中山网站建设公司优化大师下载旧版本安装
文章目录
- 什么是搜索引擎
- 项目目标
- 概念解析
- 模块划分
- 创建项目
- 关于分词
- 创建model包
- 实现索引模块
- 实现Index类
- 实现getDocInfo 和 getInverted
- 实现addDoc方法
- 实现buildForward方法
- 实现buildInverted方法
- 关于buildForward和buildInverted为什么有些代码有进行加锁
- 实现save方法
- 实现load方法
- 实现Parser类
- 实现enumFile方法
- 实现parseHTML方法
- 实现parseTitle方法
- 实现parseURL方法
- 实现parseContentByRegex方法
- 实现搜索模块
- 实现loadStopWords方法
- 实现searcher方法
- 实现mergeResult方法
- 实现getDesc方法
- 实现 web模块
什么是搜索引擎
像百度,搜狗这种搜索一个关键词,然后在结果页中展示若干条结果,每一个结果中, 又包含了图标, 标题, 描述, 展示url, 时间, 子链, 图片等;当然像这种搜索引擎属于全站搜索,这个项目是要实现站内搜索(只针对某个网站内部进行搜索)。
项目目标
实现一个 Java API 文档的简单的搜索引擎.
关于Java API 文档的获取我们直接从官网下载离线版本即可
下载版本参见 https://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/javase/downloads/index.html
下载之后看到一个 docs 目录, 里面存在一个 api 目录. 这里的 html 就和线上版本的文档是一一对应的.
下载的文档假设放在D:\doc_searcher_index\jdk-8u361-docs-all 目录中.
概念解析
- 文档(document):指的是每个待搜索的网页
- 正排索引:指的是通过文档id找到文档内容
- 倒排索引:指的是通过词找到文档id列表
举个例子,1号文档的内容是“小明去买苹果手机”;2号文档的内容是“小明去买4斤苹果”
正排索引:
1:小明去买苹果手机
2:小明去买4斤苹果
倒排索引:
小明:1,2
去:1,2
买:1,2
苹果:1,2
手机:1
4斤:1
模块划分
- 索引模块
1)扫描下载到的文档,分析文档的内容,构建出正排索引和倒排索引,并把索引内容保存到文件中
2)加载制作好的索引,并提供一些API实现查正排和查倒排这样的功能
- 搜索模块
调用索引模块,实现一个搜索的完整过程
输入:用户的查询词
输出:完整的搜索结果(包含了很多条记录,每个记录就有标题,描述,展示URL,并且能点击页面进行跳转)
- web模块:包含前端和后端(需要实现一个简单的web程序,能够通过网页的形式来和用户进行交互)
创建项目
使用IDEA创建一个spring boot项目
引入本项目所需要的依赖,列举几个比较重要的依赖:
json依赖
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.fasterxml.jackson.core/jackson-databind --><dependency><groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId><artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId><version>2.14.2</version></dependency>
ansj依赖(现成的分词库)
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.ansj/ansj_seg --><dependency><groupId>org.ansj</groupId><artifactId>ansj_seg</artifactId><version>5.1.6</version></dependency>
关于分词
用户输入查询词,我们不可能整个查询词直接拿去搜索,而是将查询词进行分词,然后将分词后的结果,一个一个去查倒排,拿到对应的文档列表,然后展示出来。
这里简单展示个案例,让大家明白如何使用ansj这个库
public class TestAnsj {public static void main(String[] args) {String str = "小明买了苹果手机";List<Term> terms = ToAnalysis.parse(str).getTerms();for (Term term : terms) {System.out.print(term.getName() + "/");}}
}
运行结果:
小明/买/了/苹果/手机/
注意:当 ansj 对英文分词时, 会自动把单词转为小写
创建model包
首先我们把这个项目所需要的实体类给创建一下
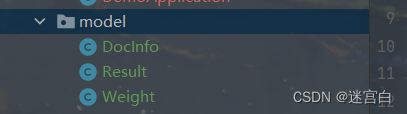
从图中可以看到model这个包主要包含3个类
/*** 这个类表示一篇文档*/
@Data
public class DocInfo {private int docId;private String title;private String url;private String content;
}
/*** 这个类把文档id和文档与词的相关性权重进行一个包裹(权重越高的文档,展示的时候就放到越前面)*/
@Data
public class Weight {//文档id,文档的身份标识private int docId;//这个weight表示文档和词之间的“相关性”,值越大,相关性越强private int weight;
}
/*** 这个类表示后端返回给前端的数据*/
@Data
public class Result {private String title;private String url;private String desc;//表示一段摘要
}
/*** 这个类用来表示词频*/
@Data
public class WordCnt {//表示这个词在标题中出现的次数public int titleCount;//表示这个词在正文中出现的次数public int contentCount;
}
关于这些类是表示什么意思,注释都有写,现在看不懂没关系,后面会明白的
实现索引模块
实现Index类
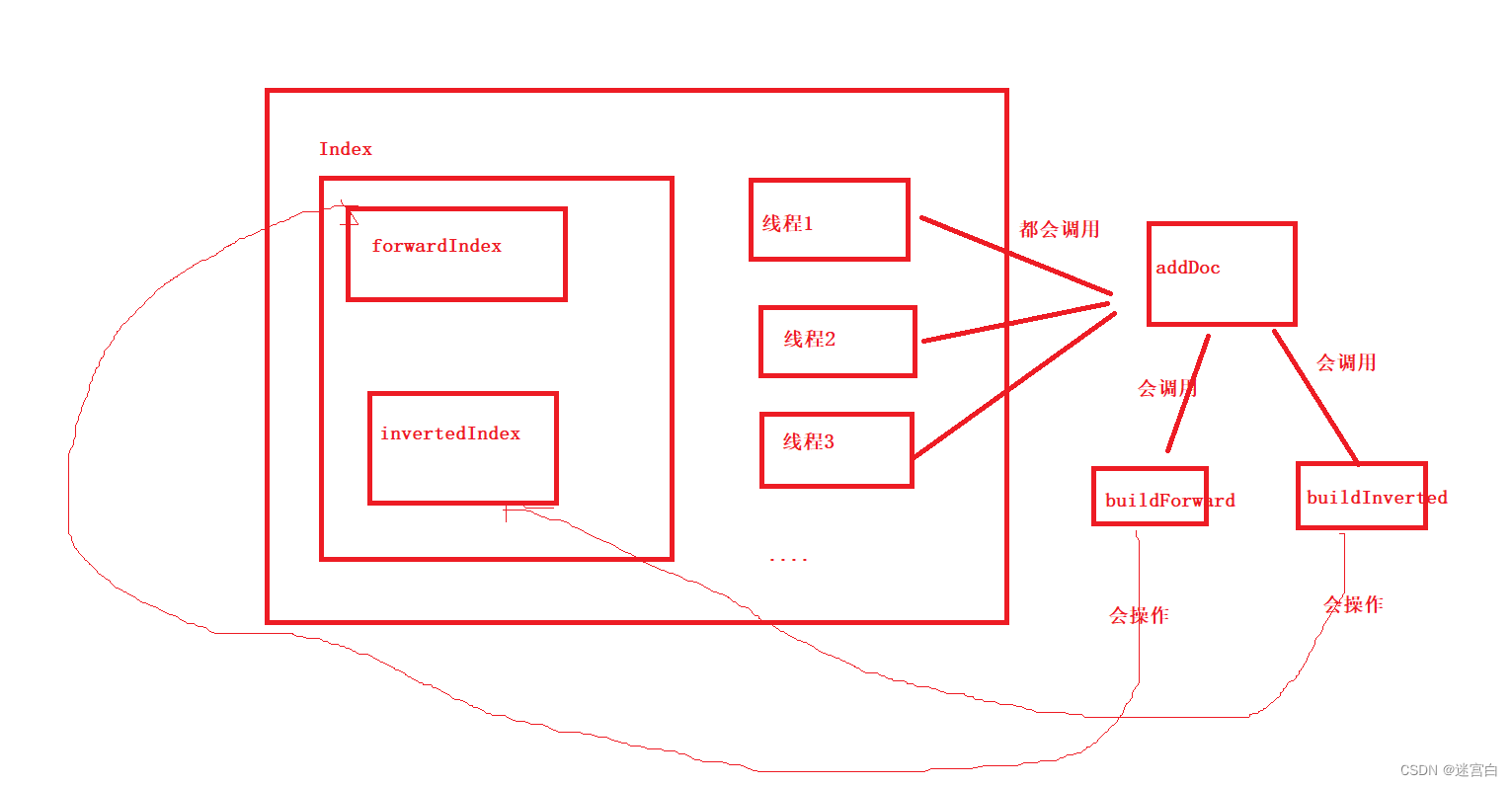
Index 负责构建索引数据结构. 主要提供以下方法:
- getDocInfo: 根据 docId 查正排.
