《算法笔记》10.5小节——图算法专题->最小生成树 问题 E: Jungle Roads
题目描述
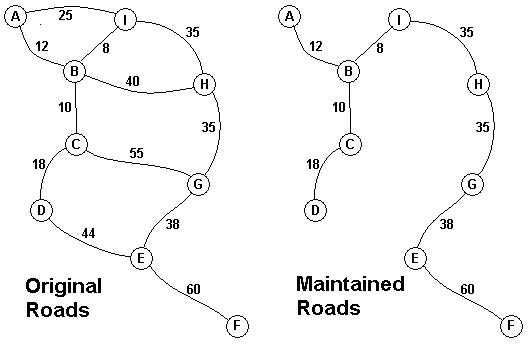
The Head Elder of the tropical island of Lagrishan has a problem. A burst of foreign aid money was spent on extra roads between villages some years ago. But the jungle overtakes roads relentlessly, so the large road network is too expensive to maintain. The Council of Elders must choose to stop maintaining some roads. The map above on the left shows all the roads in use now and the cost in aacms per month to maintain them. Of course there needs to be some way to get between all the villages on maintained roads, even if the route is not as short as before. The Chief Elder would like to tell the Council of Elders what would be the smallest amount they could spend in aacms per month to maintain roads that would connect all the villages. The villages are labeled A through I in the maps above. The map on the right shows the roads that could be maintained most cheaply, for 216 aacms per month. Your task is to write a program that will solve such problems.
输入
The input consists of one to 100 data sets, followed by a final line containing only 0. Each data set starts with a line containing only a number n, which is the number of villages, 1 < n < 27, and the villages are labeled with the first n letters of the alphabet, capitalized. Each data set is completed with n-1 lines that start with village labels in alphabetical order. There is no line for the last village. Each line for a village starts with the village label followed by a number, k, of roads from this village to villages with labels later in the alphabet. If k is greater than 0, the line continues with data for each of the k roads. The data for each road is the village label for the other end of the road followed by the monthly maintenance cost in aacms for the road. Maintenance costs will be positive integers less than 100. All data fields in the row are separated by single blanks. The road network will always allow travel between all the villages. The network will never have more than 75 roads. No village will have more than 15 roads going to other villages (before or after in the alphabet). In the sample input below, the first data set goes with the map above.
输出
The output is one integer per line for each data set: the minimum cost in aacms per month to maintain a road system that connect all the villages. Caution: A brute force solution that examines every possible set of roads will not finish within the one minute time limit.
样例输入
3
A 1 B 42
B 1 C 87
6
A 2 B 13 E 55
B 1 C 1
C 1 D 20
D 1 E 4
E 1 F 76
0
样例输出
129
114题目大意:给出 n 个城市,之后给出 n-1 行信息,第一个字符表示城市的编号 c,之后第一个数字 cnt 表示该城市出发有几条路径。之后给出 cnt 组信息,每组一个字符一个数字,表示从城市 c 到对应城市的长度。求整个图的最小生成树的总长度。
分析:最小生成树模板题。由于给出的是边信息,可以用 kruskal 算法。
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdio>
#include <queue>
#include <stack>
#include <ctime>
#include <cmath>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#define INF 0x3fffffff
#define db1(x) cout<<#x<<"="<<(x)<<endl
#define db2(x,y) cout<<#x<<"="<<(x)<<", "<<#y<<"="<<(y)<<endl
#define db3(x,y,z) cout<<#x<<"="<<(x)<<", "<<#y<<"="<<(y)<<", "<<#z<<"="<<(z)<<endl
#define db4(x,y,z,r) cout<<#x<<"="<<(x)<<", "<<#y<<"="<<(y)<<", "<<#z<<"="<<(z)<<", "<<#r<<"="<<(r)<<endl
#define db5(x,y,z,r,w) cout<<#x<<"="<<(x)<<", "<<#y<<"="<<(y)<<", "<<#z<<"="<<(z)<<", "<<#r<<"="<<(r)<<", "<<#w<<"="<<(w)<<endl
using namespace std;typedef struct node
{int t,dis;
}node;int findFather(int a,int father[])
{int z=a;while(a!=father[a])a=father[a];while(z!=a){int temp=father[z];father[z]=a,z=temp;}return a;
}int kruskal(vector<node>graph[],int n,int father[])
{int ans=0;for(int times=1;times<n;++times){int u=-1,v=-1,mini=INF;for(int i=0;i<n;++i){int len=graph[i].size();int fi=findFather(i,father);for(int j=0;j<len;++j){if(graph[i][j].dis<mini){int fj=findFather(graph[i][j].t,father);if(fi!=fj)u=i,v=j,mini=graph[i][j].dis;}}}if(u==-1)return -1;ans+=graph[u][v].dis;int fu=findFather(u,father);int fv=findFather(graph[u][v].t,father);father[fu]=fv;}return ans;
}int main(void)
{#ifdef testfreopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
// freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);clock_t start=clock();#endif //testint n;while(scanf("%d\n",&n),n){vector<node>graph[n+5];int father[n+5];for(int i=0;i<n;++i)father[i]=i;for(int t=1;t<n;++t){int cnt;char c;scanf("%c%d ",&c,&cnt);int index=c-'A';for(int i=0;i<cnt;++i){int d;char cc;scanf("%c%d",&cc,&d);getchar();node temp;temp.t=cc-'A',temp.dis=d;graph[index].push_back(temp);}}int ans=kruskal(graph,n,father);printf("%d\n",ans);}#ifdef testclockid_t end=clock();double endtime=(double)(end-start)/CLOCKS_PER_SEC;printf("\n\n\n\n\n");cout<<"Total time:"<<endtime<<"s"<<endl; //s为单位cout<<"Total time:"<<endtime*1000<<"ms"<<endl; //ms为单位#endif //testreturn 0;
}