深圳网站优化排名公司wordpress twentyten
前言
一、源码结构分析
二、模拟实现map/set
2.1 套上KeyOfT
2.2 普通迭代器实现
2.3 const迭代器实现
2.4 解决key不能修改的问题
2.5 map的[]实现
2.6 map/set以及红黑树源码
2.6.1 RBTree.h
2.6.2 set.h
2.6.3 map.h
总结
前言
之前的文章讲解了红黑树的具体实现,本篇文章就用红黑树来封装一个map/set出来,但是大家在实现前一定要保证红黑树不要出现问题,如果红黑树有问题还是要先把红黑树调好再来实现封装。
一、源码结构分析
// stl_set.h
template <class Key, class Compare = less<Key>, class Alloc = alloc>
class set {
public:typedef Key key_type;typedef Key value_type;
private:typedef rb_tree<key_type, value_type,identity<value_type>, key_compare, Alloc> rep_type;rep_type t;
};// stl_map.h
template <class Key, class T, class Compare = less<Key>, class Alloc = alloc>
class map {
public: typedef Key key_type;typedef T mapped_type;typedef pair<const Key, T> value_type;private:typedef rb_tree<key_type, value_type,select1st<value_type>, key_compare, Alloc> rep_type;rep_type t;
};// stl_tree.h
struct __rb_tree_node_base
{typedef __rb_tree_color_type color_type;typedef __rb_tree_node_base* base_ptr;color_type color;base_ptr parent;base_ptr left;base_ptr right;
};// stl_tree.h
template <class Key, class Value, class KeyOfValue, class Compare, class Alloc = alloc>
class rb_tree {
protected:typedef void* void_pointer;typedef __rb_tree_node_base* base_ptr;typedef __rb_tree_node<Value> rb_tree_node;typedef simple_alloc<rb_tree_node, Alloc> rb_tree_node_allocator;typedef __rb_tree_color_type color_type;
public:typedef Key key_type;typedef Value value_type;typedef value_type* pointer;typedef const value_type* const_pointer;typedef value_type& reference;typedef const value_type& const_reference;typedef rb_tree_node* link_type;typedef size_t size_type;typedef ptrdiff_t difference_type;
protected:size_type node_count; // keeps track of size of treelink_type header;Compare key_compare;
};// stl_tree.h
template <class Value>
struct __rb_tree_node : public __rb_tree_node_base
{typedef __rb_tree_node<Value>* link_type;Value value_field;
};
也就是说对于set来说,Key是Key,Value也是Key,对于map来说,Key是Key,Value是pair,而rb_tree的第二个模版参数Value才是真正存在节点里面的,所以set在节点中存的就是一个Key,map在节点中存的是pair。
那既然rb_tree第二个模板参数Value已经控制了红黑树结点中存储的数据类型,为什么还要传第一个模板参数Key呢?其实是因为在find/erase时的函数参数都是Key,所以第⼀个模板参数是传给find/erase等函数做形参的类型的。
那我们自己的map/set以及红黑树的修改就如下:
namespace hx
{template<class K>class set{public:private:RBTree<K, K> _t;};
}namespace hx
{template<class K, class V>class map{public:private:RBTree<K, pair<K, V>> _t;};
}enum Color
{RED,BLACK
};template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{T _data;RBTreeNode* _left;RBTreeNode* _right;RBTreeNode* _parent;Color _col;RBTreeNode(const T& data):_data(data), _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr){}
};template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
struct RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:
private:Node* _root = nullptr;
};二、模拟实现map/set
模拟实现一共分为五步:
1、套上KeyOfT
2、普通迭代器
3、const迭代器
4、解决Key不能修改的问题
5、map的[]实现
2.1 套上KeyOfT
既然已经知道了红黑树的第二个模版参数才是存在节点里的,那先对红黑树以及节点类进行一个修改
template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{T _data;RBTreeNode* _left;RBTreeNode* _right;RBTreeNode* _parent;Color _col;RBTreeNode(const T& data):_data(data), _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr){}