- getInverted :根据关键词查倒排.
- addDoc :往索引中新增一个文档(正排索引和倒排索引都要新增).
- save :往磁盘中写索引数据
- load :从磁盘加载索引数据
代码的大致框架
@Service
public class Index {//作为锁对象,其用途在后面会知道private Object locker1 = new Object();private Object locker2 = new Object();//索引制作完成后,写入磁盘时,索引数据保存的文件路径private static final String INDEX_PATH = "D:/doc_searcher_index/";//转成json格式要用到的private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();//正排索引,数组下标表示文档ID也就是docIdprivate ArrayList<DocInfo> forwardIndex = new ArrayList<>();//使用哈希表来作为倒排索引的数据结构,key表示词,val表示一组和这个词相关的文章private HashMap<String,ArrayList<Weight>> invertedIndex = new HashMap<>();/*** 根据文档id查正排* @param docId* @return*/public DocInfo getDocInfo(int docId) {}/*** 根据查询词查倒排,返回一个倒排拉链* @param term* @return*/public List<Weight> getInverted(String term) {}/*** 往索引中添加文档,正排索引的倒排索引都要添加* @param title* @param url* @param content*/public void addDoc(String title,String url,String content) {}/*** 将索引数据保存到本地磁盘中*/public void save() {}/*** 将索引数据从本地磁盘中加载到内存中*/public void load() {}}
只要把这几个方法实现完成,那么Index就算是完成了
实现getDocInfo 和 getInverted
这两个方法比较简单,因为我们构建完的正排索引和倒排索引是由下面这两个数据结构来进行保存的
//正排索引,数组下标表示文档ID也就是docIdprivate ArrayList<DocInfo> forwardIndex = new ArrayList<>();//使用哈希表来作为倒排索引的数据结构,key表示词,val表示一组和这个词相关的文章private HashMap<String,ArrayList<Weight>> invertedIndex = new HashMap<>();
所以直接返回这两个数据结构的get方法即可
/*** 根据文档id查正排* @param docId* @return*/public DocInfo getDocInfo(int docId) {return forwardIndex.get(docId);}/*** 根据查询词查倒排,返回一个倒排拉链* @param term* @return*/public List<Weight> getInverted(String term) {return invertedIndex.get(term);}
这两个方法相当于,先根据词调用getInverted()方法,然后得到的文档列表再去正排查,然后就能拿到文档的title,url,content;可能现在有点抽象,不过往后看就不难了
实现addDoc方法
当调用addDoc方法时,就会往正排索引(forwardIndex)和倒排索引(invertedIndex)中添加新文档
public void addDoc(String title,String url,String content) {//往正排索引添加文档DocInfo docInfo = buildForward(title,url,content);//往倒排索引添加文档buildInverted(docInfo);}
实现buildForward方法
我们先来实现比较简单的,往正排索引添加一个新文档
步骤1:新建一个DocInfo对象,将对应的属性填入
步骤2:将这个DocInfo对象,add到forwardIndex的末尾
private DocInfo buildForward(String title,String url,String content) {//1.新建一个DocInfo对象,将对应的属性填入DocInfo docInfo = new DocInfo();docInfo.setTitle(title);docInfo.setUrl(url);docInfo.setContent(content);//关于这里为什么要进行加锁操作,后面会详细说明synchronized (locker1) {docInfo.setDocId(forwardIndex.size());//2.往forwardIndex中add这个docInfo对象forwardIndex.add(docInfo);}return docInfo;}
实现buildInverted方法
通过这个方法往invertedIndex这个数据结构新增文档
步骤1:针对文档标题进行分词
步骤2:遍历分词结果,统计每个词出现的次数
步骤3:针对文档内容进行分词
步骤4:遍历分词结果,统计每个词出现的次数
步骤5:将上面结果汇总到一个HashMap里(最终对文档的权重的计算这里提供一个:weight = 词在标题出现次数*10 + 词在正文中出现次数)
步骤6:遍历刚才的hashmap,依次来更新倒排索引的结构
