Android InputReader与InputDispatcher
Input子系统是Android Framework的重要组成部分之一,该文章将简单梳理Android Input子系统的InputReader 和 InputDispacher
一. InputReader 和 InputDispacher的建立
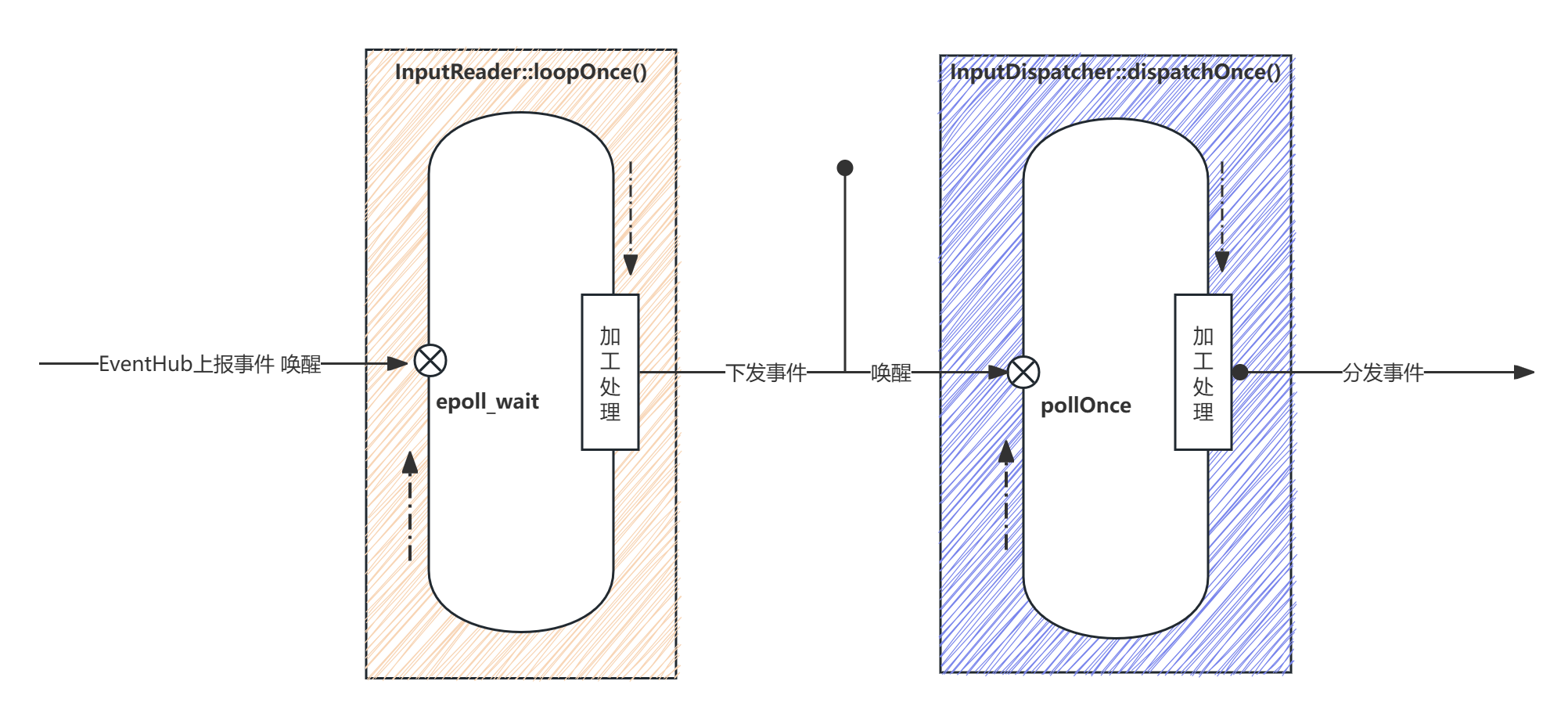
InputReader 和 InputDispacher运行在native层,在android事件分发过程中InputReader主要负责从内核读取事件,并进行初步的加工,随后把加工后的事件交给InputDispatcher,InputDispatcher主要负责对InputReader下发的事件进行再加工随后按照规则分发给正确的客户端们,大致如下图:
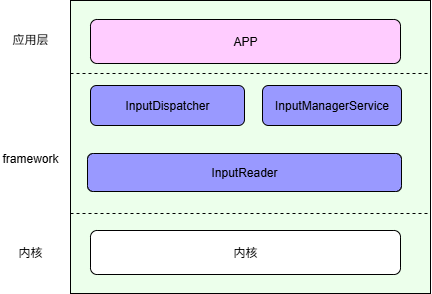
架构图我更倾向于如下图:
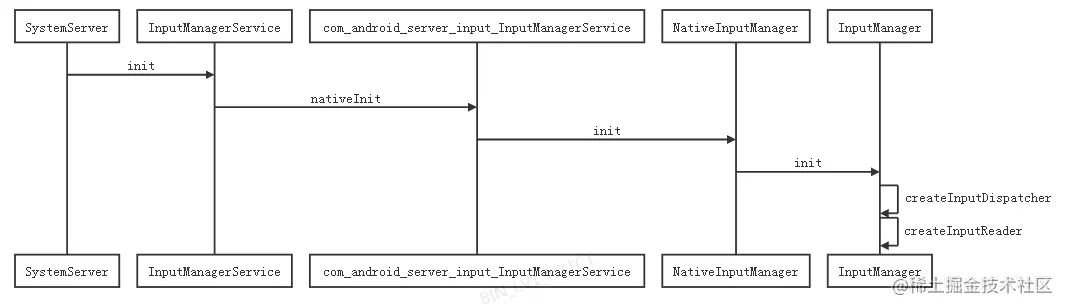
InputReader和InputDispatcher是在java层的系统服务InputManagerService启动过程中启动的,大致的调用关系如下图:
@VisibleForTestingInputManagerService(Injector injector) {// The static association map is accessed by both java and native code, so it must be// initialized before initializing the native service.mStaticAssociations = loadStaticInputPortAssociations();mContext = injector.getContext();mHandler = new InputManagerHandler(injector.getLooper());// 创建Inupt native层相关组件mNative = injector.getNativeService(this);...}public void start() {Slog.i(TAG, "Starting input manager");// start native层的服务mNative.start();// Add ourselves to the Watchdog monitors.Watchdog.getInstance().addMonitor(this);class NativeImpl implements NativeInputManagerService {/** Pointer to native input manager service object, used by native code. */@SuppressWarnings({"unused", "FieldCanBeLocal"})private final long mPtr;NativeImpl(InputManagerService service, Context context, MessageQueue messageQueue) {mPtr = init(service, context, messageQueue);}private native long init(InputManagerService service, Context context,MessageQueue messageQueue);@Overridepublic native void start();
static jlong nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jclass /* clazz */,jobject serviceObj, jobject contextObj, jobject messageQueueObj) {sp<MessageQueue> messageQueue = android_os_MessageQueue_getMessageQueue(env, messageQueueObj);if (messageQueue == nullptr) {jniThrowRuntimeException(env, "MessageQueue is not initialized.");return 0;}NativeInputManager* im = new NativeInputManager(contextObj, serviceObj,messageQueue->getLooper());im->incStrong(0);return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(im);
}static void nativeStart(JNIEnv* env, jobject nativeImplObj) {NativeInputManager* im = getNativeInputManager(env, nativeImplObj);status_t result = im->getInputManager()->start();if (result) {jniThrowRuntimeException(env, "Input manager could not be started.");}
}
最终创建Native层的InputManager对象,在该对象中通过createInputDispatcher和createInputReader分别创建出InputDispatcher和InputReader,且InputReader间接持有InputDispatcher,以便InputReader能将加工后的事件发送给InputDispatcher和唤醒InputDispatcher的工作线程去处理来自InputReader下发的事件。
InputManager::InputManager(const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& readerPolicy,const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& dispatcherPolicy) {// 构造InputDispatchermDispatcher = createInputDispatcher(dispatcherPolicy);mClassifier = std::make_unique<InputClassifier>(*mDispatcher);mBlocker = std::make_unique<UnwantedInteractionBlocker>(*mClassifier);// 构造InpputReader,且InpputReader间接持有InputDispatchermReader = createInputReader(readerPolicy, *mBlocker);
}status_t InputManager::start() {// 启动InputDispatcher的工作线程status_t result = mDispatcher->start();if (result) {ALOGE("Could not start InputDispatcher thread due to error %d.", result);return result;}// 启动InputDispatcher的工作线程result = mReader->start();if (result) {ALOGE("Could not start InputReader due to error %d.", result);mDispatcher->stop();return result;}return OK;
}
1.InputReader的构造和start
InputReader的构造:
- 1.创建eventhub,将通过epoll机制监听内核上报的事件
- 2.创建mQueuedListener,间接持有InputDispatcher
InputReader::InputReader(std::shared_ptr<EventHubInterface> eventHub,const sp<InputReaderPolicyInterface>& policy,InputListenerInterface& listener): mContext(this),// eventhub,监听驱动层上报的事件mEventHub(eventHub),mPolicy(policy),// 间接持有InputDispatchermQueuedListener(listener),....