};template<class K, class T>
struct RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:bool insert(const T& data){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;return true;}Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){// 问题出现了if (cur->_data < data){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_data > data){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return false;}}将节点类修改成一个模版参数T,insert的参数也是插入一个key,但是在cur中的_data与形参data比较的时候问题就来了,如果data是key,那么直接比较没问题,但是如果是一个pair呢?库中虽然重载了pair的比较大小,但是库中的比较方式是,first大就大,如果first相等,那second大就大,如果first和second都相等,这两个pair对象才相同。这显然不符合我们的需求,我们要的是如果first相等,那两个pair对象就是相等,那就需要上一个仿函数来自己控制这里的比较逻辑。
但是又没有办法在红黑树中写仿函数,因为对于下层来说,根本就不知道节点中存储的数据类型是什么,那下层不知道,但是上层知道,所以就可以在map和set中定义仿函数,作为模版参数传进来,通过仿函数去取出对象里面的key。
namespace hx
{template<class K>class set{struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:private:RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;};
}namespace hx
{template<class K, class V>class map{struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:private:RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;};
}template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
struct RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:bool insert(const T& data){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;return true;}// 定义对象KeyOfT kot;Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){ // 去取里面的keyif (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}// 去取里面的keyelse if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return false;}}cur = new Node(data);Node* newnode = cur;if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data)){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}// ...// 还有很多代码,但是在这里只留下需要修改的部分}
};这样就完美的解决了问题,用一个模版参数,data中存的是Key,就去把这个Key取出来,存的是pair,就去把这个pair中的Key取出来。map和set的insert直接就去调用树的insert。
// set
namespace hx
{template<class K>class set{struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:bool insert(const K& key){return _t.insert(key);}private:RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;};
}// map
namespace hx
{template<class K, class V>class map{struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _t.insert(kv);}private:RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;};
}2.2 普通迭代器实现
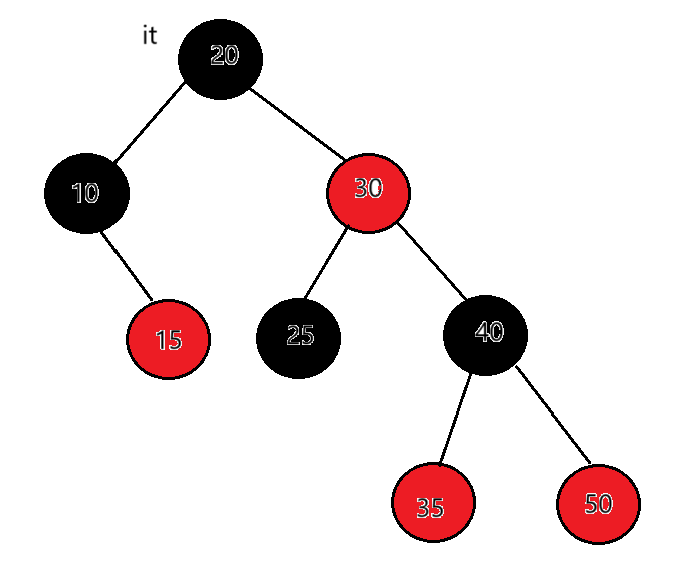
迭代器++时,如果it指向的结点的右子树不为空,代表当前结点已经访问完了,因为是左根右,左子树和根已经访问完了,要去访问右子树了,要访问下一个结点是右子树的中序第一个,一棵树中序第一个是最左结点,所以直接找右子树的最左结点即可。
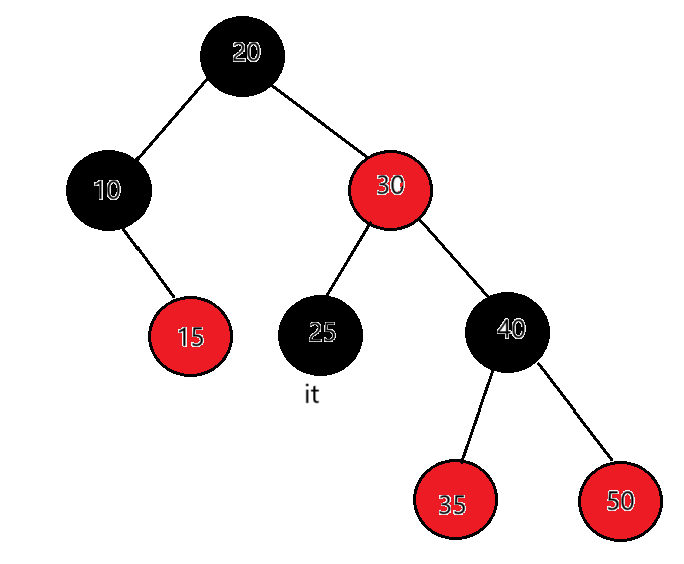
迭代器++时,如果it指向的结点的右子树为空,代表当前结点已经访问完了,且当前结点所在的子树也访问完了,要访问的下一个结点在当前结点的祖先里面,所以要沿着当前结点到根的祖先路径向上找。例如:25的右子树为空,以25做根的这棵局部子树就访问完了,要看当前节点25在父亲的哪里,父亲是30,25是30的左,那就说明下一个要访问的节点就是父亲所在的节点30。
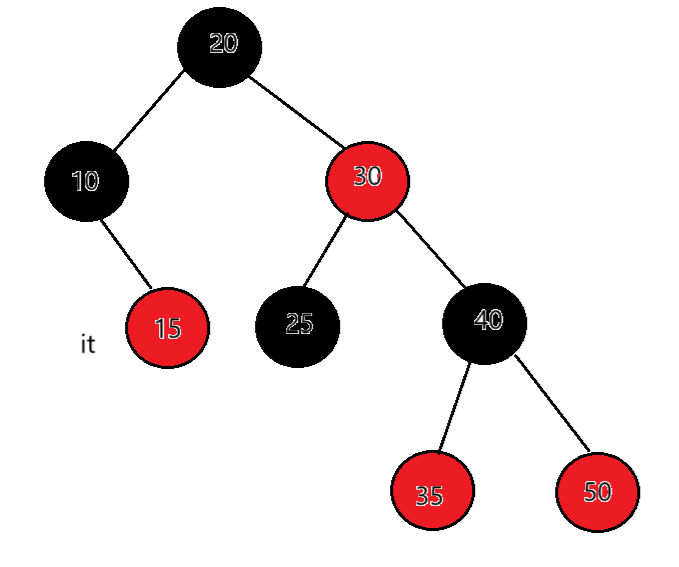
如果当前结点是父亲的右,根据中序左子树->根结点->右子树,当前结点所在的子树访问完 了,当前结点所在父亲的子树也访问完了,那么下一个访问的需要继续往根的祖先中去找,直到找 到孩子是父亲左的那个祖先就是中序要问题的下一个结点。例如:it指向15,15右为空,父亲是10,15是10的右,15所在的子树访问完了,10所在的子树也访问完了,继续往上找,父亲是20,10是20的左,那么下一个访问的结点就是18。
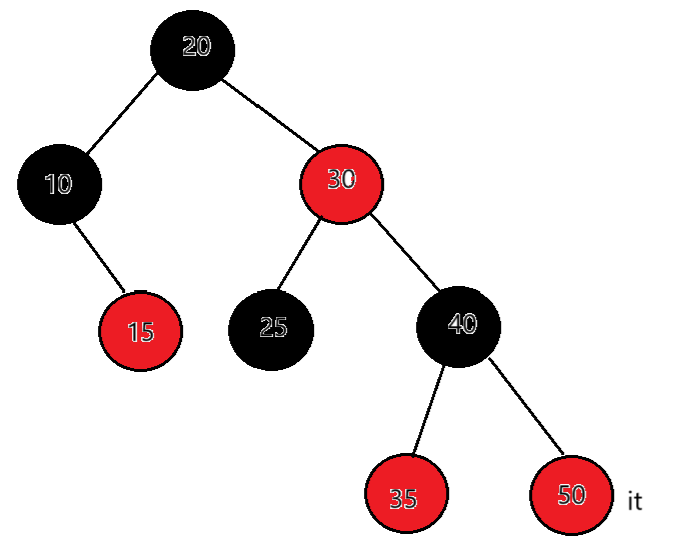