/*** 往倒排索引中添加新文档(构建倒排索引)* @param docInfo*/private void buildInverted(DocInfo docInfo) {//这个hashmap用来统计词频HashMap<String, WordCnt> wordCntHashMap = new HashMap<>();//1.针对文档标题进行分词List<Term> terms = ToAnalysis.parse(docInfo.getTitle()).getTerms();//2.遍历分词结果,统计每个词出现的次数for (Term term : terms) {String word = term.getName();WordCnt wordCnt = wordCntHashMap.get(term);//先判断term是否存在if(wordCnt==null) {//若不存在,新建一个键值对,将titleCount设为1WordCnt newWordCnt = new WordCnt();newWordCnt.titleCount=1;newWordCnt.contentCount=0;wordCntHashMap.put(word,newWordCnt);} else {//若存在则将titleCount加1wordCnt.titleCount+=1;}}//3.针对文档内容进行分词terms = ToAnalysis.parse(docInfo.getContent()).getTerms();//4.遍历分词结果,统计每个词出现的次数for(Term term : terms) {String word = term.getName();WordCnt wordCnt = wordCntHashMap.get(term);//先判断term是否存在if(wordCnt==null) {//若不存在,新建一个键值对,将titleCount设为1WordCnt newWordCnt = new WordCnt();newWordCnt.titleCount = 1;newWordCnt.contentCount = 0;wordCntHashMap.put(word,newWordCnt);} else {//若存在,则将contentCount加1wordCnt.contentCount+=1;}}//5.把上面结果汇总到一个hashmap只能(最终权重计算:titleCount*10+contentCount)//6.遍历刚才这个hashmap,依次来更新倒排索引中的结构for(Map.Entry<String,WordCnt> entry : wordCntHashMap.entrySet()) {synchronized (locker2) {//先根据这里的词去倒排索引中查一查//倒排拉链List<Weight> invertedList = invertedIndex.get(entry.getKey());if(invertedList==null) {//若为空则插入新的键值对ArrayList<Weight> newInvertedList = new ArrayList<>();//把新的文档构造成weight对象,插入进入Weight weight = new Weight();weight.setDocId(docInfo.getDocId());weight.setWeight(entry.getValue().titleCount*10 + entry.getValue().contentCount);newInvertedList.add(weight);invertedIndex.put(entry.getKey(),newInvertedList);} else {//若非空,就把当前文档构造成一个weight对象,插入到倒排拉链中Weight weight = new Weight();weight.setDocId(docInfo.getDocId());//权重计算weight.setWeight(entry.getValue().titleCount*10 + entry.getValue().contentCount);invertedList.add(weight);}}}}
关于buildForward和buildInverted为什么有些代码有进行加锁
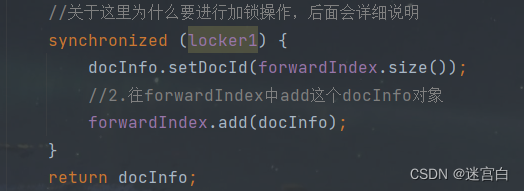
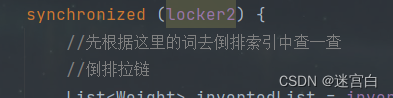
因为后面我们是通过多线程来制作索引的,那么多个线程在调用addDoc方法时,就会调用buildForward和buildInverted方法,而这两个方法会去操作存放文档的正排索引(forwardIndex)和倒排索引(invertedIndex),由于这两个数据结构是公共的,所以可能会出现多个线程修改同一个变量的问题。
实现save方法
保存索引到文件中.
生成两个文件: forward.txt 和 inverted.txt. 通过 json 格式来写入
/*** 将索引数据保存到本地磁盘中*/public void save() {long beg = System.currentTimeMillis();//使用两个文件分别保存正排索引和倒排索引的数据的数据File indexPathFile = new File(INDEX_PATH);//1.先判定一下索引目录是否存在,如果不存在,则创建if(!indexPathFile.exists()) {indexPathFile.mkdirs();}File forwardIndexFile = new File(INDEX_PATH + "forward.txt");File invertedIndexFile = new File(INDEX_PATH + "inverted.txt");try {objectMapper.writeValue(forwardIndexFile,forwardIndex);objectMapper.writeValue(invertedIndexFile,invertedIndex);} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("索引保存完成,消耗时间:"+ (end-beg));}
实现load方法
把索引文件的内容加载到内存中,赋值给两个数据结构
