中迅做网站是模板站吗长春seo排名扣费
简述
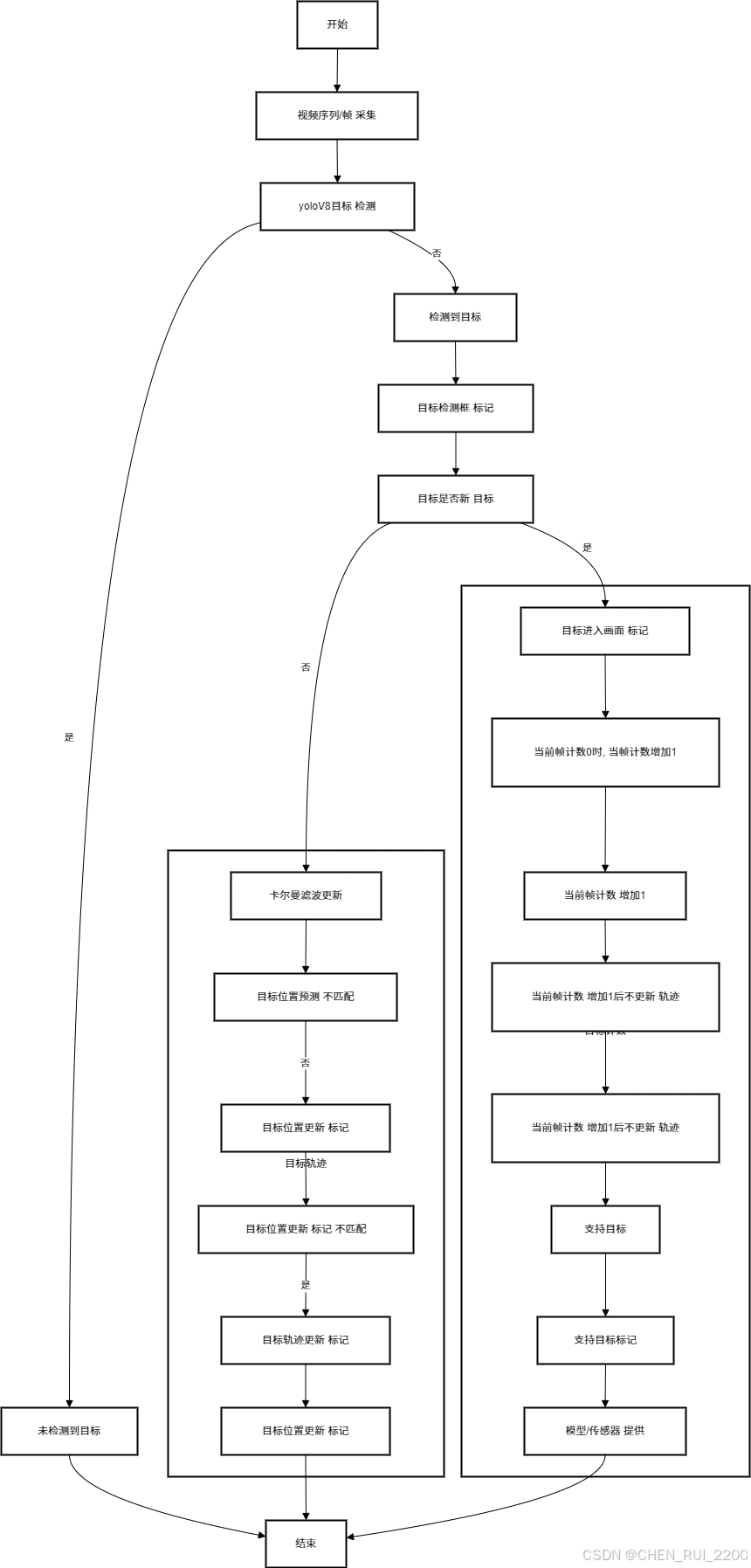
最近接了毕业生的毕业设计题,想着帮帮忙,要使用机器视觉识别,追踪和逻辑统计的方式来统计人流,要求是满足下面特性
- 高精度:YOLOv8 提供高质量检测,卡尔曼滤波平滑跟踪。
- 高效率:两者结合满足实时性需求,优化后的代码进一步提升性能。
- 稳定性:多目标跟踪更可靠,适应复杂场景。
下面是一个步行街的mp4文件, 需要统计在视频时间段内上行人流和下行人流量

我第一反应是拿出我毕业那会的做法改改,当时使用的YOLOv3 现在改用YOLOv8 是目前目标检测领域最先进的模型之一,相较于 YOLOv3,它在精度(mAP)和速度上都有显著提升,尤其是在小目标检测和复杂场景下的表现。
流程设计为:
- 使用yoloV8模型进行目标检测
- 然后使用SORT算法进行目标追踪,使用卡尔曼滤波器进行目标位置预测
- 再利用匈牙利算法对比目标的相似度,完成车标追踪
YOLOv8 相较于 YOLOv3,它在精度(mAP)和速度上都有显著提升,尤其是在小目标检测和复杂场景下的表现。自带强大的预训练权重(基于 COCO 等数据集),对常见目标(如人、车)的检测非常鲁棒开箱即用。YOLOv8 提供高质量的检测框输入,减少了噪声和误检,这为卡尔曼滤波器的状态更新提供了更可靠的观测数据。卡尔曼滤波器通过预测和平滑目标运动轨迹,可以弥补 YOLOv8 在某些帧中漏检或检测不稳定的情况,从而提高整体跟踪的鲁棒性。
卡尔曼滤波的状态模型(位置、速度等)可以根据目标运动特性调整(如加入加速度模型)
SORT 是一种基于检测的多目标跟踪(Tracking-by-Detection)算法,主要用于实时跟踪视频中的多个目标。它结合了目标检测(Detections)和卡尔曼滤波(Kalman Filter)来预测和更新目标轨迹,并通过 IoU 匹配来关联检测框和跟踪框。SORT 算法的核心思想是:
- 利用卡尔曼滤波预测目标的运动轨迹。
- 通过 IoU 匹配将检测框和预测的跟踪框进行关联。
- 根据匹配结果更新跟踪器,处理新目标、丢失目标等情况。
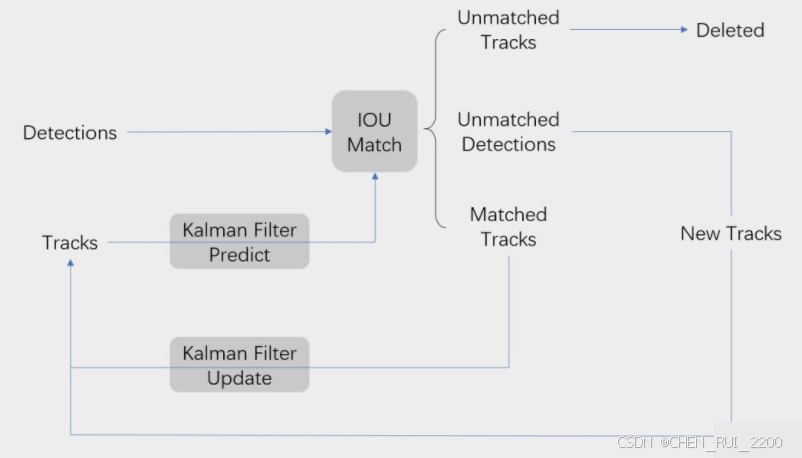
流程图展示了 SORT 算法的完整工作流程,以下是每个步骤的详细说明:
1. 输入:Detections 和 Tracks
- Detections:当前帧的目标检测框,通常由目标检测模型(如 YOLOv8)提供,格式为 [x1, y1, x2, y2, score],其中 score 是置信度。
- 在你的代码中,dets 是一个形状为 (N, 5) 的 NumPy 数组,表示当前帧的 N 个检测框。
- Tracks:前一帧的跟踪目标(由 KalmanBoxTracker 管理),每个跟踪目标有一个唯一的 ID 和状态(位置、速度等)。
- 在你的代码中,self.trackers 是一个列表,存储了所有当前的 KalmanBoxTracker 实例。
2. Kalman Filter Predict
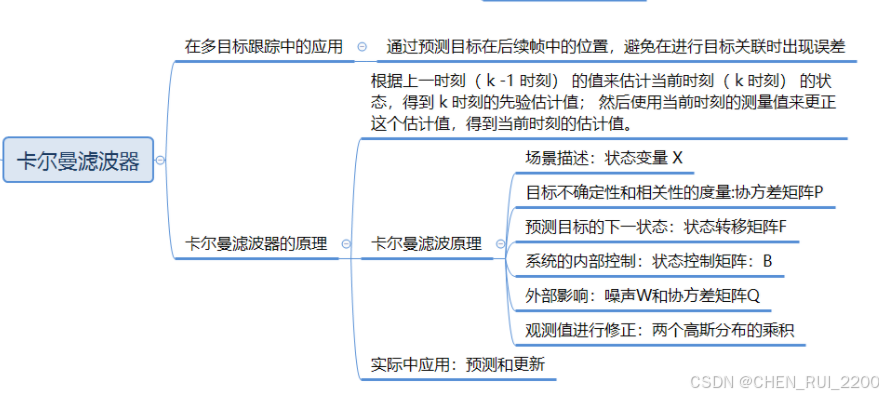
- 作用:对每个现有的跟踪目标(Track)使用卡尔曼滤波进行预测,估计其在当前帧的位置。
- 细节:
- 卡尔曼滤波基于前一帧的状态(位置、速度等)和运动模型(假设匀速运动)预测当前帧的状态。
- 预测结果是一个边界框,格式为 [x1, y1, x2, y2],表示目标的估计位置。
3. IoU Match
- 作用:将当前帧的检测框(Detections)和预测的跟踪框(Tracks)进行匹配,确定哪些检测框对应于哪些跟踪目标。
- 细节:
- 使用 IoU(Intersection over Union)作为匹配准则,计算每个检测框和每个预测框之间的 IoU。
- 通过匈牙利算法(linear_sum_assignment)找到最佳匹配对,使得整体 IoU 最大。
- 设置一个 IoU 阈值(如 0.3),低于此阈值的匹配被认为是无效的。
4. Kalman Filter Update
- 作用:对于匹配成功的跟踪目标,使用对应的检测框更新卡尔曼滤波器的状态。
- 细节:
- 卡尔曼滤波器根据观测值(检测框)和预测值进行融合,更新目标的状态(位置、速度等)。
- 更新后,跟踪目标的状态更加接近实际观测,同时保持运动的平滑性。
5 处理 Unmatched Detections
- 作用:对于未匹配的检测框,认为是新目标,创建新的跟踪器。
实时性和计算效率
- YOLOv8 的优化:
- YOLOv8 采用了更高效的网络架构(如 CSPDarknet 的改进)和推理优化,支持 GPU/CPU 加速,甚至能在边缘设备上运行(如 Jetson Nano)。
- 相比 YOLOv3 的 OpenCV DNN 实现,YOLOv8(基于 Ultralytics)直接输出检测结果,无需手动处理 blob 和多层输出,简化了代码并提升了推理速度。
- 卡尔曼滤波的轻量级特性:
- 卡尔曼滤波是一种计算开销极低的算法,尤其在你的优化版本中(向量化 IoU 和高效匹配),非常适合实时应用。
- SORT 算法本身复杂度低(O(nm) 的匈牙利匹配),结合 YOLOv8 的快速检测,可以轻松实现每秒 30 帧以上的处理速度。
多目标跟踪的稳定性
- YOLOv8 的多目标检测能力:
- YOLOv8 对多目标场景的处理能力更强,能够同时检测多个目标并提供准确的边界框和置信度。
- 支持更高的目标密度,即使在拥挤场景(如人群)中也能提供可靠的检测结果。
- 卡尔曼滤波 + SORT 的跟踪能力:
- 卡尔曼滤波通过预测目标的运动轨迹,可以在目标被短暂遮挡或检测失败时维持跟踪状态。
- SORT 算法(你的优化版本)通过 IoU 匹配和动态管理跟踪器(max_age 和 min_hits),有效处理目标的进入、离开和遮挡问题。