如果it在50,50的右为空,50为根的这棵子树访问完了,父亲是40,50是40的右,说明40所在的子树访问完了。继续向上从祖先中找,当前节点是40,父亲是30,40是30的右,说明30所在的子树访问完了。当前节点是30,父亲是20,30是20的右,说明20所在的子树访问完了。当前节点是20,父亲是空。结束遍历。
总结:当右子树不为空时,下一个要访问的节点就是右子树的最左节点,当右子树为空时,看当前节点在父亲的左还是右,如果在父亲的左,下一个要访问的节点就是父亲,如果在父亲的右,那就要到当前节点的祖先中去查找,直到找 到孩子是父亲左的那个祖先就是要访问的下一个结点,如果父亲为空了,那整棵树就遍历完了,也让当前节点去指向父亲。end()的结束我们定义成走到空就是结束。
template<class T>
struct __RBTree_Iterator
{typedef __RBTree_Iterator<T> Self;typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;Node* _node;__RBTree_Iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Self& operator++(){ // 右子树不为空if (_node->_right){_node = _node->_right;// 找右子树的最左节点while (_node->_left){_node = _node->_left;}}else{// 右子树为空Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;// 循环的找,当找到孩子是父亲的左时,父亲就是下一个要访问的节点while (parent && parent->_right == cur){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}// 无论是因为孩子是父亲的左,还是因为父亲为空了,下一个要访问的节点都是parent_node = parent;}return *this;}};迭代器--也是一样的道理,只不过就是反过来,按照右子树->根->左子树的顺序遍历。当左子树不为空时,下一个要访问的节点就是左子树的最右节点,当左子树为空时,看当前节点在父亲的左还是右,如果在父亲的右,下一个要访问的节点就是父亲,如果在父亲的左,那就要到当前节点的祖先中去查找,直到找到孩子是父亲右的那个祖先就是要访问的下一个结点,如果父亲为空了,那整棵树就遍历完了,也让当前节点去指向父亲。
Self& operator--()
{if (_node->_left){_node = _node->_left;while (_node->_right){_node = _node->_right;}}else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && parent->_left == cur){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;
}那++和--实现完了,其他的就和list的迭代器是一样的了,我们把其余功能补全
template<class T>
struct __RBTree_Iterator
{typedef __RBTree_Iterator<T> Self;typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;Node* _node;__RBTree_Iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}T& operator*(){return _node->_data;}T* operator->(){return &_node->_data;}Self& operator++(){// 右子树不为空if (_node->_right){_node = _node->_right;// 找右子树的最左节点while (_node->_left){_node = _node->_left;}}else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;// 循环的找,当找到孩子是父亲的左时,父亲就是下一个要访问的节点while (parent && parent->_right == cur){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}// 无论是因为孩子是父亲的左,还是因为父亲为空了,下一个要访问的节点都是parent_node = parent;}return *this;}Self operator++(int){Self tmp = *this;++*this;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){if (_node->_left){_node = _node->_left;while (_node->_right){_node = _node->_right;}}else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && parent->_left == cur){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp = *this;--*this;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const Self& s){return _node == s._node;}
};template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
struct RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:typedef __RBTree_Iterator<T> iterator;iterator begin(){Node* minleft = _root;while (minleft && minleft->_left){minleft = minleft->_left;}return minleft;}iterator end(){return nullptr;}
};
下层实现好了要继续来实现上层
namespace hx
{template<class K>class set{struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:// 要加上typenametypedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.begin();}iterator end(){return _t.end();}bool insert(const K& key){return _t.insert(key);}private:RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;};
