对象存储技术解析:选型对比、架构设计与动态切换实战
1. 引言
在数字化转型的浪潮中,数据已成为企业最重要的资产之一。随着数据规模的爆炸式增长和数据类型的多样化,传统的文件存储和块存储已难以满足现代应用的需求。对象存储作为一种新兴的存储技术,以其高扩展性、低成本和灵活的数据管理能力,正在成为存储海量非结构化数据的首选方案。本文将深入探讨对象存储的选型策略、架构设计、应用场景以及基于SpringBoot & SpringCloud的实战实现,为企业构建高性能、可扩展的存储架构提供选型参考。
2. 对象存储概述
2.1 对象存储定义与特点
对象存储是一种基于对象的数据管理方式,将每个文件视为独立的"对象",并为每个对象分配唯一的标识符(Key)。与传统的文件系统不同,对象存储不使用分层目录结构,而是通过平面对象池和元数据来组织和检索数据。
核心特点:
- 扁平化命名空间 :无目录层次结构,通过唯一的键值直接访问对象
- 丰富的元数据 :支持自定义元数据,便于数据分类、搜索和管理
- HTTP/HTTPS访问 :通过RESTful API进行数据操作,无需专用客户端
- 无限扩展性 :理论上可存储无限量的数据,容量可随需求线性扩展
- 高可用性 :多副本或纠删码机制确保数据安全可靠
- 低成本 :适合大规模数据的长期存储,存储成本远低于传统存储
术语定义:
- 对象存储:一种数据存储架构,将数据以对象形式存储,而非传统的文件系统或块存储
- OSS:对象存储服务(Object Storage Service)的缩写
- S3:Amazon Simple Storage Service,是对象存储的行业标准协议之一
- MinIO:开源的对象存储服务器,兼容S3协议
- CDN:内容分发网络,用于加速内容的传输
2.2 主要应用场景
对象存储特别适合存储以下类型的数据:
- 多媒体内容:图片、音频、视频等静态资源
- 文档资料:PDF、Office文档等
- 日志文件:系统日志、应用日志等
- 备份和归档数据:长期保存的历史数据
- 大数据分析源数据:支持直接计算的原始数据集
- IoT设备数据:传感器产生的时序数据
3. 主流对象存储方案对比
3.1 公有云对象存储
3.1.1 阿里云对象存储OSS
特点:
- 提供多区域、多可用区部署,确保服务高可用
- 支持多种存储类型:标准存储、低频访问存储、归档存储等
- 内置CDN加速分发能力
- 完善的安全机制:访问控制、数据加密、日志审计等
- 丰富的增值服务:图片处理、音视频转码、内容审核等
适用场景:
- 互联网应用的静态资源存储
- 企业级数据备份和归档
- 多媒体内容托管和分发
- 大数据分析平台数据源
3.1.2 AWS Simple Storage Service(S3)
特点:
- 业界标杆,S3协议的发源地
- 提供11个9的数据持久性保证
- 极其丰富的存储类别:Standard、Intelligent-Tiering、Glacier等
- 全球区域覆盖,支持跨区域复制
- 强大的生态系统和集成能力
适用场景:
- 全球性应用的数据存储
- 需要极高数据可靠性的业务
- 复杂的数据生命周期管理需求
- 与AWS其他服务深度集成的场景
3.1.3 腾讯云对象存储COS
特点:
- 完全兼容S3 API
- 支持多种存储类型和数据生命周期管理
- 与腾讯云生态深度整合
- 提供全球加速和中国境内加速服务
- 支持HDFS兼容访问模式
适用场景:
- 游戏行业的数据存储和分发
- 视频直播和点播服务
- 企业办公协作和文档管理
- 与腾讯云其他服务结合的应用
3.1.4 百度云对象存储BOS
- 特性:支持CDN加速、视频处理、图片处理
- 优势:国内访问速度快、AI功能集成
- 劣势:生态相对较弱、API与S3兼容性有限
- 典型应用场景:媒体处理、AI应用数据存储
3.2 开源自建对象存储
3.2.1 MinIO
特点:
- 100%兼容S3 API,无需修改应用代码即可迁移
- 极高的性能:单集群支持10GB/s读和写入性能
- 部署简单:单二进制文件,支持Docker容器化部署
- 支持纠删码和多副本机制
- 企业级特性:IAM身份管理、加密、审计日志等
适用场景:
- 私有云对象存储部署
- 边缘计算数据存储
- 开发和测试环境
- 对性能要求极高的应用
3.2.2 Ceph
特点:
- 统一存储架构:块存储、文件存储、对象存储一体化
- 高可扩展性:支持PB级存储容量
- 强大的纠删码支持,提高存储效率
- 完全兼容S3和Swift API
- 活跃的社区支持和丰富的文档
适用场景:
- 大规模企业级存储基础设施
- 需要多种存储服务的混合环境
- 对数据安全性和可靠性要求极高的场景
- 科研和大数据领域
3.2.3 Apache Ozone
特点:
- 为大数据和Hadoop生态系统优化
- 支持与HDFS客户端兼容的接口
- 高度可扩展,支持数十亿个对象
- 强大的一致性保证
- 支持多租户隔离
适用场景:
- 大数据分析平台
- Hadoop生态系统的存储层
- 大规模数据分析和处理场景
- 需要与大数据工具集成的应用
3.3 对比总结
| 特性 | 阿里云OSS | AWS S3 | 腾讯云COS | 百度云BOS | MinIO | Ceph | Apache Ozone |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 部署方式 | 云服务 | 云服务 | 云服务 | 云服务 | 自托管 | 自托管 | 自托管 |
| 成本模型 | 按需付费 | 按需付费 | 按需付费 | 按需付费 | 免费开源 | 免费开源 | 免费开源 |
| S3兼容性 | 兼容 | 原生 | 兼容 | 兼容 | 完全兼容 | 兼容 | 部分兼容 |
| 性能 | 优秀 | 优秀 | 优秀 | 优秀 | 优秀 | 优秀 | 优秀 |
| 部署难度 | 极低 | 极低 | 极低 | 极低 | 中等 | 高 | 中高 |
| 维护成本 | 极低 | 极低 | 极低 | 极低 | 高 | 高 | 高 |
| 适用规模 | 任何规模 | 任何规模 | 任何规模 | 任何规模 | 中小型 | 大型 | 大型 |
4. 统一API接口设计
4.1 设计原则
- 接口抽象:定义统一的抽象接口,屏蔽底层实现差异
- 依赖注入:使用Spring的依赖注入机制管理实现类
- 可扩展性:支持轻松添加新的存储实现
- 错误处理:统一的异常处理机制
4.2 核心接口定义
