多边形生成立面点云
1、背景介绍
在进行机载点云三维重建时,墙面点云缺失,可采用根据外轮廓线生成立面,根据立面与屋顶面相交,进行三维重建,即可生成三维模型。如下图,屋顶点云完整,但立面点缺失。
 |  |
| 屋顶点云分割 | 三维模型 |
2、ply格式介绍
polyfit算法默认点云格式为ply,ply格式大体如下:
文件头+数据内容,文件头从 ply 一行开始,到 end_header 为止,里面定义了此 ply文件中数据的组织形式,包括数据类型和个数。
如下为polyfit中ply格式,分别为坐标(x y z),点颜色(r g b),后续为点的标号segment_index,属于同一面的点标号相同,标号从1开始,第二个面标号为3, 以此类推。
格式为ascii 1.0版本;
顶点数:4056,总共包含的点数为4056,每个点包含点坐标、点法向量、点的颜色rgb

cloudcompare软件可以打开ply点云格式,在加载点云时,需要设置字段,如r g b nx ny nz等,加载进来可以查看点的相关属性。

3、生成原理与步骤
生成点集大体是对每一线段,根据等距离生成点集,具体步骤如下:
(1)定义多边形顶点:
建筑物外轮廓线实际是有多个有序顶点构成,因此需要事先定义多边形顶点,顶点z坐标相同。
(2)任意顶点间距离
通过计算两点之间的距离,并根据指定的间距在直线上均匀地生成点,即等距离生成点集。点之间间距可根据实际点间距来设置,如机载点云间距,可设置成0.3m。
(3)多边形内部点生成
通过遍历多边形内部的网格点,使用射线法判断点是否在多边形内部,从而生成顶部和底部的内部点集。
(4)点集保存。
4、代码测试
4.1 点集生成测试
基于PCL编写的点集,源代码下载链接:
该代码没有保留点的nx、ny、nz属性,只保留了x y z r g b idx_segments,这足够后续算法使用。
假设要生成的立面点集的多边形如下图所示,各点坐标分别为 (0,0)、(1,0)、(1,2)、(3,3)、(3,5)、(-2,5)、(-2,3)、(0,2)。

完整代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <fstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
using namespace std;// 计算两点之间的距离
double distance2pts(pcl::PointXYZ p1, pcl::PointXYZ p2) {return std::sqrt(std::pow(p2.x - p1.x, 2) + std::pow(p2.y - p1.y, 2));
}// 生成直线上的点,确保间距相同
std::vector<pcl::PointXYZ> generatePointsOnLineWithEqualSpacing(pcl::PointXYZ start, pcl::PointXYZ end, double spacing) {std::vector<pcl::PointXYZ> points;double dist = distance2pts(start, end);int numPoints = static_cast<int>(dist / spacing);for (int i = 0; i <= numPoints; ++i) {double t = static_cast<double>(i) / numPoints;pcl::PointXYZ p;p.x = start.x + t * (end.x - start.x);p.y = start.y + t * (end.y - start.y);p.z = start.z + t * (end.z - start.z);points.push_back(p);}return points;
}// 生成过直线段的竖直平面点集
std::vector<pcl::PointXYZ> generateVerticalPlanePoints(pcl::PointXYZ linePoint, double z_low, double z_high, double spacing) {std::vector<pcl::PointXYZ> points;int numPoints = static_cast<int>((z_high - z_low) / spacing);for (int i = 0; i <= numPoints; ++i) {double z = z_low + static_cast<double>(i)* spacing;pcl::PointXYZ p;p.x = linePoint.x;p.y = linePoint.y;p.z = z;points.push_back(p);}return points;
}// 检查点是否在多边形内部
bool isPointInsidePolygon(pcl::PointXYZ p, std::vector<pcl::PointXYZ> vertices) {int i, j;bool inside = false;for (i = 0, j = vertices.size() - 1; i < vertices.size(); j = i++) {if ((vertices[i].y > p.y) != (vertices[j].y > p.y) &&(p.x < (vertices[j].x - vertices[i].x) * (p.y - vertices[i].y) / (vertices[j].y - vertices[i].y) + vertices[i].x)) {inside = !inside;}}return inside;
}// 生成多边形内部点集
std::vector<pcl::PointXYZ> generatePointsInsidePolygonTop(std::vector<pcl::PointXYZ> vertices, double spacing, double top_z) {std::vector<pcl::PointXYZ> pointsInside;double minX = vertices[0].x, maxX = vertices[0].x, minY = vertices[0].y, maxY = vertices[0].y;for (const auto& p : vertices) {if (p.x < minX) minX = p.x;if (p.x > maxX) maxX = p.x;if (p.y < minY) minY = p.y;if (p.y > maxY) maxY = p.y;}for (double y = minY; y <= maxY; y += spacing) {for (double x = minX; x <= maxX; x += spacing) {pcl::PointXYZ p;p.x = x;p.y = y;p.z = top_z;if (isPointInsidePolygon(p, vertices)) {pointsInside.push_back(p);}}}return pointsInside;
}// 生成底部多边形
std::vector<pcl::PointXYZ> generatePointsInsidePolygonBottom(std::vector<pcl::PointXYZ> vertices, double spacing, double bottom_z) {std::vector<pcl::PointXYZ> pointsInside;double minX = vertices[0].x, maxX = vertices[0].x, minY = vertices[0].y, maxY = vertices[0].y;for (const auto& p : vertices) {if (p.x < minX) minX = p.x;if (p.x > maxX) maxX = p.x;if (p.y < minY) minY = p.y;if (p.y > maxY) maxY = p.y;}for (double y = minY; y <= maxY; y += spacing) {for (double x = minX; x <= maxX; x += spacing) {pcl::PointXYZ p;p.x = x;p.y = y;p.z = bottom_z;if (isPointInsidePolygon(p, vertices)) {pointsInside.push_back(p);}}}return pointsInside;
}// 保存生成ply格式的带颜色、面片属性的点集
int main()
{// 多边形的顶点std::vector<pcl::PointXYZ> vertices = {pcl::PointXYZ(0, 0, -1), pcl::PointXYZ(1, 0, -1), pcl::PointXYZ(1, 2, -1), pcl::PointXYZ(3, 3, -1),pcl::PointXYZ(3, 5, -1), pcl::PointXYZ(-2, 5, -1), pcl::PointXYZ(-2, 3, -1), pcl::PointXYZ(0, 2, -1)};double lineSpacing = 0.1; // 线上点的间距double z_lowest = -1; // 竖直平面的高度double z_high = -0.5; // 竖直平面的高度double verticalSpacing = 0.1; // 竖直平面上点的间距std::ofstream outFile("D:\\points.ply");outFile << "ply" << endl;outFile << "format ascii 1.0" << endl;outFile << "element vertex 