/*** 将索引数据从本地磁盘中加载到内存中*/public void load() {long beg = System.currentTimeMillis();//1.先设置一下加载索引的路径File forwardIndexFile = new File(INDEX_PATH + "forward.txt");File invertedIndexFile = new File(INDEX_PATH + "inverted.txt");try {//从文件中读取json格式数据,然后转成forwardIndex的数据结构forwardIndex = objectMapper.readValue(forwardIndexFile, new TypeReference<ArrayList<DocInfo>>() {});//从文件中读取json格式数据,然后转invertedIndex的数据结构invertedIndex = objectMapper.readValue(invertedIndexFile, new TypeReference<HashMap<String, ArrayList<Weight>>>() {});} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("索引加载消耗时间:"+(end-beg));}
实现Parser类
通过这个Parser类来完成制作索引的过程
Parser:读取之前下载好的这些文档,然后去解析文档的内容,并完成索引的制作
- 从制定的路径中枚举出所有的文件
- 读取每个文件, 从文件中解析出 HTML 的标题, 正文, URL
代码大致框架
public class Parser {//先指定一个加载文档的路径private static final String INPUT_PATH="D:/doc_searcher_index/jdk-8u361-docs-all/docs/api";//创建Index实例private Index index = new Index;public static void main(String[] args) {//制作索引的入口Parser parser = new Parser();parser.runByThread();}/*** 通过这个方法多线程制作索引*/private void runByThread() throws InterruptedException {long beg = System.currentTimeMillis();//1.根据上面指定的路径,枚举出该路径中所有的文件(只限html)放到file里面(递归)ArrayList<File> files = new ArrayList<>();enumFile(INPUT_PATH,files);//2.//2.循环遍历文件,多线程制作索引CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(files.size());ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(4);for (File f : files) {executorService.submit(new Runnable() {@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println("开始解析:"+f.getAbsolutePath());//解析htmlparseHTML(f);latch.countDown();}});}//3.把内存中构造好的索引数据结构保存到指定的文件中latch.await();executorService.shutdown();//手动关闭线程池index.save();long end = System.currentTimeMillis();System.out.println("索引制作消耗时间:"+(end-beg));}/*** 通过这个方法,递归扫描文档* @param inputPath* @param files*/private void enumFile(String inputPath,ArrayList<File> files) {}/*** 通过这个方法解析Html文档,然后将文档新增到索引中去* 一条搜索结果要展示标题,描述,URL,这些信息就来自于要解析html,要得到描述要先得到正文* @param f*/private void parseHTML(File f) {}
}只要把上面的方法实现完成,Parser类就算是完成了,之后只有运行这个Parser类,这样就会将本地的java文档扫描一遍,然后制作索引,将索引的数据保存到本地文件中,这样等需要搜索时,就可以直接从本地读取索引数据,就不需要每次搜索都制作一遍索引。
实现enumFile方法
这个方法会递归遍历我们指定的路径,然后将是html文件的文档加入结果集,比较简单,不难实现,主要涉及到文件操作
/*** 通过这个方法,递归扫描文档* @param inputPath* @param fileList*/private void enumFile(String inputPath,ArrayList<File> fileList) {File rootPath = new File(inputPath);//listFiles方法能获取到当前目录的文件和方法File[] files = rootPath.listFiles();for(File file : files) {if(file.isDirectory()) {enumFile(file.getAbsolutePath(),fileList);} else {if(file.getAbsolutePath().endsWith(".html")) {fileList.add(file);}}}}
实现parseHTML方法
/*** 通过这个方法解析Html文档,然后将文档新增到索引中去* 一条搜索结果要展示标题,描述,URL,这些信息就来自于要解析html,要得到描述要先得到正文* @param f*/private void parseHTML(File f) {//1.解析出html的标题String title = parseTitle(f);//2.解析出html的urlString url = parseURL(f);//3.解析出html的正文String content = parseContentByRegex(f);//4.将解析出来的信息加入到索引中去index.addDoc(title,url,content);}
从上面代码可以看出,parseHTML的工作就是解析标题,url,content,然后把解析出来的内容加入到索引当中去,从而构造索引,而addDoc在Index已经实现,所以我们调用就可以了,所以只需要实现这3个方法即可
实现parseTitle方法
首先我们知道html文件的源代码都是由各种标签构成,所以title标签顾名思义就是标题了