}这里一定要注意,在取红黑树里面的迭代器时,属于类模版中取内嵌类型,一定要加上typename,因为编译器不知道这里的iterator是类型还是对象,加上typename就是告诉编译器是类型,等模版实例化了再去找。map也是同理。
namespace hx
{template<class K, class V>class map{struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:// 一定要加typenametypedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.begin();}iterator end(){return _t.end();}bool insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _t.insert(kv);}private:RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;};
}2.3 const迭代器实现
我们知道普通迭代器和const迭代器的不同就是在operator*和operator->的返回值,和list一样,其他不变就好了
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __RBTree_Iterator
{typedef __RBTree_Iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;Node* _node;__RBTree_Iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}Self& operator++(){// 右子树不为空if (_node->_right){_node = _node->_right;// 找右子树的最左节点while (_node->_left){_node = _node->_left;}}else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;// 循环的找,当找到孩子是父亲的左时,父亲就是下一个要访问的节点while (parent && parent->_right == cur){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}// 无论是因为孩子是父亲的左,还是因为父亲为空了,下一个要访问的节点都是parent_node = parent;}return *this;}Self operator++(int){Self tmp = *this;++*this;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){if (_node->_left){_node = _node->_left;while (_node->_right){_node = _node->_right;}}else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && parent->_left == cur){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp = *this;--*this;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const Self& s){return _node == s._node;}
};template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
struct RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:typedef __RBTree_Iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __RBTree_Iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;iterator begin(){Node* minleft = _root;while (minleft && minleft->_left){minleft = minleft->_left;}return minleft;}iterator end(){return nullptr;}const_iterator begin() const{Node* minleft = _root;while (minleft && minleft->_left){minleft = minleft->_left;}return minleft;}const_iterator end() const{return nullptr;}
};namespace hx
{template<class K>class set{struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.begin();}iterator end(){return _t.end();}const_iterator begin() const{return _t.begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _t.end();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key){return _t.insert(key);}private:RBTree<K, K, SetKeyOfT> _t;};
}namespace hx
{template<class K, class V>class map{struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.begin();}iterator end(){return _t.end();}const_iterator begin() const{return _t.begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _t.end();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _t.insert(kv);}private:RBTree<K, pair<K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;};
}2.4 解决key不能修改的问题
在map和set中,key是不能修改的,map的value可以修改,在key前加上const修饰即可
namespace hx