}
InputReader的start:
- 启动命名为InputReader的工作线程,线程中循环执行InputReader::loopOnce()
status_t InputReader::start() {if (mThread) {return ALREADY_EXISTS;}// 启动命名为InputReader的工作线程,线程中循环执行InputReader::loopOnce()mThread = std::make_unique<InputThread>("InputReader", [this]() { loopOnce(); }, [this]() { mEventHub->wake(); });return OK;
}
循环执行InputReader::loopOnce(),在底层没有上报事件时,会通过epoll_wait进行阻塞
void InputReader::loopOnce() {int32_t oldGeneration;int32_t timeoutMillis;bool inputDevicesChanged = false;std::vector<InputDeviceInfo> inputDevices;{ // 1.从eventHub中获取数据,该方法中会有阻塞size_t count = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis, mEventBuffer, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE);{ if (count) {// 2.处理并初步加工输入的事件processEventsLocked(mEventBuffer, count);}....//3.初步加工后的事件交给inputDispatcher,并唤醒InputDispatcher的工作线程mQueuedListener.flush();
}在EventHub::getEvents中会有阻塞:
size_t EventHub::getEvents(int timeoutMillis, RawEvent* buffer, size_t bufferSize) {ALOG_ASSERT(bufferSize >= 1);std::scoped_lock _l(mLock);struct input_event readBuffer[bufferSize];RawEvent* event = buffer; // RawEvent buffer数组的首地址size_t capacity = bufferSize; // 256bool awoken = false;.....mLock.unlock(); // release lock before poll// 在这里阻塞 ,等待输入事件,当有时间来临时,唤醒,且 mPendingEventItems 保存事件int pollResult = epoll_wait(mEpollFd, mPendingEventItems, EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS, timeoutMillis);}.....// All done, return the number of events we read.// 返回事件的数量return event - buffer;
}
1.InputDispatcher的构造和start
InputDispatcher的构造:
- 1.创建Looper,用于阻塞与唤醒
- 2.创建mQueuedListener,间接持有InputDispatcher
InputDispatcher::InputDispatcher(InputDispatcherPolicyInterface& policy,std::chrono::nanoseconds staleEventTimeout):....{// 关键 使用了LoopermLooper = sp<Looper>::make(false);}
// 维护了一个名为mInboundQueue 的队列,同来接收来自InputReader的事件
std::deque<std::shared_ptr<EventEntry>> mInboundQueue GUARDED_BY(mLock);status_t InputDispatcher::start() {if (mThread) {return ALREADY_EXISTS;}// 启动名称为InputDispatcher的工作线程,并循环执行 InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce()mThread = std::make_unique<InputThread>("InputDispatcher", [this]() { dispatchOnce(); }, [this]() { mLooper->wake(); });return OK;
}
InputDispatcher的start:
1.启动名称为InputDispatcher的工作线程,并循环执行 InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce()
该方法会在工作线程中不断的循环执行,但在不满足循环执行条件时 通过Looper->pollOnce()进行阻塞。
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {// 先把下次的唤醒事件是设置为无穷大nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;{ // acquire lockstd::scoped_lock _l(mLock);mDispatcherIsAlive.notify_all();// Run a dispatch loop if there are no pending commands.// The dispatch loop might enqueue commands to run afterwards.// 刚开始 haveCommandsLocked返回FALSE, 即进入该逻辑,进行事件分发if (!haveCommandsLocked()) {dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);}// Run all pending commands if there are any.// If any commands were run then force the next poll to wake up immediately.if (runCommandsLockedInterruptable()) {nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN;}// If we are still waiting for ack on some events,// we might have to wake up earlier to check if an app is anr'ing.// 处理anr相关 这一步骤关键, 算出 最近一次anr唤醒的超时时间,时间到了 就唤醒.const nsecs_t nextAnrCheck = processAnrsLocked();nextWakeupTime = std::min(nextWakeupTime, nextAnrCheck);// We are about to enter an infinitely long sleep, because we have no commands or// pending or queued eventsif (nextWakeupTime == LONG_LONG_MAX) {mDispatcherEnteredIdle.notify_all();}} // release lock// Wait for callback or timeout or wake. (make sure we round up, not down)nsecs_t currentTime = now();int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime);mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);
}
二. InputReader对事件的处理
在上文中提到,在InputReader的工作线程中,循环执行InputReader::loopOnce(),会在getEvents中等待并读取内核层上报的原始输入事件
通过adb命令:getevent -l 可以直观的查看内核层上报的事件,如下
key事件:
getevent -l# /dev/input/event2 是与电源键相关联的输入设备文件。 EV_KEY:表示这是一个按键事件 KEY_POWER:表示具体的按键是 电源键 DOWN:表示按键被按下
/dev/input/event2: EV_KEY KEY_POWER DOWN
# EV_SYN:表示同步事件(Synchronization Event)用于标记一组事件的结束,确保事件的完整性。 SYN_REPORT:表示同步报告,通知系统当前输入事件已经处理完毕 00000000: 同步事件的值,通常为 0。
/dev/input/event2: EV_SYN SYN_REPORT 00000000
# UP:表示按键被释放(按键释放事件)
/dev/input/event2: EV_KEY KEY_POWER UP
/dev/input/event2: EV_SYN SYN_REPORT 00000000
触摸事件:
getevent -l# /dev/input/event4: 事件的设备节点 EV_ABS:表示这是一个绝对位置事件 ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID:表示触摸点的唯一标识符 000000c4 是当前触摸点的 ID,用于区分多个触摸点
/dev/input/event4: EV_ABS ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID 000000c4
# ABS_MT_POSITION_X:表示触摸点的 X 坐标 00000269:是触摸点的 X 坐标值
/dev/input/event4: EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_X 00000269
# ABS_MT_POSITION_X:表示触摸点的 Y 坐标 0000043d:是触摸点的 坐标值
/dev/input/event4: EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_Y 0000043d
# ABS_MT_PRESSURE:表示触摸点的压力值 00000026:是触摸点的压力值,表示触摸的力度
/dev/input/event4: EV_ABS ABS_MT_PRESSURE 00000026
