手撕算法——宽度优先搜索-BFS
宽度优先搜索的过程中,每次都会从当前点向外扩展⼀层,所以会具有⼀个最短路的特性。因此,宽搜不仅能搜到所有的状态,⽽且还能找出起始状态距离某个状态的最⼩步数。
但是,前提条件是每次扩展的代价都是 1 ,或者都是相同的数。宽搜常常被⽤于解决边权为 1 的最短路问题。
一、BFS
1. ⻢的遍历
题⽬来源:洛⾕
题⽬链接:P1443 马的遍历 - 洛谷
难度系数:★★
(1)题目描述
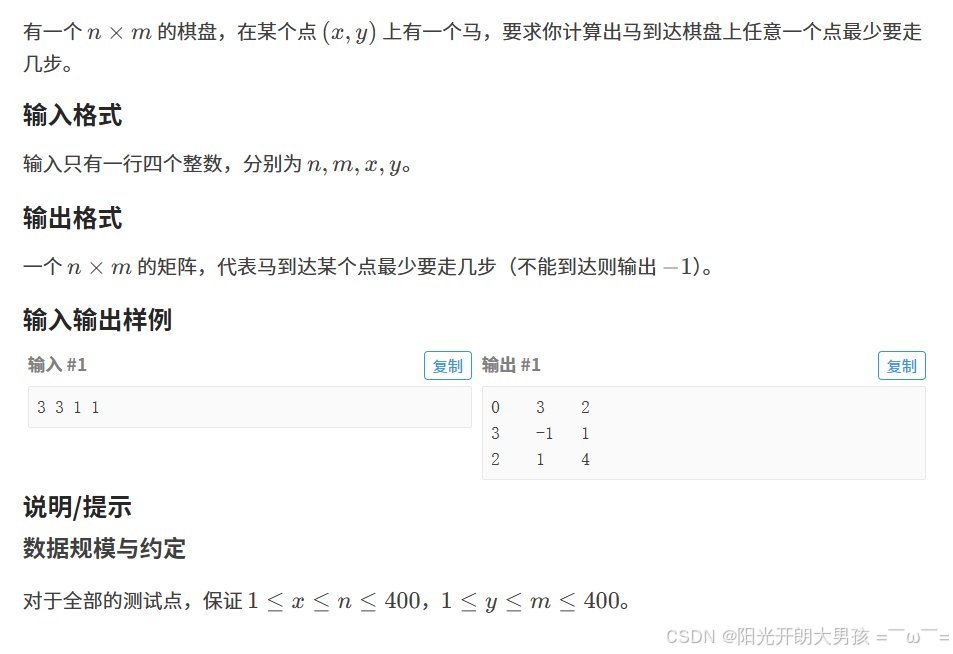
(2)算法原理
题⽬要求到达某个点最少要⾛⼏步,因此可以⽤ bfs 解决。因为当权值为 1 时,bfs 每次都是扩展
距离起点等距离的⼀层,天然具有最短性。
那就从起点开始,⼀层⼀层的往外搜,⽤⼀个 dist 数组记录最短距离。


(3)参考代码
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 410;
int n, m, x, y;
int dist[N][N];
int dx[] = {1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1};
int dy[] = {2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2};
void bfs()
{
memset(dist, -1, sizeof dist);
queue<PII> q;
q.push({x, y});
dist[x][y] = 0;
while(q.size())
{
auto t = q.front(); q.pop();
int i = t.first, j = t.second;
for(int k = 0; k < 8; k++)
{
int x = i + dx[k], y = j + dy[k];
if(x < 1 || x > n || y < 1 || y > m) continue;
if(dist[x][y] != -1) continue;
dist[x][y] = dist[i][j] + 1; // 更细结果
q.push({x, y});
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m >> x >> y;
bfs();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
cout << dist[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}2. kotori和迷宫
题⽬来源:⽜客⽹
题⽬链接:kotori和迷宫
难度系数:★★
(1)题目描述