package com.example.storage.api;import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;public interface ObjectStorageService {/*** 上传对象*/String upload(String bucketName, String objectName, InputStream inputStream, Map<String, String> metadata);/*** 上传对象(异步)*/CompletableFuture<String> uploadAsync(String bucketName, String objectName, InputStream inputStream, Map<String, String> metadata);/*** 下载对象*/InputStream download(String bucketName, String objectName);/*** 下载对象(异步)*/CompletableFuture<InputStream> downloadAsync(String bucketName, String objectName);/*** 删除对象*/boolean delete(String bucketName, String objectName);/*** 删除对象(异步)*/CompletableFuture<Boolean> deleteAsync(String bucketName, String objectName);/*** 检查对象是否存在*/boolean exists(String bucketName, String objectName);/*** 获取对象元数据*/Map<String, String> getMetadata(String bucketName, String objectName);/*** 创建存储桶*/boolean createBucket(String bucketName);/*** 删除存储桶*/boolean deleteBucket(String bucketName);/*** 列出存储桶中的对象*/List<String> listObjects(String bucketName, String prefix);
}4.3 实现类设计
4.3.1 OSS实现
package com.example.storage.impl;import com.example.storage.api.ObjectStorageService;
import com.aliyun.oss.OSS;
import com.aliyun.oss.OSSClientBuilder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Service("ossStorageService")
public class OssObjectStorageServiceImpl implements ObjectStorageService {@Value("${storage.oss.endpoint}")private String endpoint;@Value("${storage.oss.accessKeyId}")private String accessKeyId;@Value("${storage.oss.accessKeySecret}")private String accessKeySecret;private OSS getOssClient() {return new OSSClientBuilder().build(endpoint, accessKeyId, accessKeySecret);}@Overridepublic String upload(String bucketName, String objectName, InputStream inputStream, Map<String, String> metadata) {OSS ossClient = getOssClient();try {ossClient.putObject(bucketName, objectName, inputStream);return "https://" + bucketName + "." + endpoint + "/" + objectName;} finally {ossClient.shutdown();}}// 实现其他方法...
}4.3.2 MinIO实现
package com.example.storage.impl;import com.example.storage.api.ObjectStorageService;
import io.minio.MinioClient;
import io.minio.PutObjectArgs;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;@Service("minioStorageService")
public class MinioObjectStorageServiceImpl implements ObjectStorageService {@Value("${storage.minio.endpoint}")private String endpoint;@Value("${storage.minio.accessKey}")private String accessKey;@Value("${storage.minio.secretKey}")private String secretKey;private MinioClient getMinioClient() {return MinioClient.builder().endpoint(endpoint).credentials(accessKey, secretKey).build();}@Overridepublic String upload(String bucketName, String objectName, InputStream inputStream, Map<String, String> metadata) {MinioClient minioClient = getMinioClient();try {minioClient.putObject(PutObjectArgs.builder().bucket(bucketName).object(objectName).stream(inputStream, inputStream.available(), -1).build());return endpoint + "/" + bucketName + "/" + objectName;} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException("Upload failed", e);}}// 实现其他方法...
