济南网站建设公司熊掌号关键词优化公司靠谱推荐
⭐上篇文章:28.C++多态1 (多态的概念与简单使用,虚函数,final,override)-CSDN博客
⭐标⭐是比较重要的部分
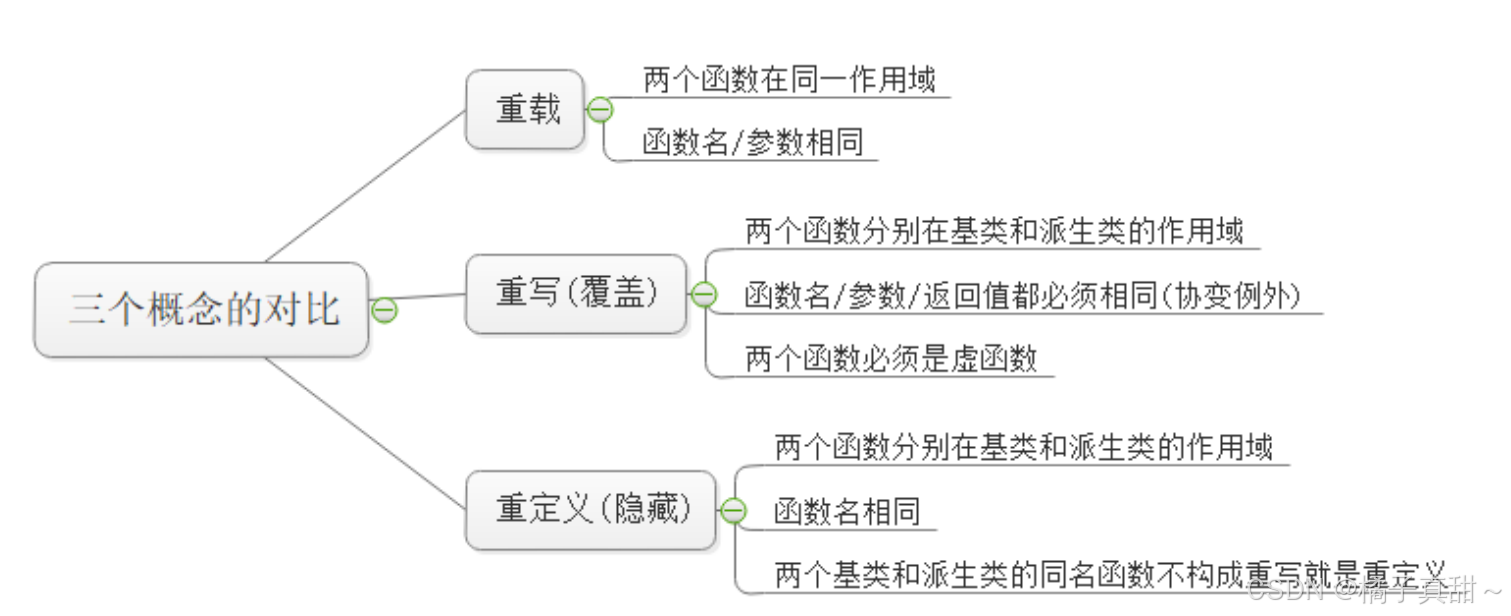
一. 重载
重载是两个函数的名称相同,参数列表不同(顺序,类型,数量不同),这样的两个函数构成重载。
比如:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;int test(int a, int b)
{return a + b;
}int test(int a, double b)
{return a + b;
}int main()
{return 0;
}上面的两个test函数构成重载
二. 重定义
重定义是有继承关系的两个类中,父类和子类都有一个同名函数,但是这个同名函数参数列表可能不同,而且没有使用virtual关键字进行修饰。
这两个函数的作用域不同
代码举例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class A
{
public:void test(){cout << "我是类A" << endl;}
};class B : public A
{
public:void test(){cout << "我是类B" << endl;}
};int main()
{A a;B b;a.test();b.test();return 0;
}上面的A类和B类中的test就构成重定义
测试结果如下:
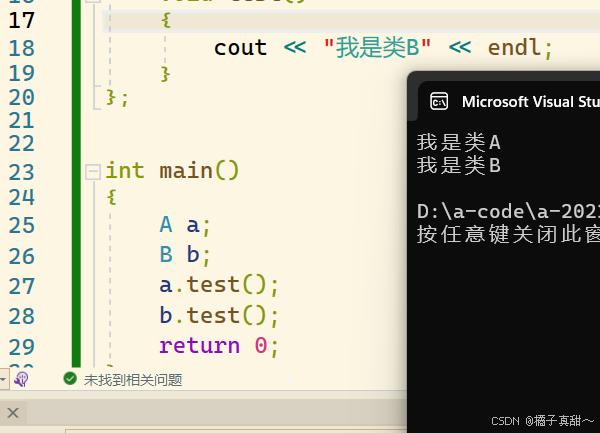
可以看到,对象调用自己类中的test函数
如果使用基类的指针或者引用去引用B类的对象,仍是调用A类的test
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class A
{
public:void test(){cout << "我是类A" << endl;}
};class B : public A
{
public:void test(){cout << "我是类B" << endl;}
};int main()
{B b;A* pa = &b;A& a = b;pa->test();a.test();return 0;
}测试结果如下:
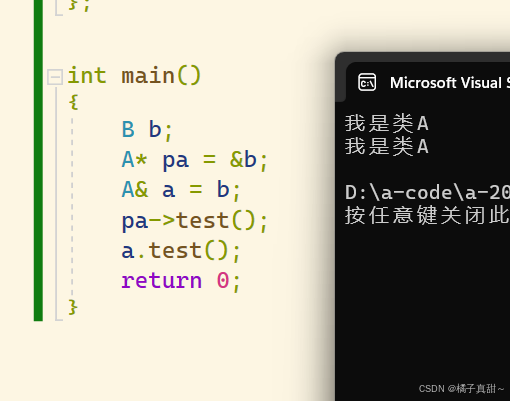
可以看到,都是调用了A类的test 输出了我是类A
三. 重写
成员函数重写是构成多态的两个条件之一,需要使用virtual关键字进行修饰。
重写的两个函数的名称和参数必须相同(协变和析构除外)
重写的两个函数需要使用virtual进行修饰
如下面代码中的两个函数就构成重写
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;class A
{
public:virtual void test(){cout << "我是类A" << endl;}
};class B : public A
{
public:virtual void test(){cout << "我是类B" << endl;}
};int main()
{A* a = new A();A* b = new B();a->test();b->test();return 0;
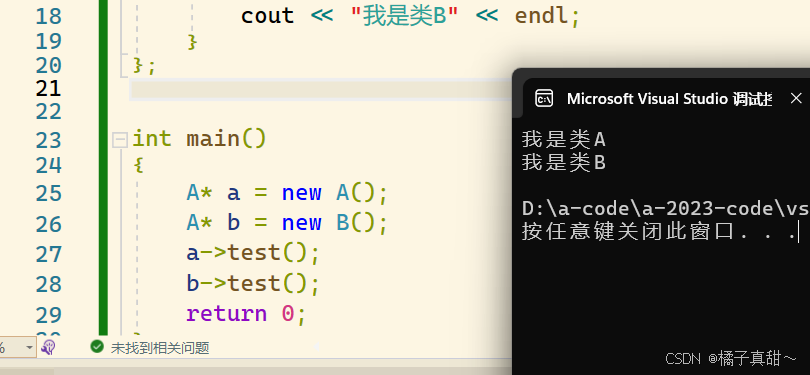
}测试结果如下:
四.总结