C++:智能指针的使用及其原理
干~,加油!!!
一、智能指针的使用场景分析
下面程序中我们可以看到,new了以后,我们也delete了,但是因为抛异常导,后面的delete没有得到执行,所以就内存泄漏了,所以我们需要new以后捕获异常,捕获到异常后delete内存,再把异常抛出,但是因为new本身也可能抛异常,连续的两个new和下面的Divide都可能会抛异常,让我们处理起来很麻烦。智能指针放到这样的场景里面就让问题简单多了。
double Divide(int a, int b)
{// 当b == 0时抛出异常if (b == 0){throw "Divide by zero condition!";}else{return (double)a / (double)b;}
}void Func()
{// 这里可以看到如果发生除0错误抛出异常,另外下面的array和array2没有得到释放。// 所以这里捕获异常后并不处理异常,异常还是交给外面处理,这里捕获了再重新抛出去。// 但是如果array2new的时候抛异常呢,就还需要套一层捕获释放逻辑,这里更好解决方案// 是智能指针,否则代码太戳了int* array1 = new int[10];int* array2 = new int[10]; // 抛异常呢try{int len, time;cin >> len >> time;cout << Divide(len, time) << endl;}catch (...){cout << "delete []" << array1 << endl;cout << "delete []" << array2 << endl;delete[] array1;delete[] array2;throw; // 异常重新抛出,捕获到什么抛出什么}// ...cout << "delete []" << array1 << endl;delete[] array1;cout << "delete []" << array2 << endl;delete[] array2;
}int main()
{try{Func();}catch (const char* errmsg){cout << errmsg << endl;}catch (const exception& e){cout << e.what() << endl;}catch (...){cout << "未知异常" << endl;}return 0;
}使用智能制造:
double Divide(int a, int b)
{// 当b == 0时抛出异常if (b == 0){throw "Divide by zero condition!";}else{return (double)a / (double)b;}
}//void Func()
//{
// // 这里可以看到如果发生除0错误抛出异常,另外下面的array和array2没有得到释放。
// // 所以这里捕获异常后并不处理异常,异常还是交给外面处理,这里捕获了再重新抛出去。
// // 但是如果array2new的时候抛异常呢,就还需要套一层捕获释放逻辑,这里更好解决方案
// // 是智能指针,否则代码太戳了
// int* array1 = new int[10];
// int* array2 = new int[10]; // 抛异常呢
// try
// {
// int len, time;
// cin >> len >> time;
// cout << Divide(len, time) << endl;
// }
// catch (...)
// {
// cout << "delete []" << array1 << endl;
// cout << "delete []" << array2 << endl;
// delete[] array1;
// delete[] array2;