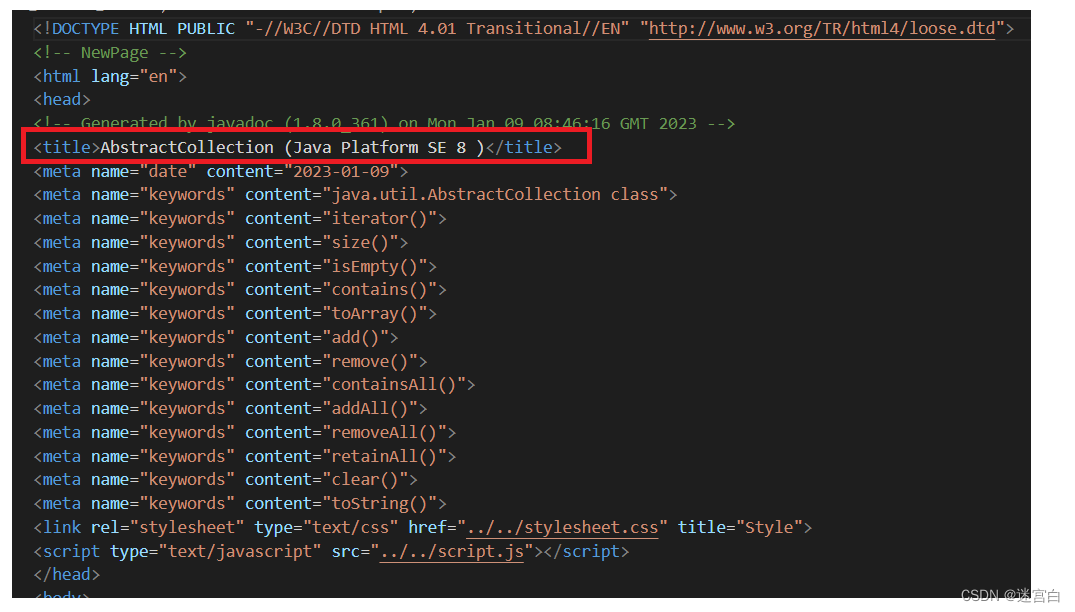
但是要一个一个字符读取然后截取出title标签的内容效率太低,所以我们可以用离线文档的文件名作为文档的标题

可以看到文件名和上面的title标签的内容基本一样,所以就选择用文件名来作为文档的标题了
private String parseTitle(File f) {//由于文件名就是标题,所以直接提取文件名即可String name = f.getName();//取文件名作为标题,但是要把.html后缀给删除掉return name.substring(0,name.length()-".html".length());}
实现parseURL方法
在真实的搜索引擎中,展示URL和跳转URL是不同的URL,但是我们当前就按照一个URL处理即可(因为我们也没有其他业务)
Java API文档存在两份
- 线上文档
- 线下文档(下载到本地的文档)
我们的期望就是用户点击搜索结果时,就能跳转到对应的线上文档页面。
首先下载之后看到一个 docs 目录, 里面存在一个 api 目录. 这里的 html 就和线上版本的文档是一一对应的.
例如, 我们熟悉的 java.util.Collection 类,
在线文档的链接是 https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/util/Collection.html
下载的文档的本地目录是 D:\doc_searcher_index\jdk-8u361-docs-all\docs\api\java\util\Collection.html
这两者存在一定的对应关系.
我们可以发现后半部分是相同的:api/java/util/Collection.html
所以我们最终跳转的URL以 https://docs.oracle.com/javase8/docs/api 为固定前缀,然后根据当前本地文档所在的路径去和前缀拼接;也就是说,把本地文档路径后半部分提取出来和前缀拼接,就构成了我们最后能够跳转的URL
/*** 最终跳转的URL以 https://docs.oracle.com/javase8/docs/api 为固定前缀* 然后提取本地文档路径的后半部分去和前缀拼接* @param f* @return*/private String parseURL(File f) {String part1 = "https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api";String part2 = f.getAbsolutePath().substring(INPUT_PATH.length());return part1+part2;}实现parseContentByRegex方法
这个方法我们采用正则表达式来实现,首先我们先看html都是什么内容
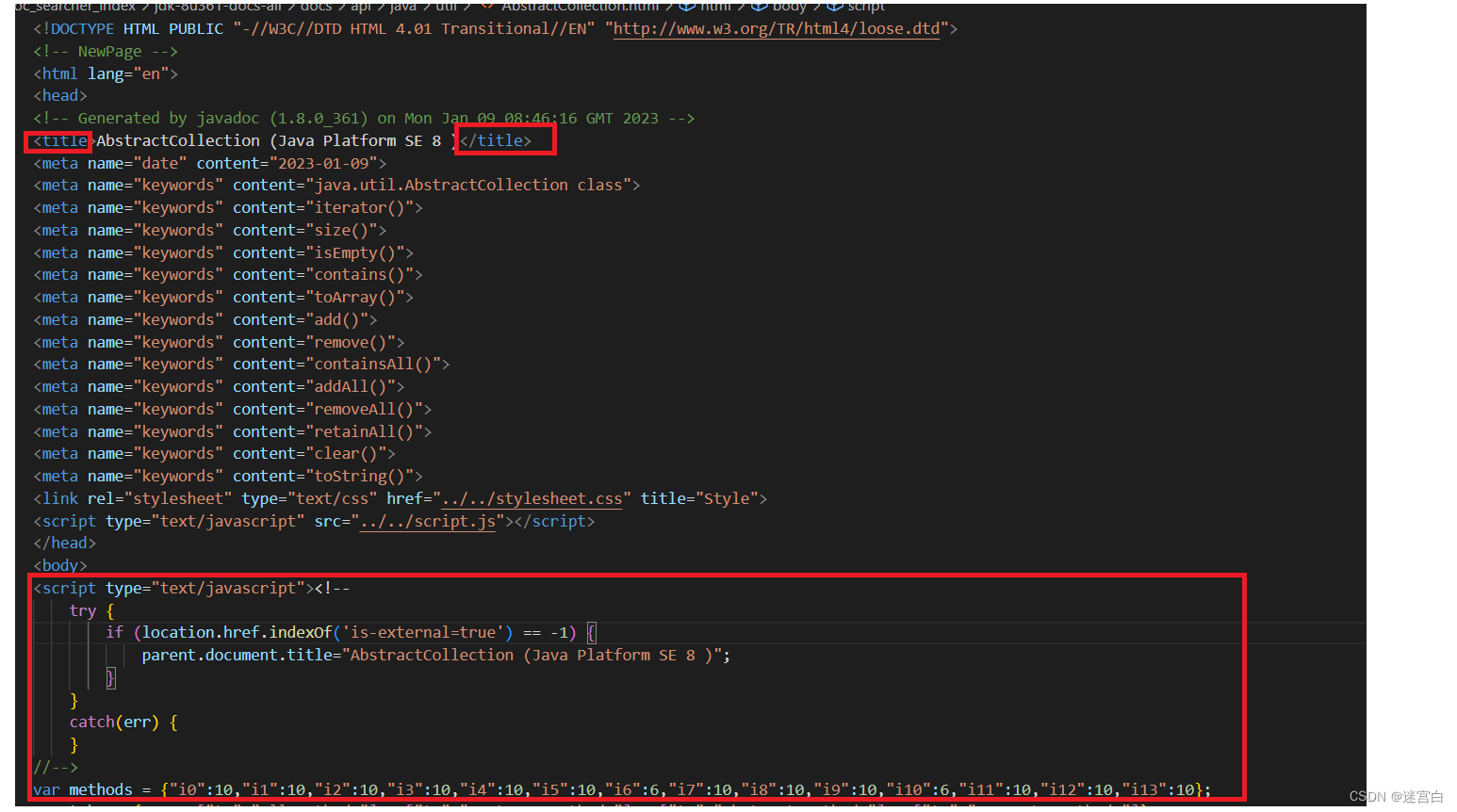
可以发现html是由各种标签构成的那我们有做到3件事
- 把
/*** 这个方法内部就是基于正则表达式实现去标签* @param f* @return*/private String parseContentByRegex(File f) {//1.先把整个文件读到一个String中String content = readFile(f);//2.替换掉script标签content = content.replaceAll("<script.*?>(.*?)</script>"," ");//3.替换掉普通的html标签content = content.replaceAll("<.*?>"," ");//4.将多余空格删除content = content.replaceAll("\\s+"," ");return content;}private String readFile(File f) {try(BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(f))) {StringBuilder content = new StringBuilder();while(true) {int ret = bufferedReader.read();if(ret==-1) {//说明读取完毕break;}char c= (char) ret;if(c=='\n' || c=='\r') {c=' ';}content.append(c);}return content.toString();} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return "";}
到这里就可以点击运行制作索引了
运行结果:
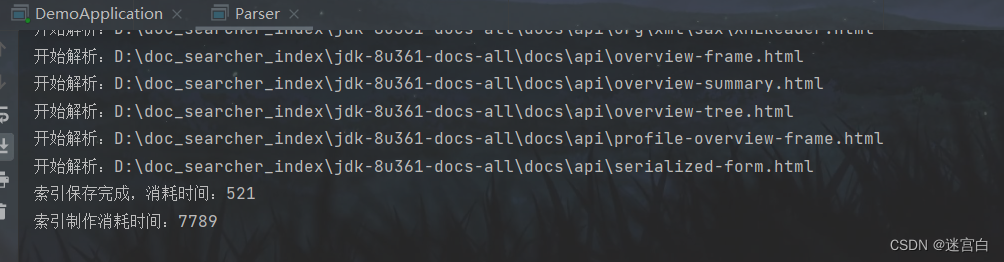

可以看到索引数据被保存到这两个文件,当我们需要搜索时,只需要加载这两个文件即可
实现搜索模块
搜索模块:调用索引模块,来完成搜索的核心过程
- 分词,针对用户输入的查询词进行分词(用户输入查询词,可能不是一个词,可能是一句话)
- 暂停词过滤:针对分词结果进行暂停词过滤
- 触发,拿着每个分词结果,去倒排索引中查,找到具有相关性的文档
- 合并:针对多个分词结果触发的相同的文档进行合并(将相同文档的权重进行合并)
- 排序,针对上面触发的结果,进行排序(按相关性降序排序)
- 包装结果,根据排序后的结果,依次查正排,获取每个文档的详细信息,包装成一定结果的数据返回出去
所谓暂停词就是没啥意义,但有很高频率出现的词,但是像这样的词按道理来说是不应该被搜索的,举个例子
搜索 array list,按ansj这个库的分词结果是:array 空格 list 那如果我们把空格这样的暂停词也给进行搜索,那几乎所有的文档都有空格,所有我们应该把空格过滤掉。
实际上, 不只空格, 像a, is, have 等高频词语,而且没有意义的词都应该过滤掉,那什么词叫暂停词呢,这种东西, 网上一搜索暂停词表就能搜到.
把搜到的暂停词结果, 放到一个文件中, 每个词占一行. D:\doc_searcher_index\stop_word.txt

大概长这样子

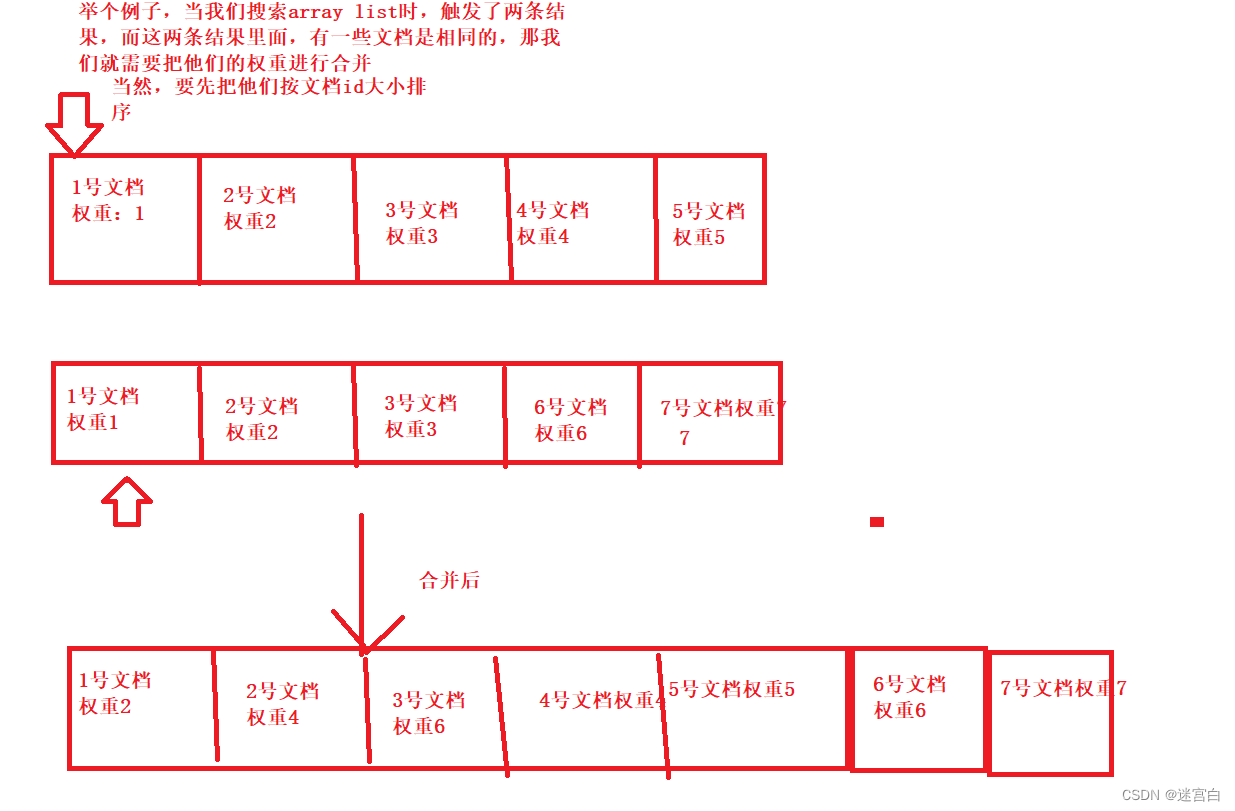
合并这一步骤可能不太理解,这里多解释一下,当搜索的查询词包含多个单词的时候, 可能同一个文档中, 会同时包含这多个分词结果.像这样的文档应该要提高权重.