# EV_KEY 表示按键事件 BTN_TOUCH:表示触摸屏的触摸事件 DOWN:表示触摸屏被按下(触摸开始
/dev/input/event4: EV_KEY BTN_TOUCH DOWN
# EV_SYN:表示同步事件(Synchronization Event)用于标记一组事件的结束,确保事件的完整性。 SYN_REPORT:表示同步报告,通知系统当前输入事件已经处理完毕 00000000: 同步事件的值,通常为 0。
/dev/input/event4: EV_SYN SYN_REPORT 00000000# ffffffff 表示触摸点的 ID 被释放(触摸点结束)
/dev/input/event4: EV_ABS ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID ffffffff
# EV_KEY 表示按键事件 BTN_TOUCH:表示触摸屏的触摸事件 DOWN:表示触摸屏被按下(触摸开始
/dev/input/event4: EV_KEY BTN_TOUCH UP
/dev/input/event4: EV_SYN SYN_REPORT 00000000
回到InputReader工作线程循环执行的InputReader::loopOnce,该方法中主要做了如下操作:
- 1.在EventHub->getEvents阻塞,读取驱动上报的事件到mEventBuffer中
- 2.处理并初步加工mEventBuffer中的事件
- 3.初步加工后的事件交给inputDispatcher,并唤醒InputDispatcher的工作线程
void InputReader::loopOnce() {int32_t oldGeneration;int32_t timeoutMillis;bool inputDevicesChanged = false;std::vector<InputDeviceInfo> inputDevices;{ // 1.从eventHub中获取数据,该方法中会有阻塞size_t count = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis, mEventBuffer, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE);{ if (count) {// 2.处理并初步加工输入的事件processEventsLocked(mEventBuffer, count);}....//3.初步加工后的事件交给inputDispatcher,并唤醒InputDispatcher的工作线程mQueuedListener.flush();
}
### 在EventHub->getEvents阻塞,读取驱动上报的事件到mEventBuffer中
接下来将以key事件简略分下主要流程:
1.在EventHub->getEvents阻塞,读取驱动上报的事件到mEventBuffer中
size_t EventHub::getEvents(int timeoutMillis, RawEvent* buffer, size_t bufferSize) {ALOG_ASSERT(bufferSize >= 1);std::scoped_lock _l(mLock);struct input_event readBuffer[bufferSize];RawEvent* event = buffer; // RawEvent buffer数组的首地址size_t capacity = bufferSize; // 256while{bool awoken = false;.....处理读取raw事件并保存在buffer中mLock.unlock(); // release lock before poll// 在这里阻塞 ,等待输入事件,当有时间来临时,唤醒,且 mPendingEventItems 保存事件int pollResult = epoll_wait(mEpollFd, mPendingEventItems, EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS, timeoutMillis);}.....}// All done, return the number of events we read.// 返回事件的数量return event - buffer;
}- 2.处理并初步加工mEventBuffer中的事件
在processEventsLocked中会对从EventHub中读取的RawEvent 按照deviceId进行分类,相同的deviceId的rawevent会放到一起统一处理, 会交给processEventsForDeviceLocked统一处理:
void InputReader::processEventsLocked(const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {for (const RawEvent* rawEvent = rawEvents; count;) {int32_t type = rawEvent->type;size_t batchSize = 1;// 输入事件相关的 进入到该分支,if (type < EventHubInterface::FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT) {// 取出deviceId,用来标记那个设备产生的事件int32_t deviceId = rawEvent->deviceId;// 把同一deviceId的事件,归到同一batch中while (batchSize < count) {if (rawEvent[batchSize].type >= EventHubInterface::FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT ||rawEvent[batchSize].deviceId != deviceId) {break;}// 计算出有几个batchbatchSize += 1;}if (DEBUG_RAW_EVENTS) {ALOGD("BatchSize: %zu Count: %zu", batchSize, count);}// 同一个batch 对应 同一设备. 同一个batch连续处理,上processEventsForDeviceLocked(deviceId, rawEvent, batchSize);} else {.....}
}
找到该设备Id对应的InputDevice调用他们的InputDevice::process处理:
void InputReader::processEventsForDeviceLocked(int32_t eventHubId, const RawEvent* rawEvents,size_t count) {auto deviceIt = mDevices.find(eventHubId);if (deviceIt == mDevices.end()) {ALOGW("Discarding event for unknown eventHubId %d.", eventHubId);return;}std::shared_ptr<InputDevice>& device = deviceIt->second;if (device->isIgnored()) {// ALOGD("Discarding event for ignored deviceId %d.", deviceId);return;}// 进一步处理device->process(rawEvents, count);
}
以key事件举例,会找到Key输入设备对应的InputDevice进行处理
在InputDevice::process会找到该InputDevice对应的InputMapper对传入的raw事件进行初步加工:
Android 的 InputMapper 是 Android 输入系统中的一个关键组件,主要用于处理和映射输入设备的事件,例如触摸屏、键盘、鼠标、游戏手柄等。它的功能是将输入设备的原始事件转换为标准化的输入事件
native\services\inputflinger\reader\InputDevice.cppvoid InputDevice::process(const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {// Process all of the events in order for each mapper.// We cannot simply ask each mapper to process them in bulk because mappers may// have side-effects that must be interleaved. For example, joystick movement events and// gamepad button presses are handled by different mappers but they should be dispatched// in the order received.for (const RawEvent* rawEvent = rawEvents; count != 0; rawEvent++) {// 进入该分支 多手指的触摸屏, mapper是services/inputflinger/reader/mapper/MultiTouchInputMapper.cppfor_each_mapper_in_subdevice(rawEvent->deviceId, [rawEvent](InputMapper& mapper) {mapper.process(rawEvent);});--count;}
}
在android代码中针对不同的硬件输入有着不同的类型的InputMapper
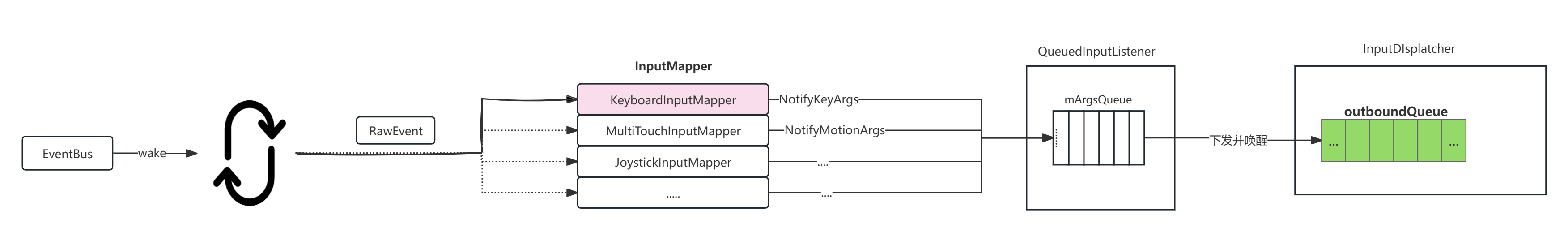
对于key事件来说,将会调用到KeyboardInputMapper对Raw时间进行加工处理:
void KeyboardInputMapper::process(const RawEvent* rawEvent) {switch (rawEvent->type) {case EV_KEY: {int32_t scanCode = rawEvent->code;int32_t usageCode = mCurrentHidUsage;mCurrentHidUsage = 0;if (isKeyboardOrGamepadKey(scanCode)) {// 对rawEvent进行加工处理:processKey(rawEvent->when, rawEvent->readTime, rawEvent->value != 0, scanCode,usageCode);}
.....