(2)算法原理
经典 bfs 问题。
从迷宫的起点位置逐层开始搜索,每搜到⼀个点就标记⼀下最短距离。当把整个迷宫全部搜索完毕之 后,扫描整个标记数组,求出出⼝的数量以及最短的距离。
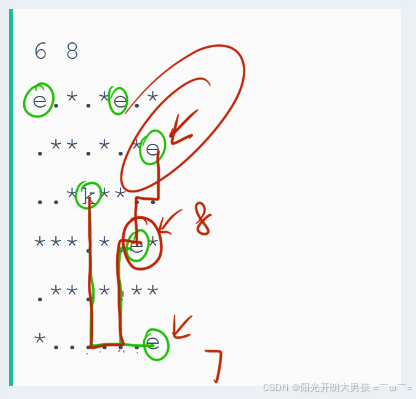
注意:走到 "e" 之后就不能继续遍历了
(3)参考代码
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 35;
int n, m, x, y;
char a[N][N];
int dist[N][N];
int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int dy[] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
void bfs()
{
memset(dist, -1, sizeof dist);
queue<PII> q;
q.push({x, y});
dist[x][y] = 0;
while(q.size())
{
auto t = q.front(); q.pop();
int i = t.first, j = t.second;
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = i + dx[k], y = j + dy[k];
if(x >= 1 && x <= n && y >= 1 && y <= m && a[x][y] != '*' && dist[x][y] == -1)
{
dist[x][y] = dist[i][j] + 1;
if(a[x][y] == 'e')
{
continue;
}
q.push({x, y});
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
cin >> a[i][j];
if(a[i][j] == 'k')
{
x = i; y = j;
}
}
}
bfs();
// 统计结果
int cnt = 0, ret = 1e9;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
if(a[i][j] == 'e' && dist[i][j] != -1)
{
cnt++;
ret = min(ret, dist[i][j]);
}
}
}
if(cnt == 0) cout << -1 << endl;
else cout << cnt << " " << ret << endl;
return 0;
}3. CatchThatCow
题⽬来源:洛⾕
题⽬链接:P1588 [USACO07OPEN] Catch That Cow S - 洛谷
难度系数:★★
(1)题目描述

(2)算法原理
可以暴⼒枚举出所有的⾏⾛路径,因为是求最少步数,所以可以⽤ bfs 解决:
- 从起点位置开始搜索,每次向外扩展三种⾏⾛⽅式;
- 当第⼀次搜到⽜的位置时,就是最短距离。
如果不做任何处理,时间和空间都会超。因为我们会搜索到很多⽆效的位置,所以我们要加上剪枝策略:
- 当 −1 减到负数的时候,剪掉;
因为如果⾛到负数位置,还是需要回头⾛到正数位置,⼀定不是最优解。
- 当 +1 操作越过 y 的时候,剪掉;
如果 +1 之后⼤于 y ,说明本⾝就在 y 位置或者 y 的右侧,你再往右⾛还是需要再向左⾛回去。⼀定不是最优解,剪掉。
- 当 y 是偶数,并且当 ×2 操作之后⼤于 y 的时候,剪掉,
因为不如先减到 y 的⼀半然后再乘;设当前数是 x ,那么:
- 先乘后减,总的步数 t1 = 2x − y + 1 ;
- 先减后乘,总的步数 t2 = x − y/2 + 1 ;
- t1 − t2 = 2x − y + 1 − (x − y/2 + 1) = x − y/2 > 0 ;
- 因此,先乘后减不如先减后乘。
设 y 是奇数的时候,那么 y + 1 就是偶数,根据 3 可得,×2 操作不能超过y + 1 。

