ES搜索知识

GET /categories/1/10?name=手机 // 按名称过滤
GET /categories/1/10?type=电子产品 // 按类型过滤
GET /categories/1/10?name=手机&type=电子产品 // 组合过滤
- 查询参数
@ApiOperation(value = "获取商品分类分页列表")@GetMapping("{page}/{limit}")public Result index(@ApiParam(name = "page", value = "当前页码", required = true)@PathVariable Long page,@ApiParam(name = "limit", value = "每页记录数", required = true)@PathVariable Long limit,@ApiParam(name = "categoryQueryVo", value = "查询对象", required = false)CategoryQueryVo categoryQueryVo) {Page<Category> pageParam = new Page<>(page, limit);IPage<Category> pageModel = categoryService.selectPage(pageParam, categoryQueryVo);return Result.ok(pageModel);}
- CategoryQueryVo categoryQueryVo存储查询参数。
在基于Nacos的服务注册与发现机制中,服务之间通过以下步骤完成数据发送:
一、服务注册与发现阶段
1. 服务提供者(service-provider)注册到Nacos
- 动作:
服务提供者(端口8070)启动时,向Nacos Server(端口8848)发送注册请求,携带自身信息:{"serviceName": "service-provider","ip": "192.168.1.100","port": 8070,"metadata": {"version": "2018"} // 图中标注的"2018"可能是版本号或其他元数据 } - 目的:
告知Nacos自己的存在,成为可被调用的服务实例。
2. 服务消费者(service-consumer)发现服务提供者
- 动作:
服务消费者(端口8080)向Nacos查询服务名为service-provider的可用实例列表。
Nacos返回服务提供者的地址信息:http://192.168.1.100:8070/。
二、服务间数据发送阶段
3. 消费者发起HTTP请求
- 动作:
服务消费者根据Nacos返回的地址,构造HTTP请求并发送:
或通过POST请求传递数据(具体方法由接口定义决定)。GET http://192.168.1.100:8070/echo?param=hello,2018
4. 提供者处理请求并返回响应