}
把上报的Raw事件初步加工为NotifyKeyArgs事件,然后把该事件缓存在mArgsQueue中:
void KeyboardInputMapper::processKey(nsecs_t when, nsecs_t readTime, bool down, int32_t scanCode,int32_t usageCode) {省略加工处理时间的过程// 生成初步加工的NotifyKeyArgs事件NotifyKeyArgs args(getContext()->getNextId(), when, readTime, getDeviceId(), mSource,getDisplayId(), policyFlags,down ? AKEY_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN : AKEY_EVENT_ACTION_UP,AKEY_EVENT_FLAG_FROM_SYSTEM, keyCode, scanCode, keyMetaState, downTime);// 把生成的NotifyKeyArgs事件加入到mArgsQueue队列中getListener().notifyKey(&args);
}
void QueuedInputListener::notifyMotion(const NotifyMotionArgs* args) {traceEvent(__func__, args->id);mArgsQueue.emplace_back(std::make_unique<NotifyMotionArgs>(*args));
}
3.初步加工后的事件交给inputDispatcher,并唤醒InputDispatcher的工作线程
上文中已经从eventHub中读取驱动层上报的事件,然后经过加工处理并保存在mArgsQueue中
在QueuedInputListener::flush()中会遍历mArgsQueue中所有暂存的事件然后,通过args->notify(mInnerListener);将事件发送给InputDIspatcher,并唤醒
void QueuedInputListener::flush() {for (const std::unique_ptr<NotifyArgs>& args : mArgsQueue) {args->notify(mInnerListener);}mArgsQueue.clear();
}void NotifyKeyArgs::notify(InputListenerInterface& listener) const {listener.notifyKey(this);
}
Key事件将会交给InputDispatcher进行如下操作:
- 1.验证Key时间的合法性
- 2.根据NotifyKeyArgs 构造出KeyEntry
- 3.将KeyEntry入队InputDispatcher的InboundQueue
- 4.唤醒InputDispatcher的工作线程
void InputDispatcher::notifyKey(const NotifyKeyArgs& args) {...// 1.验证Key时间的合法性Result<void> keyCheck = validateKeyEvent(args.action);if (!keyCheck.ok()) {LOG(ERROR) << "invalid key event: " << keyCheck.error();return;}uint32_t policyFlags = args.policyFlags;int32_t flags = args.flags;int32_t metaState = args.metaState;// InputDispatcher tracks and generates key repeats on behalf of// whatever notifies it, so repeatCount should always be set to 0constexpr int32_t repeatCount = 0;if ((policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_VIRTUAL) || (flags & AKEY_EVENT_FLAG_VIRTUAL_HARD_KEY)) {policyFlags |= POLICY_FLAG_VIRTUAL;flags |= AKEY_EVENT_FLAG_VIRTUAL_HARD_KEY;}if (policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_FUNCTION) {metaState |= AMETA_FUNCTION_ON;}policyFlags |= POLICY_FLAG_TRUSTED;int32_t keyCode = args.keyCode;accelerateMetaShortcuts(args.deviceId, args.action, keyCode, metaState);KeyEvent event;event.initialize(args.id, args.deviceId, args.source, args.displayId, INVALID_HMAC, args.action,flags, keyCode, args.scanCode, metaState, repeatCount, args.downTime,args.eventTime);.....// 2.构造 KeyEntrystd::unique_ptr<KeyEntry> newEntry =std::make_unique<KeyEntry>(args.id, args.eventTime, args.deviceId, args.source,args.displayId, policyFlags, args.action, flags, keyCode,args.scanCode, metaState, repeatCount, args.downTime);// 3.事件入队InputDispatcher的InboundQueueneedWake = enqueueInboundEventLocked(std::move(newEntry));mLock.unlock();} // release lock// 4.唤醒InputDispatcher的工作线程if (needWake) {mLooper->wake();}
}
bool InputDispatcher::enqueueInboundEventLocked(std::unique_ptr<EventEntry> newEntry) {bool needWake = mInboundQueue.empty();// 把newEntry放到mInboundQueue的最末尾mInboundQueue.push_back(std::move(newEntry));EventEntry& entry = *(mInboundQueue.back());// 在Trace上反应traceInboundQueueLengthLocked();.....return needWake;
}
二. InputDispatcher对事件的处理
如下,当InputDispatcher的工作线程被唤醒后,后进行主要进行如下操
- 1.先把线程的下次唤醒时间设置为无限大
- 2.进入到dispatchOnceInnerLocked进行事件的分发
- 3.处理anr相关,上报可能的anr,并计算出未来最近的超时时间