(3)参考代码
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int n = 1e5;
int x, y;
int dist[N];
void bfs()
{
queue<int> q;
q.push(x);
dist[x] = 0;
while(q.size())
{
auto t = q.front(); q.pop();
int a = t + 1, b = t - 1, c = t * 2;
if(a <= n && dist[a] == -1)
{
dist[a] = dist[t] + 1;
q.push(a);
}
if(b > 0 && dist[b] == -1)
{
dist[b] = dist[t] + 1;
q.push(b);
}
if(c <= n && dist[c] == -1)
{
dist[c] = dist[t] + 1;
q.push(c);
}
// 剪枝
if(a == y || b == y || c == y) return;
}
}
int main()
{
int T; cin >> T;
while(T--)
{
// 注意清空数据
memset(dist, -1, sizeof dist);
cin >> x >> y;
bfs();
cout << dist[y] << endl;
}
return 0;
}4. ⼋数码难题
题⽬来源:洛⾕
题⽬链接:P1379 八数码难题 - 洛谷
难度系数:★★★
(1)题目描述

(2)算法原理
经过之前那么多题的铺垫,这道题的解法还是容易想到的。因为要求的是最短步数,因此可以⽤bfs 解决。
- 从起始状态开始,每次扩展上下左右交换后的状态;
- 在搜索的过程中,第⼀次遇到最终状态就返回最短步数。
算法原理虽然容易,但是实现起来⽐较⿇烦,我们要想办法处理下⾯⼏件事情:
- 如何记录⼀个3 × 3 的棋盘?
可以⽤字符串。从上往下,从左往右将棋盘内的数依次存到⼀个字符串⾥,来标记棋盘的状态。
- 如何记录最短路?
可以⽤ unordered_map < string, int > 来标记最短距离;
- 如何通过⼀个字符串找到交换之后的字符串?
策略⼀:先把字符串还原成⼆维矩阵,然后交换 0 成字符串。与四周的数字,最后再把交换之后的棋盘还原成字符串。
虽然可⾏,但是太过于⿇烦。我们其实可以通过计算,快速得出⼆维坐标与⼀维下标相互转换前后的值。如下图:

这个技巧特别常⽤,我们可以推⼴到 n × m 的矩阵坐标 (x, y) ,映射成⼀个数 pos ,可以起到空间优化的效果。后续做题中我们就会遇到。
因此,我们可以直接在字符串中,找出交换前后的下标,直接交换字符串对应位置,就能得到交换之后的状态。


(3)参考代码
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
string s;
string aim = "123804765";
unordered_map<string, int> dist;
int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int dy[] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
void bfs()
{
queue<string> q;
q.push(s);
dist[s] = 0;
while(q.size())
{
string t = q.front(); q.pop();
int pos = 0;
while(t[pos] != '0') pos++;
int x = pos / 3, y = pos % 3; // 计算二维矩阵中对应的位置
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
if(a >= 0 && a <= 2 && b >= 0 && b <= 2)
{
string next = t;
// (x, y) 与 (a, b) 做交换
int p = 3 * a + b;
swap(next[p], next[pos]);
if(dist.count(next)) continue;
dist[next] = dist[t] + 1;
q.push(next);
if(next == aim) return; // 剪枝
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> s;
bfs();
cout << dist[aim] << endl;
return 0;
}二、多源BFS
- 单源最短路问题 vs 多源最短路问题
- 当问题中只存在⼀个起点时,这时的最短路问题就是单源最短路问题。
- 当问题中存在多个起点⽽不是单⼀起点时,这时的最短路问题就是多源最短路问题。
- 多源 BFS
多源最短路问题的边权都为 1 时,此时就可以⽤多源 BFS 来解决。
- 解决⽅式
把这些源点汇聚在⼀起,当成⼀个"超级源点"。然后从这个"超级源点"开始,处理最短路问题。
落实到代码上时:
- 初始化的时候,把所有的源点都加⼊到队列⾥⾯;
- 然后正常执⾏ bfs 的逻辑即可。
也就是初始化的时候,⽐普通的 bfs 多加⼊⼏个起点。

