价值很高。
3.1.1.2.1 监测项点
- Pressures
- Temperatures
- Vibrations, including deterministic characteristic: kurtosis, crest factor.spike energy,stress wave, etc.
- VoltageCurrent
- Torque
- Strain
- Moment
- Particle count
- Wind direction
- Wind speed
- Wind deviation
- Blade tip speed ratio
- Ambient temperatures
- Ambient pressures
- Power
- Position
- Set points
- Control demand signals
- Etc.
3.1.1.2.2 监测对象


4.其它
- 看到有系统处于危险状态的电子围栏警戒功能。
附录A 非例行维护章节的振动分析部分的传感器选型
它的作者仍然是:RP801的作者,朱俊达?
| Dr. Junda Zhu is currently a Systems and Analysis Engineer from Renewable NRG Systems. He is also the Chair of the AWEA Condition Monitoring Committee and a member of the AWEA Operation and Maintenance Steering Committee. Dr. Zhu got his M.S. and Ph.D. in University of Illinois at Chicago majored in Mechanical and Industrial Engineering, respectively. He is currently the lead analyst for the TurbinePHD condition monitoring system for wind applications. His research is focused on diagnostic and prognostic hardware and software development. His areas of expertise are signal processing, prognostics algorithms, machine learning and statistical modeling. |
1. Sensor selection
Velocity sensors are also relatively common in the industry. Typically, velocitymeasurements are utilized to monitor low frequency rotational faults (imbalancealignment, etc.).Some practices also use velocity to help with bearing fault de-tection in later failure stages. As modern technology evolves, dynamic range isno longer a limiting factor. Accelerometers are becoming more popular in com-parison to velocity transducers. Mathematically speaking, the best velocitytransducer is an accelerometer and integrator. Velocity is good for broadbandevaluations such as lSO 10816, but not necessary for frequency spectra since itrepresents a change in the slope of the spectrum.
2.Sensor Configuration
The confiquration of the sensor is also crucial and should be tailored to the section of the gearboxes one is monitoring. Normally, for an online retrofitted sys-tem, these are preset and can be changed by the condition monitoring systemspecialist. Each sensor is selected and configured based on the section it ismonitoring.
For a handheld system, these settings need to be constrained for the logger tofunction or to increase the fault detection capability. These configurations needto be changed based on which sections the sensor is collecting data from. Theconfigurations should be logged precisely so that the next time a technician per-forms testing, they can use the same setup to ensure reading consistency.Common sensor configurations are listed as follows:
- Sampling time
- Sampling duration
- Spectrum resolution or number of spectral lines
- Order tracking
- Frequency range (fmax or low cutoff frequency)
- Band pass filter selection
- Tachometer setting
- With or without averages, number of averages
- Detection method(peak-to-peak, RMS, etc.)