- 优化的向量化 IoU 计算和高效的匈牙利匹配进一步提升了多目标关联的准确性和速度。
代码
卡尔曼滤波
1. Detections(输入检测框)
流程图对应:流程图中的 "Detections" 表示当前帧的目标检测框,通常由目标检测模型(如 YOLOv8)提供。
代码实现:
- 在 Sort.update 方法中,dets 参数是输入的检测框集合,格式为 [[x1, y1, x2, y2, score], ...],表示当前帧的 N 个检测框。
def update(self, dets):self.frame_count += 1# dets 是一个 numpy 数组,包含当前帧的检测框- 代码会对 dets 进行后续处理,但首先需要确保输入不为空:
if dets is None or dets.size == 0:return np.empty((0, 5))2. Kalman Filter Predict(卡尔曼滤波预测)
流程图对应:流程图中的 "Kalman Filter Predict" 表示对每个现有跟踪目标(Tracks)使用卡尔曼滤波预测其在当前帧的位置。
代码实现:
- 在 Sort.update 方法中,遍历所有跟踪器(self.trackers),对每个跟踪器调用 predict 方法
trks = np.zeros((len(self.trackers), 5)) # 存储跟踪器的预测
to_del = [] # 存储要删除的目标框
for t, trk in enumerate(self.trackers):pos = self.trackers[t].predict()[0]trk[:] = [pos[0], pos[1], pos[2], pos[3], 0]if np.any(np.isnan(pos)):to_del.append(t)- KalmanBoxTracker.predict 方法实现了卡尔曼滤波的预测步骤
def predict(self):if (self.kf.x[6] + self.kf.x[2]) <= 0:self.kf.x[6] *= 0.0self.kf.predict()self.age += 1if self.time_since_update > 0:self.hit_streak = 0self.time_since_update += 1self.history.append(convert_x_to_bbox(self.kf.x))return self.history[-1]- self.kf.predict() 调用 filterpy 的卡尔曼滤波器预测方法,基于状态转移矩阵 F 和过程噪声协方差 Q 预测目标在当前帧的位置。
- convert_x_to_bbox 将卡尔曼滤波的状态向量 [x, y, s, r] 转换回边界框 [x1, y1, x2, y2]:
def convert_x_to_bbox(x, score=None):w = np.sqrt(x[2] * x[3])h = x[2] / wif score is None:return np.array([x[0] - w / 2., x[1] - h / 2., x[0] + w / 2., x[1] + h / 2.]).reshape((1, 4))else:return np.array([x[0] - w / 2., x[1] - h / 2., x[0] + w / 2., x[1] + h / 2., score]).reshape((1, 5))预测结果存储在 trks 中,用于后续的 IoU 匹配。
3. IoU Match(IoU 匹配)
流程图对应:流程图中的 "IoU Match" 表示将检测框(Detections)和预测的跟踪框(Tracks)进行匹配。
代码实现:
- 在 Sort.update 中,调用 associate_detections_to_trackers 函数进行匹配
- associate_detections_to_trackers 函数实现 IoU 匹配:
def associate_detections_to_trackers(detections, trackers, iou_threshold=0.3):if (len(trackers) == 0) or (len(detections) == 0):return np.empty((0, 2), dtype=int), np.arange(len(detections)), np.empty((0, 5), dtype=int)iou_matrix = np.zeros((len(detections), len(trackers)), dtype=np.float32)for d, det in enumerate(detections):for t, trk in enumerate(trackers):iou_matrix[d, t] = iou(det, trk)result = linear_sum_assignment(-iou_matrix)matched_indices = np.array(list(zip(*result)))unmatched_detections = []for d, det in enumerate(detections):if d not in matched_indices[:, 0]:unmatched_detections.append(d)unmatched_trackers = []for t, trk in enumerate(trackers):if t not in matched_indices[:, 1]:unmatched_trackers.append(t)matches = []for m in matched_indices:if iou_matrix[m[0], m[1]] < iou_threshold:unmatched_detections.append(m[0])unmatched_trackers.append(m[1])else:matches.append(m.reshape(1, 2))if len(matches) == 0:matches = np.empty((0, 2), dtype=int)else:matches = np.concatenate(matches, axis=0)return matches, np.array(unmatched_detections), np.array(unmatched_trackers)- IoU 计算:iou 函数计算两个边界框的交并比,使用 numba.jit 加速:
@jit
def iou(bb_test, bb_gt):xx1 = np.maximum(bb_test[0], bb_gt[0])yy1 = np.maximum(bb_test[1], bb_gt[1])xx2 = np.minimum(bb_test[2], bb_gt[2])yy2 = np.minimum(bb_test[3], bb_gt[3])w = np.maximum(0., xx2 - xx1)h = np.maximum(0., yy2 - yy1)wh = w * ho = wh / ((bb_test[2] - bb_test[0]) * (bb_test[3] - bb_test[1]) + (bb_gt[2] - bb_gt[0]) * (bb_gt[3] - bb_gt[1]) - wh)return o匹配过程:
- 计算 IoU 矩阵(iou_matrix),表示所有检测框和跟踪框之间的 IoU。
- 使用 linear_sum_assignment(匈牙利算法)进行最优匹配,matches 存储匹配成功的对 [d, t]。
- unmatched_detections 和 unmatched_trackers 分别存储未匹配的检测框和跟踪框。
4. Output Tracks(输出跟踪结果)
流程图对应:流程图中的 "Output Tracks" 表示返回当前帧的跟踪结果,包括更新后的跟踪目标和新创建的跟踪目标。
代码实现:
- 在 Sort.update 中,筛选并输出跟踪结果
ret = []
i = len(self.trackers)
for trk in reversed(self.trackers):d = trk.get_state()[0]if (trk.time_since_update < 1) and (trk.hit_streak >= self.min_hits or self.frame_count <= self.min_hits):ret.append(np.concatenate((d, [trk.id + 1])).reshape(1, -1))i -= 1if trk.time_since_update > self.max_age:self.trackers.pop(i)
if len(ret) > 0:return np.concatenate(ret)
return np.empty((0, 5))代码与流程图的对应总结
| 流程图步骤 | 代码实现 | 相关函数/类 |
|---|---|---|
| Detections | Sort.update 的输入 dets | Sort.update |
| Kalman Filter Predict | KalmanBoxTracker.predict | predict, convert_x_to_bbox |
| IoU Match | associate_detections_to_trackers | iou, linear_sum_assignment |
| Kalman Filter Update | KalmanBoxTracker.update | update, convert_bbox_to_z |
| Unmatched Detections | 创建新 KalmanBoxTracker | KalmanBoxTracker.__init__ |
| Unmatched Tracks | 删除长时间未匹配的跟踪器 | Sort.update (max_age) |
| Output Tracks | 输出当前帧的跟踪结果 | Sort.update, get_state |
kalman.py 完成代码
from __future__ import print_function
from typing import Tuple, Optional
from numba import jit
import numpy as np
from scipy.optimize import linear_sum_assignment
from filterpy.kalman import KalmanFilter# 常量定义
STATE_TRANSITION_MATRIX = np.array([[1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1],[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]
])
OBSERVATION_MATRIX = np.array([[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0]
])@jit(nopython=True)
