佛山做网站的哪个好seo网络科技有限公司
目录
进程
1.1 进程概念
1.2 查看进程
1.2.1 Windows 任务管理器
1.2.2 Linux 终端指令
1.3 进程的特点(理解)
1.4 进程的资源分配(理解)
1.5 进程的状态(记住)
1.6 进程管理--PID
1.7 进程间关系(重点)
1.8 函数名:getpid()
1.9 函数名:getppid()
1.10 创建进程
1.10.1 函数名:fork() (重点*****)
1.10.2 函数名:vfork()
1.11 结束进程
1.11.1 函数名:_exit()
1.11.2 函数名:exit()
1.12 特殊进程:
1.13 等待进程
1.13.1 函数名:wait()
1.13.2 函数名:waitpid()
1.14 进程调用
1.14.1 函数名:system()
1.14.2 exec 函数族性质
1.14.3 函数名:execl()
1.14.4 函数名:execlp()
1.14.5 函数名:glob()
安装 mpg123
1. 读取目录中所有文件名 子级目录中的文件名也要显示出来 递归方法比较简单
2. 实现 ls 主函数传参 ./a.out -l ls 只能查看可见文件 ls -a ls -l 文件类型 文件名
3. 写一个程序,实现日志保存功能,要求程序每隔 3 秒,创建一个以当前时间命名的文件,并在文件中保存一个数字,数字代表该文件是程序运行起来后的创建的第几个文件
20250402115009.log --->1
操作满足以下要求: 在目录中最多保存 10 个日志文件,如果有新的文件需要创建,则删除最老的文件,保证目录中最多只能有 10 个文件
进程
1.1 进程概念
代码:编程语言编写的内容
程序:有主函数且编译通过,生成的可执行文件(静态),硬盘中存储
进程:运行状态下的程序(动态),内存中运行
1.2 查看进程
1.2.1 Windows 任务管理器

1.2.2 Linux 终端指令
ps ps -ef ps -aux top
1.3 进程的特点(理解)
动态性:进程的实质是一次程序运行的过程,进程是动态产生动态消亡的
并发性:任何进程都可以和其他进程一起并发执行
独立性:进程是一个能独立运行的基本单位,同时也是系统分配资源和调度的基本单位
异步性:进程的执行具有间断性,多个进程间按照各自独立的不可预知的速度向下运行
1.4 进程的资源分配(理解)
系统会给每个进程开辟 4G 的虚拟内存
3G 用户内存+1G 的内核内存
堆:手动开辟
栈:局部变量
数据段:全局变量和静态变量
未初始化数据段:默认值为 0
初始化数据段:会初始化设置的初始值
文本段:常量和代码
1.5 进程的状态(记住)
执行态:进程正在占用 CPU(CPU 正在执行该进程)
就绪态:进程已经满足被 CPU 分配时间片的条件(可以被 CPU 执行),在等待 CPU 给他分配时间片
等待态:进程没有满足被 CPU 分配时间片的条件,需要等到条件满足 CPU 才会给它分配时间片

1.6 进程管理--PID
一般情况下都是通过进程的 PID 号来操作进程
1.7 进程间关系(重点)
父子关系:进程 2 是由进程 1 创建的,那么进程 1 就是进程 2 的父进程,进程 2 就是进程 1 的子进程。
进程间有且只有父子关系
1.8 函数名:getpid()
头文件:#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
函数原型:pid_t getpid(void);
函数功能:获取进程 pid
函数参数:无
函数返回值:返回 PID 号
函数使用:
1.9 函数名:getppid()
头文件:#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
函数原型:pid_t getppid(void);
函数功能:获取父进程 pid
函数参数:无
函数返回值:获取的 PPID
函数使用:
1.10 创建进程
方法一:直接运行可执行程序
方法二:在程序中去调用进程创建函数去创建进程--fork、vfork。
1.10.1 函数名:fork() (重点*****)
子进程复制父进程资源,然后和父进程从同一位置向下运行,执行的先后关系不确定
头文件:#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
函数原型:pid_t fork(void);
函数功能:创建子进程
函数参数:无
函数返回值:-1 代表子进程创建失败,0 代表子进程,大于 0 代表父进程
函数使用:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <glob.h>
int Print(void);
int main()
{int a = 0;glob_t gl = {0};pid_t pid = fork();if(pid==0){a+=5;printf("B:a=%d\n",a); // 5exit(0);}else if(pid>0){printf("A:a=%d\n",a); // 0}return 0;
} 1.10.2 函数名:vfork()
子进程占用父进程资源,然后子进程先使用资源执行,子进程结束后,父进程才能使用资源
头文件:#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
函数原型:pid_t vfork(void);
函数功能:创建子进程,返回子进程 PID
函数参数:无
函数返回值:父进程返回子进程 PID 子进程返回 0
函数使用:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <glob.h>
int Print(void);
int main()
{int a = 0;glob_t gl = {0};pid_t pid = vfork();if(pid==0){a+=5;printf("B:a=%d\n",a); // 5exit(0);}else if(pid>0){printf("A:a=%d\n",a); //5}return 0;
} 1.11 结束进程
方法一:外部信号
在终端 ctrl+c 可以结束进程
在终端输入:kill -9 PID 可以结束进程
ps -ef | grep "./a.out"
方法二:内部程序
1. main()中调用 return
2. 进程退出函数--- exit()、_exit()
1.11.1 函数名:_exit()
头文件:#include <unistd.h>
函数原型:void _exit(int status);
函数功能:退出进程,不清空缓冲区
函数参数:获取进程退出时的状态 一般填 0
函数返回值:无
函数使用: _exit(0);
1.11.2 函数名:exit()
头文件:#include <stdlib.h>
函数原型:void exit(int status);
函数功能:退出进程,清空缓冲区
函数参数:获取进程退出时的状态 一般填 0