- 4.按照计算出的时间进行休眠
以上为dispatchOnce函数的主要作用,目前跟踪事件的分发,聚焦于dispatchOnceInnerLocked,后面会介绍到dispatchOnce的其他功能
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {// 先把下次的唤醒事件是设置为无穷大nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;{ // acquire lockstd::scoped_lock _l(mLock);mDispatcherIsAlive.notify_all();// Run a dispatch loop if there are no pending commands.// The dispatch loop might enqueue commands to run afterwards.// 刚开始 haveCommandsLocked返回FALSE, 1.即进入该逻辑,进行事件分发if (!haveCommandsLocked()) {dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);}// Run all pending commands if there are any.// If any commands were run then force the next poll to wake up immediately.if (runCommandsLockedInterruptable()) {nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN;}// If we are still waiting for ack on some events,// we might have to wake up earlier to check if an app is anr'ing.// 2.处理anr相关 这一步骤关键, 算出 最近一次anr唤醒的超时时间,时间到了 就唤醒.const nsecs_t nextAnrCheck = processAnrsLocked();nextWakeupTime = std::min(nextWakeupTime, nextAnrCheck);// We are about to enter an infinitely long sleep, because we have no commands or// pending or queued eventsif (nextWakeupTime == LONG_LONG_MAX) {mDispatcherEnteredIdle.notify_all();}} // release lock// Wait for callback or timeout or wake. (make sure we round up, not down)nsecs_t currentTime = now();int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime);// 3.按照计算出的事件进行休眠mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);
}以触摸事件为例,主要关注dispatchOnceInnerLocked,即事件的具体的分发过程,首先简单了解下android的应用窗口和inputDispatcher的关联:
如下图,android系统在创建窗口的过程,或创建一些手势监听的时候,会创建用于接收输入事件的组件,该过程会来到InputDispatcher中,创建一其创建了ocket,通过一对InputChannel封装一对已经建立了连接的本地Socket(SocketPair),如下ServerChannel和ClitentChannel个持有Socket通信的各一端,后续事件分发给应用端将通过该Socket链路进行传递:
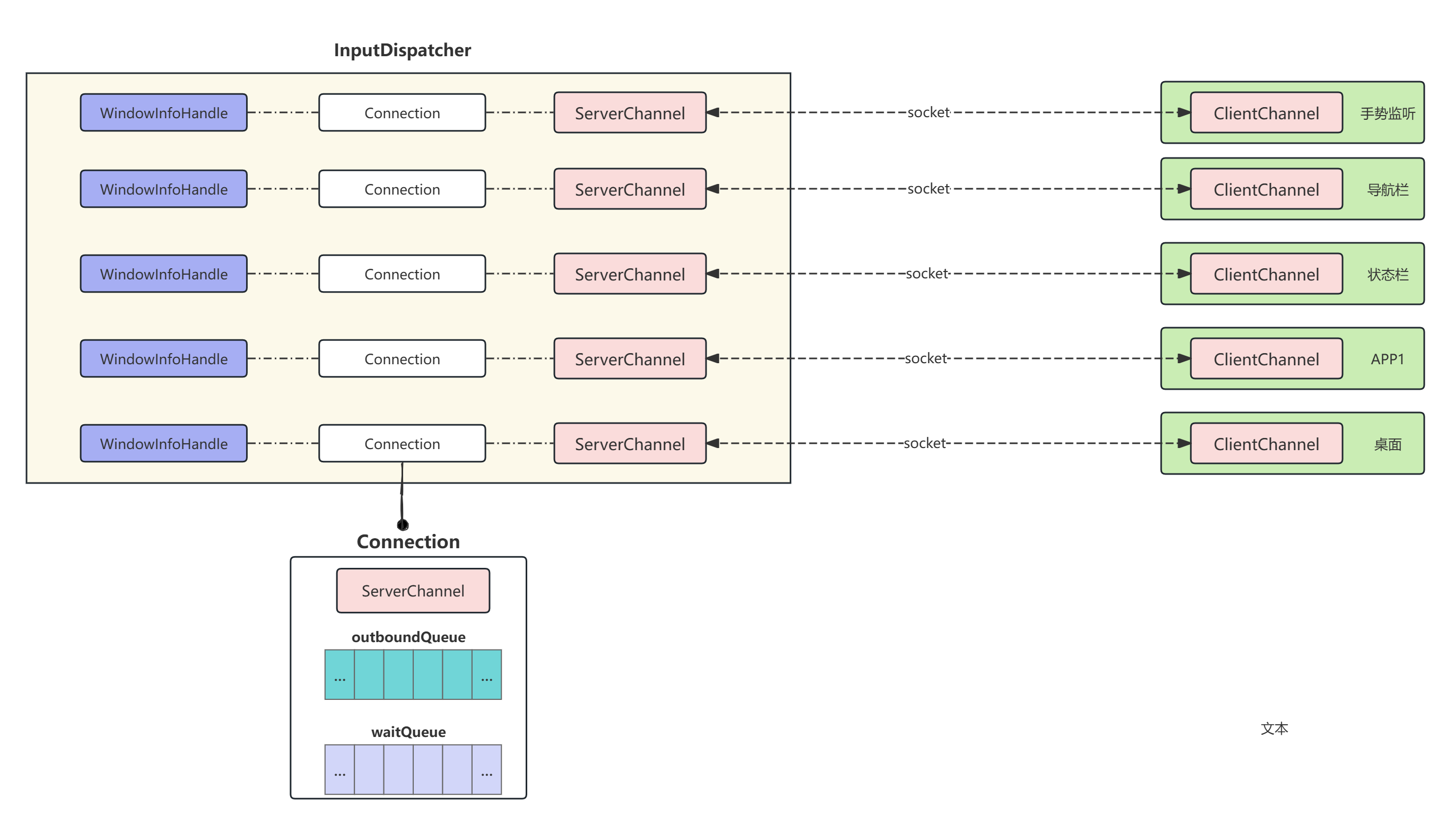
除此之外应用侧没有个可以接受事件的窗口,在InputDispatcher中为其维护了类型的WindowInfoHandle的数据结构,保存着对应窗口的位置大小 可见性 触摸区域 会否能接收事件的等基本信息, 除此之外,WindowInfoHandle 对应一个Connection,Connection中维护着 对应ServerChannel
故有以下的一一对应关系:
WindowInfoHandle----Connection------ServerChannel-----ClientChannel-----一个应用窗口
除此之外
如下图,在android的系统中所有窗口都是拥有层级关系的,比如导航栏测层级高于状态栏高于用户应用的窗口高于壁纸,处于较高层级的窗口能进口遮住层级低的窗口,同样在InputDispatcher中也维护了一个队列,队列中存放着了WindowInfoHandle,通常情况下,系统的每个窗口在该队列中有对应的WindowInfoHandle,同时该队列中的层级关系也和窗口的层级类似,较高层级的窗口越靠近队首。
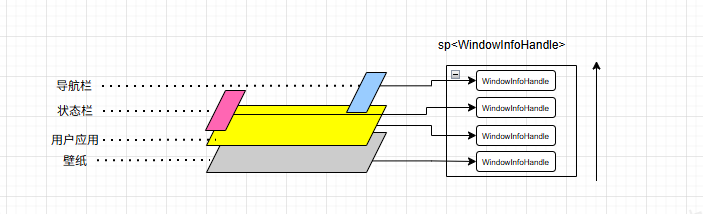
接下来将以触摸Down事件为例,梳理下事件在InputDispatcher的分发过程:
1.dispatchOnceInnerLocked中分发事件
在dispatchOnceInnerLocked中主要做了以下处理:
- 从mInboundQueue队列的队首去除一个事件,并在trace上更新
- 把事件转化为MotionEntry
- 调用dispatchMotionLocked,对触摸事件MotionEntry进行分发
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked(nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {// Inbound queue has at least one entry.// 从 mInboundQueue队列中 取队首 的mPendingEvent = mInboundQueue.front();mInboundQueue.pop_front();// trace 上体现traceInboundQueueLengthLocked();}// Poke user activity for this event.if (mPendingEvent->policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER) {//会调用到PowerManagerService,使的用户保持活动, 不要让灭屏pokeUserActivityLocked(*mPendingEvent);}}....switch (mPendingEvent->type) {......// motion事件case EventEntry::Type::MOTION: {// 转类型为motionEntrystd::shared_ptr<MotionEntry> motionEntry =std::static_pointer_cast<MotionEntry>(mPendingEvent);.......// 继续分发done = dispatchMotionLocked(currentTime, motionEntry, &dropReason, nextWakeupTime);break;}.......}....