// throw; // 异常重新抛出,捕获到什么抛出什么
// }
// // ...
// cout << "delete []" << array1 << endl;
// delete[] array1;
// cout << "delete []" << array2 << endl;
// delete[] array2;
//}
template<class T>
class SmartPtr
{
public:SmartPtr(T* ptr):_ptr(ptr){}~SmartPtr(){cout << "delete" << _ptr << endl;delete[] _ptr;}// 重载运算符,模拟指针的行为,方便访问资源T& operator*(){return *_ptr;}T* operator->(){return _ptr;}T& operator[](int i){return _ptr[i];}
private:T* _ptr;
};
void Func()
{// 正常结束还是异常结束,析构都可以保障new的资源正常释放SmartPtr<int> sp1 = new int[10];SmartPtr<int> sp2 = new int[10];sp1[0] = 0;int len, time;cin >> len >> time;cout << Divide(len, time) << endl;
}int main()
{//int* p1 = new int[10];//SmartPtr<int> sp1(p1);//SmartPtr<int> sp1 = new int[10];try{Func();}catch (const char* errmsg){cout << errmsg << endl;}catch (const exception& e){cout << e.what() << endl;}catch (...){cout << "未知异常" << endl;}return 0;
}二、RAII和智能指针的设计思路
• RAII是Resource Acquisition Is Initialization的缩写,他是一种管理资源的类的设计思想,本质是一种利用对象生命周期来管理获取到的动态资源,避免资源泄漏,这里的资源可以是内存、文件指针、网络连接、互斥锁等等。RAII 在获取资源时把资源委托给一个对象,接着控制对资源的访问,资源在对象的生命周期内始终保持有效,最后在对象析构的时候释放资源,这样保障了资源的正常释放,避免资源泄漏问题
• 智能指针类除了满足 RAII 的设计思路,还要方便资源的访问,所以智能指针类还会像迭代器类一样,重载 operator* / operator-> / operator[] 等运算符,方便访问资源。
三、C++标准库智能指针的使用
• C++标准库中的智能指针都在<memeoy>这个头文件下面,我们包含就可以是使用了, 智能指针有好几种,除了 weak_ptr 他们都符合 RAII和像指针一样访问的行为,原理上而言主要是解决智能指针拷贝时的思路不同。
auto_ptr - C++ Reference
• auto_ptr 是C++98时设计出来的智能指针,他的特点是拷贝时把被拷贝对象的资源的管理权转移给拷贝对象,这是一个非常糟糕的设计,因为他会有被拷贝对象悬空,访问报错的问题,C++11设计出新的智能指针后,强烈建议不要使用 auto_ptr。
unique_ptr - C++ Reference
• unique_ptr是C++11设计出来的智能指针,他的名字翻译出来是唯一指针,他的特点的不支持拷贝,只支持移动。如果不需要拷贝的场景就非常建议使用他。
shared_ptr - C++ Reference
• shared_ptr是C++11设计出来的智能指针,他的名字翻译出来是共享指针,他的特点是支持拷贝, 也支持移动。如果需要拷贝的场景就需要使用他了。底层是用引用计数的方式实现的。