1. 矩阵距离
题⽬来源:⽜客⽹
题⽬链接:矩阵距离
难度系数:★★
(1)题目描述
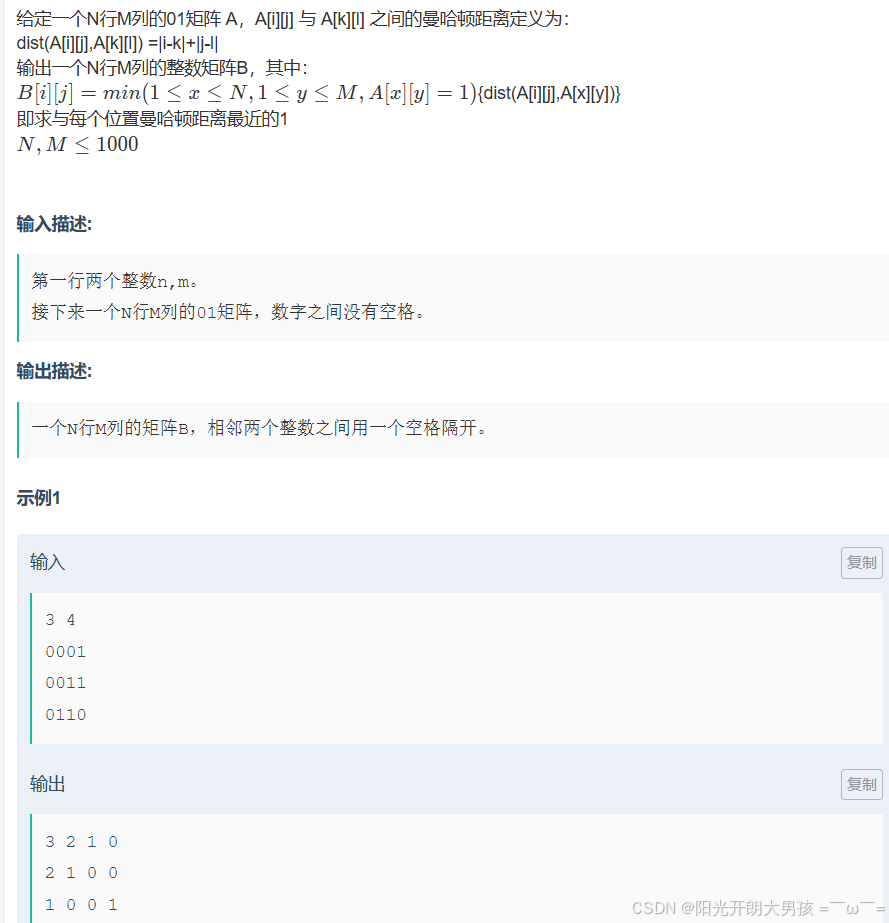
(2)算法原理

正难则反:
- 如果针对某⼀个点,直接去找最近的 1 ,我们需要对所有的 0 都来⼀次 bfs,这个时间复杂度是 接受不了的。
- 但是我们如果反着来想,从 1 开始向外扩展,每遍历到⼀个 0 就更新⼀下最短距离。这样仅需⼀ 次 bfs,就可以把所有点距离 1 的最短距离更新出来。
由于 1 的数量很多,因此可以把所有的 1 看成⼀个超级源点,从这个超级源点开始⼀层⼀层的向外 扩展。实现起来也很简单,就是在初始化阶段把所有 1 的坐标加⼊到队列中,然后正常 bfs 。
(3)参考代码
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 1010;
int n, m;
char a[N][N];
int dist[N][N];
int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int dy[] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
void bfs()
{
memset(dist, -1, sizeof dist);
queue<PII> q;
// 1. 所有的起点加入到队列里面
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
if(a[i][j] == '1')
{
q.push({i, j});
dist[i][j] = 0;
}
// 2. 正常的 bfs
while(q.size())
{
auto t = q.front(); q.pop();
int x = t.first, y = t.second;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
if(a >= 1 && a <= n && b >= 1 && b <= m && dist[a][b] == -1)
{
dist[a][b] = dist[x][y] + 1;
q.push({a, b});
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
cin >> a[i][j];
bfs();
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
cout << dist[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}2. 刺杀⼤使
题⽬来源:洛⾕
题⽬链接:P1902 刺杀大使 - 洛谷
难度系数:★★★
(1)题目描述

