网站添加外链客户关系管理名词解释
要和 1.6Runnable 和 Thread 类,几种创建线程方式比较。
创建线程几种方式呢?5 种
- 继承 Thread 类
- Runnable 接口
- Java 5 后,实现 Callable 接口
- Java 线程池
- ComplatableFuture
5.1 Callable 和 Runnable 区别
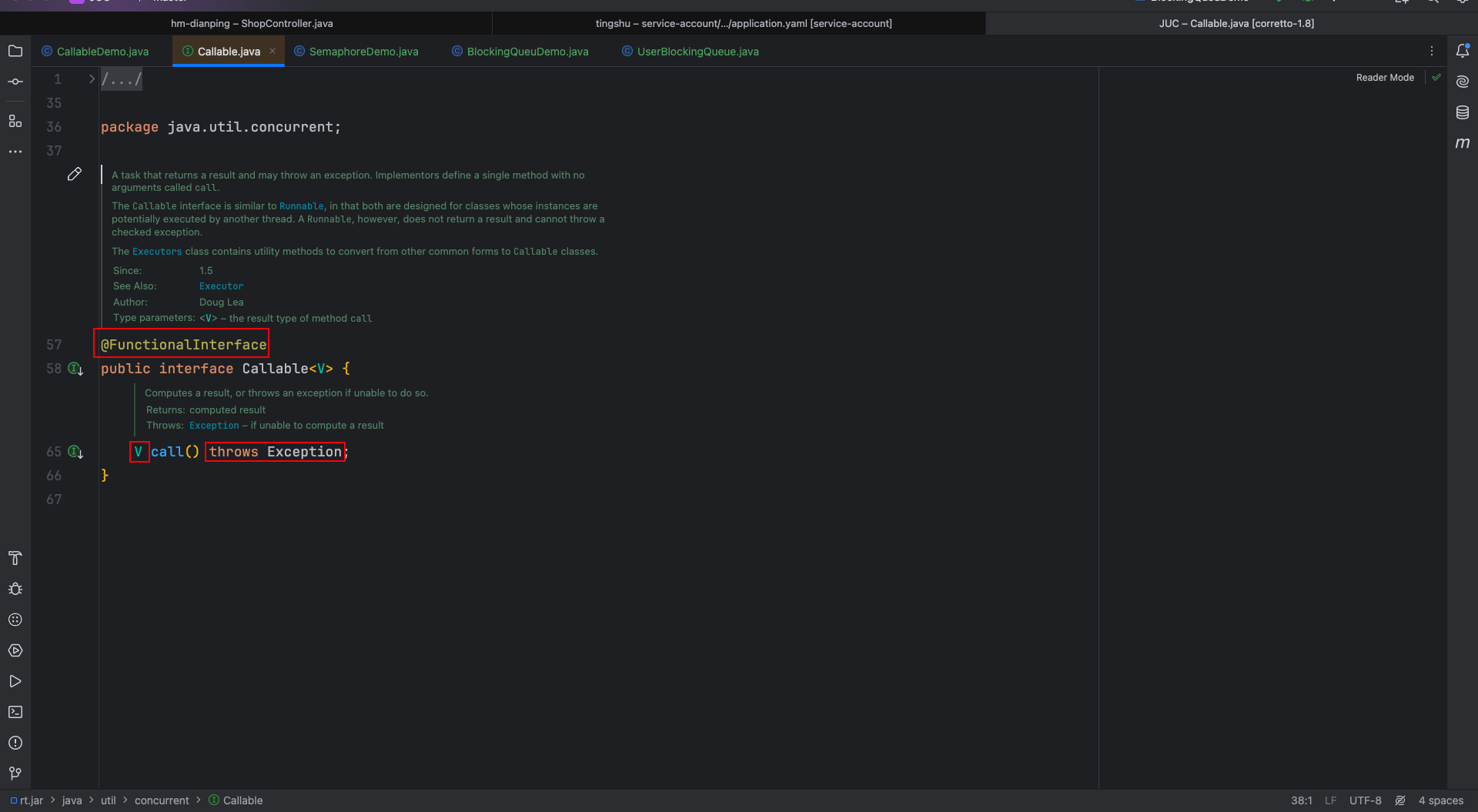
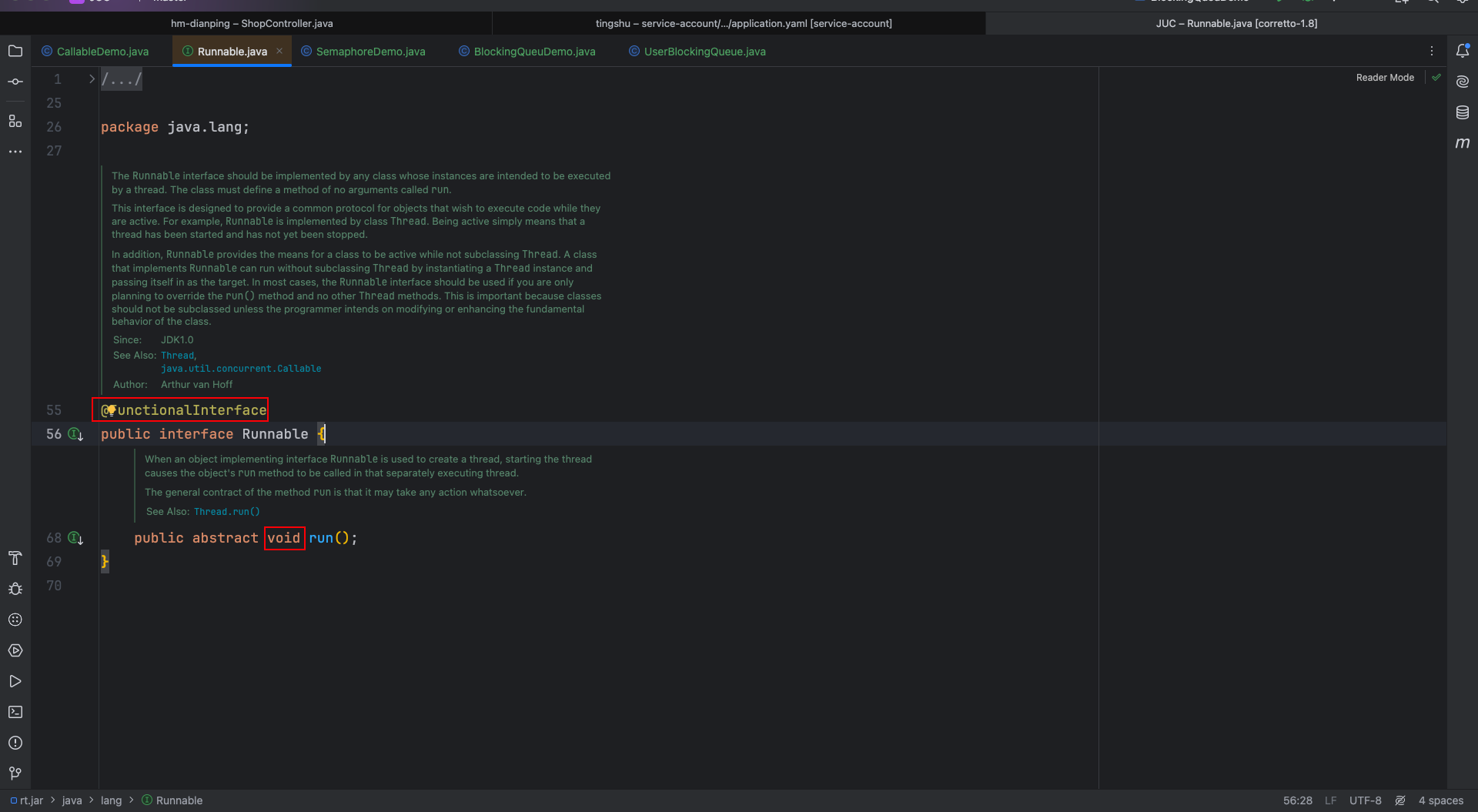
有三个区别:
- 具体方法不同:一个是run,一个是call
- Runnable没有返回值;Callable可以返回执行结果,是个泛型
- Callable接口的call()方法允许抛出异常;Runnable的run()方法异常只能在内部消化,不能往上继续抛
FutureTask futureTask = new FutureTask(new Callable());
Thread t = new Thread(FutureTask);
t.start();
Thread t = new Thread(new Runnable());
t.start();5.2 Callable 创建线程
new Thread()是不接收Callable对象的,只能接收Runnable对象,那到底该如何使用Callable呢?