weak_ptr - C++ Reference
• weak_ptr是C++11设计出来的智能指针,他的名字翻译出来是弱指针,他完全不同于上面的智能指针,他不支持RAII,也就意味着不能用它直接管理资源,weak_ptr的产生本质是要解决shared_ptr 的一个循环引用导致内存泄漏的问题。具体细节下面细讲。
• 智能指针析构时默认是进行 delete 释放资源,这也就意味着如果不是 new 出来的资源,交给智能指针管理,析构时就会崩溃。智能指针支持在构造时给一个删除器,所谓删除器本质就是一个可调用对象,这个可调用对象中实现你想要的释放资源的方式,当构造智能指针时,给了定制的删除器, 在智能指针析构时就会调用删除器去释放资源。因为new[]经常使用,所以为了简洁一点, unique_ptr 和 shared_ptr 都特化了一份[]的版本,使用时
unique_ptr up1(new Date[5]); shared_ptr sp1(new Date[5]);就可以管理new[]的资源。
• shared_ptr 除了支持用指向资源的指针构造,还支持 make_shared 用初始化资源对象的值 直接构造。
• shared_ptr 和 unique_ptr 都支持了 operator bool 的类型转换,如果智能指针对象是一个空对象没有管理资源,则返回false,否则返回true,意味着我们可以直接把智能指针对象给if判断是否为空。
• shared_ptr 和 unique_ptr 都得构造函数都使用 explicit 修饰,防止普通指针隐式类型转换成智能指针对象。
struct Date
{int _year;int _month;int _day;Date(int year = 1, int month = 1, int day = 1):_year(year), _month(month), _day(day){}~Date(){cout << "~Date()" << endl;}
};#include <memory>
int main()
{auto_ptr<Date> ap1(new Date);ap1->_year++;auto_ptr<Date> ap2(ap1);//ap1->_day++; 报错这里的ap1已经是空的了(管理权转移,被拷贝对象悬空)ap2->_month++;unique_ptr<Date> up1(new Date);//unique_ptr<Date> up2(up1);// 禁止拷贝// 可以移动unique_ptr<Date> up2(move(up1));// 可以拷贝可以引动,底层通过引用计数实现shared_ptr<Date> sp1(new Date);shared_ptr<Date> sp2(sp1);cout << sp1.use_count() << endl;cout << sp2.use_count() << endl;// 移动会导致sp1管理的资源被转移,sp1悬空shared_ptr<Date> sp3(move(sp1));cout << sp1 << endl;cout << sp2 << endl;cout << sp3 << endl;if (!sp1)cout << "sp1空" << endl;if (sp2){sp2.reset(); // sp2不再管理,手动释放,但是有其他对象管理的话,就是引用计数减减}Date* ptr = sp3.get();cout << ptr << endl;int* p = new int(10);shared_ptr<int> a(new int(20));shared_ptr<int> b(a, p);cout << a.use_count() << endl;cout << b.use_count() << endl;return 0;
}template<class T>