(2)算法原理

直接找答案显然是不现实的,因为能⾛的路径实在是太多了,如果全都枚举出来时间上吃不消。但是题⽬要求的是最⼤值最⼩化,可以尝试⽤⼆分来优化枚举。
设最终结果是 x ,会发现⼀个性质:
- 当规定搜索过程中的最⼤值⼤于等于 x 时,我们⼀定可以从第⼀⾏⾛到最后⼀⾏;
- 当规定搜索过程中的最⼤值⼩于 x 时,我们⼀定不能⾛到最后⼀⾏。
因此,我们可以⼆分最终结果,通过 bfs 或者 dfs 来判断是否能⾛到最后⼀⾏。
如果⽤ dfs ,那就从第⼀⾏的每⼀列开始,全都搜索⼀遍。如果⽤ bfs ,可以看成多源 bfs 问题,直接把所有的源点加⼊队列中,然后正常搜索即可。
(3)参考代码
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 1010;
int n, m;
int p[N][N];
bool st[N][N]; // 在宽搜的过程中,不走重复路
int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int dy[] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
// 伤害不超过 mid 的情况下,能够到达第 n 行
bool bfs(int mid)
{
if(n == 1) return true;
memset(st, 0, sizeof st);
queue<PII> q;
// 1. 把所有的源点加入到队列里面
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
q.push({1, j});
st[1][j] = true;
}
while(q.size())
{
auto t = q.front(); q.pop();
int x = t.first, y = t.second;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
if(a >= 1 && a <= n && b >= 1 && b <= m && p[a][b] <= mid && st[a][b] == false)
{
st[a][b] = true;
q.push({a, b});
if(a == n) return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
int l = 0, r = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
cin >> p[i][j];
r = max(r, p[i][j]);
}
}
// 二分答案
while(l < r)
{
int mid = (l + r) / 2;
if(bfs(mid)) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
cout << l << endl;
return 0;
}三、01 BFS
01 BFS ⼜称 双端队列 BFS。
在最短路问题中,边权值可能为 1 也可能为 0。那么,在 BFS 的过程中,可以将边权为 0 扩展出来的点放到队⾸,边权为 1 扩展出来的点放到队尾。这样就能保证像普通 BFS ⼀样整个队列队⾸到队尾权值单调不下降。

注意:
不同于普通的 bfs 问题,01bfs 问题在遍历的过程中,如果遇到之前已经遍历过的结点,有可能会找到⼀条更优的路线。在写代码的时候,要注意判断这⼀点。
1. ⼩明的游戏
题⽬来源:洛⾕
题⽬链接:P4554 小明的游戏 - 洛谷
难度系数:★★
(1)题目描述

