langchain_agent智能体
1 什么是agent
在 AI 领域,Agent(智能体)简单说就是能自主理解任务、规划步骤、调用工具并完成目标的智能系统,核心是 “自己能做决策并行动”,而非被动等待指令。它和普通 AI(比如单纯的聊天机器人)最大的区别在于:普通 AI 只能根据输入直接输出答案,而 Agent 能像人一样 “思考”—— 比如判断 “这个任务需要查实时数据”,然后自己调用搜索引擎,拿到数据后再决定 “要不要整理成表格”,最终一步步完成复杂目标。
2 如何使用自定义tool
from langchain import hub
from langchain.agents import create_structured_chat_agent, AgentExecutor
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
from langchain.schema import HumanMessage
from langchain.tools import BaseTool
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAImodel = ChatOpenAI(model="qwen-plus",openai_api_key="你的api",openai_api_base="https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1",temperature=0)model.invoke([HumanMessage(content="'我是一个非常聪明的人工智能助手',这句话的字数是多少?")])class TextLengthTool(BaseTool):name = "文本字数计算工具"#工具名称description = "当你被要求计算文本的字数时,使用此工具"#工具描述def _run(self, text):return len(text)
#工具用类来定义,继承BaseTool这个父类tools = [TextLengthTool()]prompt = hub.pull("hwchase17/structured-chat-agent")#初始化agent
agent = create_structured_chat_agent(llm=model,tools=tools,prompt=prompt
)
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(memory_key='chat_history',return_messages=True
)#定义agent执行器
agent_executor = AgentExecutor.from_agent_and_tools(agent=agent, tools=tools, memory=memory, verbose=True, handle_parsing_errors=True#出现错误也不会停止推理,而是返回大模型让大模型判断
)agent_executor.invoke({"input": "'我是一个非常聪明的人工智能助手',这句话的字数是多少?"})
agent_executor.invoke({"input": "请你充当我的数学老师,告诉我什么是勾股定理"})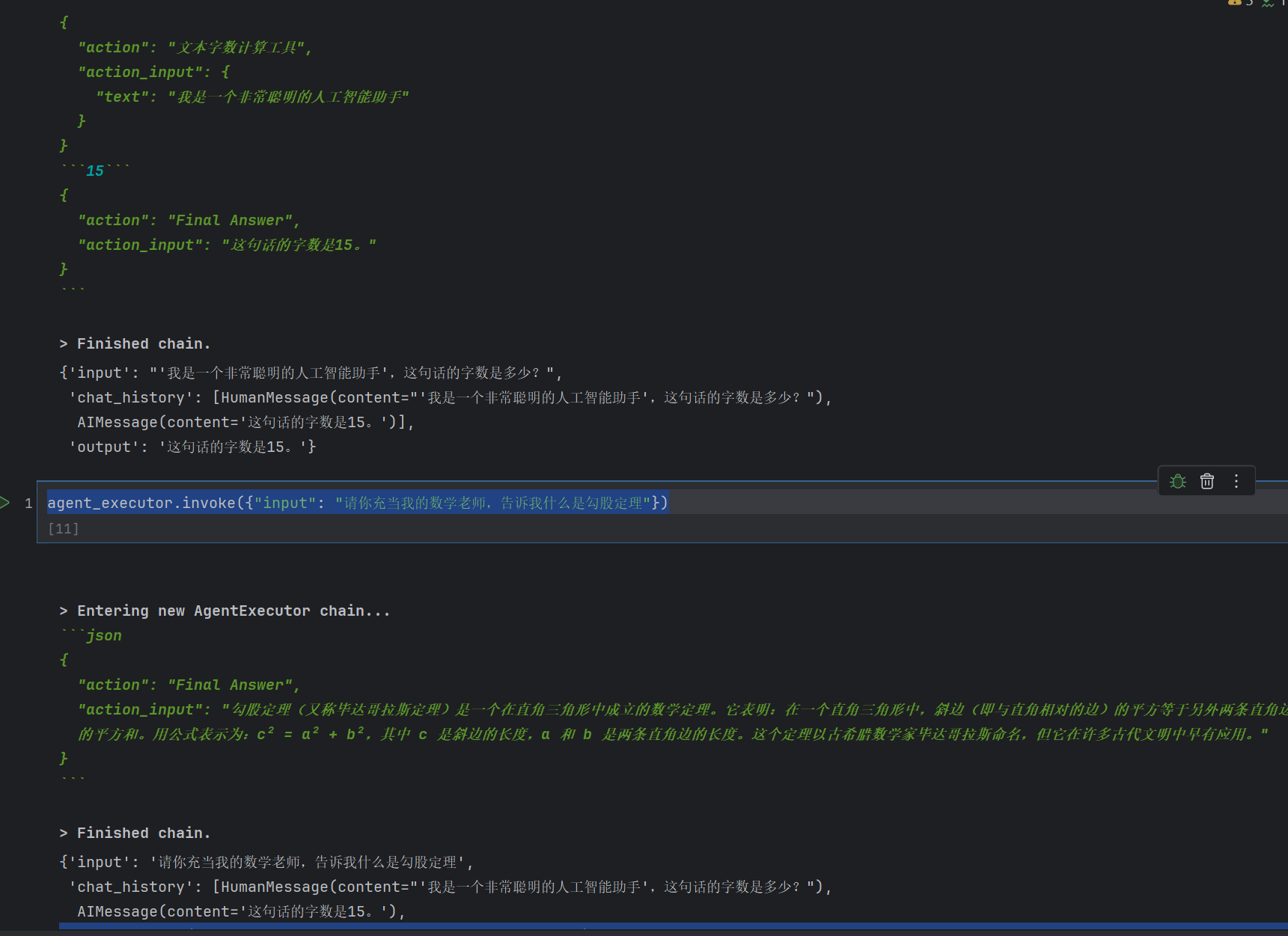
前面我们定义了一个工具也就是一个类,可以去得到我们用户信息的长度。后面我们也可以看到,我们用户消息问,“这段话的长度是多少”。然后我们的智能体agent会识别到,然后去调用我们的tools工具。
3 使用系统工具
from langchain_experimental.agents.agent_toolkits import create_python_agent
from langchain_experimental.tools import PythonREPLTool
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
#%%#%%
tools = [PythonREPLTool()]
#%% md
PythonREPLTool() 是 langchain_experimental 库中提供的一个Python 代码执行工具,核心作用是让 LangChain Agent 能够在本地直接运行 Python 代码,实现 “思考 + 执行代码” 的闭环。
简单说,它相当于给 Agent 内置了一个 “迷你 Python 终端”,Agent 可以根据任务需求自动生成代码,再通过这个工具执行代码并获取结果(比如计算数据、处理文件、调用其他库等)。
#%%
agent_executor = create_python_agent(llm=ChatOpenAI(model="qwen-plus",openai_api_key="你的api",openai_api_base="https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1",temperature=0),tool=PythonREPLTool(),verbose=True,agent_executor_kwargs={"handle_parsing_errors": True}
)
#%%
agent_executor
#%%