4056" << endl;outFile << "property float x" << endl;outFile << "property float y" << endl;outFile << "property float z" << endl;outFile << "property int r" << endl;outFile << "property int g" << endl;outFile << "property int b" << endl;outFile << "property int segment_index" << endl;//面片的编号从1开始计数outFile << "end_header" << endl;//面片的编号从1开始计数// 生成多边形立面的点集int idx_segments = 1;for (size_t i = 0; i < vertices.size(); ++i){int r = rand() % 255;int g = rand() % 255;int b = rand() % 255;pcl::PointXYZ start = vertices[i];pcl::PointXYZ end = vertices[(i + 1) % vertices.size()]; // 循环回到第一个点std::vector<pcl::PointXYZ> linePoints = generatePointsOnLineWithEqualSpacing(start, end, lineSpacing);vector<pcl::PointXYZ> planeallpts;//计算面的方程//(1)先统计所有点for (pcl::PointXYZ p : linePoints){planeallpts.push_back(p);std::vector<pcl::PointXYZ> verticalPoints = generateVerticalPlanePoints(p, z_lowest, z_high, verticalSpacing);for (pcl::PointXYZ vp : verticalPoints){planeallpts.push_back(vp);}}for (pcl::PointXYZ p : linePoints){outFile << p.x << " " << p.y << " " << p.z << " " << r << " " << g << " " << b << " " << idx_segments << endl;std::vector<pcl::PointXYZ> verticalPoints = generateVerticalPlanePoints(p, z_lowest, z_high, verticalSpacing);for (pcl::PointXYZ vp : verticalPoints){outFile << vp.x << " " << vp.y << " " << vp.z << " " << r << " " << g << " " << b << " " << idx_segments << endl;}}idx_segments = idx_segments + 1;}// 生成多边形内部的点集 