{template<class K>class set{public:typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;private:RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT> _t;};
}namespace hx
{template<class K, class V>class map{public:typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;private:RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;};
}注意map中,const可不要加在pair前面了,加在pair前面那就是first和second都不能修改,但我们要的只是first不能修改。
2.5 map的[]实现
[]中要调用insert,所以要先把insert的返回值修改成pair<iterator, bool>类型

pair<iterator, bool> insert(const T& data)
{if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;return { _root, true };}// 定义对象KeyOfT kot;Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){// 去取里面的keyif (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}// 去取里面的keyelse if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return { cur, false };}}cur = new Node(data);// 重新定义出来一个节点newnodeNode* newnode = cur;if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data)){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;cur->_col = RED;// ... 调平衡_root->_col = BLACK;return { newnode, true };
}如果根为空就,就返回{_root, true},代表插入成功,如果值已经存在,就返回已经存在的节点{cur, false},如果根不为空,也没有这个值,返回的节点指针一定不要用cur,因为在调整平衡的时候cur可能已经不知道走到哪去了,提前记录一个newnode,用{newnode, true}返回。
// set
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key)
{return _t.insert(key);
}// map
pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv)
{return _t.insert(kv);
}V& operator[](const K& key)
{pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.insert({ key, V() });return ret.first->second;
}[]的实现是先去调用insert,插入一个value的匿名对象就可以,会去调用value的默认构造,并且接收返回值,ret.first拿到的就是迭代器对象,里面存储的就是节点的指针,不管这个key是之前就存在,还是新插入进去的,都是这个节点的指针,迭代器对象去调用operator->拿到pair的地址,再解引用拿second,为了可读性两个->省略成了一个。
2.6 map/set以及红黑树源码
2.6.1 RBTree.h
{RED,BLACK
};template<class T>
struct RBTreeNode
{T _data;RBTreeNode* _left;RBTreeNode* _right;RBTreeNode* _parent;Color _col;RBTreeNode(const T& data):_data(data), _left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _parent(nullptr){}
};template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct __RBTree_Iterator
{typedef __RBTree_Iterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;Node* _node;__RBTree_Iterator(Node* node):_node(node){}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}Self& operator++(){// 右子树不为空if (_node->_right){_node = _node->_right;// 找右子树的最左节点while (_node->_left){_node = _node->_left;}}else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;// 循环的找,当找到孩子是父亲的左时,父亲就是下一个要访问的节点while (parent && parent->_right == cur){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}// 无论是因为孩子是父亲的左,还是因为父亲为空了,下一个要访问的节点都是parent_node = parent;}return *this;}Self operator++(int){Self tmp = *this;++*this;return tmp;}Self& operator--(){if (_node->_left){_node = _node->_left;while (_node->_right){_node = _node->_right;}}else{Node* cur = _node;Node* parent = cur->_parent;while (parent && parent->_left == cur){cur = parent;parent = parent->_parent;}_node = parent;}return *this;}Self operator--(int){Self tmp = *this;--*this;return tmp;}bool operator!=(const Self& s){return _node != s._node;}bool operator==(const Self& s){return _node == s._node;}