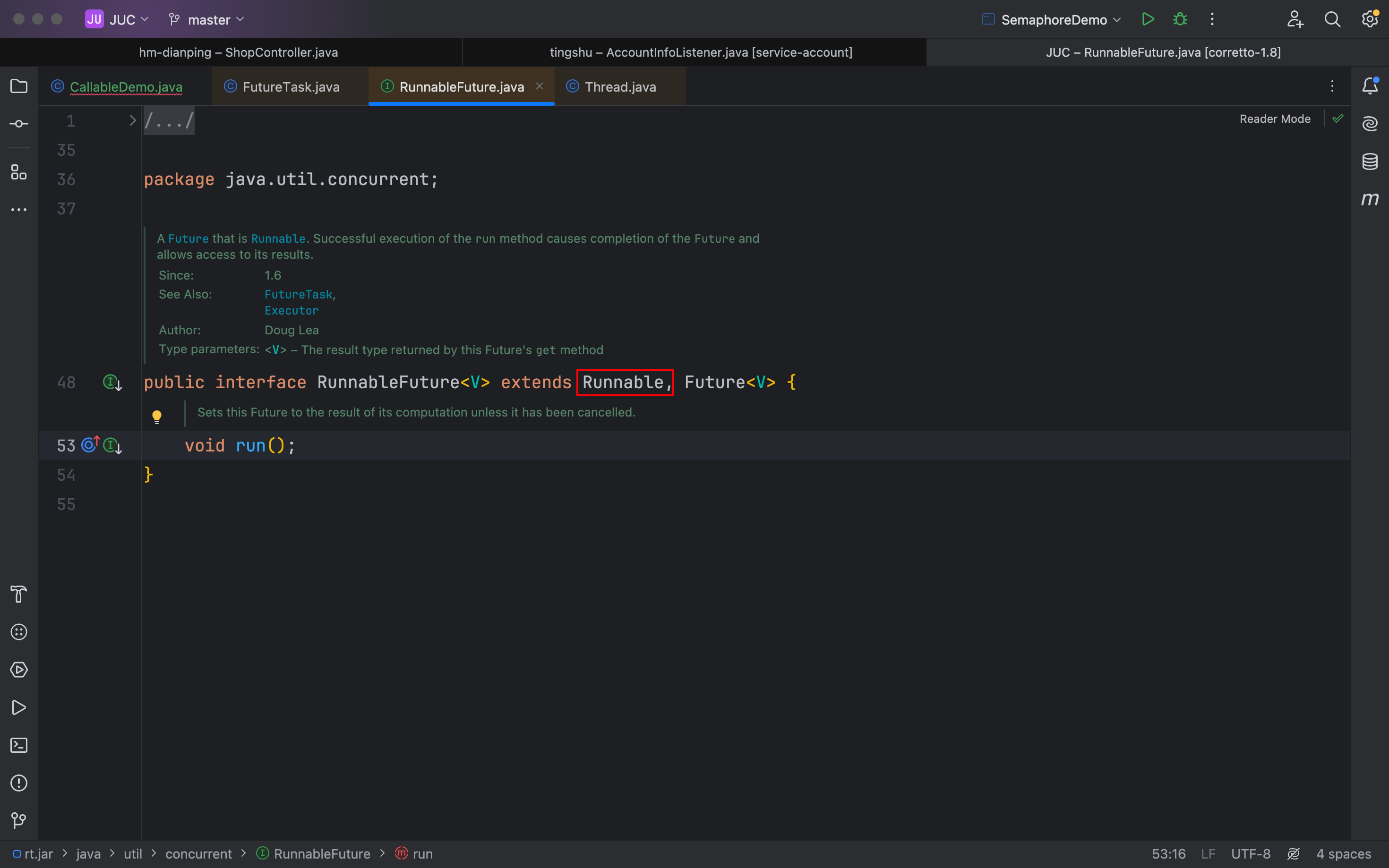
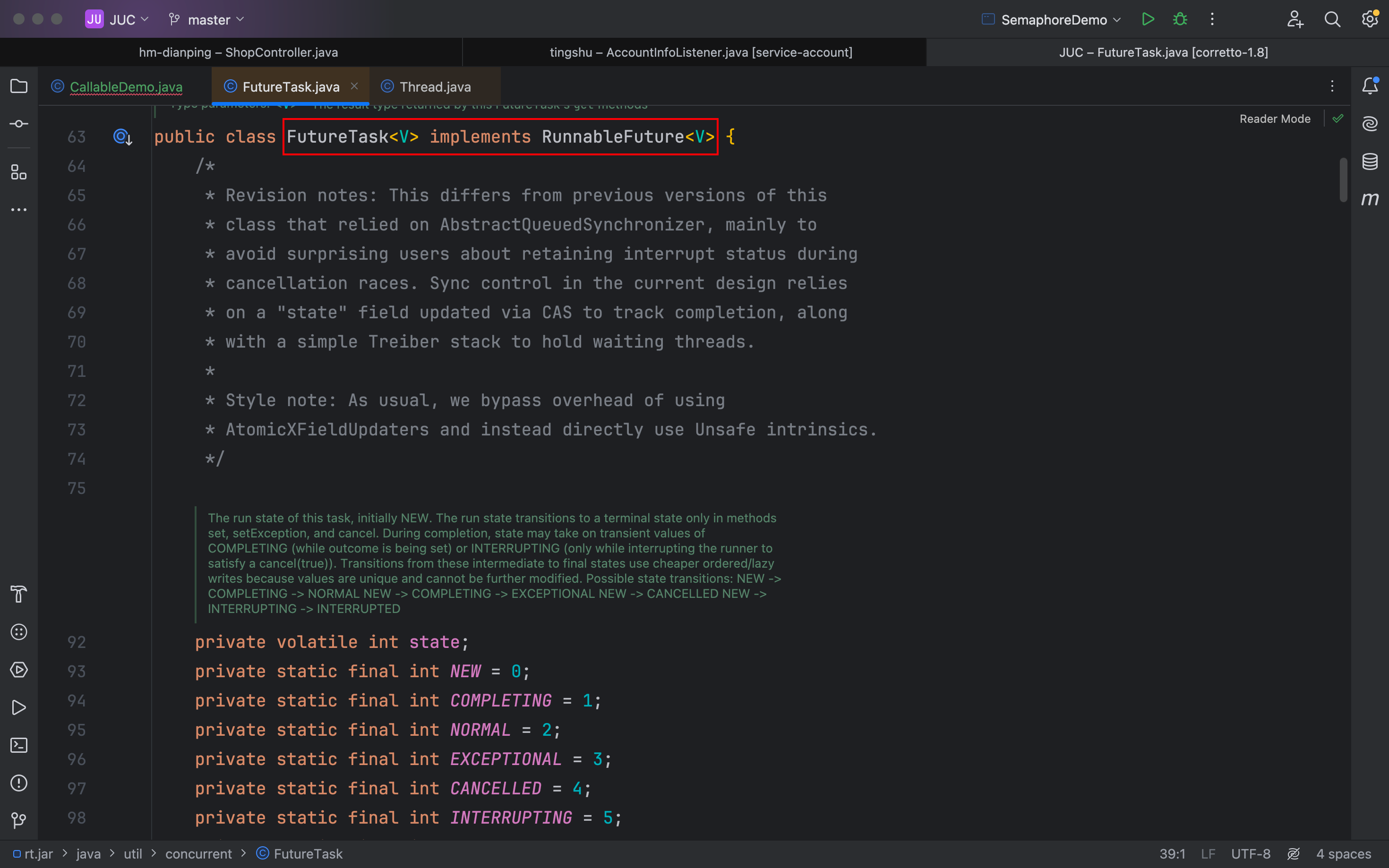
这时候借助一个FutureTask -> RunnableFuture -> Runnable
所以其实根本上,还是因为它实现了RunnableFuture接口,这个接口继承于Runnable接口
所以肯定是可以运行起来了!
new Thread(new FutureTask<>(new CallableFun()), "Callable").start();
class CallableFun implements Callable<Integer> {@Overridepublic Integer call() throws Exception {Thread.sleep(6);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "Callable is running!");return 666;}
}class RunnableFun implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Thread.sleep(10);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "Runnable is running!");}
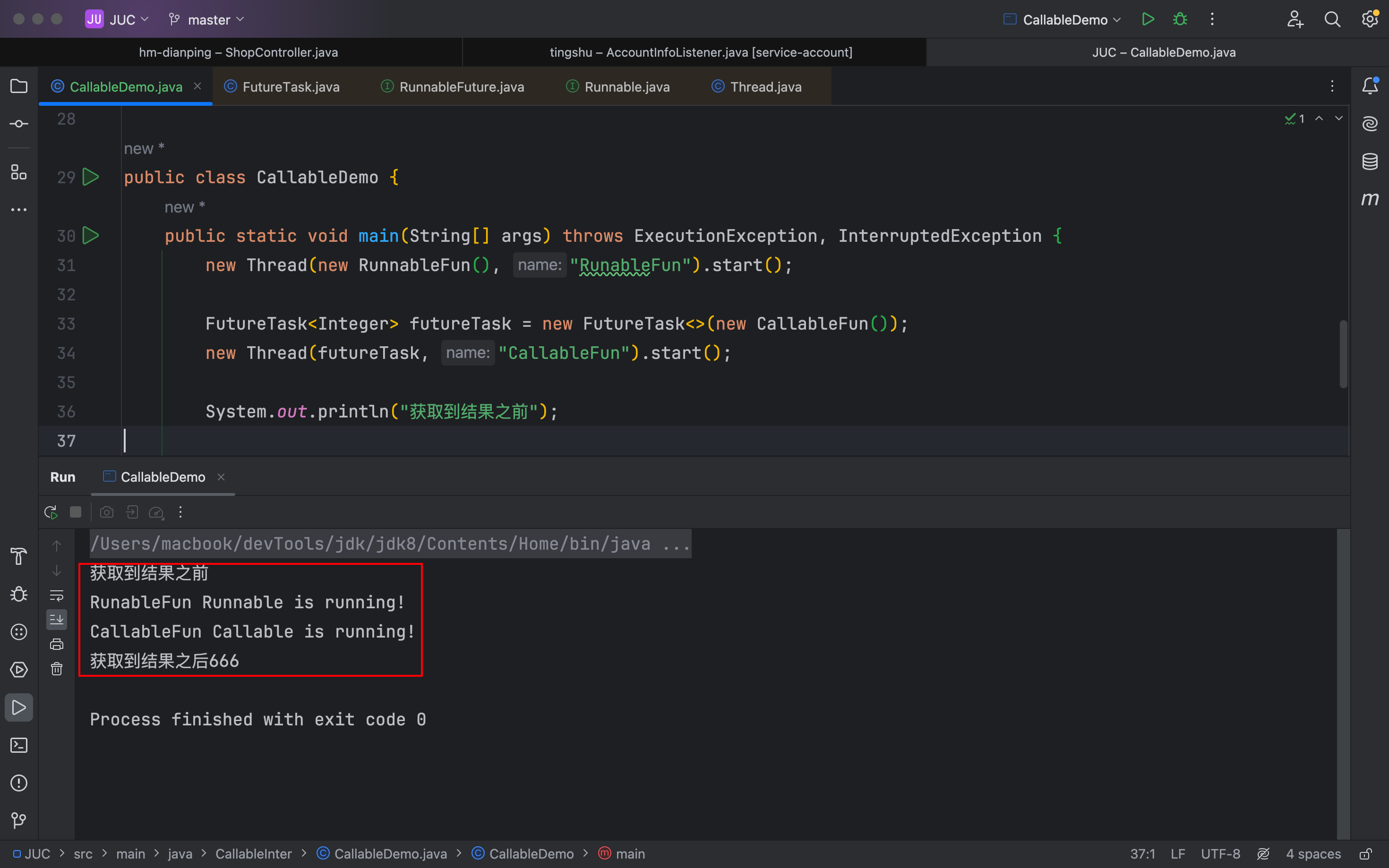
}public class CallableDemo {public static void main(String[] args) {new Thread(new RunnableFun(), "RunableFun").start();new Thread(new FutureTask<>(new CallableFun()), "Callable").start();}