}4.4 工厂模式实现
package com.example.storage.factory;import com.example.storage.api.ObjectStorageService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import java.util.Map;@Component
public class ObjectStorageFactory {@Autowiredprivate Map<String, ObjectStorageService> storageServices;public ObjectStorageService getStorageService(String type) {ObjectStorageService service = storageServices.get(type + "StorageService");if (service == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unsupported storage type: " + type);}return service;}
}5. 动态切换策略
5.1 策略模式设计
为了实现不同对象存储服务的动态切换,我们采用策略模式结合工厂模式:
public class StorageServiceFactory {private static final Map<String, ObjectStorageService> STORAGE_SERVICE_MAP = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();@Autowiredpublic StorageServiceFactory(List<ObjectStorageService> storageServices) {// 注册所有存储服务实现for (ObjectStorageService service : storageServices) {Component component = service.getClass().getAnnotation(Component.class);if (component != null) {String beanName = component.value();STORAGE_SERVICE_MAP.put(beanName, service);}}}/*** 根据存储类型获取对应的存储服务*/public ObjectStorageService getStorageService(String storageType) {ObjectStorageService service = STORAGE_SERVICE_MAP.get(storageType + "StorageService");if (service == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("不支持的存储类型: " + storageType);}return service;}/*** 获取默认存储服务*/@Value("${storage.default-type:minio}")private String defaultStorageType;public ObjectStorageService getDefaultStorageService() {return getStorageService(defaultStorageType);}
}5.2 配置中心实现
结合Spring Cloud Config或Nacos实现存储服务的动态切换:
# application.yml
storage:default-type: minio # 默认存储类型minio:endpoint: http://localhost:9000access-key: minioadminsecret-key: minioadminbucket-name: mybucketaliyun:endpoint: https://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.comaccess-key: your-access-keysecret-key: your-secret-keybucket-name: myaliyunbucket存储配置类:
@RefreshScope
@Configuration
public class StorageConfig {@Value("${storage.default-type:minio}")private String defaultStorageType;// 动态获取当前配置的存储类型public String getCurrentStorageType() {return defaultStorageType;}
}5.2 注解驱动实现
使用AOP实现基于注解的存储服务切换:
package com.example.storage.annotation;import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface StorageType {String value() default "minio";
}5.3 AOP实现动态切换
package com.example.storage.aop;import com.example.storage.annotation.StorageType;
import com.example.storage.api.ObjectStorageService;
import com.example.storage.config.StorageConfig;
import com.example.storage.factory.ObjectStorageFactory;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import java.lang.reflect.Method;@Aspect
@Component
public class StorageTypeAspect {@Autowiredprivate ObjectStorageFactory storageFactory;@Autowiredprivate StorageConfig storageConfig;/*** 存储服务上下文,用于存储当前线程使用的存储服务类型*/private static final ThreadLocal<String> storageContext = new ThreadLocal<>();/*** 存储原始的存储服务类型,用于方法执行完毕后还原*/private static final ThreadLocal<String> originalStorageContext = new ThreadLocal<>();/*** 环绕通知,处理@StorageType注解*/@Around("@annotation(com.example.storage.annotation.StorageType) || @within(com.example.storage.annotation.StorageType)")public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {// 保存原始存储类型String originalType = storageContext.get();originalStorageContext.set(originalType);try {// 获取方法上的@StorageType注解MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();Method method = signature.getMethod();StorageType annotation = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, StorageType.class);// 如果方法上没有注解,则获取类上的注解if (annotation == null) {annotation = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(joinPoint.getTarget().getClass(), StorageType.class);}// 设置存储类型String storageType = annotation != null && !annotation.value().isEmpty() ? annotation.value() : storageConfig.getDefaultType();// 切换存储服务switchStorage(storageType);// 执行目标方法return joinPoint.proceed();} finally {// 还原存储类型restoreStorage();}}/*** 切换存储服务类型*/public static void switchStorage(String storageType) {storageContext.set(storageType);}/*** 还原存储服务类型*/public static void restoreStorage() {String originalType = originalStorageContext.get();if (originalType != null) {storageContext.set(originalType);} else {storageContext.remove();}originalStorageContext.remove();}/*** 获取当前存储服务类型*/public static String getCurrentStorageType() {return storageContext.get();}
}5.3.1 存储服务代理类
package com.example.storage.proxy;import com.example.storage.api.ObjectStorageService;
import com.example.storage.aop.StorageTypeAspect;
import com.example.storage.config.StorageConfig;
import com.example.storage.factory.StorageServiceFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;/*** 存储服务代理类,根据当前线程上下文动态选择存储服务实现*/
@Component("objectStorageService")
public class ObjectStorageServiceProxy implements ObjectStorageService {@Autowiredprivate StorageServiceFactory storageFactory;@Autowiredprivate StorageConfig storageConfig;/*** 获取当前使用的存储服务实例*/private ObjectStorageService getCurrentStorageService() {String storageType = StorageTypeAspect.getCurrentStorageType();if (storageType == null) {storageType = storageConfig.getDefaultType();}return storageFactory.getStorageService(storageType);}@Overridepublic String upload(String bucketName, String objectName, InputStream inputStream, Map<String, String> metadata) {return getCurrentStorageService().upload(bucketName, objectName, inputStream, metadata);}@Overridepublic CompletableFuture<String> uploadAsync(String bucketName, String objectName, InputStream inputStream, Map<String, String> metadata) {return getCurrentStorageService().uploadAsync(bucketName, objectName, inputStream, metadata);}@Overridepublic InputStream download(String bucketName, String objectName) {return getCurrentStorageService().download(bucketName, objectName);}@Overridepublic CompletableFuture<InputStream> downloadAsync(String bucketName, String objectName) {return getCurrentStorageService().downloadAsync(bucketName, objectName);}@Overridepublic boolean delete(String bucketName, String objectName) {return getCurrentStorageService().delete(bucketName, objectName);}@Overridepublic CompletableFuture<Boolean> deleteAsync(String bucketName, String objectName) {return getCurrentStorageService().deleteAsync(bucketName, objectName);}@Overridepublic boolean exists(String bucketName, String objectName) {return getCurrentStorageService().exists(bucketName, objectName);}@Overridepublic Map<String, String> getMetadata(String bucketName, String objectName) {return getCurrentStorageService().getMetadata(bucketName, objectName);}@Overridepublic boolean createBucket(String bucketName) {return getCurrentStorageService().createBucket(bucketName);}@Overridepublic boolean deleteBucket(String bucketName) {return getCurrentStorageService().deleteBucket(bucketName);}@Overridepublic List<String> listObjects(String bucketName, String prefix) {return getCurrentStorageService().listObjects(bucketName, prefix);}