}
在dispatchMotionLocked过程中,
- 首先会新建一个InputTargets列表将去保存用于接收时间的窗口信息
- 找到处理该事件的 窗口们,把他们添加到InputTargets中
- 把当前屏幕上的全局触摸事件监听添加到InputTargets
- 通过dispatchEventLocked将输入事件分发给InputTargets每一个对应的窗口或者监听
bool InputDispatcher::dispatchMotionLocked(nsecs_t currentTime, std::shared_ptr<MotionEntry> entry,DropReason* dropReason, nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {.......// Identify targets.//1.用于保存触摸事件的 目标窗口std::vector<InputTarget> inputTargets;bool conflictingPointerActions = false;InputEventInjectionResult injectionResult;if (isPointerEvent) {// 2.触摸事件 进入到该分支 寻找 目标窗口, inputTargets是个向量,说明触摸事件的目标窗口可以是多个// Pointer event. (eg. touchscreen)injectionResult =findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked(currentTime, *entry, inputTargets, nextWakeupTime,&conflictingPointerActions);}.....// Add monitor channels from event's or focused display.// 3.全局监控 常见 的就是 开发者模式的 的触摸追踪,addGlobalMonitoringTargetsLocked(inputTargets, getTargetDisplayId(*entry));// Dispatch the motion.if (conflictingPointerActions) {CancelationOptions options(CancelationOptions::CANCEL_POINTER_EVENTS,"conflicting pointer actions");synthesizeCancelationEventsForAllConnectionsLocked(options);}// 3.向 inputTargets中的所有window派发事件dispatchEventLocked(currentTime, entry, inputTargets);return true;
}
寻找能处理当前down事件的窗口们
接下来将会去寻找能处理该触摸事件的窗口,如下代码,先获取该触摸事件对应的屏幕id,如果是第一个手指的down事件的话,则意味着是新的手势的开始,则会重置 保存接收事件的tempTouchState。
然后获取当前down事件在屏幕上的坐标 和屏幕id等信息,调用findTouchedWindowAtLocked,该方法中会从上到下遍历当前屏幕对应的WindowInfoHandle列表,如果触摸事件的坐标刚好落在了WindowInfoHandle的接收触摸事件的区域范围内,遍历终止,该WindowInfoHandle负责接收当前的触摸down事件,该WindowInfoHandle 一般对应的是窗口
但是能接收到事件不仅仅只有普通的窗口,各种系统手势也都在后台默默捕捉着触摸事件,随后则通过findTouchedSpyWindowsAtLocked,获得把手势相关的WindowInfoHandle们,
随后把上两个步骤中收集到的WindowInfoHandle 汇总到名为 newTouchedWindows列表中,
接下来要对上面收集到的WindowInfoHandle 们进行过滤,过滤掉那那些目前不能接受事件的WindowInfoHandle比如
- 当前WindowInfoHandle 配置了暂时事件分发
- 当前WindowInfoHandle 已经anr了,没有响应
- 如果涉及到了事件的透传,则过滤掉不能透传的WindowInfoHandle
经过过滤后将经过筛选的窗口加入到 tempTouchState,再将touchedWindow中的为WIndow加入到 inputTargets,inputTargets中
// 寻找触摸的目标窗口
InputEventInjectionResult InputDispatcher::findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked(nsecs_t currentTime, const MotionEntry& entry, std::vector<InputTarget>& inputTargets,nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime, bool* outConflictingPointerActions) {ATRACE_CALL();// For security reasons, we defer updating the touch state until we are sure that// event injection will be allowed.const int32_t displayId = entry.displayId; // 获取当前MotionEntry的屏幕.....// Update the touch state as needed based on the properties of the touch event.InputEventInjectionResult injectionResult = InputEventInjectionResult::PENDING;sp<WindowInfoHandle> newHoverWindowHandle(mLastHoverWindowHandle);sp<WindowInfoHandle> newTouchedWindowHandle;// Copy current touch state into tempTouchState.// This state will be used to update mTouchStatesByDisplay at the end of this function.// If no state for the specified display exists, then our initial state will be empty.const TouchState* oldState = nullptr;TouchState tempTouchState; // TouchState 保存着 可以接受触摸事件窗口的集合/if (const auto it = mTouchStatesByDisplay.find(displayId); it != mTouchStatesByDisplay.end()) {oldState = &(it->second);tempTouchState = *oldState;}........//如果该事件为 AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN 则认为是一个新的手势const bool newGesture = (maskedAction == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN ||maskedAction == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_SCROLL || isHoverAction);const bool isFromMouse = isFromSource(entry.source, AINPUT_SOURCE_MOUSE);bool wrongDevice = false;if (newGesture) {.... // 重置 tempTouchStatetempTouchState.reset();tempTouchState.down = down;tempTouchState.deviceId = entry.deviceId;tempTouchState.source = entry.source;tempTouchState.displayId = displayId;isSplit = false;} else if (switchedDevice && maskedAction == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_MOVE) {ALOGI("Dropping move event because a pointer for a different device is already active ""in display %" PRId32,displayId);// TODO: test multiple simultaneous input streams.injectionResult = InputEventInjectionResult::FAILED;switchedDevice = false;wrongDevice = true;goto Failed;}if (newGesture || (isSplit && maskedAction == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_DOWN)) {/* Case 1: New splittable pointer going down, or need target for hover or scroll. */int32_t x;int32_t y;// 取出多指的indexconst int32_t pointerIndex = getMotionEventActionPointerIndex(action);// Always dispatch mouse events to cursor position.if (isFromMouse) {......} else {// 取出手指对应的 x y 坐标x = int32_t(entry.pointerCoords[pointerIndex].getAxisValue(AMOTION_EVENT_AXIS_X));y = int32_t(entry.pointerCoords[pointerIndex].getAxisValue(AMOTION_EVENT_AXIS_Y));}const bool isDown = maskedAction == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN;const bool isStylus = isPointerFromStylus(entry, pointerIndex);// 去寻找对应的WindowInfoHandle, 能找到的话 ,就只能找到一个newTouchedWindowHandle = findTouchedWindowAtLocked(displayId, x, y, &tempTouchState,isStylus, isDown /*addOutsideTargets*/);......