}- 那么如何处理返回值呢?
使用Thread进行过去,发现没有那样的方法
这里使用FutureTask.get进行获取返回值,因为嵌在它里面,也可以理解
public class CallableDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {new Thread(new RunnableFun(), "RunableFun").start();FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(new CallableFun());new Thread(futureTask, "CallableFun").start();System.out.println("获取到结果之前");Integer res = futureTask.get();System.out.println("获取到结果之后" + res);}
}主线程,在 Callable 执行完之后才打印值,就是等他们执行完才得到返回值,get 方法会阻塞主线程。
- 因为
Callable接口有throw可以处理异常,所以需要抛出去 - 需要将
睡眠时间更改一下
class CallableFun implements Callable<Integer> {@Overridepublic Integer call() throws Exception {Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Callable is running!");return 666;}
}class RunnableFun implements Runnable {@Overridepublic void run() {try {Thread.sleep(500);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Runnable is running!");}
}5.3 FutureTask使用
一个FutureTask对象之后就只有一个结果输出,虽然是两个线程
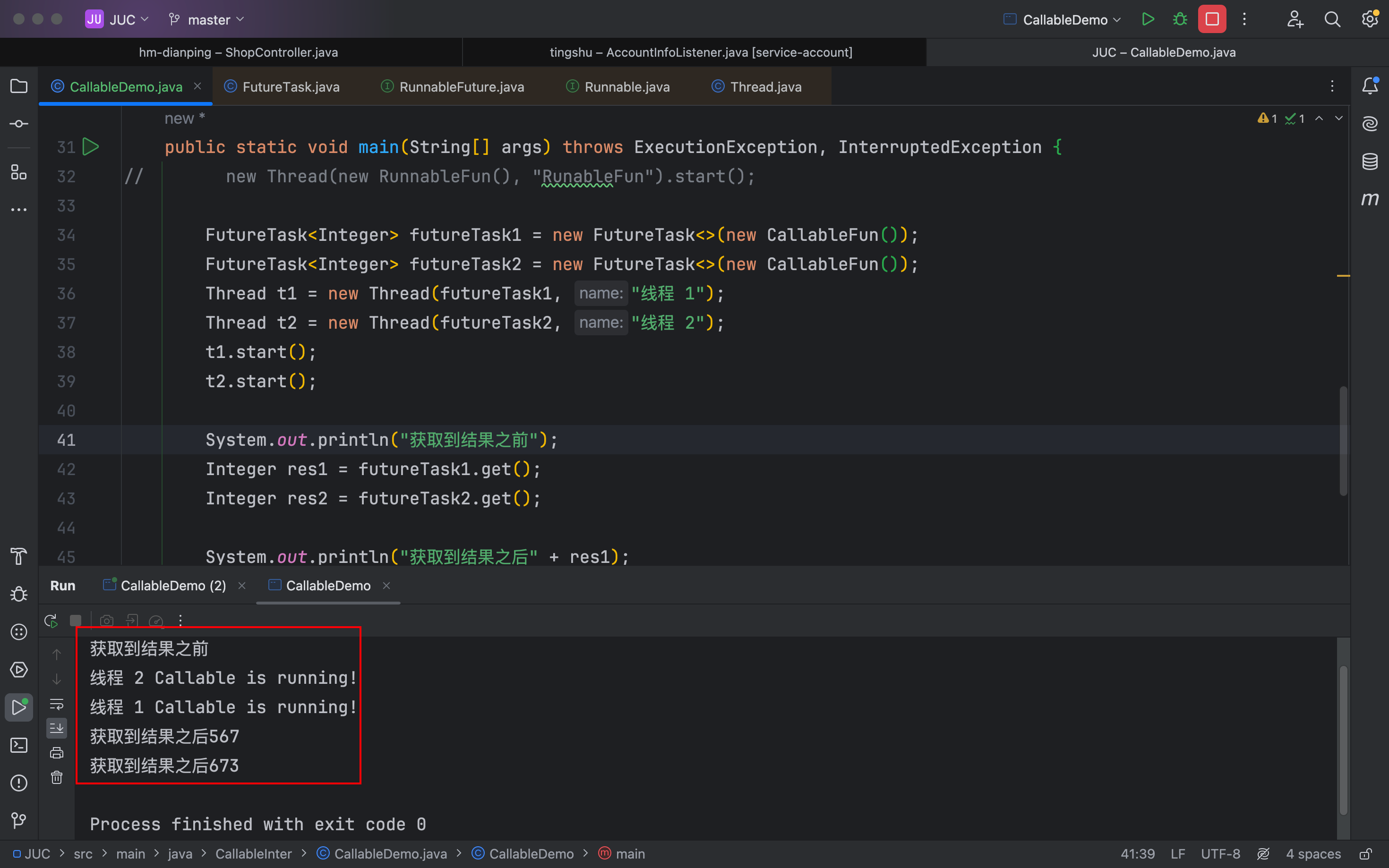
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(new CallableFun());Thread t1 = new Thread(futureTask, "线程 1");Thread t2 = new Thread(futureTask, "线程 2");t1.start();t2.start();System.out.println("获取到结果之前");Integer res = futureTask.get();System.out.println("获取到结果之后" + res);
}2 个FutureTask对象之后才会有 2 个结果输出
class CallableFun implements Callable<Integer> {@Overridepublic Integer call() throws Exception {Thread.sleep(500);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Callable is running!");return new Random().nextInt(1000);}