def iou(bb_test: np.ndarray, bb_gt: np.ndarray) -> float:"""计算两个边界框的交并比 (IoU)。Args:bb_test (np.ndarray): 测试框,格式 [x1, y1, x2, y2]bb_gt (np.ndarray): 真实框,格式 [x1, y1, x2, y2]Returns:float: 交并比值"""xx1 = max(bb_test[0], bb_gt[0])yy1 = max(bb_test[1], bb_gt[1])xx2 = min(bb_test[2], bb_gt[2])yy2 = min(bb_test[3], bb_gt[3])w = max(0., xx2 - xx1)h = max(0., yy2 - yy1)wh = w * ho = wh / ((bb_test[2] - bb_test[0]) * (bb_test[3] - bb_test[1]) +(bb_gt[2] - bb_gt[0]) * (bb_gt[3] - bb_gt[1]) - wh)return odef iou_batch(detections: np.ndarray, trackers: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:"""向量化计算多个检测框和跟踪框之间的 IoU。Args:detections (np.ndarray): 检测框,形状 (N, 4),格式 [x1, y1, x2, y2]trackers (np.ndarray): 跟踪框,形状 (M, 4),格式 [x1, y1, x2, y2]Returns:np.ndarray: IoU 矩阵,形状 (N, M)"""xx1 = np.maximum(detections[:, 0][:, None], trackers[:, 0])yy1 = np.maximum(detections[:, 1][:, None], trackers[:, 1])xx2 = np.minimum(detections[:, 2][:, None], trackers[:, 2])yy2 = np.minimum(detections[:, 3][:, None], trackers[:, 3])w = np.maximum(0., xx2 - xx1)h = np.maximum(0., yy2 - yy1)wh = w * harea_det = (detections[:, 2] - detections[:, 0]) * (detections[:, 3] - detections[:, 1])area_trk = (trackers[:, 2] - trackers[:, 0]) * (trackers[:, 3] - trackers[:, 1])iou = wh / (area_det[:, None] + area_trk - wh)return ioudef convert_bbox_to_z(bbox: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:"""将 [x1, y1, x2, y2] 形式的检测框转为滤波器的状态表示 [x, y, s, r]。Args:bbox (np.ndarray): 检测框,格式 [x1, y1, x2, y2]Returns:np.ndarray: 状态向量,格式 [x, y, s, r],形状 (4, 1)Raises:ValueError: 如果边界框坐标无效"""if np.any(bbox < 0) or bbox[2] <= bbox[0] or bbox[3] <= bbox[1]:raise ValueError("Invalid bounding box coordinates")w = bbox[2] - bbox[0]h = bbox[3] - bbox[1]x = bbox[0] + w / 2.y = bbox[1] + h / 2.s = w * hr = w / float(h)return np.array([x, y, s, r]).reshape((4, 1))def convert_x_to_bbox(x: np.ndarray, score: Optional[float] = None) -> np.ndarray:"""将 [x, y, s, r] 的状态转为 [x1, y1, x2, y2] 的边界框。Args:x (np.ndarray): 状态向量,格式 [x, y, s, r]score (Optional[float]): 置信度,可选Returns:np.ndarray: 边界框,格式 [x1, y1, x2, y2] 或 [x1, y1, x2, y2, score]"""w = np.sqrt(x[2] * x[3])h = x[2] / wif score is None:return np.array([x[0] - w / 2., x[1] - h / 2., x[0] + w / 2., x[1] + h / 2.]).reshape((1, 4))return np.array([x[0] - w / 2., x[1] - h / 2., x[0] + w / 2., x[1] + h / 2., score]).reshape((1, 5))class KalmanBoxTracker:"""单个目标的卡尔曼滤波跟踪器"""count = 0def __init__(self, bbox: np.ndarray):"""初始化卡尔曼滤波器和跟踪器。