}5.3.2 手动切换存储服务工具类
package com.example.storage.util;import com.example.storage.aop.StorageTypeAspect;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;/*** 存储服务切换工具类,提供手动切换存储服务的能力*/
public class StorageSwitcher {private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(StorageSwitcher.class);/*** 切换到指定的存储服务*/public static void switchTo(String storageType) {logger.info("Switching storage service to: {}", storageType);StorageTypeAspect.switchStorage(storageType);}/*** 切换到OSS存储服务*/public static void switchToOss() {switchTo("oss");}/*** 切换到MinIO存储服务*/public static void switchToMinio() {switchTo("minio");}/*** 还原存储服务*/public static void restore() {logger.info("Restoring storage service");StorageTypeAspect.restoreStorage();}/*** 执行指定的操作,并在操作完成后还原存储服务*/public static <T> T executeWithStorage(String storageType, StorageOperation<T> operation) {switchTo(storageType);try {return operation.execute();} finally {restore();}}/*** 函数式接口,用于定义需要在特定存储服务下执行的操作*/@FunctionalInterfacepublic interface StorageOperation<T> {T execute();}
}5.3.3 使用示例
package com.example.controller;import com.example.storage.annotation.StorageType;
import com.example.storage.api.ObjectStorageService;
import com.example.storage.util.StorageSwitcher;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.web.multipart.MultipartFile;import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/storage")
public class StorageController {@Autowiredprivate ObjectStorageService objectStorageService;/*** 使用默认存储服务上传文件*/@PostMapping("/upload")public String uploadFile(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file) throws Exception {try (InputStream inputStream = file.getInputStream()) {Map<String, String> metadata = new HashMap<>();metadata.put("Content-Type", file.getContentType());return objectStorageService.upload("default-bucket", file.getOriginalFilename(), inputStream, metadata);}}/*** 使用OSS存储服务上传文件*/@StorageType("oss")@PostMapping("/upload/oss")public String uploadFileToOss(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file) throws Exception {try (InputStream inputStream = file.getInputStream()) {Map<String, String> metadata = new HashMap<>();metadata.put("Content-Type", file.getContentType());return objectStorageService.upload("oss-bucket", file.getOriginalFilename(), inputStream, metadata);}}/*** 使用MinIO存储服务上传文件*/@StorageType("minio")@PostMapping("/upload/minio")public String uploadFileToMinio(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file) throws Exception {try (InputStream inputStream = file.getInputStream()) {Map<String, String> metadata = new HashMap<>();metadata.put("Content-Type", file.getContentType());return objectStorageService.upload("minio-bucket", file.getOriginalFilename(), inputStream, metadata);}}/*** 手动切换存储服务示例*/@PostMapping("/upload/dynamic")public String uploadFileWithDynamicStorage(@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file, @RequestParam("storageType") String storageType) throws Exception {return StorageSwitcher.executeWithStorage(storageType, () -> {try (InputStream inputStream = file.getInputStream()) {Map<String, String> metadata = new HashMap<>();metadata.put("Content-Type", file.getContentType());String bucketName = storageType + "-bucket";return objectStorageService.upload(bucketName, file.getOriginalFilename(), inputStream, metadata);} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}});}
}5.3.4 切换存储服务和还原的测试代码
package com.example.storage.test;import com.example.storage.api.ObjectStorageService;
import com.example.storage.util.StorageSwitcher;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;@SpringBootTest
public class StorageSwitchTest {@Autowiredprivate ObjectStorageService objectStorageService;@Testpublic void testStorageSwitching() {// 测试使用默认存储服务String defaultResult = StorageSwitcher.executeWithStorage(null, () -> {// 执行默认存储操作return objectStorageService.createBucket("test-default-bucket");});assertTrue(defaultResult);// 测试切换到OSSString ossResult = StorageSwitcher.executeWithStorage("oss", () -> {// 执行OSS存储操作return objectStorageService.createBucket("test-oss-bucket");});assertTrue(ossResult);// 测试切换到MinIOString minioResult = StorageSwitcher.executeWithStorage("minio", () -> {// 执行MinIO存储操作return objectStorageService.createBucket("test-minio-bucket");});assertTrue(minioResult);// 测试手动切换和还原try {StorageSwitcher.switchToOss();boolean existsOss = objectStorageService.exists("test-oss-bucket");assertTrue(existsOss);StorageSwitcher.switchToMinio();boolean existsMinio = objectStorageService.exists("test-minio-bucket");assertTrue(existsMinio);} finally {// 确保无论测试是否异常都还原存储服务StorageSwitcher.restore();}// 验证还原后使用默认存储服务boolean existsDefault = objectStorageService.exists("test-default-bucket");assertTrue(existsDefault);}
}6. 并发控制与性能优化
6.1 分片上传优化
6.1.1 分片上传实现
package com.example.storage.service;import com.example.storage.api.ObjectStorageService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.UUID;
import java.util.concurrent.*;@Service