例如 查询词为 “array list”
那么分词结果就是array和list,那么肯定会有文档同时出现array和list这样的词,那么当我们搜索array这个词是会触发一次文档,当我们搜索list又会触发一次文档,这样就会出现相同的文档出现两次,那么我们只要把这两个相同的文档合并成一个,其实就是把它们的权重相加
合并的思路就是多个有序数组合并成一个数组的思路,看图就能理解了
如果读者还不理解合并的思路,后序可以出一篇文章专门详细讲一讲,这里篇幅有限,就不展开了
@Service
public class DocSearcher {private Index index ;//暂停词存放路径private static final String STOP_WORD_PATH = "D:/doc_searcher_index/stop_word.txt";//使用这个hashset来保存暂停词private HashSet<String> stopWords = new HashSet<>();@Autowiredpublic DocSearcher(Index index) {this.index = index;index.load();//这个方法用来加载暂停词到hashset当中loadStopWords();}/*** 通过这个方法来加载暂停词保存到hashset中*/private void loadStopWords() {}/*** 这个方法会根据查询词, 进行搜索, 得到搜索结果集合.* 结果集合中包含若干条记录, 每个记录中包含搜索结果的标题, 描述, url* @param query* @return*/private List<Result> searcher (String query) {}
}只要把上面这两个方法实现那么这个类也算是完成了
实现loadStopWords方法
/*** 通过这个方法来加载暂停词保存到hashset中*/private void loadStopWords() {try(BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(STOP_WORD_PATH))) {while(true) {String line = bufferedReader.readLine();if(line == null) {//读取完毕break;}stopWords.add(line);}} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
实现searcher方法
步骤1:分词:针对query这个查询词进行分词
步骤2:针对分词结果使用暂停词进行过滤
步骤3:触发:针对分词结果进行查倒排,
步骤4:合并:针对多个分词结果触发的相同的文档进行合并
步骤5:排序:针对触发结果按权重排序
步骤6:包装结果:针对排序结果去查正排,构造返回数据
/*** 这个方法会根据查询词, 进行搜索, 得到搜索结果集合.* 结果集合中包含若干条记录, 每个记录中包含搜索结果的标题, 描述, url* @param query* @return*/private List<Result> searcher (String query) {//步骤1:分词:针对query这个查询词进行分词List<Term> oldTerms = ToAnalysis.parse(query).getTerms();List<Term> terms = new ArrayList<>();//步骤2:针对分词结果使用暂停词进行过滤for (Term term : oldTerms) {String word = term.getName();if(stopWords.contains(word)) {continue;}terms.add(term);}//步骤3:触发:针对分词结果进行查倒排,List<List<Weight>> termResult = new ArrayList<>();for (Term term : terms) {String word = term.getName();List<Weight> invertedList = index.getInverted(word);if(invertedList==null) {//说明这个词在所有文档中不存在continue;}termResult.add(invertedList);}//步骤4:合并:针对多个分词结果触发的相同的文档进行合并List<Weight> allTermResult = mergeResult(termResult);//步骤5:排序:针对触发结果按权重排序allTermResult.sort(new Comparator<Weight>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Weight o1, Weight o2) {//权重高的排前面return o2.getWeight()-o1.getWeight();}});//步骤6:包装结果:针对排序结果去查正排,构造返回数据List<Result> results = new ArrayList<>();for (Weight weight : allTermResult) {DocInfo docInfo = index.getDocInfo(weight.getDocId());Result result = new Result();result.setTitle(docInfo.getTitle());result.setUrl(docInfo.getUrl());//通过getDesc方法获取摘要result.setDesc(getDesc(docInfo.getContent(),terms));results.add(result);}return results;}
可以看到searcher方法还涉及到mergeResult方法和getDesc方法
mergeResult方法会针对多个分词结果触发的相同文档进行合并
实现mergeResult方法
/*** 进行合并操作* 在进行合并的时候, 是把多个行合并成一行了.* 合并过程中势必是需要操作这个二维数组(二维List) 里面的每个元素* 操作元素就涉及到 "行" "列" 这样的概念~~ 要想确定二维数组中的一个元素, 就需要明确知道 行 和 列* 所以我们建一个内部类表示二维数组中的元素在几行几列* @param source* @return*/private List<Weight> mergeResult(List<List<Weight>> source) {//1.先针对每一行进行排序(按文档id进行升序排序)for(List<Weight> curRow : source) {curRow.sort(new Comparator<Weight>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Weight o1, Weight o2) {return o1.getDocId()-o2.getDocId();}});}//2.借助优先级队列进行合并List<Weight> target = new ArrayList<>();PriorityQueue<Pos> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Pos>() {@Overridepublic int compare(Pos o1, Pos o2) {//先根据pos值找对应的weight对象,然后根据Weight的docId来排序Weight w1 = source.get(o1.row).get(o1.col);Weight w2 = source.get(o2.row).get(o2.col);return w1.getDocId()-w2.getDocId();}});//2.1 把每一行的每一个元素都放到优先级队列里for (int row = 0;row<source.size();row++) {queue.offer(new Pos(row,0));}//2.2循环取队首元素while (!queue.isEmpty()) {Pos minPos = queue.poll();Weight curWeight = source.get(minPos.row).get(minPos.col);//2.3看这个取的Weight的docId是否和前一个插入到target中的结果是一样的docId,如果是就合并if(target.size()>0) {//取出上次插入的元素Weight lastWeight = target.get(target.size()-1);if(lastWeight.getDocId()==curWeight.getDocId()) {//合并权重lastWeight.setWeight(lastWeight.getWeight()+curWeight.getWeight());} else {target.add(curWeight);}} else {target.add(curWeight);}//2.4当前元素处理完毕后,当前元素所在的列表col++(光标往后移,处理下一个元素)Pos newPos = new Pos(minPos.row,minPos.col+1);if(newPos.col>=source.get(newPos.row).size()) {//如果当前列表到达最后一个元素continue;}queue.offer(newPos);}return target;}