- 动作:
服务提供者接收到请求后,执行echo(string)方法处理参数:public String echo(String input) {return input.split(",")[1]; // 示例中返回"2018" } - 响应:
返回HTTP响应体:2018(即从输入中提取的元数据)。
三、关键技术细节
1. HTTP协议通信
- 通信方式:
服务消费者通过HTTP协议(RESTful API)调用服务提供者。
示例:- 请求路径:
/echo - 参数传递:通过URL参数(
param=hello,2018)或请求体(JSON/XML)。
- 请求路径:
2. 服务标识解耦
- 服务名代替硬编码IP:
消费者通过服务名(service-provider)调用服务,而非直接依赖IP地址。
优势:- 动态扩缩容:提供者实例变化时,Nacos自动更新可用地址列表。
- 负载均衡:Nacos支持返回多个实例,消费者可轮询或随机选择(需集成Ribbon等组件)。
3. 元数据(Metadata)传递
- 用途:
注册时携带的元数据(如version=2018)可用于:- 灰度发布:根据版本号路由请求。
- 环境隔离:区分测试/生产环境实例。
调用示例:
消费者可通过元数据筛选特定实例(如请求version=2018的提供者)。
四、完整流程示例
1. 服务提供者启动 → 注册到Nacos(IP:8070,元数据version=2018)
2. 消费者启动 → 向Nacos查询service-provider地址 → 获得http://192.168.1.100:8070/
3. 消费者发送HTTP请求 → GET http://192.168.1.100:8070/echo?param=hello,2018
4. 提供者处理请求 → 提取"2018" → 返回HTTP响应"2018"
5. 消费者收到响应 → 完成数据交互
五、扩展场景
1. 负载均衡
- 多实例场景:
若存在多个service-provider实例(如8070、8071、8072),Nacos返回所有实例地址。
消费者行为:
可结合Ribbon实现负载均衡(如轮询、随机选择实例)。
2. 健康检查
- 自动剔除故障节点:
Nacos定期检查提供者心跳,若8070端口服务宕机,自动从列表中移除,确保消费者不会调用失效实例。
3. 动态配置
- 配置中心集成:
Nacos可管理服务配置(如超时时间、路由规则),服务重启时自动同步最新配置。
总结
服务间数据发送的核心流程为:
注册(Provider → Nacos)→ 发现(Consumer ← Nacos)→ 调用(HTTP请求)→ 响应。
通过Nacos解耦服务依赖,结合HTTP协议实现灵活通信,是微服务架构中高效协作的基础。
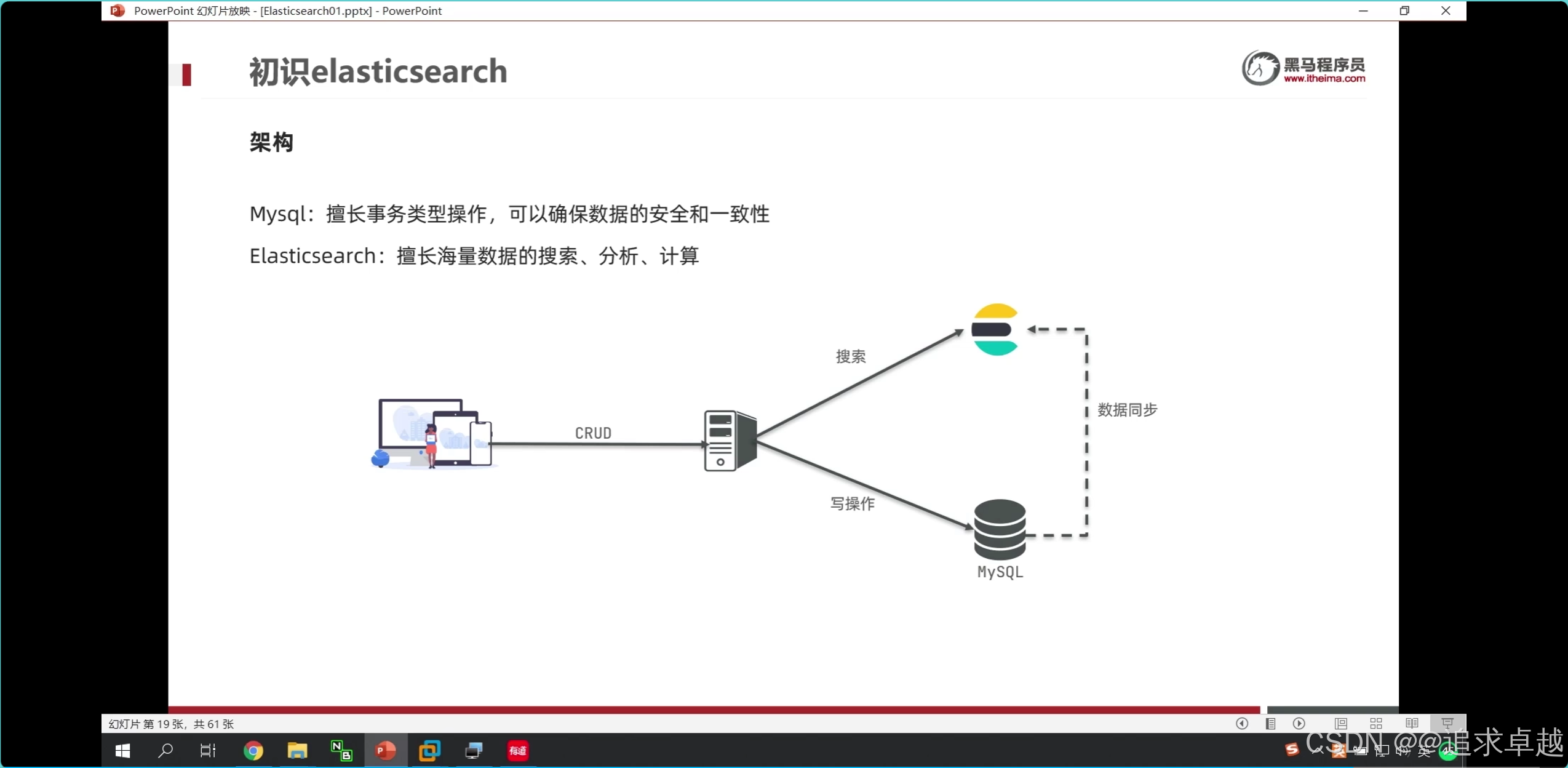
- 商品上下架过程中,修改数据库表上下架状态,之后通过RabbitMQ发送消息,最终实现ES中数据同步。