agent_executor.invoke({"input": "5的3.6次方是多少?"})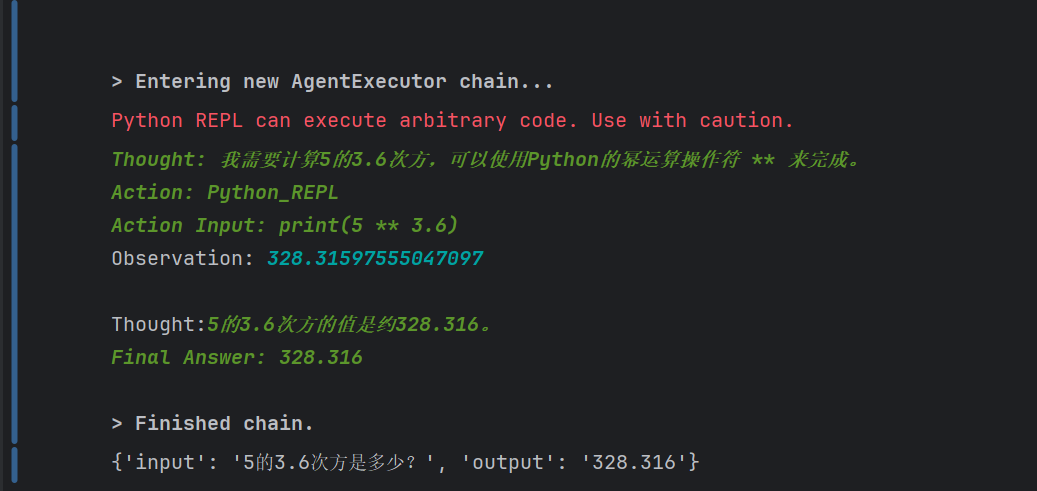
这个我们可以看到我们调用了python编辑器,就是说我们问一个问题,然后agent会识别到会用到我们的工具,然后就会去用工具,然后调用python的一部分代码去实现这个。
4 使用多个工具
# 导入必要的库
from langchain import hub
from langchain.agents import create_structured_chat_agent, AgentExecutor
from langchain.memory import ConversationBufferMemory
from langchain.tools import BaseTool
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from typing import Optional, Type
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
from langchain.schema import HumanMessage
# ---------------------- 1. 初始化大语言模型 ----------------------
# 使用通义千问模型作为基础LLM,配置API密钥和基础URL
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="qwen-plus", # 模型名称openai_api_key="sk-be596483fa8c4684aa9611075c9b06be", # API密钥openai_api_base="https://dashscope.aliyuncs.com/compatible-mode/v1", # 阿里云API基础地址temperature=0.3 # 控制输出随机性,0.3表示略保守
)# ---------------------- 2. 定义学习相关工具 ----------------------
# 工具1:知识存储工具 - 用于记录学习内容
class KnowledgeStorageTool(BaseTool):# 工具元数据:名称和描述(供Agent判断何时使用)name = "知识存储工具"description = "当需要记录新的学习知识时使用,接收文本内容作为输入并保存"# 定义工具输入参数格式(使用Pydantic模型规范)class ArgsSchema(BaseModel):content: str = Field(description="需要存储的学习内容文本")args_schema: Type[BaseModel] = ArgsSchema # 绑定输入参数模型# 工具核心执行方法def _run(self, content: str) -> str:# 实际应用中可替换为数据库存储,这里用简单文件存储示例with open("learned_knowledge.txt", "a", encoding="utf-8") as f:f.write(f"- {content}\n")return f"已成功存储知识:{content[:20]}..." # 返回存储结果(截断长文本)# 工具2:知识查询工具 - 用于检索已学习内容
class KnowledgeQueryTool(BaseTool):name = "知识查询工具"description = "当需要查询已学习的知识时使用,可按关键词搜索"class ArgsSchema(BaseModel):keyword: str = Field(description="用于查询的关键词")args_schema: Type[BaseModel] = ArgsSchemadef _run(self, keyword: str) -> str:try:# 读取存储的知识并筛选包含关键词的内容with open("learned_knowledge.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:knowledge = f.readlines()# 筛选包含关键词的知识results = [line.strip() for line in knowledge if keyword in line]if results:return f"找到相关知识:\n" + "\n".join(results)else:return f"未找到包含'{keyword}'的知识"except FileNotFoundError:return "尚未学习任何知识,请先存储知识"# 工具3:知识复习工具 - 用于随机抽取已学内容进行复习