Args:bbox (np.ndarray): 初始检测框,格式 [x1, y1, x2, y2]"""self.kf = KalmanFilter(dim_x=7, dim_z=4)self.kf.F = STATE_TRANSITION_MATRIXself.kf.H = OBSERVATION_MATRIXself.kf.R[2:, 2:] *= 10.self.kf.P[4:, 4:] *= 1000. # 高不确定性给初始速度self.kf.P *= 10.self.kf.Q[-1, -1] *= 0.01self.kf.Q[4:, 4:] *= 0.01self.kf.x[:4] = convert_bbox_to_z(bbox)self.time_since_update = 0self.id = KalmanBoxTracker.countKalmanBoxTracker.count += 1self.history = []self.hits = 0self.hit_streak = 0self.age = 0def update(self, bbox: np.ndarray) -> None:"""使用观测到的边界框更新状态。Args:bbox (np.ndarray): 观测框,格式 [x1, y1, x2, y2]"""self.time_since_update = 0self.history = []self.hits += 1self.hit_streak += 1self.kf.update(convert_bbox_to_z(bbox))def predict(self) -> np.ndarray:"""预测下一帧的状态并返回边界框估计。Returns:np.ndarray: 预测的边界框,格式 [x1, y1, x2, y2]"""if (self.kf.x[6] + self.kf.x[2]) <= 0:self.kf.x[6] *= 0.0self.kf.predict()self.age += 1if self.time_since_update > 0:self.hit_streak = 0self.time_since_update += 1self.history.append(convert_x_to_bbox(self.kf.x))return self.history[-1]def get_state(self) -> np.ndarray:"""获取当前边界框估计。Returns:np.ndarray: 当前边界框,格式 [x1, y1, x2, y2]"""return convert_x_to_bbox(self.kf.x)def associate_detections_to_trackers(detections: np.ndarray,trackers: np.ndarray,iou_threshold: float = 0.3
) -> Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:"""将检测框与跟踪框进行关联匹配。Args:detections (np.ndarray): 检测框,形状 (N, 4),格式 [x1, y1, x2, y2]trackers (np.ndarray): 跟踪框,形状 (M, 4),格式 [x1, y1, x2, y2]iou_threshold (float): IoU 阈值Returns:Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:- 匹配成功的矩阵,形状 (K, 2),格式 [det_idx, trk_idx]- 未匹配的检测框索引,形状 (L,)- 未匹配的跟踪框索引,形状 (M,)"""if len(trackers) == 0 or len(detections) == 0:return (np.empty((0, 2), dtype=int),np.arange(len(detections)),np.arange(len(trackers)))iou_matrix = iou_batch(detections, trackers)result = linear_sum_assignment(-iou_matrix)matched_indices = np.array(list(zip(*result)))unmatched_detections = [d for d in range(len(detections)) if d not in matched_indices[:, 0]]unmatched_trackers = [t for t in range(len(trackers)) if t not in matched_indices[:, 1]]matches = []for m in matched_indices:if iou_matrix[m[0], m[1]] < iou_threshold:unmatched_detections.append(m[0])unmatched_trackers.append(m[1])else:matches.append(m.reshape(1, 2))matches = np.concatenate(matches, axis=0) if matches else np.empty((0, 2), dtype=int)return matches, np.array(unmatched_detections), np.array(unmatched_trackers)class Sort:"""多目标跟踪器,基于 SORT 算法"""def __init__(self, max_age: int = 1, min_hits: int = 3, iou_threshold: float = 0.3):"""初始化 SORT 跟踪器。Args:max_age (int): 最大未检测帧数,超过后删除跟踪器min_hits (int): 最小命中次数,低于此值不输出(除非刚开始)iou_threshold (float): IoU 匹配阈值"""self.max_age = max_ageself.min_hits = min_hitsself.iou_threshold = iou_thresholdself.trackers = []self.frame_count = 0def update(self, dets: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:"""更新跟踪器状态并返回当前帧的跟踪结果。