- Binding Key:队列绑定到交换机时设定的 “路由规则”(收件规则)。
Routing Key:生产者发送消息时指定的 “消息标签”(快递单号)。
匹配结果:交换机根据两者的匹配关系,决定消息投递到哪些队列。
话题交换机
- bindingkey和routingkey是可以(多个 routingKey 之间以.分割)。广播和定向是只能一个。
- 交换机是具体的名字。routingkey是固定的名字,bingkey是可以有#。
bindkey相当于信箱的收件规则;routeingkey是消息的快递号。
ES



- 手机% 才会对索引生效。


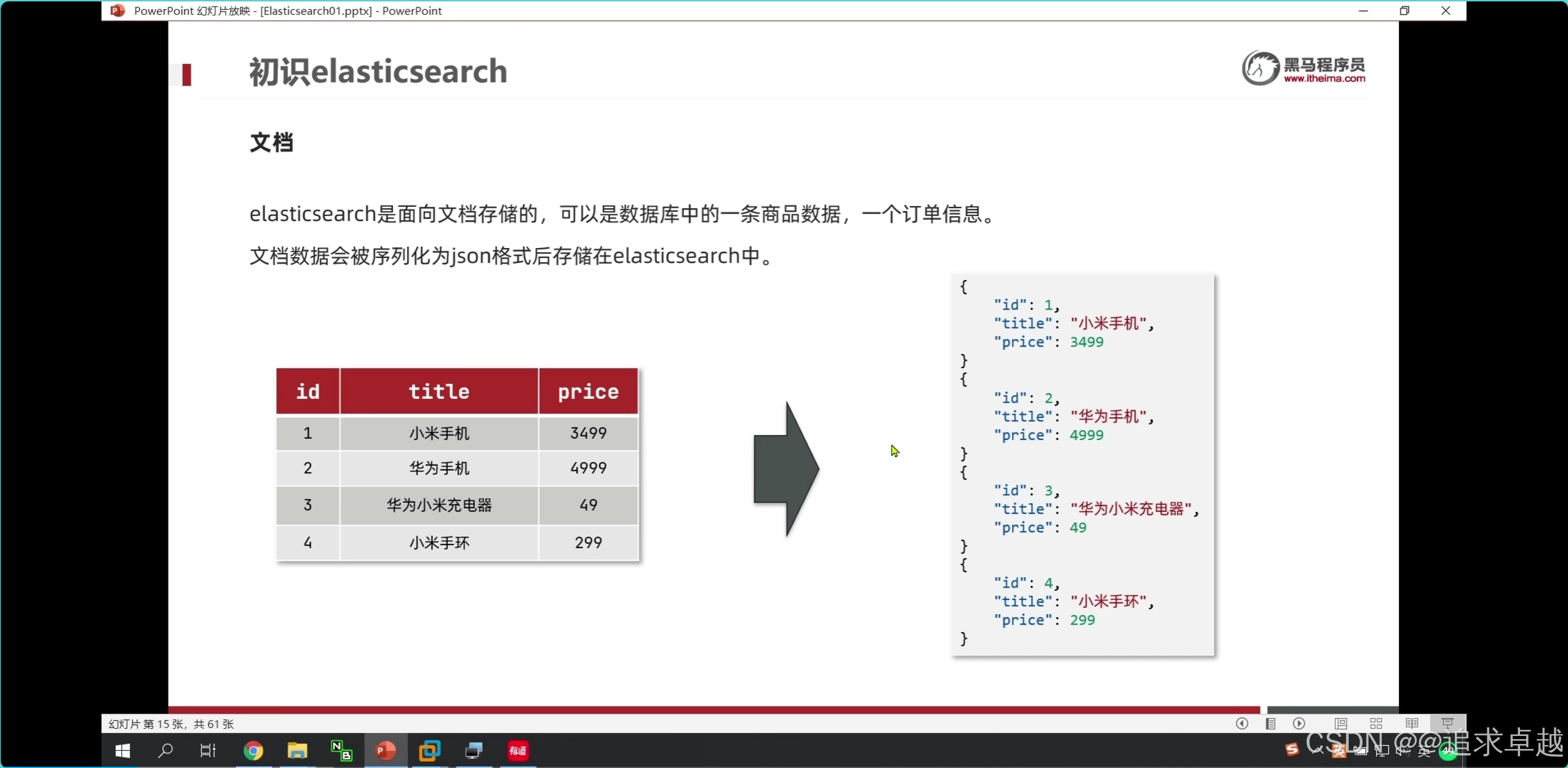




- ik分词器是创建倒排索引和搜索分词的。




问题


结论:
- text是创建到倒排索引的,而且会分词。
- keyword也会创建倒排,但是如果使用index:false的话是不会创建的。所以不会放到倒排中。
问题 :索引库和倒排索引有什么关系?
- 索引库就是存储到es中的文档数据。
- 倒排索引就是基于索引库的文档创建的。


- 搜索就是根据分词器先分词之后匹配倒排索引库。之后查询。
- 存储就是先分词和存储索引库。


- put用于操作索引库的字段和新增字段。全量修改。
- 新增使用post
- 获得使用get
- 删除delete。



PUT /hotel
{"mappings": {"properties": {"id":{"type":"keyword"},"name":{"type":"text","analyzer": "ik_max_word","copy_to": "all"},"address":{"type":"keyword","index":false},"price":{"type":"integer"},"score":{"type":"integer"},"brand":{"type":"keyword","copy_to": "all"},"city":{"type":"keyword"},"starName":{"type":"keyword"},"business":{"type":"keyword","copy_to": "all"},"location":{"type": "geo_point"},"pic":{"type":"keyword","index": false},"all":{"type": "text","analyzer": "ik_max_word"}}}
}
- id在es中是不可分割的。
- 把品牌和名字和商圈给到all.就是参与复合搜索。

public void test2() throws IOException {CreateIndexRequest request=new CreateIndexRequest("hotel1");request.source(MAPPING_TEMPLATE,XContentType.JSON);client.indices().create(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);}酒店的crud

新增就是post /hotel/_doc/1