// 把当前屏幕上 用于监听事件的SpyWindows对应的WindowInfoHandle们,SpyWindows在系统层一般是 手势监听std::vector<sp<WindowInfoHandle>> newTouchedWindows =findTouchedSpyWindowsAtLocked(displayId, x, y, isStylus);// 汇总上面两个流程找到的 WindowInfoHandle 保存到newTouchedWindows中if (newTouchedWindowHandle != nullptr) {// Process the foreground window first so that it is the first to receive the event.newTouchedWindows.insert(newTouchedWindows.begin(), newTouchedWindowHandle);}if (newTouchedWindows.empty()) {ALOGI("Dropping event because there is no touchable window at (%d, %d) on display %d.",x, y, displayId);injectionResult = InputEventInjectionResult::FAILED;goto Failed;}// 遍历找到的WindowInfoHandle,排除不能接收事件的 WindowInfoHandlefor (const sp<WindowInfoHandle>& windowHandle : newTouchedWindows) {const WindowInfo& info = *windowHandle->getInfo();// Skip spy window targets that are not valid for targeted injection.if (const auto err = verifyTargetedInjection(windowHandle, entry); err) {continue;}// 比如当前窗口配置了暂时事件分发 if (info.inputConfig.test(WindowInfo::InputConfig::PAUSE_DISPATCHING)) {ALOGI("Not sending touch event to %s because it is paused",windowHandle->getName().c_str());continue;}// Ensure the window has a connection and the connection is responsive// 比如该窗口已经anr了,没有响应const bool isResponsive = hasResponsiveConnectionLocked(*windowHandle);if (!isResponsive) {ALOGW("Not sending touch gesture to %s because it is not responsive",windowHandle->getName().c_str());continue;}// Drop events that can't be trusted due to occlusion// 如果涉及到时间的透传,但是该窗口么有权利被透传if (mBlockUntrustedTouchesMode != BlockUntrustedTouchesMode::DISABLED) {// 计算出当前窗口的 遮盖信息TouchOcclusionInfo occlusionInfo =computeTouchOcclusionInfoLocked(windowHandle, x, y);if (!isTouchTrustedLocked(occlusionInfo)) {if (DEBUG_TOUCH_OCCLUSION) {ALOGD("Stack of obscuring windows during untrusted touch (%d, %d):", x, y);for (const auto& log : occlusionInfo.debugInfo) {ALOGD("%s", log.c_str());}}sendUntrustedTouchCommandLocked(occlusionInfo.obscuringPackage);if (mBlockUntrustedTouchesMode == BlockUntrustedTouchesMode::BLOCK) {ALOGW("Dropping untrusted touch event due to %s/%d",occlusionInfo.obscuringPackage.c_str(), occlusionInfo.obscuringUid);continue;}}}......// Update the temporary touch state.BitSet32 pointerIds;pointerIds.markBit(entry.pointerProperties[pointerIndex].id);// 将经过筛选的窗口加入到 tempTouchStatetempTouchState.addOrUpdateWindow(windowHandle, targetFlags, pointerIds);}}......// 把 touchedWindow中的为WIndow加入到 inputTargetsfor (const TouchedWindow& touchedWindow : tempTouchState.windows) {addWindowTargetLocked(touchedWindow.windowHandle, touchedWindow.targetFlags,touchedWindow.pointerIds, inputTargets);}
上文中找到了用于接收触摸事件的InputTarget们,包含了应用窗口和spy类型的全局手势监听,随后还会通过addGlobalMonitoringTargetsLocked添加GlobalMonitoring监听,这个也是当前屏幕上的监听,旧的android版本里面GlobalMonitoring可能会用于系统手势监听,在新版本的android上手势监听通过spy类型的全局手势监听来实现,GlobalMonitoring在新版上最常见的应用是开发者选项里面显示触摸轨迹中监听触摸的实现。
void InputDispatcher::addGlobalMonitoringTargetsLocked(std::vector<InputTarget>& inputTargets,int32_t displayId) {auto monitorsIt = mGlobalMonitorsByDisplay.find(displayId);if (monitorsIt == mGlobalMonitorsByDisplay.end()) return;for (const Monitor& monitor : selectResponsiveMonitorsLocked(monitorsIt->second)) {InputTarget target;target.inputChannel = monitor.inputChannel;target.flags = InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS;if (const auto& it = mDisplayInfos.find(displayId); it != mDisplayInfos.end()) {target.displayTransform = it->second.transform;}target.setDefaultPointerTransform(target.displayTransform);inputTargets.push_back(target);}
}
上文中我们收集了所有能接受事件的InputTarget们,其中包含了应用窗口对应的InputTarget和手势监听对应的InputTarget。接收触摸式事件的候选者们已经产生,接下来将要向他们分发:
- 通过pokeUserActivityLocked,会间接的调用到PowerManagerService,使的用户保持活动, 不要让灭屏
- 遍历将InputTarget们,获取他们各自对应的Connection,正如上文所描述,Connection中保存着和应用端进行通信的Socket的Server端
- 随后调用prepareDispatchCycleLocked开始向目标们分发事件
void InputDispatcher::dispatchEventLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,std::shared_ptr<EventEntry> eventEntry,const std::vector<InputTarget>& inputTargets) {ATRACE_CALL();if (DEBUG_DISPATCH_CYCLE) {ALOGD("dispatchEventToCurrentInputTargets");}updateInteractionTokensLocked(*eventEntry, inputTargets);ALOG_ASSERT(eventEntry->dispatchInProgress); // should already have been set to true// //会调用到PowerManagerService,使的用户保持活动, 不要让灭屏pokeUserActivityLocked(*eventEntry);// inputTargets 为 找到的目标窗口for (const InputTarget& inputTarget : inputTargets) {// 获取该InputTarget对应的 connectionsp<Connection> connection =getConnectionLocked(inputTarget.inputChannel->getConnectionToken());if (connection != nullptr) {// 分发prepareDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, eventEntry, inputTarget);} else {if (DEBUG_FOCUS) {ALOGD("Dropping event delivery to target with channel '%s' because it ""is no longer registered with the input dispatcher.",inputTarget.inputChannel->getName().c_str());}}}
}
void InputDispatcher::prepareDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,const sp<Connection>& connection,std::shared_ptr<EventEntry> eventEntry,const InputTarget& inputTarget) {// 到这里进行入队enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked(currentTime, connection, eventEntry, inputTarget);
}
继续调用到enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked:
- 1.把事件添加到该Connection的outboundQueue中.