(2)算法原理

01bfs 模板题。
- 如果⾛到相同格⼦,权值为 0 ,更新最短距离,然后加⼊到队头;
- 如果⾛到不同格⼦,权值为 0 ,更新最短距离,然后加⼊到队尾。
其余的搜索⽅式与常规 bfs ⼀模⼀样,但是注意松弛操作。
注意:
输入时要从 0 开始,不能从 1 开始,因为给的坐标中可能有 0 ;
(3)参考代码
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 510;
int n, m, x1, y1, x2, y2;
char a[N][N];
int dist[N][N];
int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int dy[] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
void bfs()
{
if(x1 == x2 && y1 == y2)
{
dist[x2][y2] = 0;
return;
}
memset(dist, -1, sizeof dist);
deque<PII> q;
q.push_back({x1, y1});
dist[x1][y1] = 0;
while(q.size())
{
auto t = q.front(); q.pop_front();
int i = t.first, j = t.second;
if(i == x2 && j == y2) return; // 剪枝
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = i + dx[k], y = j + dy[k];
if(x >= 0 && x < n && y >= 0 && y < m)
{
char cur = a[i][j], next = a[x][y];
int w = (cur == next ? 0 : 1);
if(dist[x][y] == -1)
{
dist[x][y] = dist[i][j] + w;
// 01 BFS
if(w == 0) q.push_front({x, y});
else q.push_back({x, y});
}
else if(dist[i][j] + w < dist[x][y]) // 虽然是第二次遇到,但是这种情况更优
{
// 松弛操作
dist[x][y] = dist[i][j] + w;
}
// if(x == x2 && y == y2) return;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
while(cin >> n >> m, n && m)
{
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for(int j = 0; j < m; j++)
cin >> a[i][j];
cin >> x1 >> y1 >> x2 >> y2;
bfs();
cout << dist[x2][y2] << endl;
}
return 0;
}2. ThreeStates
题⽬来源:洛⾕
题⽬链接:CF590C Three States - 洛谷
难度系数:★★★★
(1)题目描述

(2)算法原理
正难则反:
- 直接找出结果点是很⿇烦的,需要枚举所有的点,然后每个点都要来⼀次 bfs ,这样是会超时的。
- 可以依次从三个国家出发,⽤ bfs 计算出来到达所有点的最短距离。求出所有距离之后,重新遍历所有的点,分情况求出到三个国家的最短距离。
算法原理很简单,但是⾥⾯有很多细节需要注意:
- 因为每个国家可能有很多点,并且国家的点与点之间不连通,因此我们要⽤ 多源bfs 求某个国家到所有点的最短距离;
- 国家与国家之间的点如果相连,它们之间的距离是 0 (⽆论是不是同⼀个国家,在我们这道题⾥⾯,它们的距离都是 0 ,因为都不需要修路)。那么我们这道题⾥⾯边的权值要么是0 ,要么是1 。因此需要⽤ 01bfs 来更新所有的距离;
- 计算某⼀个点到三个国家的最短距离时,应该分情况讨论。设 a, b, c 分别表⽰三个国家到该点的最短距离:
- 如果该点是⼀个国家,最短距离为 a + b + c ;
- 如果该点是⼀个荒地,最短距离为 a +b+c−2 ,因为我们计算最短距离的时候,荒地会被计算三次,所以要减去两次。

(3)参考代码
#include <iostream>
#include <deque>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 1010;
int n, m;
char a[N][N];
int dist[4][N][N];
// dist[1] dist[2] dist[3]
int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, -1};
int dy[] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
void bfs(int num)
{
memset(dist[num], -1, sizeof dist[num]);
// 多源bfs
deque<PII> q;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
if(a[i][j] - '0' == num)
{
q.push_back({i, j});
dist[num][i][j] = 0;
}
}
// 01bfs
while(q.size())
{
auto t = q.front(); q.pop_front();
int i = t.first, j = t.second;
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = i + dx[k], y = j + dy[k];
if(x >= 1 && x <= n && y >= 1 && y <= m && a[x][y] != '#')
{
int w = (a[x][y] == '.' ? 1 : 0);
if(dist[num][x][y] == -1) // 第一次遇到
{
dist[num][x][y] = dist[num][i][j] + w;
if(w) q.push_back({x, y});
else q.push_front({x, y});
}
else if(dist[num][i][j] + w < dist[num][x][y])
{
dist[num][x][y] = dist[num][i][j] + w;
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
cin >> a[i][j];
bfs(1); bfs(2); bfs(3);
int ret = 0x3f3f3f3f;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
if(a[i][j] == '#') continue;
int x = dist[1][i][j], y = dist[2][i][j], z = dist[3][i][j];
if(x == -1 || y == -1 || z == -1) continue;
if(a[i][j] == '.') ret = min(ret, x + y + z - 2);
else ret = min(ret, x + y + z);
}
if(ret == 0x3f3f3f3f) cout << -1 << endl;
else cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}四、Floodfill 问题
Floodfill 算法,⼜称漫⽔填充,像素法,本质是在寻找具有相同性质的联通块。
1. LakeCounting
题⽬来源:洛⾕
题⽬链接:P1596 [USACO10OCT] Lake Counting S - 洛谷
难度系数:★
(1)题目描述