- 第一次都是从数据库获得对应数据,之后存储到es中。
- es和mysql的pojo是需要两个的。因为es的维度经度是一个。javabean是两个。
@Testpublic void test5() throws IOException {Hotel byId = hotelService.getById(38609);System.out.println(byId);HotelDoc hotelDoc = new HotelDoc(byId);// post /hotel/_doc/1IndexRequest hotel = new IndexRequest("hotel").id(hotelDoc.getId().toString());hotel.source(JSON.toJSONString(hotelDoc), XContentType.JSON);client.index(hotel, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);// IndexRequest indexRequest=new IndexRequest("hotel1").id("1");
// indexRequest.source("",RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// client.index(indexRequest,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);}

// post /hotel/_update/1
// 更新@Testpublic void test7() throws IOException {UpdateRequest hotel = new UpdateRequest("hotel", "38609");hotel.doc("price", 100,"city","上海浦东");client.update(hotel,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);}- DELETE /hotel/_doc/38609

搜索数据





全局搜索


GET /hotel/_search
{"query": {"match": {"all": "外滩如家"}}
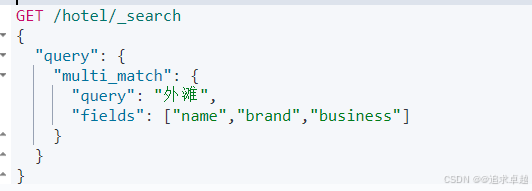
}GET /hotel/_search
{"query": {"multi_match": {"query": "外滩","fields": ["name","brand","business"]}}
}
- name brand business是分词的字段。
- query 里面就是查询类型。
- match_all就是查询所有类型。
全文检索:对词语进行分词,之后查询索引库,获得索引。


GET /hotel/_search
{"query": {"match_all": {}}
}GET /hotel/_search
{"query": {"match": {"all": "外滩如家"}}
}- 第一个是查询全部的。
- 第二个是查询一个字段的。
- 查询出来的相关度越高排名越靠前。