函数返回值:无
函数使用: exit(0);
1.12 特殊进程:
了解:
0 号进程:操作系统启动的引导程序 祖先进程
1 号进程:操作系统启动的第一个程序
掌握:
孤儿进程: 父进程死了,子进程还在运行。孤儿进程会被系统中设置好的一个进程收养,并且等孤儿进程死了之后给它收尸
僵尸进程: 子进程死了,父进程没有给自己去收尸。这个时候子进程就会变成一个僵尸进程,僵尸进程所占用的资源基本上会被完全释放,除了它所占用的进程号。父进程在退出之前,一定会给所有的僵尸进程收 尸。但是有些工程中的父进程需要长时间不停机运行,会导致僵尸进程的资源无法得到及时的回收处理。所以咱们在编写代码的过程中,一定要尽量避免僵尸进程的产生。
可以通过在父进程中调用,下面的进程的等待函数来避免僵尸进程的产生。

1.13 等待进程
1.13.1 函数名:wait()
头文件:#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
函数原型:pid_t wait(int *wstatus);
函数功能:阻塞,等待任意子进程结束
函数参数:进程结束状态 一般填 NULL
函数返回值:返回结束的子进程 pid
函数使用:
1.13.2 函数名:waitpid()
头文件:#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
函数原型:pid_t waitpid(pid_t pid, int *wstatus, int options);
函数功能:等待,子进程结束
函数参数:
pid:
负数:进程组号(进程的 PID 的绝对值)
0:当前进程组中任意子进程
正数:指定的进程号 PID
<0 任意子进程
0 进程组中的任意子进程
>0 等待的子进程 pid
wstatus:保存子进程的退出状态,一般填 NULL
options:
WNOHANG:非阻塞,等待子进程结束
0:阻塞,等待子进程结束
函数返回值:返回结束的子进程 pid,非阻塞情况下子进程未结束返回-1
函数使用: wait(NULL) == waitpid(0,NULL,0);
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
int Print(void);
int main()
{int a = 0;pid_t pid = fork();if(pid==0){printf("B:%d\n",getpid());printf("B:A:%d\n",getppid());a+=5;printf("B:a=%d\n",a);}else if(pid>0){//wait(NULL);//waitpid(0,NULL,0);//waitpid(pid,NULL,0);waitpid(pid,NULL,WNOHANG);printf("A:a=%d\n",a);Print();printf("A end!!!\n");}return 0;
}
int Print(void)
{printf("A:%d\n",getpid());//_exit(0);exit(0);return 0;
} 1.14 进程调用
1.14.1 函数名:system()
头文件:#include <stdlib.h>
函数原型:int system(const char *command);
函数功能:在一个进程中调用系统指令
函数参数:系统指令的字符串形式 “clear”
函数返回值:成功返回 0,失败返回-1
函数使用:
1.14.2 exec 函数族性质
system()执行完成之后,会继续执行进程剩余内容
exec 函数族在原进程中调用另一个进程执行指令
执行完成之后,不会继续执行原进程剩余内容
int execl(const char *pathname, const char *arg, ... * (char *) NULL */);
int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg, ... * (char *) NULL */);
int execle(const char *pathname, const char *arg, ... *, (char *) NULL, char *const envp[] */);
int execv(const char *pathname, char *const argv[]);
int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]);
int execvpe(const char *file, char *const argv[],char *const envp[]);
1.14.3 函数名:execl()
头文件:#include <unistd.h>
函数原型:int execl(const char *pathname, const char *arg, ... * (char *) NULL */);
函数功能:调用进程
函数参数:
const char *pathname:路径+可执行程序
const char *arg, ...:指令,其他参数
函数返回值:错误返回-1,错误码
函数使用:
1.14.4 函数名:execlp()
头文件:#include <unistd.h>
函数原型:int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg, ... * (char *) NULL */);
函数功能:调用进程
函数参数:
const char * file:可执行程序
const char *arg, ...:指令,其他参数
函数返回值:错误返回-1,错误码
函数使用:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <glob.h>
int Print(void);
int main()
{int a = 0;pid_t pid = vfork();if(pid==0){system("clear");//execl("/usr/bin/ls","ls","-a",NULL);//execlp("ls","ls","-a",NULL);execlp("ls","ls","./log","-a",NULL);printf("B:end!!!\n");exit(0);}else if(pid>0){//wait(NULL);system("ls -a");}return 0;
}1.14.5 函数名:glob()
头文件:#include <glob.h>
函数原型:int glob(const char *pattern,
int flags,
int (*errfunc) (const char *epath, int eerrno),
glob_t *pglob);
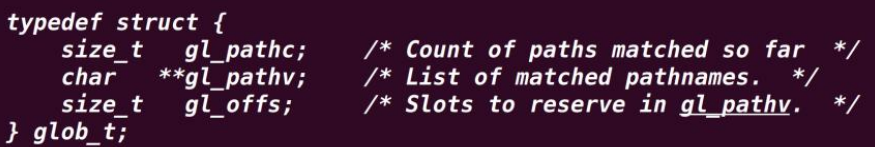
函数功能:在指定路径下查找指定格式的文件并保存信息
函数参数:
const char *pattern:文件格式 “./*.mp3”
int flags:0
int (*errfunc) (const char *epath, int eerrno):NULL
glob_t *pglob:保存信息的结构体地址
函数返回值:成功返回 0
函数使用:
安装 mpg123
sudo apt-get install mpg123
使用: mpg123 歌曲名
退出: q
测试并分析代码执行结果为什么是这样
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/wait.h>
#include <glob.h>
int main()
{fork();fork();fork();printf("hello\n");return 0;
} 
1. 读取目录中所有文件名 子级目录中的文件名也要显示出来 递归方法比较简单
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
//1. 读取目录中所有文件名 子级目录中的文件名也要显示出来 递归方法比较简单
void fun(char *path);int main(int argc, int *argv[])
{fun(argv[1]);return 0;
}void fun(char *path)
{DIR *dirp = NULL;dirp = opendir(path);struct dirent *dent = NULL;while(dent = readdir(dirp)){if((!strcmp(".",dent->d_name)) ||(!strcmp("..",dent->d_name))){continue;}if(dent->d_type == 8){char *p = dent->d_name;p += strlen(dent->d_name)-2;if(strcmp(".c", p) == 0){printf("%s\n", dent->d_name);}}else if(dent->d_type == 4){chdir(path);fun(dent->d_name);chdir("..");}}}2. 实现 ls 主函数传参 ./a.out -l ls 只能查看可见文件 ls -a ls -l 文件类型 文件名
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
// 0000 ls
// 0001 ls -a
// 0010 ls -l
// 0011 ls -al
//2. 实现 ls 主函数传参 ./a.out -l ls 只能查看可见文件 ls -a ls -l 文件类型 文件名
void fun(char *path, unsigned char flag);
unsigned char flag = 0;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{char *path = ".";for(int i = 1, j = 0; i < argc; i++){if(argv[i][j] == '-'){while(argv[i][j + 1]){if(argv[i][j + 1] == 'a'){flag |= 0x01 << 0;}else if(argv[i][j + 1] == 'l'){flag |= 0x01 << 1;}j++;}}else if(argv[i] != NULL){path = argv[i];printf("%s\n",argv[i]);}}fun(path, flag);return 0;
}void fun(char *path, unsigned char flag)
{DIR *dirp = opendir(path);struct dirent *dent = NULL;while(dent = readdir(dirp)){if((flag == 0x00) && dent->d_name[0] != '.'){printf("%s\t", dent->d_name);}else if(flag == 0x01){printf("%s\t", dent->d_name);}}printf("\n");
}
3. 写一个程序,实现日志保存功能,要求程序每隔 3 秒,创建一个以当前时间命名的文件,并在文件中保存一个数字,数字代表该文件是程序运行起来后的创建的第几个文件
20250402115009.log --->1
操作满足以下要求: 在目录中最多保存 10 个日志文件,如果有新的文件需要创建,则删除最老的文件,保证目录中最多只能有 10 个文件
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <dirent.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <glob.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>int n = 1;
void gettime(char * buf);
int log_remove(void);
int log_creat(void);int main()
{int s = 0;while(1){if(s % 3 == 0){log_remove();log_creat();}s++;sleep(1);//非阻塞}return 0;
}int log_creat(void)
{char filename[50] = {0};gettime(filename);int fd = open(filename, O_CREAT|O_WRONLY,0664);if(fd == -1){perror("open");return -1;}char data[10] = {0};sprintf(data, "%d", n);write(fd, data, strlen(data));close(fd);n++;return 0;
}void gettime(char *buf)
{time_t tm = time(0);struct tm *lm = localtime(&tm);sprintf(buf,"%04d%02d%02d%02d%02d%02d.log",lm->tm_year+1900,lm->tm_mon+1,lm->tm_mday,lm->tm_hour,lm->tm_min,lm->tm_sec);
}int log_remove(void)
{glob_t gl = {0};glob("*.log", 0, NULL, &gl);if(gl.gl_pathc >= 10){char *p = gl.gl_pathv[0];for(int i; i < gl.gl_pathc; i++){if(strcmp(p,gl.gl_pathv[i]) > 0){p = gl.gl_pathv[i];}}remove(p);}
}