Args:dets (np.ndarray): 检测框,形状 (N, 5),格式 [x1, y1, x2, y2, score]Returns:np.ndarray: 跟踪结果,形状 (M, 5),格式 [x1, y1, x2, y2, id]Raises:ValueError: 如果检测框格式错误"""if dets is None or dets.size == 0:return np.empty((0, 5))if dets.shape[1] != 5:raise ValueError("Detections must have shape (N, 5)")self.frame_count += 1trks = np.zeros((len(self.trackers), 5))to_del = []for t, trk in enumerate(self.trackers):pos = trk.predict()[0]trks[t, :4] = posif np.any(np.isnan(pos)):to_del.append(t)trks = np.ma.compress_rows(np.ma.masked_invalid(trks))matched, unmatched_dets, unmatched_trks = associate_detections_to_trackers(dets[:, :4], trks[:, :4], self.iou_threshold)for t, trk in enumerate(self.trackers):if t not in unmatched_trks:d = matched[matched[:, 1] == t, 0][0]trk.update(dets[d, :4])for i in unmatched_dets:self.trackers.append(KalmanBoxTracker(dets[i, :4]))ret = []i = len(self.trackers) - 1while i >= 0:trk = self.trackers[i]d = trk.get_state()[0]if (trk.time_since_update < 1) and (trk.hit_streak >= self.min_hits or self.frame_count <= self.min_hits):ret.append(np.concatenate((d, [trk.id + 1])))if trk.time_since_update > self.max_age:self.trackers.pop(i)i -= 1return np.array(ret) if ret else np.empty((0, 5))# 示例使用
if __name__ == "__main__":tracker = Sort(max_age=1, min_hits=3, iou_threshold=0.3)dets = np.array([[100, 100, 150, 150, 0.9], [200, 200, 250, 250, 0.8]])tracks = tracker.update(dets)print("Tracks:\n", tracks)yolov8 追踪
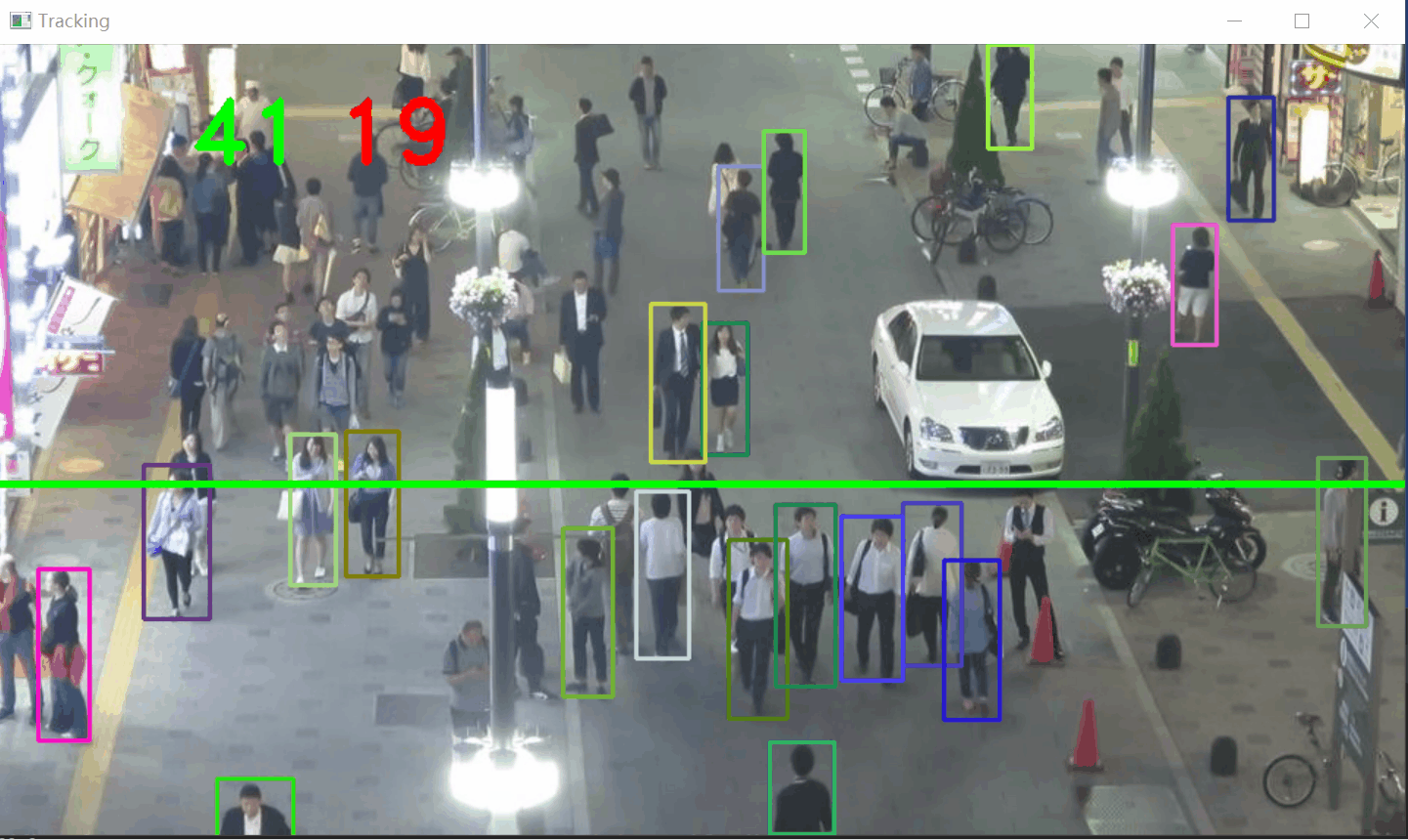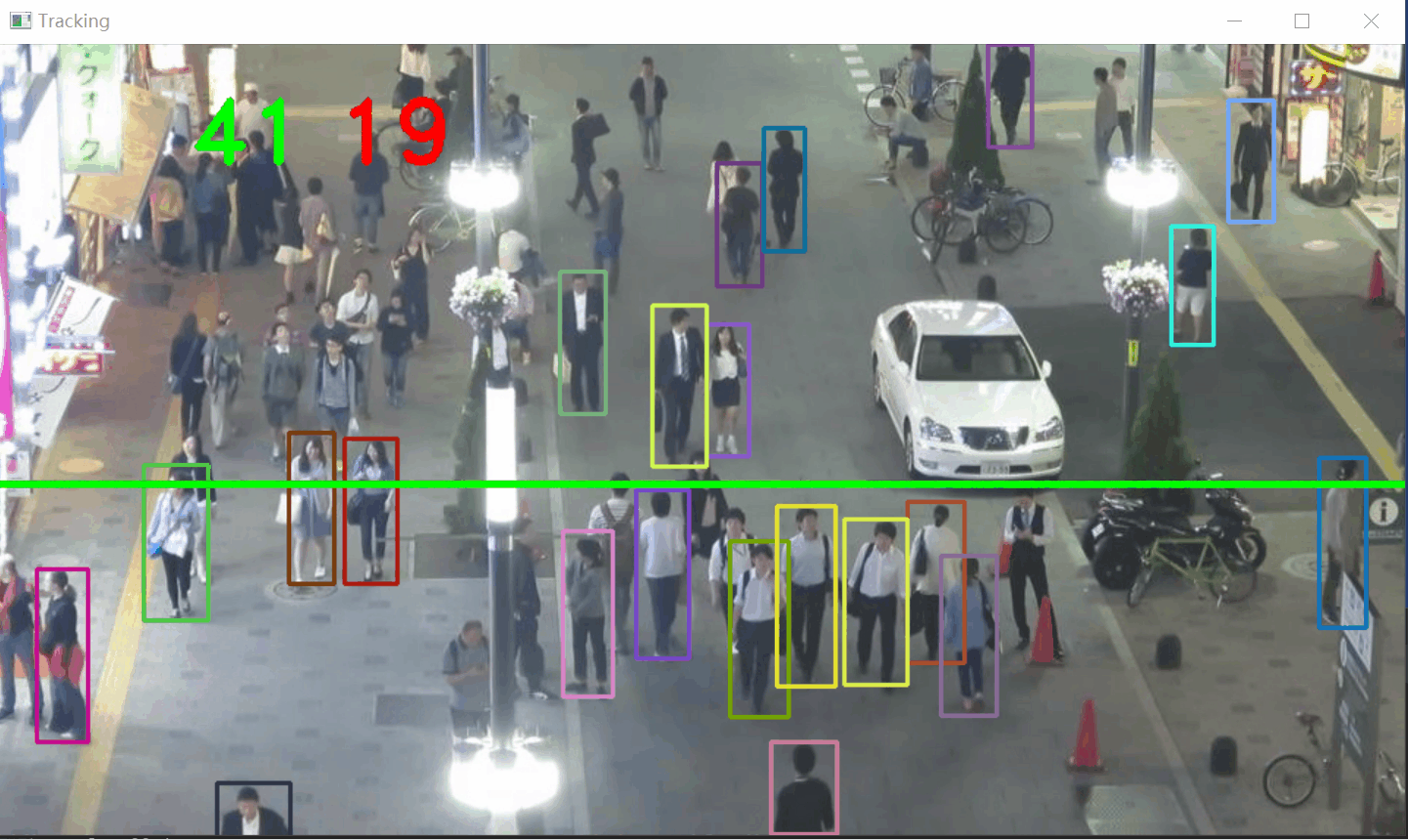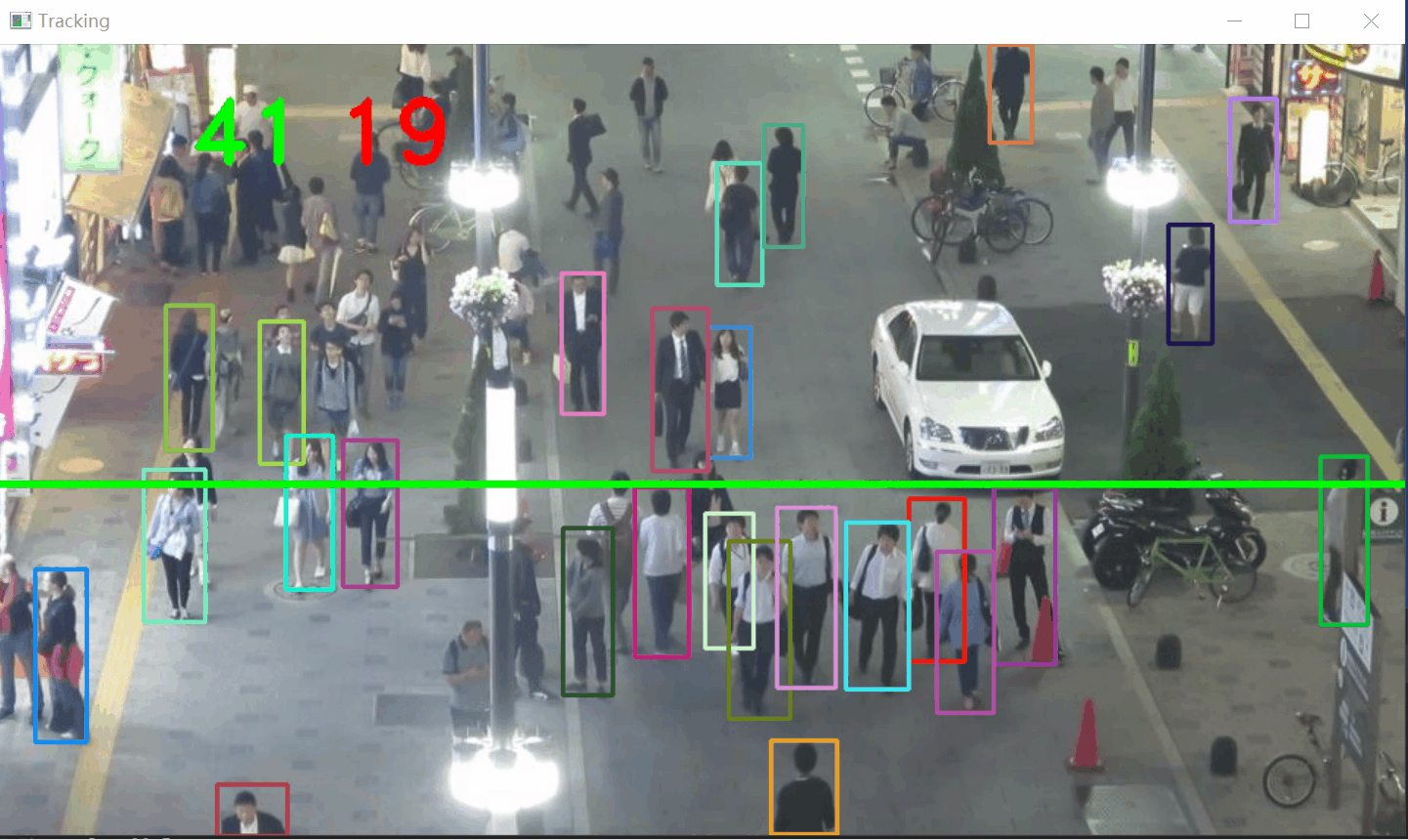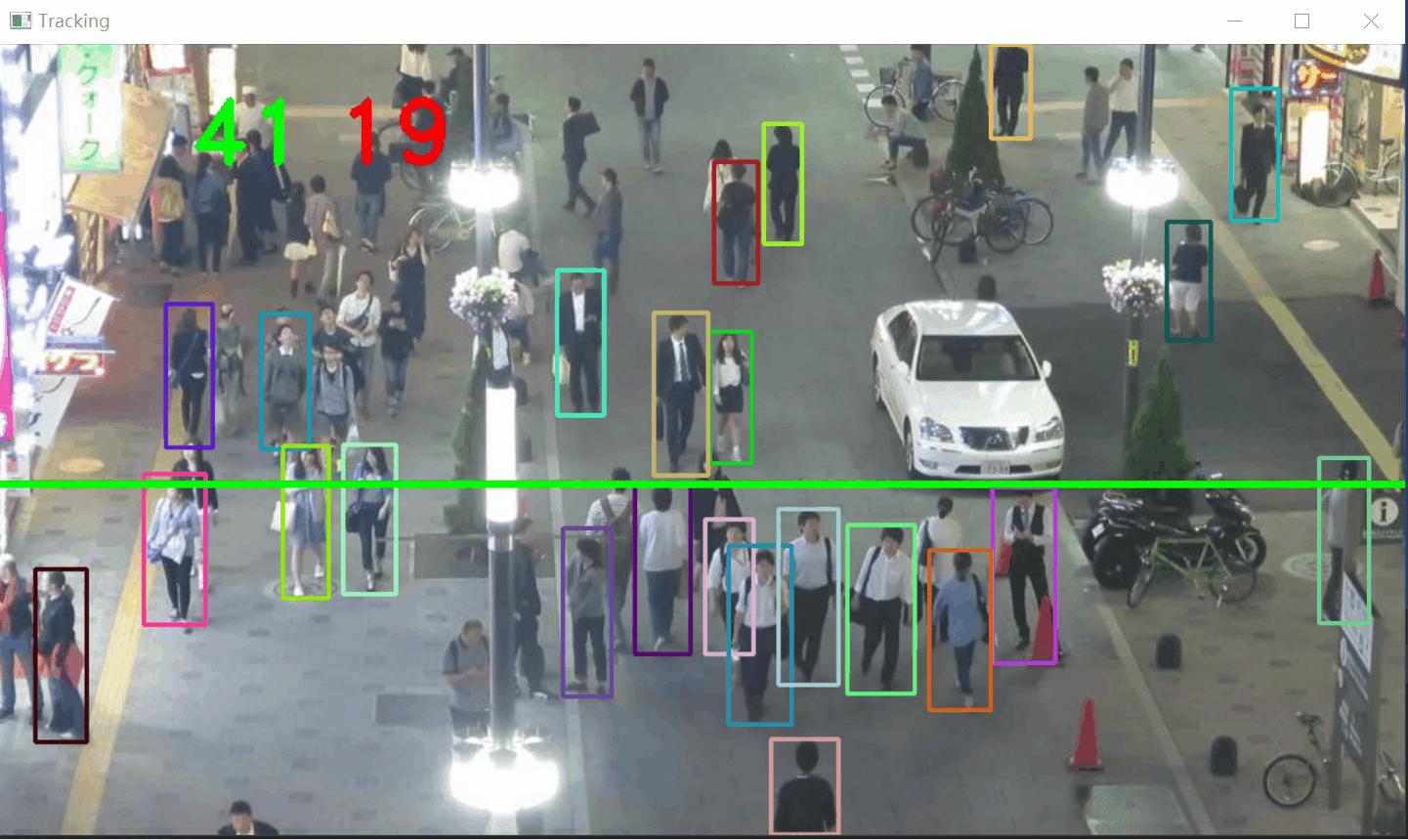
从视频中检测行人(使用 YOLOv8),跟踪他们的运动轨迹(使用 SORT 算法),并通过一条计数线计算行人穿越的数量和方向。
步骤:
- 加载视频和 YOLOv8 模型:读取视频帧并初始化 YOLOv8 模型。
- 目标检测:使用 YOLOv8 检测视频帧中的行人,获取检测框。
- 目标跟踪:使用 SORT 算法(基于卡尔曼滤波和 IoU 匹配)跟踪检测到的行人。
- 轨迹分析:通过轨迹和计数线的碰撞检测,统计行人穿越数量和方向。
碰撞检测函数
def ccw(A, B, C):return (C[1] - A[1]) * (B[0] - A[0]) > (B[1] - A[1]) * (C[0] - A[0])def intersect(A, B, C, D):return ccw(A, C, D) != ccw(B, C, D) and ccw(A, B, C) != ccw(A, B, D)- ccw:计算三点 A, B, C 是否按逆时针方向排列,用于判断线段是否相交。
- intersect:判断两条线段 AB 和 CD 是否相交。这里用于检测目标轨迹(从上一帧位置到当前帧位置的线段)是否与计数线相交。
目标跟踪(SORT)
np.set_printoptions(formatter={'float': lambda x: "{0:0.3f}".format(x)})
dets = np.asarray(dets)if np.size(dets) == 0:continue
else:tracks = tracker.update(dets)- 格式化:dets 转换为 NumPy 数组,SORT 算法需要此格式。
- 空检测处理:如果当前帧没有检测到目标,则跳过。
- tracker.update(dets):调用 SORT 算法更新跟踪器,返回当前帧的跟踪结果 tracks,格式为 [x1, y1, x2, y2, id]。
跟踪框处理