- 可以查询多个索引库。
为什么使用all更快呢?
- 因为每个被分词的字段都会被构建一个索引库,所以有时候需要查询多个。
- 但是all也是分词的,只需要查询一遍索引库。
- 要给字段类型给 “type”: “text”。
普通多字段查询(如 multi_match):
- 需要分别检索每个字段的倒排索引,例如同时查询 name、address、 escription 三个字段。
性能损耗:
多次倒排索引查找(每个字段一次)
合并多个字段的匹配结果(相关性计算更复杂)
可能涉及不同字段的分词器和词项差异 - all 字段查询:
所有目标字段的内容在 索引阶段 已合并到 all 字段中,只需检索一个倒排索引。
性能优势:
单次倒排索引查找
统一的分词器(确保词项一致性)
无需跨字段合并结果
📊 性能对比示例
假设 name、address、description 各有独立的倒排索引:
- 查询方式 倒排索引访问次数 词项合并复杂度
multi_match 3次 高
all 字段 1次 低
问题: 一般是不是经常在搜索框的是字段用分词,在下面固定的使用不分词

精确查询:无需进行分词


#range查询
GET /hotel/_search
{"query": {"range": {"price": {"gte": 200,"lte": 300}} }
}
- 范围查询。对于integer类型很好用。
经纬度查询


# 已自己为中心点。周围5km。
GET /hotel/_search
{"query": {"geo_distance": {"distance":"5km","location":"40.048969, 116.619566"} }
}



{"query": {"bool": {"must": [ ... ], // AND 逻辑(必须满足)"should": [ ... ], // OR 逻辑(至少满足一个)"must_not": [ ... ], // NOT 逻辑(必须不满足)"filter": [ ... ] // 精确过滤(不计算相关性得分,性能更高)}}
}
- 在多条件查询中,必须在外面bool。
- query -> bool -> must、should、must_not、filter。
GET /hotel/_search
{"query": {"bool": {"must": [{"term": {"city": "上海"}}],"should": [{"term":{"brand":"如家"}},{"term":{"brand":"华美达"}}],"must_not": [{"range":{"price": {"gte": 300}}}],"filter": [{"range": {"score": {"gte": 30,"lte": 40}}}]}}
}
- match和multi_match是分词查询的。
- term是精确
- range是范围
排序


# 排序
GET /hotel/_search
{"query": {"match_all": {}},"sort": [{"score": {"order": "asc"},"price": {"order": "desc"}}]
}
# 地图排序
GET /hotel/_search
{"query": {"match_all": {}},"sort": [{"_geo_distance": {"location": {"lat": 31.034661,"lon": 121.612282},"order": "asc","unit": "km"}}]
}
分页:es获得990到1000的数据,是先找出0-1000数据,之后进行截取的,不擅长做这个。

