辽宁烟草电子商务网站可以发外链的网站整理
C. Phase Shift
题目:
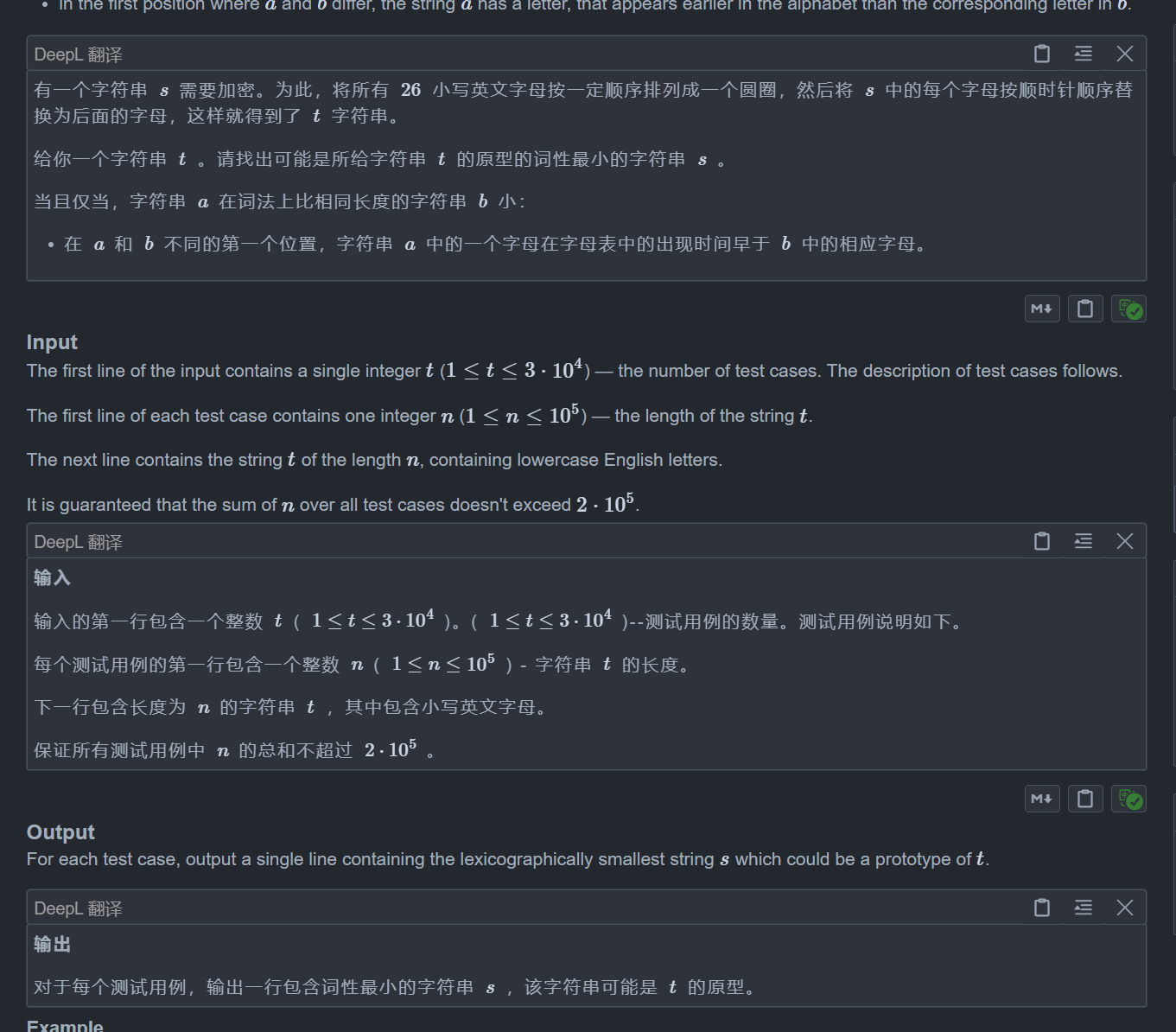
思路:
好题,值得多看
这题我们看题目就能想到一个很显然的做法,那就是贪心地把每一个字母换成最前面的没使用过的字母
但是这样直接写是有问题的,因为题目说了最后要让所有的字母成一个换,比如如果是ba,如果我们换成ab,那么就会有一个a->b->a的环了,这显然不符合题意
所以对于每一个还未替换的字符,我们从a~z中选一个最先的最符合的字符,他要满足以下条件:
①.这个字符还没选过
②.这个字符不与现在这个字符相同
③.选完之后不能构成环,如果构成了,那只能是构成长度为26的环
确定好后按照题意模拟即可
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cctype>
#include<string>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <stack>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES\n"
#define no cout << "NO\n"bool check(char a, char b,const map<char, char>& mp2)
{vector<int> vis(26, 0);map<char, char> mp = mp2;mp[a] = b;int hasc = 0;int ccnt = 0;while (mp[a]){if (vis[a - 'a']){hasc = true;break;}vis[a - 'a'] = 1;ccnt++;a = mp[a];}if (hasc && ccnt < 26){return false;}return true;
}void solve()
{int n;cin >> n;string s;cin >> s;map<char, char> mp;vector<bool> used(26, 0);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){if (mp[s[i]]){continue;}else{for (int j = 0; j < 26; j++){int t = 'a' + j;if (used[j] || s[i] == t){continue;}if (check(s[i], t, mp)){used[j] = true;mp[s[i]] = t;break;}}}}for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){cout << mp[s[i]];}cout << endl;
}signed main()
{cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(false);int t = 1;cin >> t;while (t--){solve();}return 0;
}B. Playing with GCD
题目:
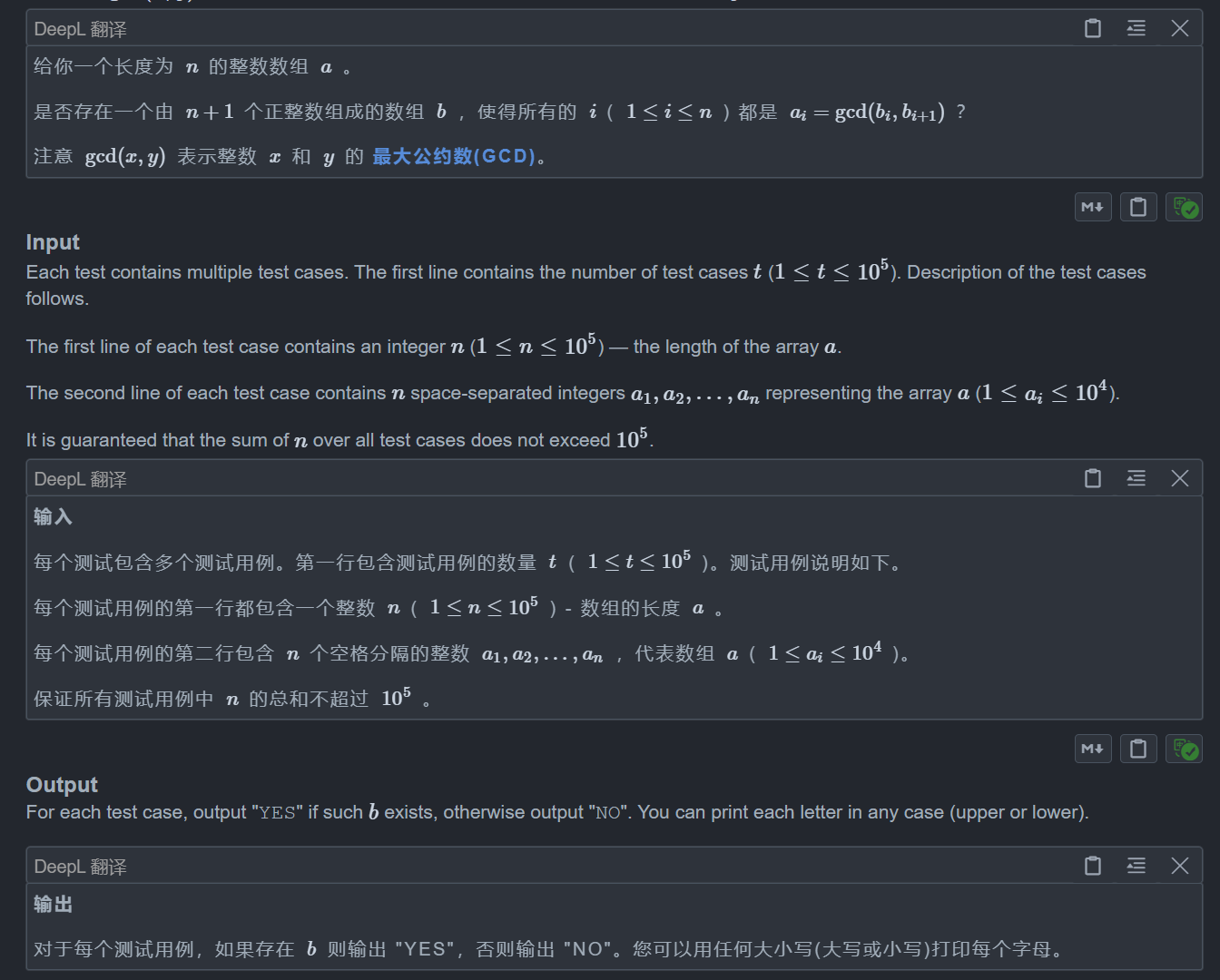
思路:
想难了,不过挺不错的
一个显然的构造方法是 b[i] 取a[i] 和 a[i-1] 的lcm,因为我们要保证 gcd 恰好等于 a[i],所以最大只能取这个,同时 b[i] 与两个 a 都有关系,所以也只能这样取,否则如果是k*lcm,那么就会多个系数,这样最后可能就不会等于 a[i] 了
最后我们再检查一下 b[i] 是不是真的都符合即可
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cctype>
#include<string>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <stack>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES\n"
#define no cout << "NO\n"int gcd(int a, int b)
{return !b ? a : gcd(b, a % b);
}int lcm(int a,int b)
{return a * b / gcd(a, b);
}void solve()
{int n;cin >> n;vector<int> a(n+2,1),b(n+2,1);for (int i = 1; i <= n+1; i++){if(i <= n)cin >> a[i];b[i] = lcm(a[i], a[i - 1]);}for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){if (gcd(b[i],b[i+1]) != a[i]) {no;return;}}yes;