(2)算法原理
遍历整个矩阵,当遇到⼀个没有标记过的⽔坑时:
- 计数;
- 然后⽤ bfs 或者 dfs 将整个湖全都标记⼀下。
整个矩阵遍历⼀遍,就能得出湖的数量。
(3)参考代码
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 110;
int n, m;
char a[N][N];
bool st[N][N]; // 标记哪些区域已经被搜索过了
int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, -1, 1, 1, -1, -1};
int dy[] = {1, -1, 0, 0, 1, -1, 1, -1};
void dfs(int i, int j)
{
st[i][j] = true;
for(int k = 0; k < 8; k++)
{
int x = i + dx[k], y = j + dy[k];
if(x >= 1 && x <= n && y >= 1 && y <= m && a[x][y] == 'W' && st[x][y] == false)
{
dfs(x, y);
}
}
}
void bfs(int i, int j)
{
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push({i, j});
st[i][j] = true;
while(q.size())
{
auto t = q.front(); q.pop();
int i = t.first, j = t.second;
for(int k = 0; k < 8; k++)
{
int x = i + dx[k], y = j + dy[k];
if(x >= 1 && x <= n && y >= 1 && y <= m && a[x][y] == 'W' && st[x][y] == false)
{
st[x][y] = true;
q.push({x, y});
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
cin >> a[i][j];
int ret = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for(int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
if(a[i][j] == 'W' && st[i][j] == false)
{
ret++;
// dfs(i, j); // 把这块区域打上标记
bfs(i, j); // 把这块区域打上标记
}
}
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}2. 填涂颜⾊
题⽬来源:洛⾕
题⽬链接:P1162 填涂颜色 - 洛谷
难度系数:★★
(1)题目描述

(2)算法原理
正难则反:
直接找出被 1包围的 0 是很困难的,因为很难确定当前搜索到的这个 0 是否是被包围的。但是,我们如果从边缘的 0开始搜索,搜索到的 0 ⼀定是没有被包围的。
因此,我们可以从边缘的 0 开始搜索,标记所有与边缘 0 相连的联通块。那么,没有被标记过的 0 就是被包围的。
⼩技巧:
- 我们可以把整个矩阵的外围包上⼀层 0 ,这样只⽤从 [0, 0] 位置开始搜即可。不⽤遍历第⼀⾏第⼀列,最后⼀⾏以及最后⼀列
(3)参考代码
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N = 35;
int n;
int a[N][N];
bool st[N][N]; // 只会标记边缘的 0
int dx[] = {0, 0, -1, 1};
int dy[] = {1, -1, 0, 0};
void dfs(int i, int j)
{
st[i][j] = true;
for(int k = 0; k < 4; k++)
{
int x = i + dx[k], y = j + dy[k];
// 注意此时的边界
if(x >= 0 && x <= n + 1 && y >= 0 && y <= n + 1 && a[x][y] == 0 && st[x][y] == 0)
{
dfs(x, y);
}
}
}
int main()
{
while(cin >> n)
{
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
cin >> a[i][j];
dfs(0, 0);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if(a[i][j]) cout << a[i][j] << " ";
else if(st[i][j]) cout << 0 << " ";
else cout << 2 << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}