+
GET /hotel/_search
{"query": {"match_all": {}},"from":1,"size":10
}
在这里插入图片描述

- 一个es就是排序之后获得前面1000,之后进行截取。
- 多个就是先排序获得前面1000,之后合在一个,进行排序获得前面1000,之后进行截取。


高亮处理


- 这种不是前端写的



GET /hotel/_search
{"query": {"match": {"all": "如家"}},"highlight": {"fields": {"name": {"require_field_match": "false"}}}
}
DSL查询作用
package cn.itcast.hotel;import cn.itcast.hotel.pojo.Hotel;
import cn.itcast.hotel.pojo.HotelDoc;
import cn.itcast.hotel.service.IHotelService;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.action.admin.indices.delete.DeleteIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.bulk.BulkRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.delete.DeleteRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.get.GetRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.get.GetResponse;
import org.elasticsearch.action.index.IndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.action.update.UpdateRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RequestOptions;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.CreateIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.client.indices.GetIndexRequest;
import org.elasticsearch.common.blobstore.DeleteResult;
import org.elasticsearch.common.xcontent.XContentType;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.List;import static cn.itcast.hotel.constants.HotelIndexConstants.MAPPING_TEMPLATE;@SpringBootTest
class HotelIndexTest {private RestHighLevelClient client;@Testvoid testCreateIndex() throws IOException {// 1.准备Request PUT /hotelCreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("hotel");// 2.准备请求参数request.source(MAPPING_TEMPLATE, XContentType.JSON);// 3.发送请求client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);}@Testvoid testExistsIndex() throws IOException {// 1.准备RequestGetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest("hotel");// 3.发送请求boolean isExists = client.indices().exists(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);System.out.println(isExists ? "存在" : "不存在");}@Testvoid testDeleteIndex() throws IOException {// 1.准备RequestDeleteIndexRequest request = new DeleteIndexRequest("hotel");// 3.发送请求client.indices().delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);}@BeforeEachvoid setUp() {
// client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(
// HttpHost.create("http://192.168.150.101:9200")
// ));this.client= new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(HttpHost.create("http://127.0.0.1:9200")));}@AfterEachvoid tearDown() throws IOException {client.close();}@Testpublic void test1(){System.out.println(client);}@Testpublic void test2() throws IOException {CreateIndexRequest request=new CreateIndexRequest("hotel1");request.source(MAPPING_TEMPLATE,XContentType.JSON);client.indices().create(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);}@Testpublic void test3() throws IOException {DeleteIndexRequest request=new DeleteIndexRequest("hotel1");client.indices().delete(request,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);}@Testpublic void test4() throws IOException {GetIndexRequest hotel1 = new GetIndexRequest("hotel1");boolean exists = client.indices().exists(hotel1, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);System.out.println(exists);}@Autowiredprivate IHotelService hotelService;@Testpublic void test5() throws IOException {Hotel byId = hotelService.getById(38609);System.out.println(byId);HotelDoc hotelDoc = new HotelDoc(byId);// post /hotel/_doc/1IndexRequest hotel = new IndexRequest("hotel").id(hotelDoc.getId().toString());hotel.source(JSON.toJSONString(hotelDoc), XContentType.JSON);client.index(hotel, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);// IndexRequest indexRequest=new IndexRequest("hotel1").id("1");
// indexRequest.source("",RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// client.index(indexRequest,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);}@Testpublic void test6() throws IOException {GetRequest hotel = new GetRequest("hotel", "38609");GetResponse documentFields = client.get(hotel, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);String sourceAsString = documentFields.getSourceAsString();System.out.println(sourceAsString);HotelDoc hotelDoc = JSON.parseObject(sourceAsString, HotelDoc.class);System.out.println(hotelDoc);}
// post /hotel/_update/1
// 更新@Testpublic void test7() throws IOException {UpdateRequest hotel = new UpdateRequest("hotel", "38609");hotel.doc("price", 100,"city","上海浦东");client.update(hotel,RequestOptions.DEFAULT);}@Test //删除public void test8() throws IOException {DeleteRequest deleteRequest = new DeleteRequest("hotel","38609");client.delete(deleteRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);}// 这是一个从数据库很多数据拿到拿到es中。@Testpublic void test9() throws IOException {BulkRequest bulkRequest = new BulkRequest();List<Hotel> hotelList = hotelService.list();for (Hotel hotel : hotelList) {HotelDoc hotelDoc = new HotelDoc(hotel);bulkRequest.add(new IndexRequest("hotel").id(hotelDoc.getId().toString()).source(JSON.toJSONString(hotelDoc), XContentType.JSON));}client.bulk(bulkRequest, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);}
}
- 这是一个存储的。
多条件查询。
GET /your_index/_search
{"query": {"match": {"all": "搜索关键词" // 在 all 字段中匹配关键词}},"from": 0, // 分页起始位置(页码-1)*每页数量"size": 10, // 每页返回文档数"sort": [ // 排序规则(可多字段){ "price": "desc" }, // 按价格降序{ "_score": "desc" } // 按相关性评分降序(可选)]
}@Overridepublic PageResult search(RequestParams params) throws IOException {SearchRequest hotel = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 这个是分词查找,all是字段if(params.getKey() != null||params.getKey()!=""){hotel.source().query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("all", params.getKey()));} else{hotel.source().query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());}//分页int page = params.getPage();int size = params.getSize();hotel.source().from((page-1)*size).size(size);//高亮显示hotel.source().highlighter(new HighlightBuilder().field("name").requireFieldMatch(false));SearchResponse search = restClient.search(hotel, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);return handleResponse(search);}public PageResult handleResponse(SearchResponse response) {List<HotelDoc> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();SearchHits hits = response.getHits();
//获得个数。long value = hits.getTotalHits().value;SearchHit[] hits1 = hits.getHits();for (SearchHit hit : hits1) {String sourceAsString = hit.getSourceAsString();HotelDoc hotelDoc = JSON.parseObject(sourceAsString, HotelDoc.class);arrayList.add(hotelDoc);}return new PageResult(value,arrayList);}
- 搜索一个字段下面每个都一个字段还有分页操作。