}public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {FutureTask<Integer> futureTask1 = new FutureTask<>(new CallableFun());FutureTask<Integer> futureTask2 = new FutureTask<>(new CallableFun());Thread t1 = new Thread(futureTask1, "线程 1");Thread t2 = new Thread(futureTask2, "线程 2");t1.start();t2.start();System.out.println("获取到结果之前");Integer res1 = futureTask1.get();Integer res2 = futureTask2.get();System.out.println("获取到结果之后" + res1);System.out.println("获取到结果之后" + res2);
}
FutureTask的方法
get:阻塞主线程isDone:判断异步线程是否执行完毕isCancelled:是否被取消了cancel
- true:打断子线程执行,并且抛出异常,无返回结果
- false:不打断子线程执行,并且抛出异常,无返回结果
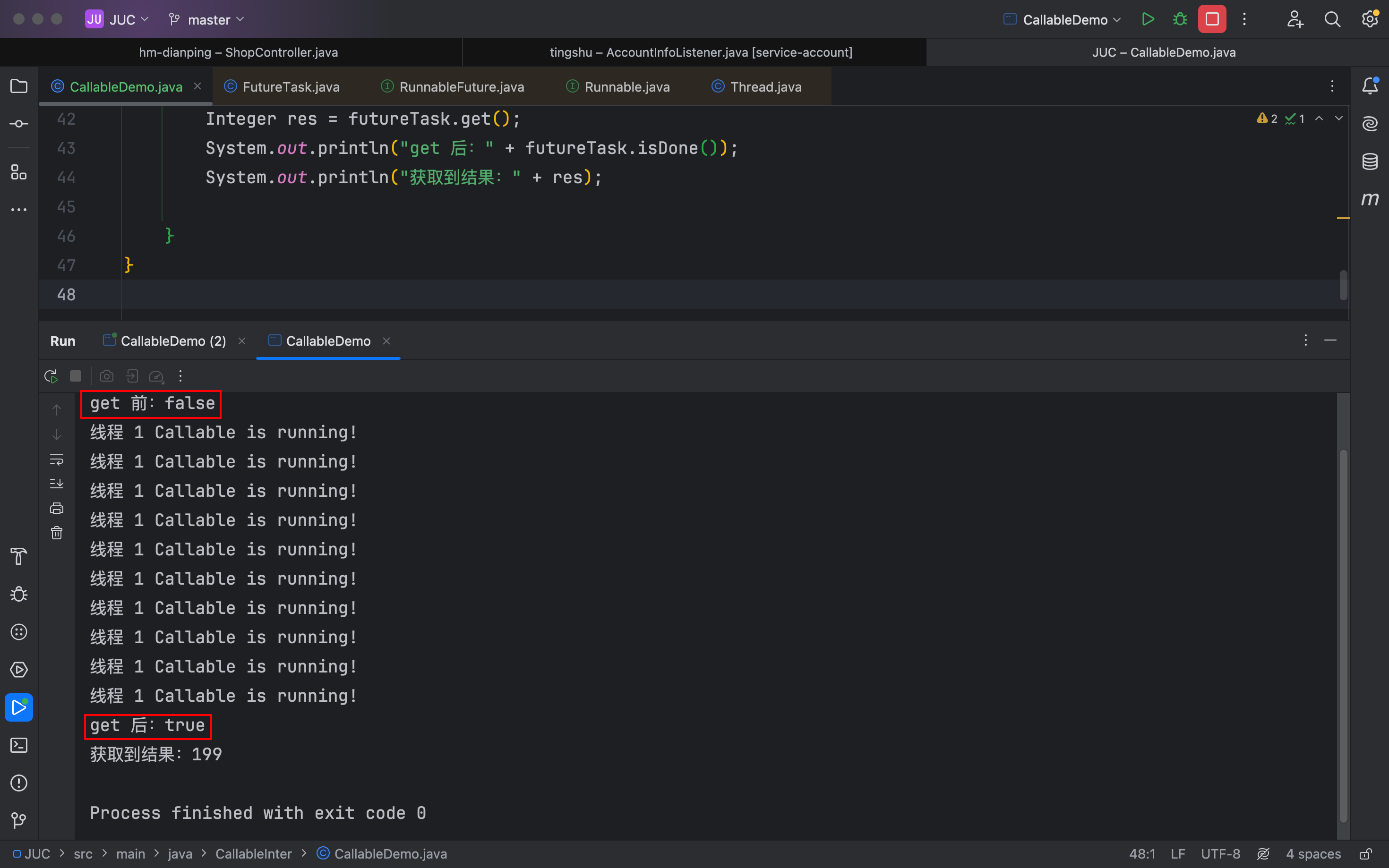
isDone方法:就是另一种判断是否get完成的方法
class CallableFun implements Callable<Integer> {@Overridepublic Integer call() throws Exception {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {Thread.sleep(500);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Callable is running!");}return new Random().nextInt(1000);}
}public class CallableDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(new CallableFun());new Thread(futureTask, "线程 1").start();System.out.println();;System.out.println("get 前:" + futureTask.isDone());Integer res = futureTask.get();System.out.println("get 后:" + futureTask.isDone());System.out.println("获取到结果:" + res);}
}
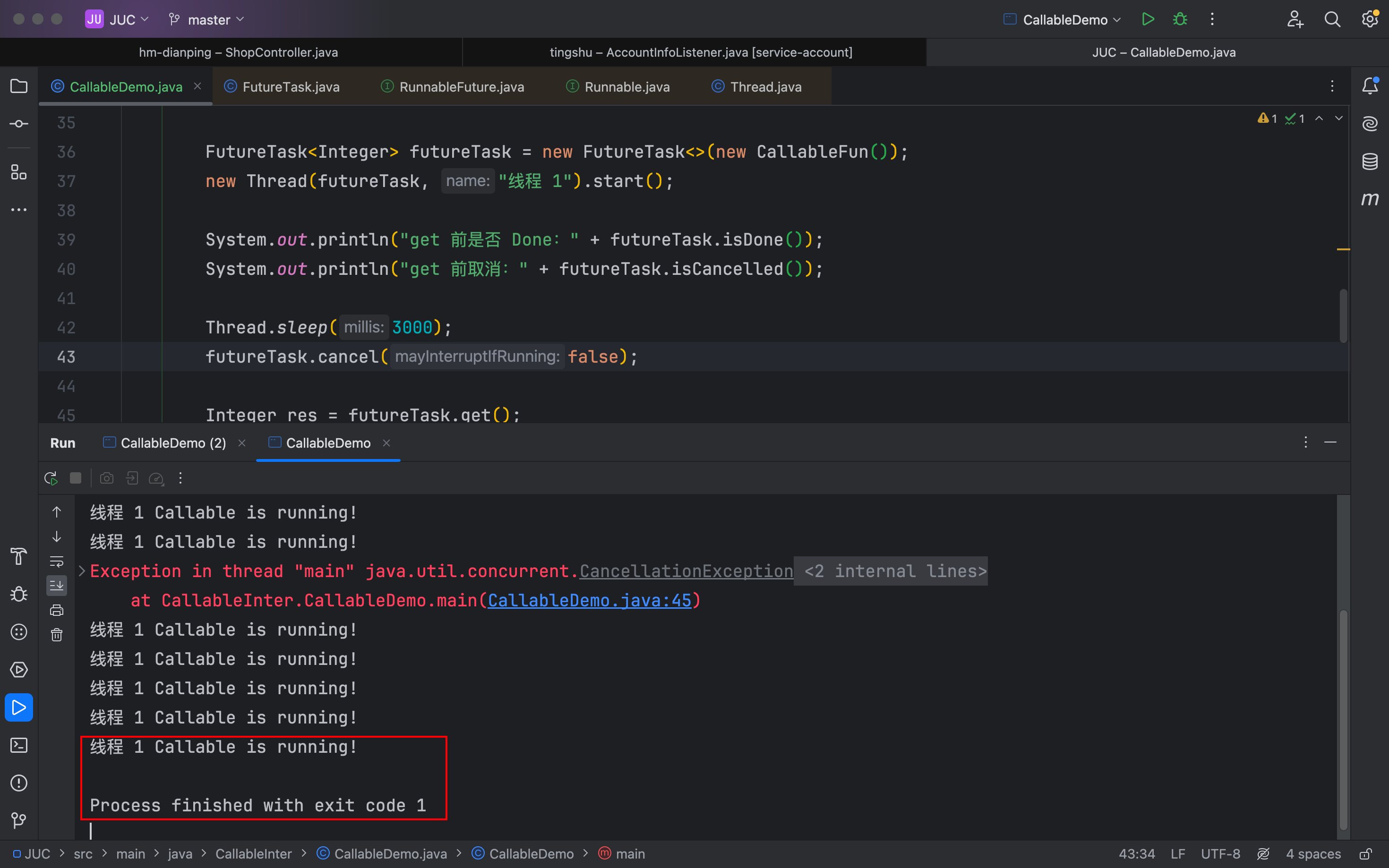
isCancelled、cancel方法
这里Thread.sleep是为了让主线程睡眠,子线程继续执行futureTask任务,来判断是否让子线程继续执行。
package CallableInter;import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;class CallableFun implements Callable<Integer> {@Overridepublic Integer call() throws Exception {for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {Thread.sleep(500);System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " Callable is running!");}return new Random().nextInt(1000);}
}public class CallableDemo {public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {// new Thread(new RunnableFun(), "RunableFun").start();FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(new CallableFun());new Thread(futureTask, "线程 1").start();System.out.println("get 前是否 Done:" + futureTask.isDone());System.out.println("get 前取消:" + futureTask.isCancelled());Thread.sleep(3000);futureTask.cancel(false);Integer res = futureTask.get();System.out.println("get 后取消:" + futureTask.isCancelled());System.out.println("get 后是否 Done:" + futureTask.isDone());System.out.println("获取到结果:" + res);}
}false不打断子线程的执行,会执行结束