};template<class K, class T, class KeyOfT>
struct RBTree
{typedef RBTreeNode<T> Node;
public:typedef __RBTree_Iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef __RBTree_Iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;iterator begin(){Node* minleft = _root;while (minleft && minleft->_left){minleft = minleft->_left;}return minleft;}iterator end(){return nullptr;}const_iterator begin() const{Node* minleft = _root;while (minleft && minleft->_left){minleft = minleft->_left;}return minleft;}const_iterator end() const{return nullptr;}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const T& data){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(data);_root->_col = BLACK;return { _root, true };}// 定义对象KeyOfT kot;Node* cur = _root;Node* parent = nullptr;while (cur){// 去取里面的keyif (kot(cur->_data) < kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}// 去取里面的keyelse if (kot(cur->_data) > kot(data)){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return { cur, false };}}cur = new Node(data);Node* newnode = cur;if (kot(parent->_data) < kot(data)){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}cur->_parent = parent;cur->_col = RED;while (parent && parent->_col == RED){Node* grandfather = parent->_parent;if (grandfather->_left == parent){Node* uncle = grandfather->_right;// 调整if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED) // 叔叔存在且为红{// 变色parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK;grandfather->_col = RED;// 继续向上调整cur = grandfather;parent = cur->_parent;}else // 叔叔不存在或叔叔存在且为黑{if (parent->_left == cur){RotateR(grandfather);grandfather->_col = RED;parent->_col = BLACK;}else{RotateL(parent);RotateR(grandfather);grandfather->_col = RED;cur->_col = BLACK;}break; // 旋转完子树平衡,不需要继续调整}}else //grandfather->_right == parent{Node* uncle = grandfather->_left;if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED) // 叔叔存在且为红{parent->_col = uncle->_col = BLACK; // 变色grandfather->_col = RED;// 继续向上调整grandfather = cur;parent = cur->_parent;}else // 叔叔不存在或叔叔存在且为黑{if (parent->_right == cur){RotateL(grandfather);grandfather->_col = RED;parent->_col = BLACK;}else{RotateR(parent);RotateL(grandfather);grandfather->_col = RED;cur->_col = BLACK;}break; // 旋转完子树平衡,不需要继续调整}}}_root->_col = BLACK;return { newnode, true };}void RotateR(Node* parent){Node* cur = parent->_left;Node* curright = cur->_right;parent->_left = curright;if (curright)curright->_parent = parent;cur->_right = parent;Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = cur;if (parent == _root){_root = cur;cur->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parentParent->_left == parent){parentParent->_left = cur;}else{parentParent->_right = cur;}cur->_parent = parentParent;}}void RotateL(Node* parent){Node* cur = parent->_right;Node* curleft = cur->_left;parent->_right = curleft;if (curleft)curleft->_parent = parent;cur->_left = parent;Node* parentParent = parent->_parent;parent->_parent = cur;if (parent == _root){_root = cur;cur->_parent = nullptr;}else{if (parentParent->_left == parent){parentParent->_left = cur;}else{parentParent->_right = cur;}cur->_parent = parentParent;}}bool find(const K& key){KeyOfT kot;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (kot(cur->_data) < key){cur = cur->_right;}else if (kot(cur->_data) > key){cur = cur->_left;}else{return true;}}return false;}void InOrder(){_InOrder(_root);cout << endl;}void _InOrder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return;_InOrder(root->_left);cout << root->_kv.first << " ";_InOrder(root->_right);}int Height(){return _Height(_root);}int _Height(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return 0;int retleft = _Height(root->_left);int retright = _Height(root->_right);return retleft > retright ? retleft + 1 : retright + 1;}int size(){return _size(_root);}int _size(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return 0;return _size(root->_left) + _size(root->_right) + 1;}bool Check(Node* root, int refersum, int cursum){if (root == nullptr){// 走到空与基准值refersum作比较,检查规则四if (refersum != cursum){cout << "每条路径上黑色节点的数量不相等" << endl;return false;}return true;}// 检查规则三if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent && root->_parent->_col == RED){cout << "出现连续的红色节点" << endl;return false;}// 遇到黑色节点就++if (root->_col == BLACK)cursum++;// 继续递归去检查return Check(root->_left, refersum, cursum)&& Check(root->_right, refersum, cursum);}bool isBalance(){// 空树也是红黑树if (_root == nullptr)return true;// 检查规则二if (_root->_col == RED)return false;// 用最左边的路径作为参考值int BlackSum = 0;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_col == BLACK)BlackSum++;cur = cur->_left;}return Check(_root, BlackSum, 0);}private:Node* _root = nullptr;
};2.6.2 set.h
namespace hx
{template<class K>class set{struct SetKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const K& key){return key;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.begin();}iterator end(){return _t.end();}const_iterator begin() const{return _t.begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _t.end();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const K& key){return _t.insert(key);}private:RBTree<K, const K, SetKeyOfT> _t;};
}2.6.3 map.h
namespace hx
{template<class K, class V>class map{struct MapKeyOfT{const K& operator()(const pair<K, V>& kv){return kv.first;}};public:typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::iterator iterator;typedef typename RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT>::const_iterator const_iterator;iterator begin(){return _t.begin();}iterator end(){return _t.end();}const_iterator begin() const{return _t.begin();}const_iterator end() const{return _t.end();}pair<iterator, bool> insert(const pair<K, V>& kv){return _t.insert(kv);}V& operator[](const K& key){pair<iterator, bool> ret = _t.insert({ key, V() });return ret.first->second;}private:RBTree<K, pair<const K, V>, MapKeyOfT> _t;};
}总结
本篇文章讲的非常细致,一步一步去实现,没有跨越什么,大家在实现的时候也一定要一步一步的来,写完这一步,测试没有问题了,再去搞下一步,不要想着一口吃个胖子,可千万不要出现最后功能都实现好了,结果红黑树的实现有问题这种情况。对于map和set我们实现这些功能就可以了,那如果大家觉得小编写的还不错,可以给小编一个三连表示支持!!!感谢大家!