BoolQueryBuilder boolQuery = QueryBuilders.boolQuery().should(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("name", "泳池")) // 条件1.should(QueryBuilders.boolQuery() // 嵌套条件2.must(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("address", "外滩")).must(QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("price").lte(600)));
- 只有一个的话不需要
- 多个条件的话就是BoolQueryBuilder。
多条件问题

- must是and ,should是or ,must_no是非。
- term是准确,match 是分词,range范围.

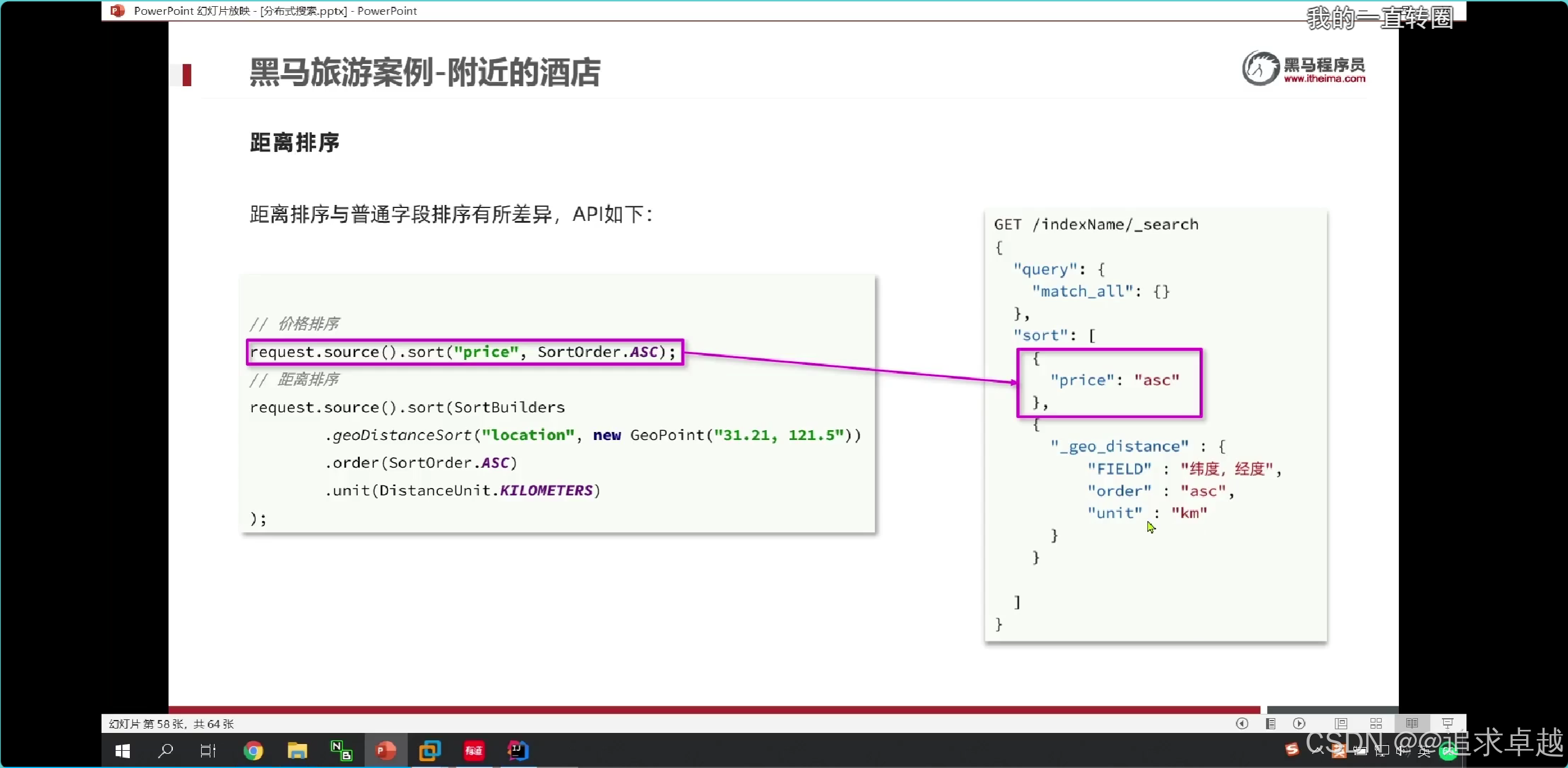
距离排序

广告定制

- functionScore是增加算分的。

{"from": (page-1)*size,"size": size,"query": {"function_score": {"query": {"bool": {"must": [{"match": {"all": "用户输入的关键词"}}],"filter": [{"term": {"city": "城市参数"}},{"term": {"brand": "品牌参数"}},{"term": {"starName": "星级参数"}},{"range": {"price": {"gte": 最低价,"lte": 最高价}}}]}},"functions": [{"filter": {"term": {"isAD": true}},"weight": 10}]}},"sort": [{"_geo_distance": {"location": "纬度,经度","order": "asc","unit": "km"}}]
}拼音分词
GET /_analyze
{"text": ["如家酒店"], "analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
GET /_analyze
{"text": ["如家酒店"], "analyzer": "pinyin"
}

- 使用pinyin的话是, 他只有一个字一个拼音。
# 自定义分词器。
PUT /test1
{"settings": {"analysis": {"analyzer": {"my_analyzer": {"tokenizer": "ik_max_word","filter": "py"}},"filter": {"py": {"type": "pinyin","keep_joined_full_pinyin": true,"keep_full_pinyin": false,"keep_original": true,"remove_duplicated_term": true}}}},"mappings": {"properties": {"name":{"type":"text","analyzer": "my_analyzer"}}}
}- 只会影响 name 字段.
分词器,会把分词字段分到倒排索引中;自定义分词器是分出拼音和汉字到倒排中。
GET /test1/_analyze