class KnowledgeReviewTool(BaseTool):name = "知识复习工具"description = "当需要复习已学习的知识时使用,随机返回部分内容"class ArgsSchema(BaseModel):count: Optional[int] = Field(default=2, description="需要复习的知识数量,默认2条")args_schema: Type[BaseModel] = ArgsSchemadef _run(self, count: int = 2) -> str:try:with open("learned_knowledge.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:knowledge = [line.strip() for line in f.readlines()]if not knowledge:return "没有可复习的知识"# 随机选择指定数量的知识(不超过总数量)import randomreview_count = min(count, len(knowledge))review_items = random.sample(knowledge, review_count)return f"复习内容(共{review_count}条):\n" + "\n".join(review_items)except FileNotFoundError:return "尚未学习任何知识,请先存储知识"# 工具4:知识总结工具 - 用于总结已学内容
class KnowledgeSummaryTool(BaseTool):name = "知识总结工具"description = "当需要总结已学习的所有知识时使用,生成简洁概述"def _run(self) -> str:try:with open("learned_knowledge.txt", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:knowledge = f.read()if not knowledge.strip():return "没有可总结的知识"# 调用LLM生成总结(利用基础模型进行文本总结)summary_prompt = f"请简洁总结以下知识:\n{knowledge}\n总结:"summary = llm.invoke([HumanMessage(content=summary_prompt)]).contentreturn f"知识总结:\n{summary}"except FileNotFoundError:return "尚未学习任何知识,请先存储知识"# ---------------------- 3. 配置Agent核心组件 ----------------------
# 1. 组装工具列表
tools = [KnowledgeStorageTool(),KnowledgeQueryTool(),KnowledgeReviewTool(),KnowledgeSummaryTool()
]# 2. 获取结构化聊天Agent的提示词模板
# 该模板定义了Agent的行为规范,包括如何使用工具、处理记忆等
prompt = hub.pull("hwchase17/structured-chat-agent")# 3. 创建对话记忆(保存多轮对话历史,支持上下文理解)
memory = ConversationBufferMemory(memory_key="chat_history", # 与prompt中的变量名对应return_messages=True # 以消息对象形式返回历史,便于Agent理解
)# 4. 创建结构化聊天Agent
# 将LLM、工具和提示词组合,形成具有工具使用能力的智能体
agent = create_structured_chat_agent(llm=llm, # 基础语言模型tools=tools, # Agent可使用的工具集合prompt=prompt # 指导Agent行为的提示词模板
)# 5. 创建Agent执行器(负责协调Agent运行和工具调用)
agent_executor = AgentExecutor(agent=agent,tools=tools,memory=memory, # 传入对话记忆,支持多轮对话verbose=True, # 开启详细日志(调试时查看Agent思考过程)handle_parsing_errors=True # 自动处理解析错误
)# ---------------------- 4. 测试学习型Agent ----------------------
if __name__ == "__main__":# 任务1:学习新知识并存储task1 = "我想学习Python的基础知识:Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言。"print(f"任务1:{task1}")result1 = agent_executor.invoke({"input": task1})print(f"结果1:{result1['output']}\n")# 任务2:学习另一个知识点task2 = "再记一个:LangChain是一个用于开发由语言模型驱动的应用程序的框架,它提供了工具调用、记忆等功能。"print(f"任务2:{task2}")result2 = agent_executor.invoke({"input": task2})print(f"结果2:{result2['output']}\n")# 任务3:查询已学知识task3 = "帮我查一下关于'Python'的知识"print(f"任务3:{task3}")result3 = agent_executor.invoke({"input": task3})print(f"结果3:{result3['output']}\n")# 任务4:复习已学内容task4 = "我想复习一下刚才学的知识,给我3条"print(f"任务4:{task4}")result4 = agent_executor.invoke({"input": task4})print(f"结果4:{result4['output']}\n")# 任务5:总结所有知识task5 = "请总结一下我今天学的所有内容"print(f"任务5:{task5}")result5 = agent_executor.invoke({"input": task5})print(f"结果5:{result5['output']}")结果展示:
任务1:我想学习Python的基础知识:Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言。> Entering new AgentExecutor chain...
D:\agent\demo1\langchain_agent\venv\Lib\site-packages\langchain_core\tools.py:304: PydanticDeprecatedSince20: The `parse_obj` method is deprecated; use `model_validate` instead. Deprecated in Pydantic V2.0 to be removed in V3.0. See Pydantic V2 Migration Guide at https://errors.pydantic.dev/2.12/migration/result = input_args.parse_obj(tool_input)
D:\agent\demo1\langchain_agent\venv\Lib\site-packages\langchain_core\tools.py:307: PydanticDeprecatedSince20: The `dict` method is deprecated; use `model_dump` instead. Deprecated in Pydantic V2.0 to be removed in V3.0. See Pydantic V2 Migration Guide at https://errors.pydantic.dev/2.12/migration/for k, v in result.dict().items()
{"action": "知识存储工具","action_input": {"content": "Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言。"}
}已成功存储知识:Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态...{"action": "Final Answer","action_input": "已成功存储关于Python的基础知识:Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言。"
}> Finished chain.
结果1:已成功存储关于Python的基础知识:Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言。任务2:再记一个:LangChain是一个用于开发由语言模型驱动的应用程序的框架,它提供了工具调用、记忆等功能。> Entering new AgentExecutor chain...
```
{"action": "知识存储工具","action_input": {"content": "LangChain是一个用于开发由语言模型驱动的应用程序的框架,它提供了工具调用、记忆等功能。"}
}
```已成功存储知识:LangChain是一个用于开发由语言模...D:\agent\demo1\langchain_agent\venv\Lib\site-packages\langchain_core\tools.py:304: PydanticDeprecatedSince20: The `parse_obj` method is deprecated; use `model_validate` instead. Deprecated in Pydantic V2.0 to be removed in V3.0. See Pydantic V2 Migration Guide at https://errors.pydantic.dev/2.12/migration/result = input_args.parse_obj(tool_input)
D:\agent\demo1\langchain_agent\venv\Lib\site-packages\langchain_core\tools.py:307: PydanticDeprecatedSince20: The `dict` method is deprecated; use `model_dump` instead. Deprecated in Pydantic V2.0 to be removed in V3.0. See Pydantic V2 Migration Guide at https://errors.pydantic.dev/2.12/migration/for k, v in result.dict().items()
```
{"action": "Final Answer","action_input": "已成功存储关于LangChain的知识:LangChain是一个用于开发由语言模型驱动的应用程序的框架,它提供了工具调用、记忆等功能。"
}
```> Finished chain.