public class ConcurrentUploadService {@Autowiredprivate ObjectStorageService objectStorageService;// 分片大小 10MBprivate static final long CHUNK_SIZE = 10 * 1024 * 1024;// 线程池配置private final ExecutorService executorService = new ThreadPoolExecutor(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors(),Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2,60L,TimeUnit.SECONDS,new LinkedBlockingQueue<>(100),new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());/*** 分片上传文件*/public String uploadByChunks(String bucketName, String objectName, File file) throws Exception {long fileSize = file.length();int chunkCount = (int) Math.ceil((double) fileSize / CHUNK_SIZE);String uploadId = UUID.randomUUID().toString();Map<Integer, CompletableFuture<String>> futures = new HashMap<>();// 并行上传分片for (int i = 0; i < chunkCount; i++) {final int chunkIndex = i;long start = i * CHUNK_SIZE;long end = Math.min(start + CHUNK_SIZE, fileSize);long currentChunkSize = end - start;futures.put(chunkIndex, CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {try (InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file)) {// 跳过前面的字节inputStream.skip(start);// 创建分片文件名String chunkObjectName = objectName + ".chunk" + chunkIndex + "." + uploadId;// 上传分片return objectStorageService.upload(bucketName, chunkObjectName, inputStream, new HashMap<>());} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException("Upload chunk " + chunkIndex + " failed", e);}}, executorService));}// 等待所有分片上传完成CompletableFuture<Void> allOf = CompletableFuture.allOf(futures.values().toArray(new CompletableFuture[0]));allOf.join();// 合并分片(在实际实现中,这取决于存储服务的具体API)// 这里简化处理,直接返回原始文件名return objectName;}/*** 关闭线程池*/public void shutdown() {executorService.shutdown();}
}6.1.2 断点续传实现
package com.example.storage.service;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import java.io.File;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;@Service
public class ResumeUploadService {@Autowiredprivate ConcurrentUploadService concurrentUploadService;@Autowiredprivate RedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;private static final String UPLOAD_PREFIX = "upload:chunk:";private static final long EXPIRE_TIME = 24; // 24小时过期/*** 记录已上传的分片*/public void recordChunk(String uploadId, int chunkIndex) {String key = UPLOAD_PREFIX + uploadId;redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key, String.valueOf(chunkIndex), "1");redisTemplate.expire(key, EXPIRE_TIME, TimeUnit.HOURS);}/*** 获取已上传的分片索引*/public Set<String> getUploadedChunks(String uploadId) {String key = UPLOAD_PREFIX + uploadId;return redisTemplate.opsForHash().keys(key);}/*** 断点续传*/public String resumeUpload(String bucketName, String objectName, File file, String uploadId) throws Exception {// 检查是否有未完成的分片上传if (uploadId == null || uploadId.isEmpty()) {// 新的上传任务uploadId = java.util.UUID.randomUUID().toString();} // 获取已上传的分片信息Set<String> uploadedChunks = getUploadedChunks(uploadId); // 继续上传未完成的分片String result = concurrentUploadService.uploadByChunks(bucketName, objectName, file); // 上传完成后清理分片记录cleanChunksRecord(uploadId); return result;}/*** 清理分片记录*/public void cleanChunksRecord(String uploadId) {String key = UPLOAD_PREFIX + uploadId;redisTemplate.delete(key);}
}6.2 缓存策略
6.2.1 多级缓存架构
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class CachingConfig {@Beanpublic RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig().entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(10)).serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer())).serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()));return RedisCacheManager.builder(factory).cacheDefaults(config).withCacheConfiguration("objectMetadataCache", RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig().entryTtl(Duration.ofHours(1))).build();}@Beanpublic CacheManager caffeineCacheManager() {CaffeineCacheManager cacheManager = new CaffeineCacheManager("hotObjects");cacheManager.setCaffeine(Caffeine.newBuilder().expireAfterWrite(5, TimeUnit.MINUTES).maximumSize(1000));return cacheManager;}
}6.2.2 缓存使用示例
@Service
public class CachingObjectService {@Cacheable(value = "objectMetadataCache", key = "#bucketName + '-' + #objectKey")public ObjectMetadata getObjectMetadata(String storageType, String bucketName, String objectKey) {ObjectStorageService storageService = storageServiceFactory.getStorageService(storageType);return storageService.getObjectMetadata(bucketName, objectKey);}@CacheEvict(value = "objectMetadataCache", key = "#bucketName + '-' + #objectKey")public void evictObjectMetadata(String bucketName, String objectKey) {// 缓存自动清除}
}7.与NoSQL集成方案
7.1 Redis缓存集成
package com.example.storage.service;import com.example.storage.api.ObjectStorageService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;@Service
public class CachedStorageService {@Autowiredprivate ObjectStorageService objectStorageService;@Autowiredprivate RedisTemplate<String, byte[]> redisTemplate;private static final String CACHE_PREFIX = "storage:cache:";private static final long CACHE_TTL = 60; // 60分钟过期/*** 从缓存或存储服务获取对象*/public byte[] getObject(String bucketName, String objectName) throws Exception {String cacheKey = CACHE_PREFIX + bucketName + ":" + objectName; // 尝试从缓存获取byte[] cachedData = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(cacheKey);if (cachedData != null) {return cachedData;} // 从存储服务获取并缓存try (InputStream inputStream = objectStorageService.download(bucketName, objectName)) {byte[] data = inputStream.readAllBytes();redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(cacheKey, data, CACHE_TTL, TimeUnit.MINUTES);return data;}}/*** 上传对象并清除缓存*/public String uploadObject(String bucketName, String objectName, InputStream inputStream, Map<String, String> metadata) {String cacheKey = CACHE_PREFIX + bucketName + ":" + objectName; // 清除旧缓存redisTemplate.delete(cacheKey); // 上传到存储服务return objectStorageService.upload(bucketName, objectName, inputStream, metadata);}/*** 删除对象并清除缓存*/public boolean deleteObject(String bucketName, String objectName) {String cacheKey = CACHE_PREFIX + bucketName + ":" + objectName; // 清除缓存redisTemplate.delete(cacheKey); // 从存储服务删除return objectStorageService.delete(bucketName, objectName);}
}7.2 MongoDB元数据存储
package com.example.storage.model;import org.springframework.data.annotation.Id;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.core.mapping.Document;import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Map;@Document(collection = "object_metadata")
public class ObjectMetadata {@Idprivate String id;private String bucketName;private String objectName;private String storageType;private long size;private Date createdAt;private Date updatedAt;private Map<String, String> metadata;// getters and setters// ...