class DeleteArray
{
public:void operator()(T* ptr){delete[] ptr;}
};class Fclose
{
public:void operator()(FILE* ptr){cout << "fclose:" << ptr << endl;fclose(ptr);}
};int main()
{unique_ptr<Date[]> up1(new Date[10]);shared_ptr<Date[]> sp1(new Date[10]);// 定制删除器shared_ptr<Date> sp2(new Date[10], DeleteArray<Date>());shared_ptr<Date> sp3(new Date[10], [](Date* ptr) {delete[] ptr; });// unique_ptr和shared_ptr支持删除的方式有所不同// unique_ptr是在类模板参数支持的,shared_ptr是构造函数参数支持的// (这里没有使用相同的方式还是很不好的)unique_ptr<Date, DeleteArray<Date>> up2(new Date[5]);auto del = [](Date* ptr) {delete[] ptr; };unique_ptr<Date,decltype(del)> up3(new Date[5], del);// C++20支持//unique_ptr<Date, decltype(del)> up4(new Date[5]);shared_ptr<FILE> sp5(fopen("Test.cpp", "r"), Fclose());shared_ptr<FILE> sp6(fopen("Test.cpp", "r"), [](FILE* ptr) {cout << "fclose:" << ptr << endl;fclose(ptr);});shared_ptr<Date> sp10(new Date(2025,10,12));//shared_ptr<Date> sp11 = make_shared<Date>(2025, 10, 12);auto sp11 = make_shared<Date>(2025, 10, 12);//不支持指针隐式类型转换//shared_ptr<Date> sp12 = new Date;shared_ptr<Date> sp12(new Date);return 0;
}四、智能指针的原理
• 下面我们模拟实现了auto_ptr 和 unique_ptr 的核心功能,这两个智能指针的实现比较简单,了解一下原理即可。auto_ptr的思路是拷贝时转移资源管理权给被拷贝对象,这种思路是不被认可 的,也不建议使用。unique_ptr的思路是不支持拷贝。
• 重点: shared_ptr 是如何设计的,尤其是引用计数的设计,这里一份资源就需要一个引用计数,所以引用计数用静态成员的方式是无法实现的,要使用堆上动态开辟的方式,构造智能指针对象时来一份资源,就要new一个引用计数出来。多个shared_ptr指向资源时就++引用计数,shared_ptr 对象析构时就--引用计数,引用计数减到0时代表当前析构的shared_ptr是最后一个管理资源的对象,则析构资源。
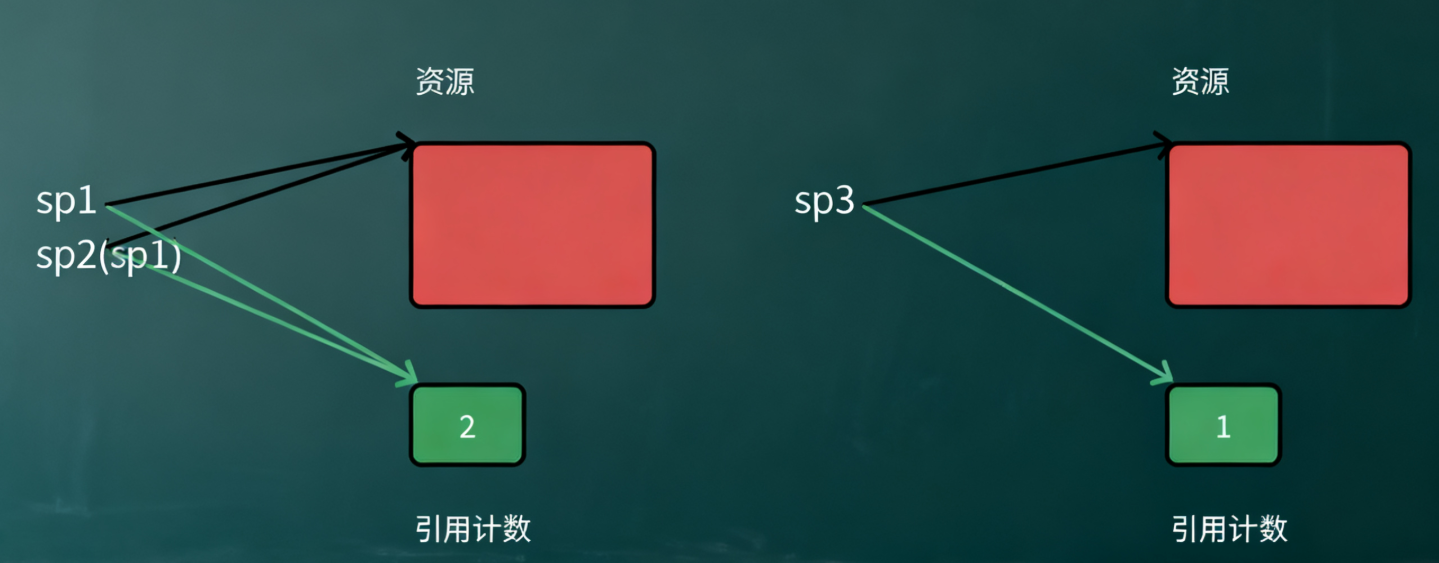
#include <functional>
namespace mymemory