结果2:已成功存储关于LangChain的知识:LangChain是一个用于开发由语言模型驱动的应用程序的框架,它提供了工具调用、记忆等功能。任务3:帮我查一下关于'Python'的知识> Entering new AgentExecutor chain...
```
{"action": "知识查询工具","action_input": {"keyword": "Python"}
}
```D:\agent\demo1\langchain_agent\venv\Lib\site-packages\langchain_core\tools.py:304: PydanticDeprecatedSince20: The `parse_obj` method is deprecated; use `model_validate` instead. Deprecated in Pydantic V2.0 to be removed in V3.0. See Pydantic V2 Migration Guide at https://errors.pydantic.dev/2.12/migration/result = input_args.parse_obj(tool_input)
D:\agent\demo1\langchain_agent\venv\Lib\site-packages\langchain_core\tools.py:307: PydanticDeprecatedSince20: The `dict` method is deprecated; use `model_dump` instead. Deprecated in Pydantic V2.0 to be removed in V3.0. See Pydantic V2 Migration Guide at https://errors.pydantic.dev/2.12/migration/for k, v in result.dict().items()
找到相关知识:
- Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言。
- Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言。
- Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言。
- Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言。
- Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言。
- Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言。
- Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言。
- Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言。```
{"action": "Final Answer","action_input": "Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言。"
}
```> Finished chain.
结果3:Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言。任务4:我想复习一下刚才学的知识,给我3条> Entering new AgentExecutor chain...
```
{"action": "知识复习工具","action_input": {"count": 3}
}
```复习内容(共3条):
- LangChain是一个用于开发由语言模型驱动的应用程序的框架,它提供了工具调用、记忆等功能。
- Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言。
- LangChain是一个用于开发由语言模型驱动的应用程序的框架,它提供了工具调用、记忆等功能。D:\agent\demo1\langchain_agent\venv\Lib\site-packages\langchain_core\tools.py:304: PydanticDeprecatedSince20: The `parse_obj` method is deprecated; use `model_validate` instead. Deprecated in Pydantic V2.0 to be removed in V3.0. See Pydantic V2 Migration Guide at https://errors.pydantic.dev/2.12/migration/result = input_args.parse_obj(tool_input)
D:\agent\demo1\langchain_agent\venv\Lib\site-packages\langchain_core\tools.py:307: PydanticDeprecatedSince20: The `dict` method is deprecated; use `model_dump` instead. Deprecated in Pydantic V2.0 to be removed in V3.0. See Pydantic V2 Migration Guide at https://errors.pydantic.dev/2.12/migration/for k, v in result.dict().items()
```
{"action": "Final Answer","action_input": "复习内容(共3条):\n1. Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言。\n2. LangChain是一个用于开发由语言模型驱动的应用程序的框架,它提供了工具调用、记忆等功能。\n3. (重复项)LangChain是一个用于开发由语言模型驱动的应用程序的框架,它提供了工具调用、记忆等功能。"
}
```> Finished chain.
结果4:复习内容(共3条):
1. Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言。
2. LangChain是一个用于开发由语言模型驱动的应用程序的框架,它提供了工具调用、记忆等功能。
3. (重复项)LangChain是一个用于开发由语言模型驱动的应用程序的框架,它提供了工具调用、记忆等功能。任务5:请总结一下我今天学的所有内容> Entering new AgentExecutor chain...
{"action": "知识总结工具","action_input": {}
}知识总结:
Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态类型的高级编程语言。LangChain是一个用于构建由语言模型驱动的应用程序的框架,支持工具调用、记忆等核心功能。```
{"action": "Final Answer","action_input": "今天学习的内容总结如下:\n1. Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言。\n2. LangChain是一个用于开发由语言模型驱动的应用程序的框架,提供了工具调用、记忆等功能。"
}
```> Finished chain.
结果5:今天学习的内容总结如下:
1. Python是一种解释型、面向对象、动态数据类型的高级程序设计语言。
2. LangChain是一个用于开发由语言模型驱动的应用程序的框架,提供了工具调用、记忆等功能。
像上面那样,我们的agent会有许多工具,然后根据我们的问题去实现任务。而且我们的agent还有记忆功能。