如果看不懂实现的思路可以在评论区留言,后续可以考虑出一篇文章来进行细讲
实现getDesc方法
我们遍历分词结果的关键词,然后在正文中找到这个关键词之后,把这个关键词往前50个字符作为起点,然后往后150个字符作为终点,截取出来,这截取出来的部分就作为摘要(这部分要提取多少个字符都可以,只要到时前端页面不要太难看都可以)
这个方法还要做一个工作就是当我们把摘要提取出来后,要找到摘要中的关键词然后给它套上一层标签,这样我们在后面可以对关键词进行标红处理
举个例子:
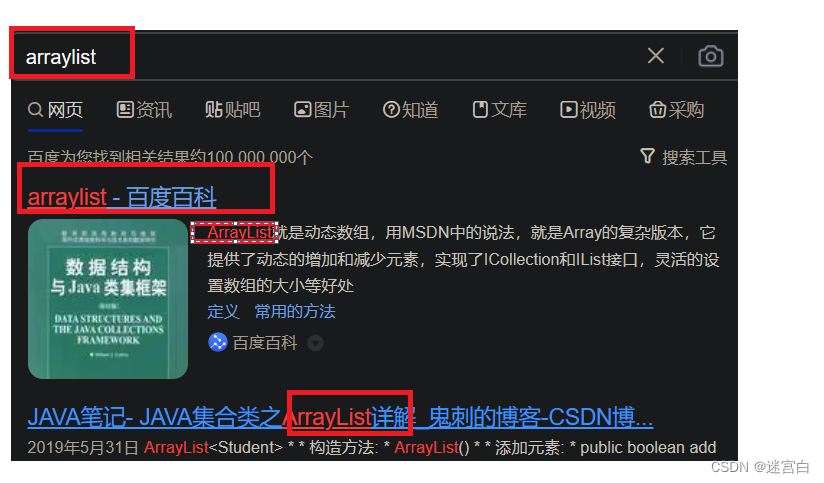
当我们在百度搜索引擎上输入关键词arraylist时,出来的搜索结果的关键词arraylist会被标红处理,那我们也可以模仿这样展示
这里的实现主要涉及到正则表达式
/*** 通过这个方法来获取摘要* @param content* @param terms* @return*/private String getDesc(String content, List<Term> terms) {//1.先遍历content,看哪个关键词在content中出现int firstPos = -1;//分词会直接针对词进行转小写,所以要把正文转成小写content = content.toLowerCase();for(Term term : terms) {String word = term.getName();//此处采用“全写匹配”,让word独立成词,才要查找出来,而不是作为词的一部分//这里的正则表达式表示将 分隔符word分隔符替换成 空格word空格,只要查询就会找到整个单词而不是单词的一部分//比如输入array,但是搜索结果是arraylist,是它的一部分,所以要找到单独成词content = content.replaceAll("\\b" + word + "\\b"," " + word + " ");firstPos = content.indexOf(" " + word + " ");if(firstPos!=-1) {//找到关键词break;}}if(firstPos == -1) {//所有分词结果都不再正文中存在,这属于极端情况,直接返回一个空或正文前150个字符if(content.length()<150) {return content;}return content.substring(0,150) + "...";}//以firstPos作为基准位置,往前找50个字符,作为描述起始位置String desc = "";int descBeg = firstPos >50 ? firstPos-50 : 0;if(descBeg+150 > content.length()) {desc = content.substring(descBeg);} else {desc = content.substring(descBeg,descBeg+150);}//在此处加上一个替换操作,把描述中和分词结果相同的词加上一层<i>标签,可以通过replace实现(正则表达式)for(Term term : terms) {String word = term.getName();//注意此处要全字匹配,(?i) 表示所在位置右侧的表达式开启忽略大小写模式desc = desc.replaceAll("(?i) " + word +" ","<i> " + word + " </i>");}return desc;}
到这里搜索模块也完成了
实现 web模块
提供一个web接口,最终以网页的形式把程序呈现给用户
前端(html+css+js)+后端(java,spring boot)
我们约定前端是GET请求,url是/searcher?query=关键词
后端返回json格式数据,当然这里我用spring boot的统一返回数据格式处理,给它包上一层hashmap,然后直接返回
我们先来实现统一返回数据格式处理的代码
先看一下它的目录

对于统一返回数据格式的处理的写法,通过@ControllerAdvice 注解和实现接口 ResponseBodyAdvice 来实现,然后重写supports 方法和beforeBodyWrite即可,这里就不做展开直接展示代码
@ControllerAdvice
public class ResponseAdvice implements ResponseBodyAdvice {@Overridepublic boolean supports(MethodParameter returnType, Class converterType) {return true;}@SneakyThrows@Overridepublic Object beforeBodyWrite(Object body, MethodParameter returnType, MediaType selectedContentType, Class selectedConverterType, ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response) {if(body instanceof HashMap) {return body;}//如果body是字符串需要进行特殊处理,将返回值进行手动转换if(body instanceof String) {ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();return objectMapper.writeValueAsString(AjaxResult.success(body));}return AjaxResult.success(body);}
}/*** 自定义统一返回对象*/
public class AjaxResult {/*** 业务执行成功进行返回的方法* @param data* @return*/public static HashMap<String,Object> success(Object data) {HashMap<String,Object> result = new HashMap<>();result.put("code",200);result.put("msg","");result.put("data",data);return result;}
}
那么接下来就是web后端处理前端发送过来的http请求的代码
@RestController
public class DocSearcherController {@Autowiredprivate DocSearcher docSearcher;@RequestMapping(value = "/searcher", produces = "application/json;charset=utf-8")@ResponseBodypublic List<Result> search(@RequestParam("query") String query) throws JsonProcessingException {//参数query是来自于url中的query string中的query中的keyList<Result> results = docSearcher.searcher(query);return results;}
}接下来就是前端的代码就直接展示吧
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head><meta charset="UTF-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"><meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"><title>java_doc_search</title>
</head>