{"text": ["如家酒店"], "analyzer": "my_analyzer"
}# 自定义分词器。
PUT /test1
{"settings": {"analysis": {"analyzer": {"my_analyzer": {"tokenizer": "ik_max_word","filter": "py"}},"filter": {"py": {"type": "pinyin","keep_joined_full_pinyin": true,"keep_full_pinyin": false,"keep_original": true,"remove_duplicated_term": true}}}},"mappings": {"properties": {"name":{"type":"text","analyzer": "my_analyzer"}}}
}- 拼音分词器就是name把所有的词语有中文、英文变到倒排索引库中。


- 在shizi拼音的时候可以有1,2。查询狮子就只有一个1.

- 在存储的时候是拼音中文都存出倒排索引中。
- 在搜索的时候只能中文查询中文,拼音查询拼音的。只有使用ik分词器。
GET /test1
POST /test1/_doc
{"name":"狮子","id":1
}
POST /test1/_doc
{"name":"师资","id":2
}GET /test1/_search
{"query": {"match": {"name": "师资"}}
}

自动补全

+

# 自定义分词器。
PUT /test1
{"settings": {"analysis": {"analyzer": {"my_analyzer": {"tokenizer": "ik_max_word","filter": "py"}},"filter": {"py": {"type": "pinyin","keep_joined_full_pinyin": true,"keep_full_pinyin": false,"keep_original": true,"remove_duplicated_term": true}}}},"mappings": {"properties": {"name":{"type":"completion","analyzer": "my_analyzer","search_analyzer": "ik_smart"}}}
}DELETE /test1
GET /test1
POST /test1/_doc
{"name":"狮子","id":1
}
POST /test1/_doc
{"name":"师资","id":2
}GET /test1/_search
{"query": {"match": {"name": "师资"}}
}POST test1/_doc
{"name":["Sony","WH-1000XM3"]
}POST test1/_doc
{"name":["Sk-II","POYera"]
}
GET /test1/_search
{"suggest": {"name_suggest": {"text": "so","completion": {"field": "name","skip_duplicates":true,"size":10}}}
}

上面就是给title设置一个自定义分词器,让倒排索引有拼音和中文混合的。但是搜索就用ik分词;之后给这个字段设置类型,之后给他搜索词。
酒店数据补全
 ## 自动补全字段的是分词器里面是使用keyword的。
## 自动补全字段的是分词器里面是使用keyword的。