{template<class T>class auto_ptr{public:auto_ptr(T* ptr):_ptr(ptr){ }auto_ptr(auto_ptr<T>& sp):_ptr(sp._ptr){// 管理权限转移sp._ptr = nullptr;}auto_ptr& operator=(const auto_ptr<T>& ap){// 检测是否自己给自己赋值if (this != &ap){// 释放当前对象中资源if (_ptr)delete _ptr;// 转移ap中资源到当前对象中_ptr = ap._ptr;ap._ptr = NULL;}return *this;}~auto_ptr(){if (_ptr){cout << "delete:" << _ptr << endl;delete _ptr;}}// 像指针⼀样使⽤T& operator*(){return *_ptr;}T* operator->(){return _ptr;}private:T* _ptr;};template<class T>class unique_ptr{public:explicit unique_ptr(T* ptr):_ptr(ptr){}~unique_ptr(){if (_ptr){cout << "delete:" << _ptr << endl;delete _ptr;}}// 像指针⼀样使⽤T& operator*(){return *_ptr;}T* operator->(){return _ptr;}unique_ptr(const unique_ptr<T>&sp) = delete;unique_ptr<T>& operator=(const unique_ptr<T>&sp) = delete;unique_ptr(unique_ptr<T> && sp):_ptr(sp._ptr){sp._ptr = nullptr;}unique_ptr<T>& operator=(unique_ptr<T> && sp){delete _ptr;_ptr = sp._ptr;sp._ptr = nullptr;}private:T* _ptr;};template<class T>class shared_ptr{public:explicit shared_ptr(T* ptr = nullptr) // 禁止隐式类型转换: _ptr(ptr), _pcount(new int(1)){}template<class D>shared_ptr(T* ptr, D del): _ptr(ptr), _pcount(new int(1)), _del(del){}shared_ptr(const shared_ptr<T>& sp): _ptr(sp._ptr), _pcount(sp._pcount), _del(sp._del){++(*_pcount);}int use_count(){return *_pcount;}void release(){if (--(*_pcount) == 0){_del(_ptr);delete _pcount;_ptr = nullptr;_pcount = nullptr;}}shared_ptr<T>& operator=(const shared_ptr<T>& sp){if (_ptr != sp._ptr){release();_ptr = sp._ptr;_pcount = sp._pcount;++(*_pcount);_del = sp._del;}}~shared_ptr(){release();}T* get() const{return _ptr;}int use_conut() const{return *_pcount;}T& operator*(){return *_ptr;}T* operator->(){return _ptr;}private:T* _ptr;int* _pcount;function<void(T*)> _del = [](T* ptr) {delete ptr;};};//需要注意的是我们这⾥实现的shared_ptr和weak_ptr都是以最简洁的⽅式实现的,// 只能满⾜基本的功能,这⾥的weak_ptr lock等功能是⽆法实现的,想要实现就要// 