}元数据存储仓库接口:
package com.example.storage.repository;import com.example.storage.model.ObjectMetadata;
import org.springframework.data.mongodb.repository.MongoRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;import java.util.List;
import java.util.Optional;@Repository
public interface ObjectMetadataRepository extends MongoRepository<ObjectMetadata, String> {Optional<ObjectMetadata> findByBucketNameAndObjectName(String bucketName, String objectName);List<ObjectMetadata> findByBucketName(String bucketName);List<ObjectMetadata> findByStorageType(String storageType);void deleteByBucketNameAndObjectName(String bucketName, String objectName);
}元数据存储服务类:
package com.example.storage.service;import com.example.storage.api.ObjectStorageService;
import com.example.storage.model.ObjectMetadata;
import com.example.storage.repository.ObjectMetadataRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import java.io.InputStream;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.UUID;@Service
public class MetadataStorageService {@Autowiredprivate ObjectStorageService objectStorageService;@Autowiredprivate ObjectMetadataRepository metadataRepository;@Autowiredprivate StorageConfig storageConfig;/*** 上传对象并保存元数据*/public String uploadWithMetadata(String bucketName, String objectName, InputStream inputStream, Map<String, String> metadata) throws Exception {// 获取当前存储类型String storageType = StorageTypeAspect.getCurrentStorageType();if (storageType == null) {storageType = storageConfig.getDefaultType();} // 上传文件String url = objectStorageService.upload(bucketName, objectName, inputStream, metadata); // 保存元数据ObjectMetadata objectMetadata = new ObjectMetadata();objectMetadata.setId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());objectMetadata.setBucketName(bucketName);objectMetadata.setObjectName(objectName);objectMetadata.setStorageType(storageType);objectMetadata.setMetadata(metadata);objectMetadata.setCreatedAt(new Date());objectMetadata.setUpdatedAt(new Date()); metadataRepository.save(objectMetadata);return url;}/*** 获取对象元数据*/public ObjectMetadata getMetadata(String bucketName, String objectName) {return metadataRepository.findByBucketNameAndObjectName(bucketName, objectName).orElse(null);}/*** 删除对象并删除元数据*/public boolean deleteWithMetadata(String bucketName, String objectName) {// 从存储服务删除boolean deleted = objectStorageService.delete(bucketName, objectName); // 删除元数据if (deleted) {metadataRepository.deleteByBucketNameAndObjectName(bucketName, objectName);}return deleted;}
}8. 云与自建方案对比
8.1 成本分析
8.1.1 云存储成本构成
- 存储费用:按存储容量计费
- 流量费用:按出网流量计费
- 请求费用:按API调用次数计费
- 数据处理费用:如图片处理、视频转码等增值服务费用
8.1.2 自建存储成本构成
- 硬件成本:服务器、存储设备、网络设备
- 机房成本:机房租金、电力、空调
- 运维成本:人员工资、培训费用
- 软件成本:可能的许可费用
8.1.3 成本对比表
| 因素 | 云存储 | 自建存储 |
|---|---|---|
| 初期投入 | 低(按需付费) | 高(硬件、机房) |
| 长期成本 | 随数据量增长线性增长 | 固定成本+少量维护成本 |
| 弹性扩展 | 高(按需扩容) | 低(需要提前规划) |
| 运维复杂度 | 低(由云服务商负责) | 高(需要专业团队) |
| 数据安全责任 | 部分(与云服务商共享) | 全部(自己负责) |
8.2 性能对比
| 指标 | 云存储 | 自建存储 |
|---|---|---|
| 读写性能 | 优秀(针对大规模优化) | 可定制(根据硬件配置) |
| 网络延迟 | 取决于地域和网络环境 | 内网访问延迟低 |
| 并发能力 | 高(多数据中心支持) | 有限(受硬件限制) |
| 可用性 | 极高(99.99%+) | 取决于冗余设计 |
8.3 决策建议
- 小团队/初创企业:优先选择云存储,降低初期投入和运维成本
- 大规模企业:可考虑混合模式,热数据存放在云存储,冷数据存放在自建存储
- 有特殊合规要求:可考虑自建存储或私有云方案
- 预算充足且注重稳定性:选择成熟的公有云方案
- 技术团队强大且有长期规划:可考虑自建存储
9. Spring Boot & Spring Cloud架构设计示例
9.1 整体架构概述
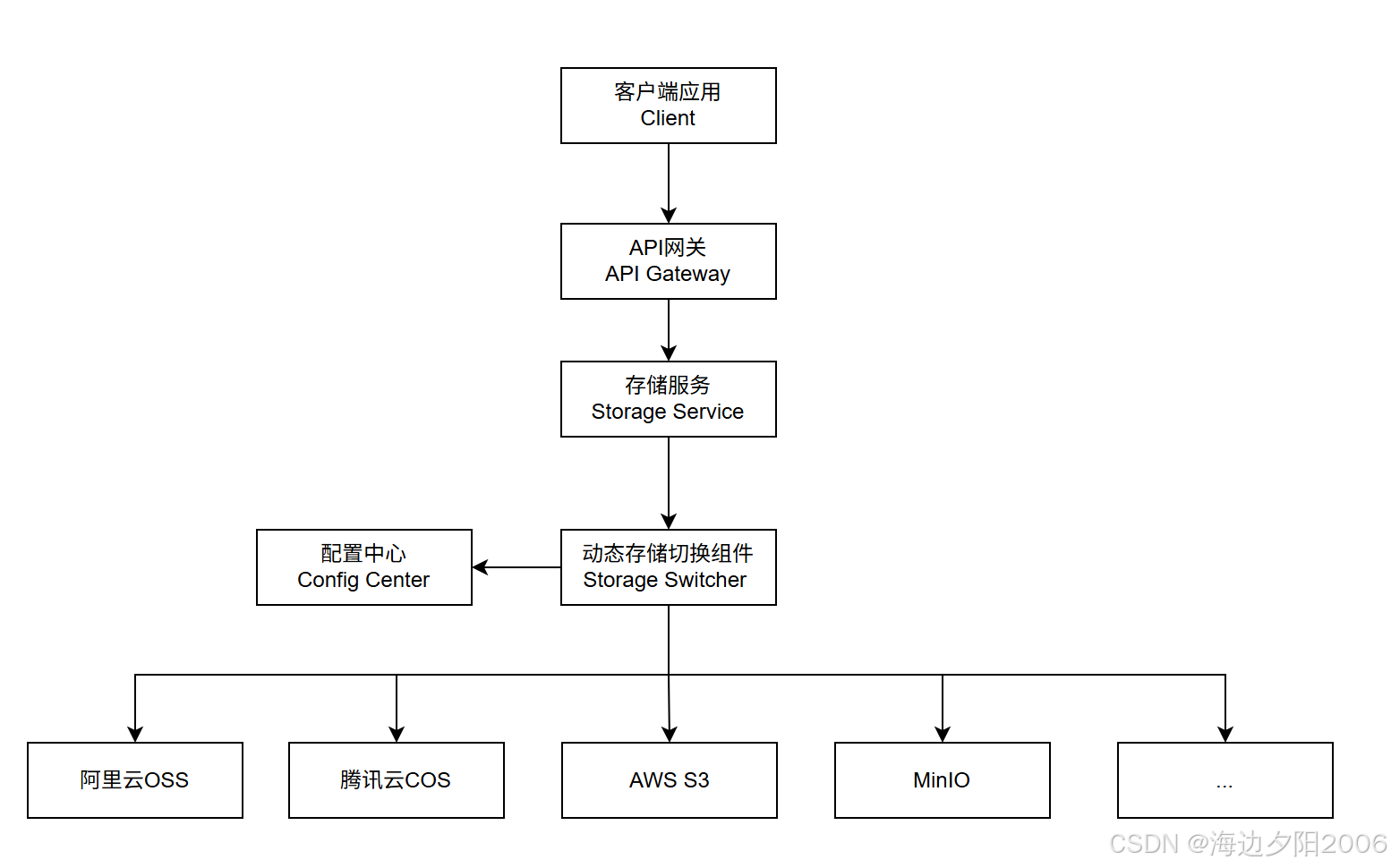
9.2 关键组件配置
9.2.1 依赖配置(pom.xml)