}signed main()
{cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(false);int t = 1;cin >> t;while (t--){solve();}return 0;
}C1. Good Subarrays (Easy Version)
题目:
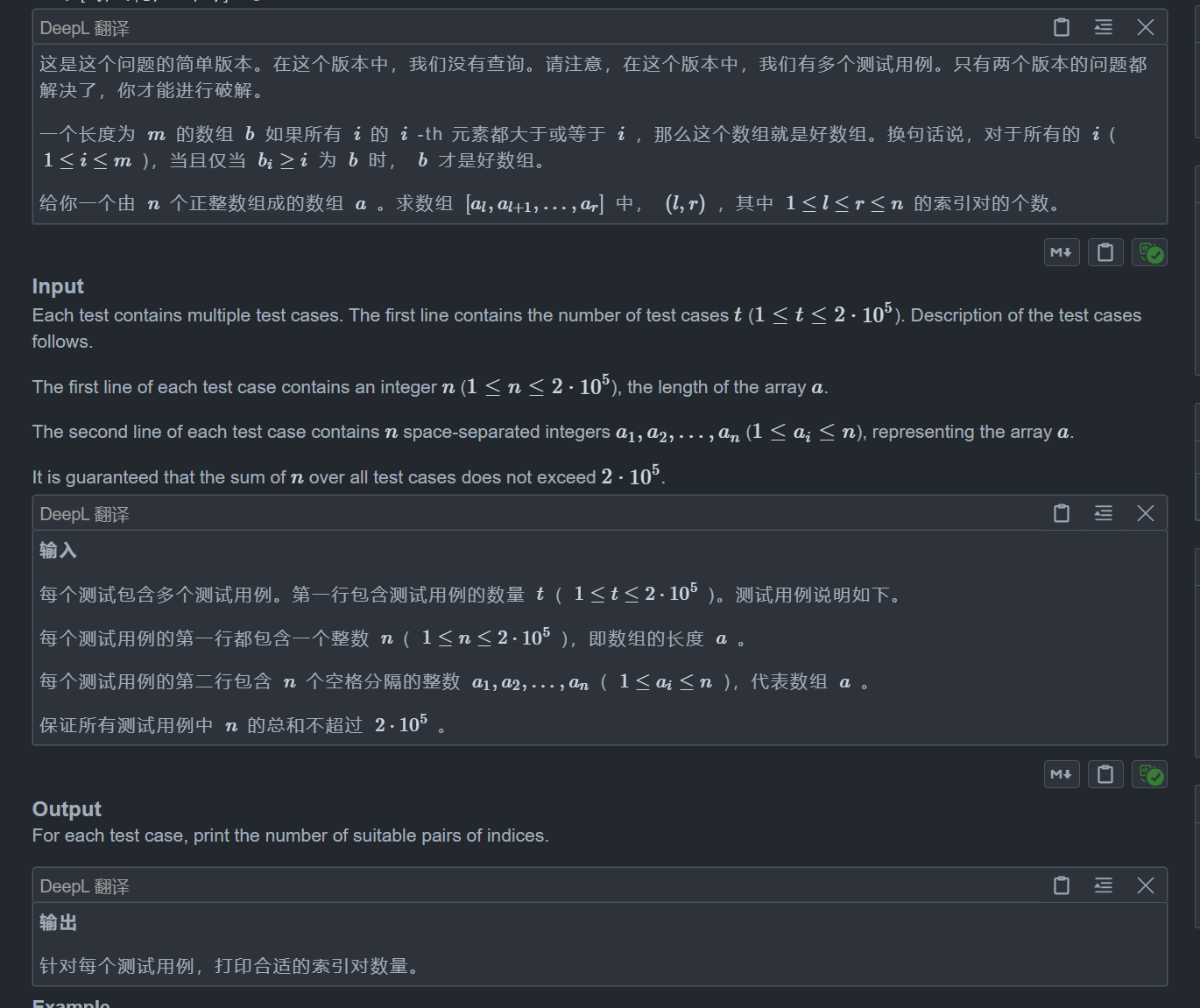
思路:
双指针题
这道题由于求的是一个区间l~r,那么我们就可以来观察一下这个区间有没有什么特性
一个显然的特性是,如果l~r符合,那么l+1~r肯定也符合
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cctype>
#include<string>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <cmath>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_set>
#include <map>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <stack>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define yes cout << "YES\n"
#define no cout << "NO\n"void solve()
{int n;cin >> n;vector<int> a(n);for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){cin >> a[i];}int l = 0, r = 0,res = 0;while (l < n){while (r < n && a[r] >= r-l+1){r++;}res += r - l;l++;}cout << res << endl;
}signed main()
{cin.tie(0)->sync_with_stdio(false);int t = 1;cin >> t;while (t--){solve();}return 0;
}