<body><!-- 通过.container 来表示整个页面元素的容器 --><div class="container"><!-- 1.搜索框 + 搜索按钮 --><div class="header"><input type="text"><button id="search-btn">搜索</button></div><!-- 2.显示搜索结果 --><div class="result"><!-- 包含很多条记录 --><!-- 每条.item就表示一条记录 --><!-- <div class="item"><a href="#">我是标题</a><div class="desc">我是描述 Lorem, ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Inventore adipisci qui ratione minus aliquid aperiam tenetur quidem atque sunt perferendis architecto, a quia veniam facilis cupiditate porro. Totam, perferendis provident.</div><div class="url">我是url</div></div><div class="item"><a href="#">我是标题</a><div class="desc">我是描述 Lorem, ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Inventore adipisci qui ratione minus aliquid aperiam tenetur quidem atque sunt perferendis architecto, a quia veniam facilis cupiditate porro. Totam, perferendis provident.</div><div class="url">我是url</div></div><div class="item"><a href="#">我是标题</a><div class="desc">我是描述 Lorem, ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Inventore adipisci qui ratione minus aliquid aperiam tenetur quidem atque sunt perferendis architecto, a quia veniam facilis cupiditate porro. Totam, perferendis provident.</div><div class="url">我是url</div></div><div class="item"><a href="#">我是标题</a><div class="desc">我是描述 Lorem, ipsum dolor sit amet consectetur adipisicing elit. Inventore adipisci qui ratione minus aliquid aperiam tenetur quidem atque sunt perferendis architecto, a quia veniam facilis cupiditate porro. Totam, perferendis provident.</div><div class="url">我是url</div></div> --><!-- 接下来通过访问服务器的方式搜索结果,并且由js动态调整 --></div></div><style>/* 这部分代码用来写样式 *//* 先去掉浏览器的默认样式 */* {margin: 0;padding: 0;box-sizing: border-box;}/* 给整体页面指定一个高度(和浏览器窗口一样高) */html,body {height: 100%;/* 设置背景图 */background-image: url(image/background.jpg);/* 设置不平铺 */background-repeat: no-repeat;/* 设置背景图位置 */background-position: center center;/* 设置背景图大小 */background-size: cover;}/* 针对.container也设置样式,实现版心效果 */.container {/* 此处的宽度也可以设置成百分数的形式,当前使用一个固定宽度 */width: 1200px;height: 100%;/* 设置水平居中 */margin: 0 auto;/* 设置背景色,让版心和背景图能够区分开 */background-color: rgba(255, 255, 255, 0.8);/* 设置圆角矩形 */border-radius: 10px;/* 设置内边距,避免文字内容紧贴着边距 */padding: 20px;/* 超出元素的部分会自动加一个滚动条 */overflow: auto;}.header {width: 100%;height: 50px;display: flex;justify-content: space-between;align-items: center;}.header>input {width: 1000px;height: 50px;font-size: 22px;line-height: 50px;padding-left: 10px;border-radius: 10px;}.header>button {width: 100px;height: 50px;background-color: rgb(42, 107, 205);color: #fff;font-size: 22px;line-height: 50px;border-radius: 10px;border: none;}.header>button:active {background: gray;}.item {width: 100%;margin-top: 20px;}.item a {display: block;height: 40px;font-size: 22px;line-height: 40px;font-weight: 700;color: rgb(100, 107, 205);}.item .desc {font-size: 18px;}.item .url {font-size: 18px;color: rgb(0, 128, 0);}.item .desc i {color: red;font-style: normal;}.result .count {color: gray;margin-top: 10px;}</style><script src="js/jquery.min.js"></script><script>let button = document.querySelector("#search-btn");button.onclick = function() {//先获取输入框的内容let input = document.querySelector(".header input");let query = input.value;console.log("query:"+query);jQuery.ajax({type:"GET",url: "searcher?query=" + query,success:function(body,status) {if(body.code==200) {//body参数表示拿到结果数据//status参数表示http状态码buildResult(body.data);}}});}//通过这个方法把响应数据进行构造页面function buildResult(data) {let result = document.querySelector(".result");result.innerHTML = '';let countDiv = document.createElement('div');countDiv.innerHTML = '当前找到' + data.length + '个结果!';countDiv.className = 'count';result.appendChild(countDiv);for(let item of data) {let itemDiv = document.createElement('div');itemDiv.className = 'item';let title = document.createElement('a');title.href = item.url;title.innerHTML = item.title;title.target = '_blank';itemDiv.append(title);let desc = document.createElement('div');desc.className = 'desc';desc.innerHTML = item.desc;itemDiv.appendChild(desc);let url = document.createElement('div');url.className = 'url';url.innerHTML = item.url;itemDiv.appendChild(url);result.appendChild(itemDiv);}}</script>
</body>
</html>
最后运行效果:
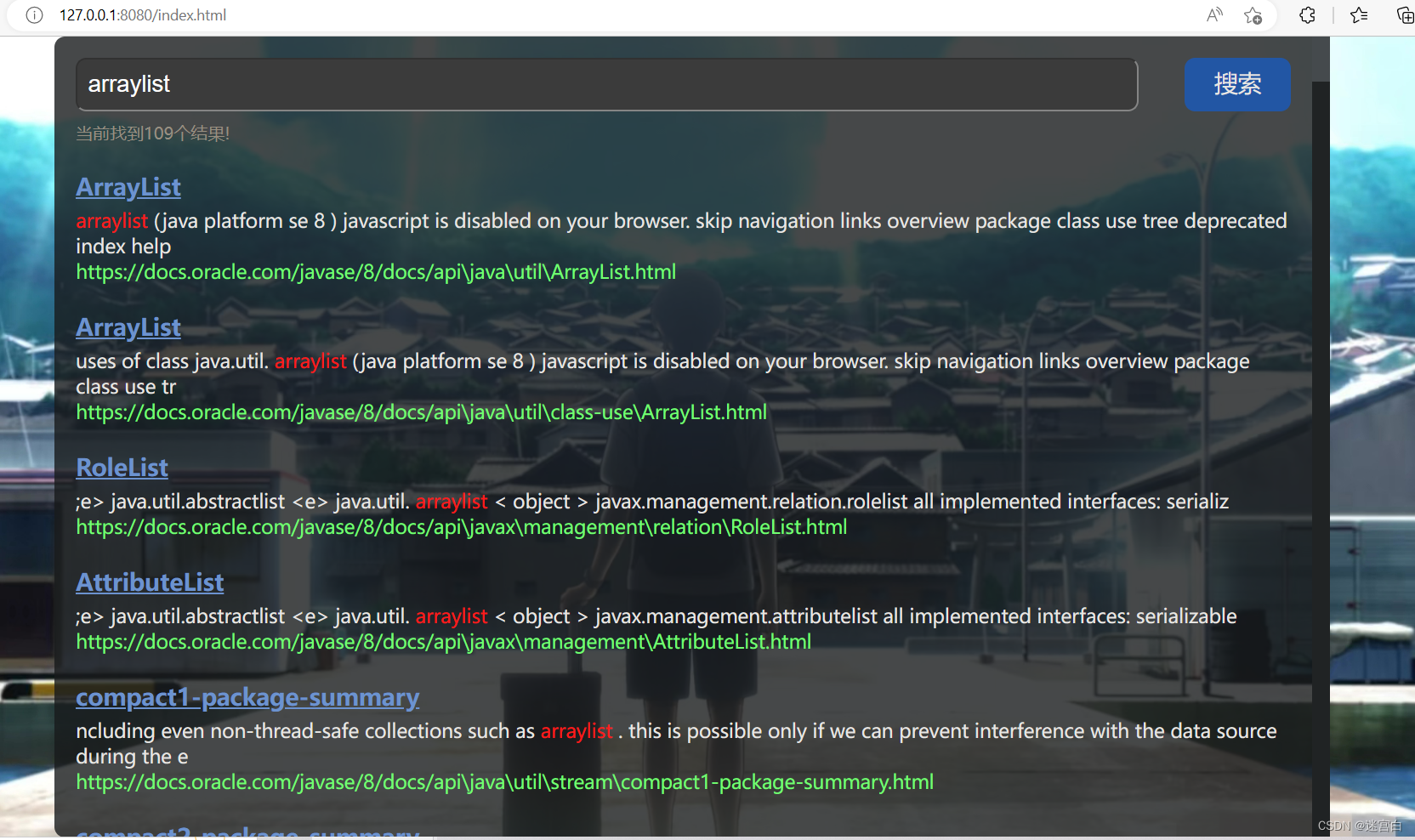
源码链接:
https://gitee.com/maze-white/project/tree/master/java_doc_searcher_ssm
成品链接:
http://43.139.58.117:8080/index.html