<dependencies><!-- Spring Boot --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId><version>3.2.0</version></dependency><!-- Spring Cloud --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId><version>2023.0.0</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bootstrap</artifactId><version>4.1.0</version></dependency><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId><artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-config</artifactId><version>4.1.0</version></dependency><!-- AOP --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId><version>3.2.0</version></dependency><!-- Redis --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId><version>3.2.0</version></dependency><!-- MongoDB --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-mongodb</artifactId><version>3.2.0</version></dependency><!-- MinIO --><dependency><groupId>io.minio</groupId><artifactId>minio</artifactId><version>8.5.8</version></dependency><!-- 阿里云OSS --><dependency><groupId>com.aliyun.oss</groupId><artifactId>aliyun-sdk-oss</artifactId><version>3.17.1</version></dependency><!-- AWS SDK --><dependency><groupId>software.amazon.awssdk</groupId><artifactId>s3</artifactId><version>2.20.150</version></dependency><!-- 测试 --><dependency><groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId><artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId><version>3.2.0</version><scope>test</scope></dependency>
</dependencies>9.2.2 配置文件(application.yml)
# application.yml
spring:application:name: object-storage-servicecloud:nacos:discovery:server-addr: localhost:8848namespace: publicgroup: DEFAULT_GROUPconfig:server-addr: localhost:8848namespace: publicgroup: DEFAULT_GROUPfile-extension: yaml# Redis配置redis:host: localhostport: 6379database: 0# MongoDB配置data:mongodb:uri: mongodb://localhost:27017/storagedatabase: storage# 存储服务配置
storage:# 默认存储类型default-type: minio# MinIO配置minio:endpoint: http://localhost:9000accessKey: minioadminsecretKey: minioadmin# OSS配置oss:endpoint: oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.comaccessKeyId: your-access-key-idaccessKeySecret: your-access-key-secret# S3配置s3:endpoint: s3.amazonaws.comregion: us-east-1accessKey: your-access-keysecretKey: your-secret-key# 线程池配置
concurrent:thread-pool:core-size: 8max-size: 16queue-capacity: 100keep-alive-seconds: 60# 日志配置
logging:level:com.example.storage: info9.3 核心组件实现
9.3.1 服务配置类
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "storage")
@Data
public class StorageProperties {private String defaultType = "minio";private Map<String, Map<String, String>> providers = new HashMap<>();public Map<String, String> getProviderProperties(String providerName) {return providers.getOrDefault(providerName, new HashMap<>());}
}9.3.2 MinIO配置类
@Configuration
public class MinioConfig {@Autowiredprivate StorageProperties storageProperties;@Bean@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "storage.default-type", havingValue = "minio", matchIfMissing = true)public MinioClient minioClient() {Map<String, String> props = storageProperties.getProviderProperties("minio");return MinioClient.builder().endpoint(props.getOrDefault("endpoint", "http://localhost:9000")).credentials(props.getOrDefault("access-key", "minioadmin"),props.getOrDefault("secret-key", "minioadmin")).build();}
}9.3.3 阿里云OSS配置类
@Configuration