boxes = []
indexIDs = []
previous = memory.copy()
memory = {}COLORS = np.random.randint(0, 255, size=(200, 3), dtype='uint8')for track in tracks:boxes.append([track[0], track[1], track[2], track[3]])indexIDs.append(int(track[4]))memory[indexIDs[-1]] = boxes[-1]- boxes 和 indexIDs:从 tracks 中提取边界框和目标 ID。
- previous 和 memory:memory 存储当前帧的目标位置,previous 存储上一帧的目标位置,用于轨迹计算。
- COLORS:生成随机颜色,用于可视化不同目标的跟踪框。
碰撞检测和计数
if len(boxes) > 0:i = 0for box in boxes:(x, y) = (int(box[0]), int(box[1]))(w, h) = (int(box[2]), int(box[3]))color = [int(c) for c in COLORS[indexIDs[i] % len(COLORS)]]cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (w, h), color, 2)if indexIDs[i] in previous:previous_box = previous[indexIDs[i]](x2, y2) = (int(previous_box[0]), int(previous_box[1]))(w2, h2) = (int(previous_box[2]), int(previous_box[3]))p1 = (int(x2 + (w2 - x2) / 2), int(y2 + (h2 - y2) / 2))p0 = (int(x + (w - x) / 2), int(y + (h - y) / 2))if intersect(p0, p1, line[0], line[1]):counter += 1if y2 > y:counter_down += 1else:counter_up += 1i += 1- 绘制跟踪框:为每个目标绘制矩形框,颜色根据目标 ID 分配。
- 轨迹计算:
- p0:当前帧目标的中心点 (x + (w - x) / 2, y + (h - y) / 2)。
- p1:上一帧目标的中心点。
- 碰撞检测:
- 使用 intersect 函数判断目标轨迹(p0 到 p1)是否与计数线(line[0] 到 line[1])相交。
- 如果相交,counter 增加 1。
- 方向判断:
- 如果 y2 > y(上一帧 y 坐标大于当前帧 y 坐标),目标向下移动,counter_down 增加 1。
- 否则,目标向上移动,counter_up 增加 1。
yolov8_count.py 完成代码
from ultralytics import YOLO
import imutils
import time
import cv2
from kalman8 import *line = [(0, 300), (2560, 300)]
counter = 0
counter_up = 0
counter_down = 0# 创建跟踪器对象(假设你有 Sort 实现)
tracker = Sort()
memory = {}# 碰撞检测函数保持不变
def ccw(A, B, C):return (C[1] - A[1]) * (B[0] - A[0]) > (B[1] - A[1]) * (C[0] - A[0])def intersect(A, B, C, D):return ccw(A, C, D) != ccw(B, C, D) and ccw(A, B, C) != ccw(A, B, D)# 加载 YOLOv8 模型
model = YOLO("./yolov8/yolov8n.pt")# 视频输入
vs = cv2.VideoCapture('./input/MOT16-03.mp4')
(W, H) = (None, None)
writer = Nonetry:prop = cv2.cv.CV_CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNT if imutils.is_cv2() else cv2.CAP_PROP_FRAME_COUNTtotal = int(vs.get(prop))print("INFO:{} total Frame in video".format(total))
except:print("[INFO] could not determine frames in video")# 主循环
while True:(grabbed, frame) = vs.read()if not grabbed:breakif W is None or H is None:(H, W) = frame.shape[:2]# 使用 YOLOv8 进行目标检测start = time.time()results = model(frame) # YOLOv8 直接接受帧输入end = time.time()# 处理检测结果boxes = []confidences = []classIDs = []dets = []# 解析 YOLOv8 的结果for result in results:for box in result.boxes:confidence = box.conf.item() # 置信度if confidence > 0.3:classID = int(box.cls.item()) # 