把shared_ptr和weak_ptr⼀起改了,把引⽤计数拿出来放到⼀个单独类型,shared_ptr// 和weak_ptr都要存储指向这个类的对象才能实现,有兴趣可以去翻翻源代码template<class T>class weak_ptr{public:weak_ptr(){}weak_ptr(const shared_ptr<T>& sp):_ptr(sp.get()){}weak_ptr<T>& operator=(const shared_ptr<T>& sp){_ptr = sp.get();return *this;}private:T* _ptr = nullptr;};
}int main()
{mymemory::auto_ptr<Date> ap1(new Date);// 拷⻉时,管理权限转移,被拷⻉对象ap1悬空mymemory::auto_ptr<Date> ap2(ap1);// 空指针访问,ap1对象已经悬空//ap1->_year++;mymemory::unique_ptr<Date> up1(new Date);// 不⽀持拷⻉//unique_ptr<Date> up2(up1);// ⽀持移动,但是移动后up1也悬空,所以使⽤移动要谨慎mymemory::unique_ptr<Date> up3(move(up1));mymemory::shared_ptr<Date> sp1(new Date);// ⽀持拷⻉mymemory::shared_ptr<Date> sp2(sp1);mymemory::shared_ptr<Date> sp3(sp2);cout << sp1.use_count() << endl;sp1->_year++;cout << sp1->_year << endl;cout << sp2->_year << endl;cout << sp3->_year << endl;return 0;
}五、shared_ptr循环引用问题
• shared_ptr 大多数情况下管理资源非常合适,支持RAII,也支拷贝。但是在循环引用的场景下会 导致资源没得到释放内存泄漏,所以我们要认识循环引用的场景和资源没释放的原因,并且学会使 用weak_ptr解决这种问题。
• 如下图所述场景,n1和n2析构后,管理两个节点的引用计数减到1
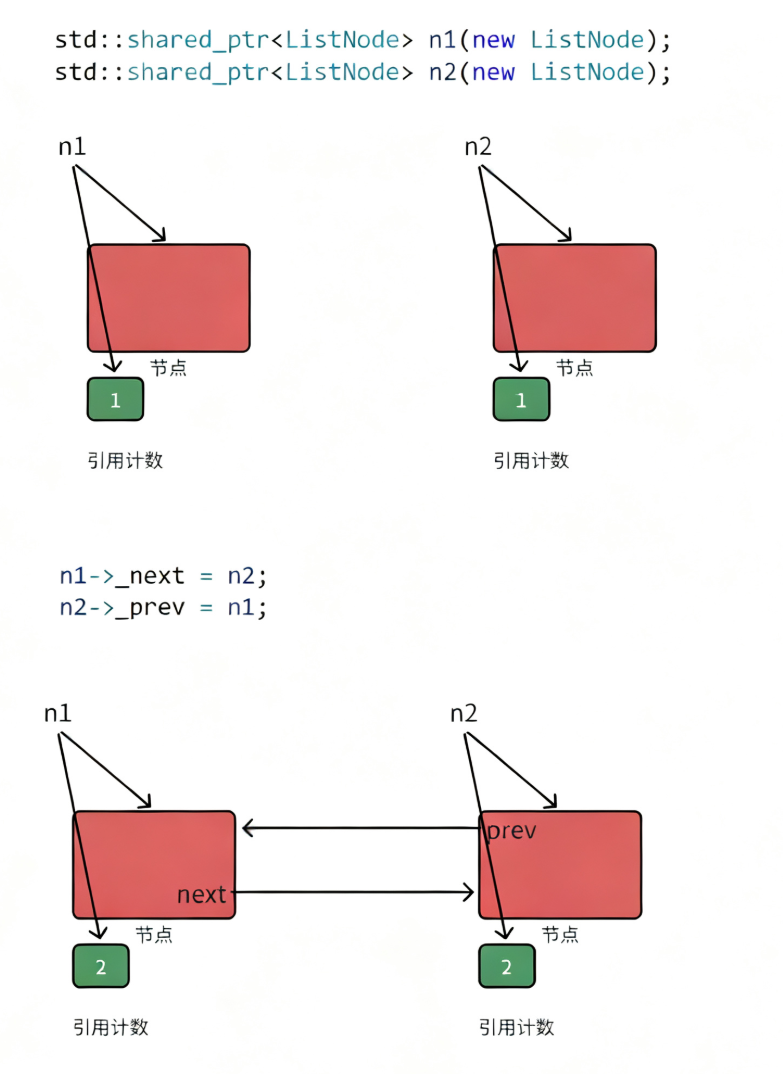
n1和n2析构:
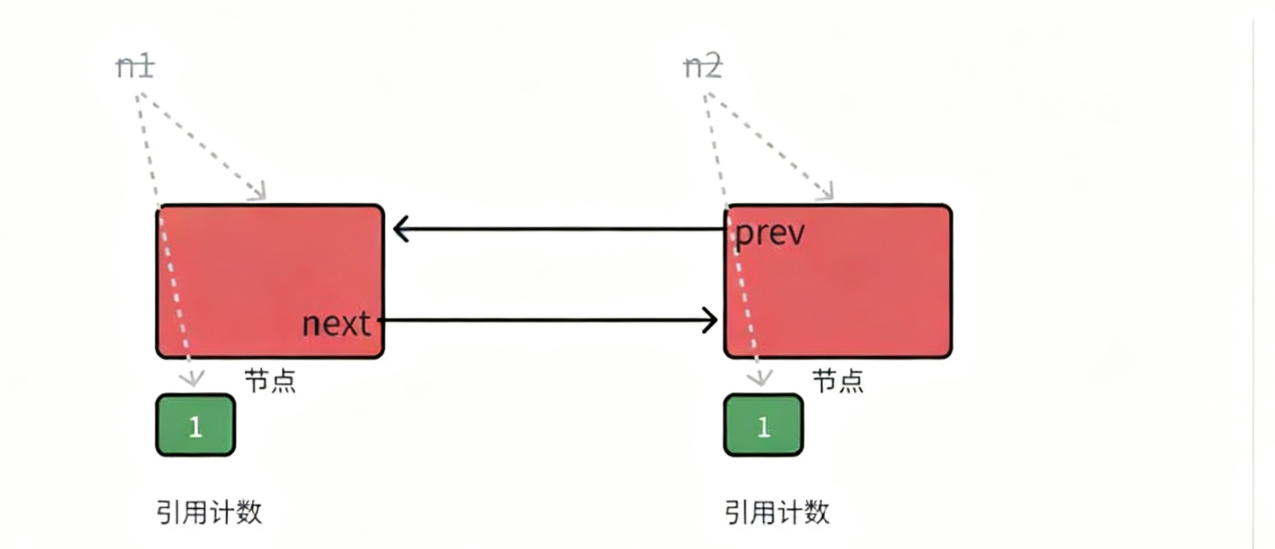
因为prev和next的存在,导致引用节点最后都是1,但是已经没有智能指针来管理了,所以就导致了内存泄漏。
struct ListNode
{int _data;/*std::shared_ptr<ListNode> _next;std::shared_ptr<ListNode> _prev;*/weak_ptr<ListNode> _next;weak_ptr<ListNode> _prev;ListNode(int val):_data(val){}~ListNode(){cout << "~ListNode()" << endl;}
};int main()
{shared_ptr<ListNode> n1(new ListNode(1));shared_ptr<ListNode> n2(new ListNode(2));cout << n1.use_count() << endl;cout << n2.use_count() << endl;n1->_next = n2;n2->_prev = n1;cout << n1.use_count() << endl;cout << n2.use_count() << endl;// weak_ptr 不⽀持管理资源,不⽀持 RAII// weak_ptr 是专⻔绑定 shared_ptr ,不增加他的引⽤计数,作为⼀些场景的辅助管理 // std::weak_ptr wp(new ListNode);return 0;