顶部std::vector<pcl::PointXYZ> pointsInside = generatePointsInsidePolygonTop(vertices, lineSpacing, z_high);int r = rand() % 255;int g = rand() % 255;int b = rand() % 255;for (const auto& p : pointsInside) {outFile << p.x << " " << p.y << " " << p.z << " " << r << " " << g << " " << b << " " << idx_segments << endl;}idx_segments = idx_segments + 1;// 生成多边形内部的点集 底部pointsInside = generatePointsInsidePolygonBottom(vertices, lineSpacing, z_lowest);r = rand() % 255;g = rand() % 255;b = rand() % 255;for (pcl::PointXYZ p : pointsInside) {outFile << p.x << " " << p.y << " " << p.z << " " << r << " " << g << " " << b << " " << idx_segments << endl;}outFile.close();return 0;
}
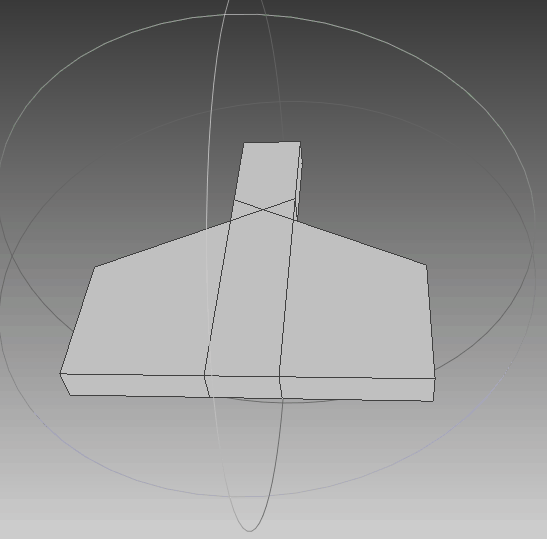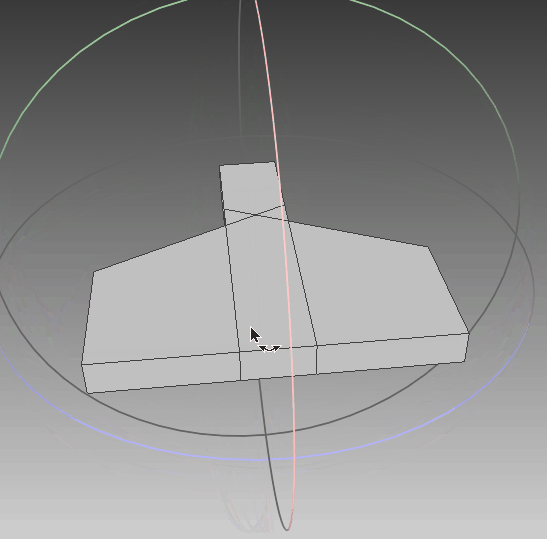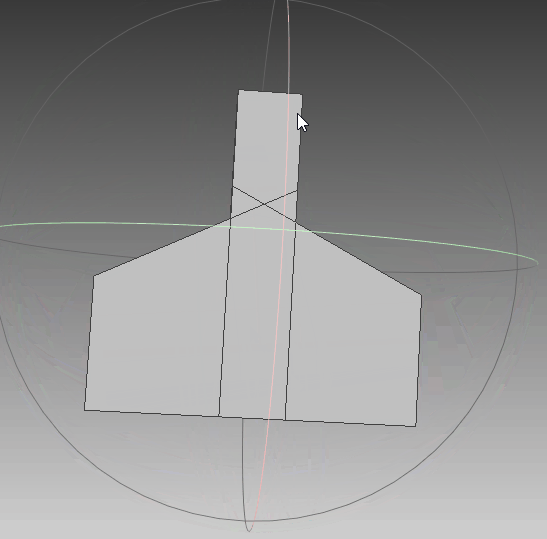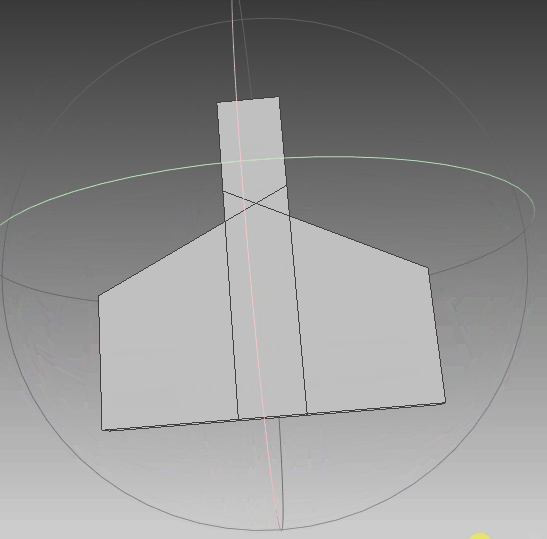
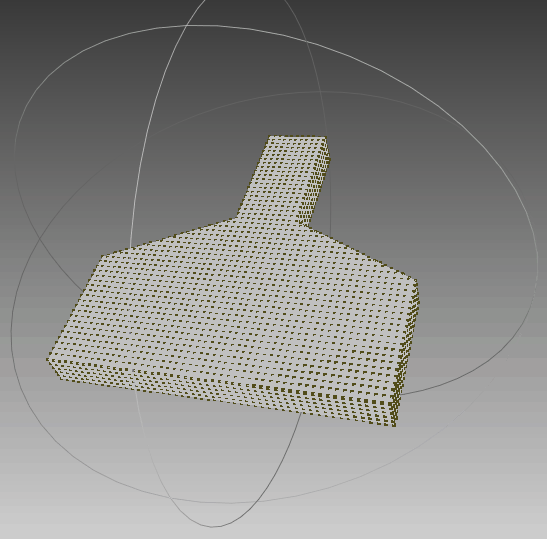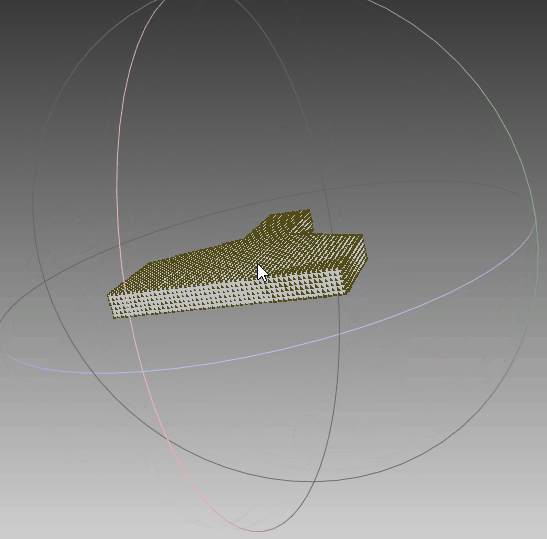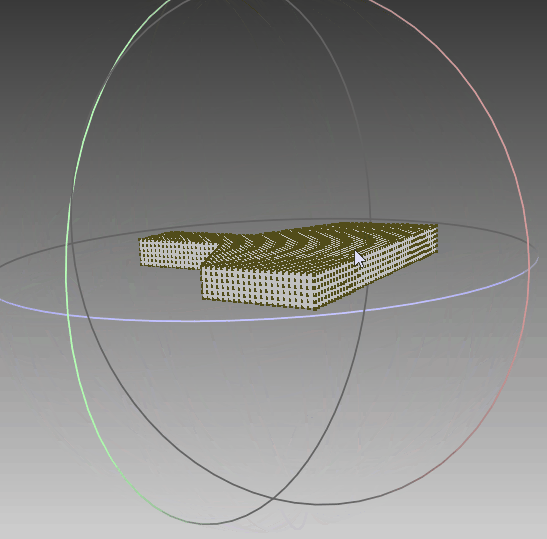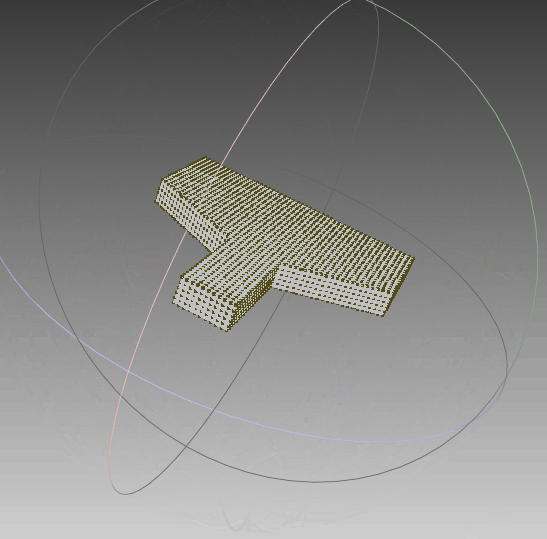
依据上述多边形,生成的点集如下图所示,可以发现生成的点集符合要求。
 |  |  |
| 俯视图 | 侧视图 | 动图 |
4.2 三维重建
根据前面生成的点集,利用polyfit算法对其进行三维重建,可以看到,实体模型与想要的一致。线框与真实情况一致,只是将任意面片相交的线框均保留,不够简洁,需要优化。点云与模型同时可视化,点与实体相吻合,说明其重建效果比较符合外形。‘
备注:CGAL中已经有polyfit重建算法,具体如何使用可以参考之前的博客:CGAL中Polyfit编译(Win11 CGAL 6.0.1 VS 2019)-CSDN博客
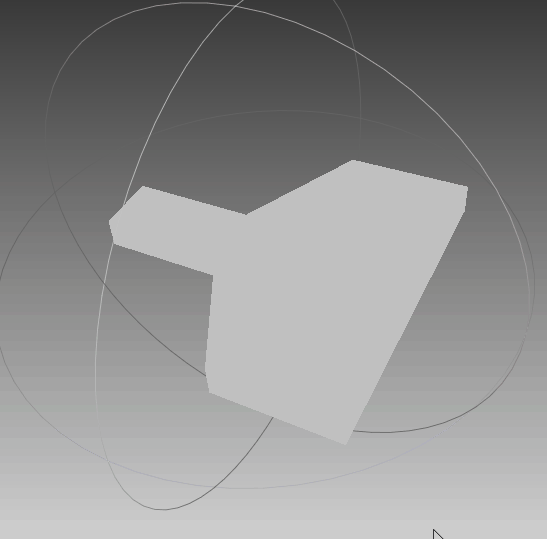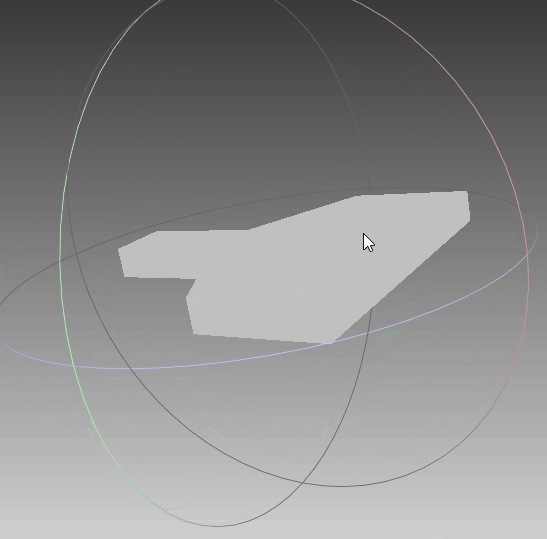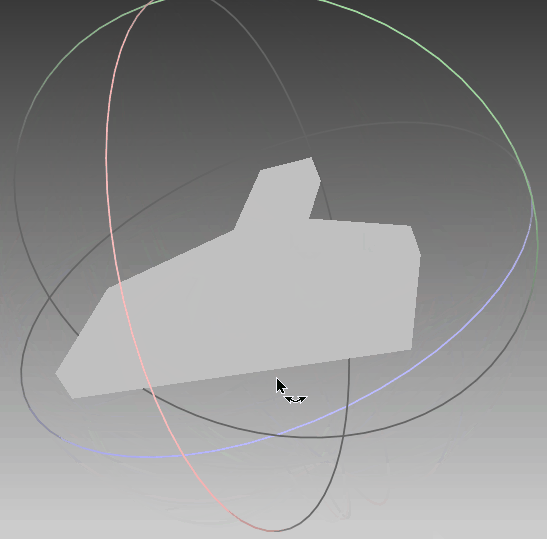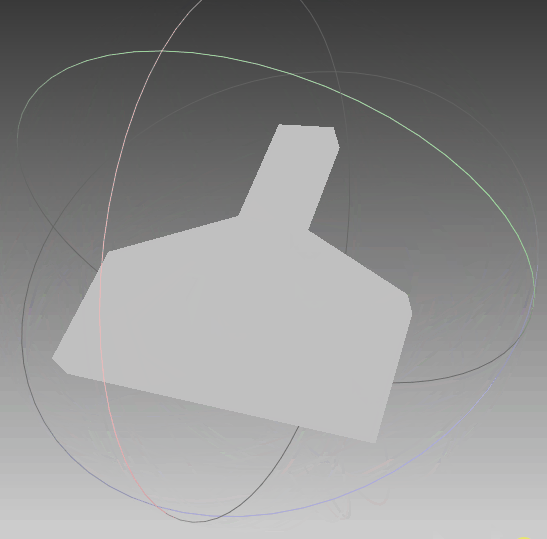 |  |  |
| 实体模型 | 实体+线框模型 | 实体+线框+点集 |