类别ID# YOLOv8 返回的 xyxy 格式x, y, w, h = box.xyxy[0].tolist()x, y, w, h = int(x), int(y), int(w), int(h)# 只检测 "person" 类 (COCO 数据集中 person 的 ID 是 0)if model.names[classID] == "person":boxes.append([x, y, w - x, h - y])confidences.append(float(confidence))classIDs.append(classID)dets.append([x, y, w, h, confidence])# 转换为 numpy 数组np.set_printoptions(formatter={'float': lambda x: "{0:0.3f}".format(x)})dets = np.asarray(dets)# SORT 目标跟踪if np.size(dets) == 0:continueelse:tracks = tracker.update(dets)# 跟踪框处理boxes = []indexIDs = []previous = memory.copy()memory = {}COLORS = np.random.randint(0, 255, size=(200, 3), dtype='uint8')for track in tracks:boxes.append([track[0], track[1], track[2], track[3]])indexIDs.append(int(track[4]))memory[indexIDs[-1]] = boxes[-1]# 碰撞检测if len(boxes) > 0:i = 0for box in boxes:(x, y) = (int(box[0]), int(box[1]))(w, h) = (int(box[2]), int(box[3]))color = [int(c) for c in COLORS[indexIDs[i] % len(COLORS)]]cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (w, h), color, 2)if indexIDs[i] in previous:previous_box = previous[indexIDs[i]](x2, y2) = (int(previous_box[0]), int(previous_box[1]))(w2, h2) = (int(previous_box[2]), int(previous_box[3]))p1 = (int(x2 + (w2 - x2) / 2), int(y2 + (h2 - y2) / 2))p0 = (int(x + (w - x) / 2), int(y + (h - y) / 2))if intersect(p0, p1, line[0], line[1]):counter += 1if y2 > y:counter_down += 1else:counter_up += 1i += 1# 绘制计数线和文本cv2.line(frame, line[0], line[1], (0, 255, 0), 3)cv2.putText(frame, str(counter_up), (130, 80), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, 2.0, (0, 255, 0), 3)cv2.putText(frame, str(counter_down), (230, 80), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, 2.0, (0, 0, 255), 3)# 保存视频if writer is None:fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*"mp4v")writer = cv2.VideoWriter("./output/output.mp4", fourcc, 30, (frame.shape[1], frame.shape[0]), True)writer.write(frame)cv2.imshow("Tracking", frame)if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):break# 释放资源
writer.release()
vs.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()测试效果
测试下上行人流和下行人流统计

日志输出
0: 384x640 26 persons, 1 car, 1 motorcycle, 100.7ms
Speed: 2.3ms preprocess, 100.7ms inference, 2.5ms postprocess per image at shape (1, 3, 384, 640)0: 384x640 26 persons, 1 car, 1 motorcycle, 97.7ms
Speed: 2.5ms preprocess, 97.7ms inference, 1.9ms postprocess per image at shape (1, 3, 384, 640)0: 384x640 26 persons, 1 car, 1 motorcycle, 102.8ms
Speed: 2.2ms preprocess, 102.8ms inference, 2.6ms postprocess per image at shape (1, 3, 384, 640)...