}七、weak_ptr
weak_ptr - C++ Reference![]() https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/memory/weak_ptr/
https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/memory/weak_ptr/
• weak_ptr 不支持 RAII,也不支持访问资源,所以我们看文档发现 weak_ptr 构造时不支持绑定到资源,只支持绑定到 shared_ptr,绑定到 shared_ptr 时,不增加 shared_ptr 的引用计数,那么就可以解决上述的循环引用问题。
• weak_ptr 也没有重载 operator* 和 operator-> 等,因为他不参与资源管理,那么如果他绑定的 shared_ptr 已经释放了资源,那么他去访问资源就是很危险的。weak_ptr支持 expired 检查指向的 资源是否过期,use_count 也可获取 shared_ptr 的引用计数,weak_ptr想访问资源时,可以调用 lock返回一个管理资源的shared_ptr,如果资源已经被释放,返回的shared_ptr是一个空对象,如 果资源没有释放,则通过返回的shared_ptr访问资源是安全的。
int main()
{std::shared_ptr<string> sp1(new string("111111"));std::shared_ptr<string> sp2(sp1);std::weak_ptr<string> wp = sp1;cout << wp.expired() << endl;cout << wp.use_count() << endl;// sp1和sp2都指向了其他资源,则weak_ptr就过期了sp1 = make_shared<string>("222222");cout << wp.expired() << endl;cout << wp.use_count() << endl;sp2 = make_shared<string>("333333");cout << wp.expired() << endl;cout << wp.use_count() << endl << endl;wp = sp1;//std::shared_ptr<string> sp3 = wp.lock();// 要访问资源,一定lock出一个新的shared_ptr对象auto sp3 = wp.lock();sp1.reset();cout << wp.expired() << endl;cout << wp.use_count() << endl;*sp3 += "###";cout << *sp3 << endl;
}八、C++11和boost中智能指针的关系
• Boost库是为C++语言标准库提供扩展的一些C++程序库的总称,Boost社区建立的初衷之一就是为C++的标准化工作提供可供参考的实现,Boost社区的发起人 Dawes 本人就是C++标准委员会的成员之一。在Boost库的开发中,Boost社区也在这个方向上取得了丰硕的成果,C++11及之后的新语法和库有很多都是从Boost中来的。
• C++98中产生了第一个智能指针auto_ptr。
• C++boost给出了更实用的 scoped_ptr/scoped_array 和 shared_ptr/shared_array和weak_ptr等.
• C++TR1,引入了shared_ptr等,不过注意的是TR1并不是标准版。
• C++11,引入了unique_ptr和shared_ptr和weak_ptr。需要注意的是unique_ptr对应boost的 scoped_ptr。并且这些智能指针的实现原理是参考boost中的实现的。