public class AliyunOssConfig {@Autowiredprivate StorageProperties storageProperties;@Bean@ConditionalOnProperty(name = "storage.default-type", havingValue = "aliyun")public OSS ossClient() {Map<String, String> props = storageProperties.getProviderProperties("aliyun");return new OSSClientBuilder().build(props.get("endpoint"),props.get("access-key"),props.get("secret-key"));}
}9.4 服务发现与注册
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableDiscoveryClient
public class ObjectStorageApplication {public static void main(String[] args) {SpringApplication.run(ObjectStorageApplication.class, args);}
}9.5 高可用设计
9.5.1 Sentinel集成配置
@Configuration
public class SentinelConfig {@PostConstructpublic void init() {// 配置限流规则List<FlowRule> flowRules = new ArrayList<>();// 上传接口限流规则FlowRule uploadRule = new FlowRule();uploadRule.setResource("object:upload");uploadRule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS);uploadRule.setCount(50); // 每秒50个请求uploadRule.setLimitApp("default");flowRules.add(uploadRule);// 下载接口限流规则FlowRule downloadRule = new FlowRule();downloadRule.setResource("object:download");downloadRule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS);downloadRule.setCount(100); // 每秒100个请求downloadRule.setLimitApp("default");flowRules.add(downloadRule);// 加载规则FlowRuleManager.loadRules(flowRules);// 配置熔断规则List<DegradeRule> degradeRules = new ArrayList<>();DegradeRule rule = new DegradeRule();rule.setResource("object:upload");rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.DEGRADE_GRADE_EXCEPTION_RATIO);rule.setCount(0.5); // 异常比例超过50%rule.setTimeWindow(10); // 熔断10秒degradeRules.add(rule);// 加载熔断规则DegradeRuleManager.loadRules(degradeRules);}
}9.5.2 限流使用示例
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/objects")
public class ObjectStorageController {@Autowiredprivate StorageServiceFactory storageServiceFactory;@PostMapping("/upload")@SentinelResource(value = "object:upload", blockHandler = "handleBlock", fallback = "handleFallback")public ResponseEntity<Map<String, String>> uploadObject(@RequestParam("bucketName") String bucketName,@RequestParam("file") MultipartFile file,@RequestParam(value = "storageType", defaultValue = "minio") String storageType) {try {ObjectStorageService storageService = storageServiceFactory.getStorageService(storageType);String objectKey = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + "-" + file.getOriginalFilename();String eTag = storageService.uploadObject(bucketName, objectKey, file.getInputStream(), null);Map<String, String> response = new HashMap<>();response.put("objectKey", objectKey);response.put("eTag", eTag);return ResponseEntity.ok(response);} catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException("上传失败", e);}}// 限流处理public ResponseEntity<Map<String, String>> handleBlock(Exception ex) {Map<String, String> error = new HashMap<>();error.put("error", "请求过于频繁,请稍后再试");return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.TOO_MANY_REQUESTS).body(error);}// 降级处理public ResponseEntity<Map<String, String>> handleFallback(Exception ex) {Map<String, String> error = new HashMap<>();error.put("error", "服务暂时不可用,请稍后再试");return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE).body(error);}
}10. 结论与建议
10.1 选型建议
- 对于大多数应用场景,建议采用统一API接口设计,支持多种存储方案的动态切换
- 根据业务规模和预算,选择合适的云存储或自建存储方案
- 考虑数据增长速度和未来扩展性需求
10.2 最佳实践
- 使用AOP和代理模式实现存储服务的动态切换
- 结合Redis实现热点数据缓存,提高访问性能
- 使用MongoDB存储对象元数据,便于查询和管理
- 实现分片上传和断点续传功能,提升大文件处理能力
- 设计完善的错误处理和重试机制,提高系统稳定性
10.3 未来展望
- 考虑引入更智能的存储分层策略,根据访问频率自动迁移数据
- 实现存储服务的熔断和限流,提高系统弹性
- 探索Serverless架构在对象存储领域的应用
- 结合AI技术实现智能数据分类和管理
通过本文档提供的架构设计和实现方案,开发团队可以构建一个灵活、可扩展、高性能的对象存储服务系统,满足不同业务场景的需求。