- 2.事件已经放到了 Connection对应的outboundQueue ,向应用分发
void InputDispatcher::enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,const sp<Connection>& connection,std::shared_ptr<EventEntry> eventEntry,const InputTarget& inputTarget) {if (ATRACE_ENABLED()) {std::string message =StringPrintf("enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked(inputChannel=%s, id=0x%" PRIx32 ")",connection->getInputChannelName().c_str(), eventEntry->id);ATRACE_NAME(message.c_str());}bool wasEmpty = connection->outboundQueue.empty();.....// 事件放如Connection的outboundQueueenqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS);......// If the outbound queue was previously empty, start the dispatch cycle going.if (wasEmpty && !connection->outboundQueue.empty()) {// 事件已经放到了 connection 对应的outboundQueue ,开始分发startDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection);}
}件添加到该Connection的outboundQueue中
在enqueueDispatchEntryLocked中:
- 把事件连同inputTarget封装为EventEntry
- 根据事件的类型,对EventEntry进行一些加工
- 把加工后的EventEntry放到Connection的 outboundQueue,并在trace上体现
void InputDispatcher::enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(const sp<Connection>& connection,std::shared_ptr<EventEntry> eventEntry,const InputTarget& inputTarget,int32_t dispatchMode) {// 把事件连同inputTarget封装为EventEntrystd::unique_ptr<DispatchEntry> dispatchEntry =createDispatchEntry(inputTarget, eventEntry, inputTargetFlags);// Use the eventEntry from dispatchEntry since the entry may have changed and can now be a// different EventEntry than what was passed in.EventEntry& newEntry = *(dispatchEntry->eventEntry);// Apply target flags and update the connection's input state.// 根据事件的类型,对EventEntry进行一些加工switch (newEntry.type) {......case EventEntry::Type::MOTION: {const MotionEntry& motionEntry = static_cast<const MotionEntry&>(newEntry);// Assign a default value to dispatchEntry that will never be generated by InputReader,// and assign a InputDispatcher value if it doesn't change in the if-else chain below.constexpr int32_t DEFAULT_RESOLVED_EVENT_ID =static_cast<int32_t>(IdGenerator::Source::OTHER);dispatchEntry->resolvedEventId = DEFAULT_RESOLVED_EVENT_ID;if (dispatchMode & InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_OUTSIDE) {dispatchEntry->resolvedAction = AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_OUTSIDE;} else if (dispatchMode & InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_HOVER_EXIT) {dispatchEntry->resolvedAction = AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_HOVER_EXIT;} else if (dispatchMode & InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_HOVER_ENTER) {dispatchEntry->resolvedAction = AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_HOVER_ENTER;} else if (dispatchMode & InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_EXIT) {dispatchEntry->resolvedAction = AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_CANCEL;} else if (dispatchMode & InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_ENTER) {dispatchEntry->resolvedAction = AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN;} else {// 走这个分支 设置一些属性dispatchEntry->resolvedAction = motionEntry.action;dispatchEntry->resolvedEventId = motionEntry.id;}if (dispatchEntry->resolvedAction == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_HOVER_MOVE &&!connection->inputState.isHovering(motionEntry.deviceId, motionEntry.source,motionEntry.displayId)) {if (DEBUG_DISPATCH_CYCLE) {ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ enqueueDispatchEntryLocked: filling in missing hover ""enter event",connection->getInputChannelName().c_str());}// We keep the 'resolvedEventId' here equal to the original 'motionEntry.id' because// this is a one-to-one event conversion.dispatchEntry->resolvedAction = AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_HOVER_ENTER;}dispatchEntry->resolvedFlags = motionEntry.flags;if (dispatchEntry->targetFlags & InputTarget::FLAG_WINDOW_IS_OBSCURED) {dispatchEntry->resolvedFlags |= AMOTION_EVENT_FLAG_WINDOW_IS_OBSCURED;}if (dispatchEntry->targetFlags & InputTarget::FLAG_WINDOW_IS_PARTIALLY_OBSCURED) {dispatchEntry->resolvedFlags |= AMOTION_EVENT_FLAG_WINDOW_IS_PARTIALLY_OBSCURED;}// 进行记录 检测是不是出现非法的事件if (!connection->inputState.trackMotion(motionEntry, dispatchEntry->resolvedAction,dispatchEntry->resolvedFlags)) {if (DEBUG_DISPATCH_CYCLE) {ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ enqueueDispatchEntryLocked: skipping inconsistent motion ""event",connection->getInputChannelName().c_str());}return; // skip the inconsistent event}dispatchEntry->resolvedEventId =dispatchEntry->resolvedEventId == DEFAULT_RESOLVED_EVENT_ID? mIdGenerator.nextId(): motionEntry.id;if (ATRACE_ENABLED() && dispatchEntry->resolvedEventId != motionEntry.id) {std::string message = StringPrintf("Transmute MotionEvent(id=0x%" PRIx32") to MotionEvent(id=0x%" PRIx32 ").",motionEntry.id, dispatchEntry->resolvedEventId);ATRACE_NAME(message.c_str());}if ((motionEntry.flags & AMOTION_EVENT_FLAG_NO_FOCUS_CHANGE) &&(motionEntry.policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_TRUSTED)) {// Skip reporting pointer down outside focus to the policy.break;}dispatchPointerDownOutsideFocus(motionEntry.source, dispatchEntry->resolvedAction,inputTarget.inputChannel->getConnectionToken());break;}.......}// Remember that we are waiting for this dispatch to complete.if (dispatchEntry->hasForegroundTarget()) {incrementPendingForegroundDispatches(newEntry);}// Enqueue the dispatch entry.// 把加工后的EventEntry放到Connection的 outboundQueueconnection->outboundQueue.push_back(dispatchEntry.release());// 在trace上体现traceOutboundQueueLength(*connection);
}
随后调用startDispatchCycleLocked,正式的开始通过socket连接把事件正式的发送给应用端:
void InputDispatcher::startDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,const sp<Connection>& connection) {while (connection->status == Connection::Status::NORMAL && !connection->outboundQueue.empty()) {// 从 connection的outboundQueue取出 队首的DispatchEntryDispatchEntry* dispatchEntry = connection->outboundQueue.front();// 把deliveryTime 事件设置为当前事时间dispatchEntry->deliveryTime = currentTime;const std::chrono::nanoseconds timeout = getDispatchingTimeoutLocked(connection);// 记录该dispatchEntry的timeoutTime时间为当前的事件 + 5000msdispatchEntry->timeoutTime = currentTime + timeout.count();// Publish the event.status_t status;const EventEntry& eventEntry = *(dispatchEntry->eventEntry);switch (eventEntry.type) {......// Publish the motion event.// 开始分发 libs/input/InputTransport.cppstatus = connection->inputPublisher.publishMotionEvent(dispatchEntry->seq,dispatchEntry->resolvedEventId,motionEntry.deviceId, motionEntry.source,motionEntry.displayId, std::move(hmac),dispatchEntry->resolvedAction,motionEntry.actionButton,dispatchEntry->resolvedFlags,motionEntry.edgeFlags, motionEntry.metaState,motionEntry.buttonState,motionEntry.classification,dispatchEntry->transform,motionEntry.xPrecision, motionEntry.yPrecision,motionEntry.xCursorPosition,motionEntry.yCursorPosition,dispatchEntry->rawTransform,motionEntry.downTime, motionEntry.eventTime,motionEntry.pointerCount,motionEntry.pointerProperties, usingCoords);break;}.....// Re-enqueue the event on the wait queue.// 发送事件结束剔除outboundQueue队首的事件,并保存在dispatchEntry中connection->outboundQueue.erase(std::remove(connection->outboundQueue.begin(),connection->outboundQueue.end(),dispatchEntry));traceOutboundQueueLength(*connection);// 把刚才分发了的 dispatchEntry 放到 该connection 对应的waitQueueconnection->waitQueue.push_back(dispatchEntry);// 然后向AnrTracker添加一条该dispatchEntry相关的记录if (connection->responsive) {// 随后把该 dispatchEntry 放到 mAnrTracker 用于跟踪事件相关的anrmAnrTracker.insert(dispatchEntry->timeoutTime,// 获取之前设置的timeoutTime时间connection->inputChannel->getConnectionToken());}//traceWaitQueueLength(*connection);}
}
上文中
- 获取该Connection的outboundQueue队首的DispatchEntry,记录当前的事件,同时设置dispatchEntry的超时时间,通常为当前时间 +5000ms
- 对dispatchEntry再做一些处理后,随机通过connection->inputPublisher.publishMotionEvent 正式的向客户端发送输入事件
- 发送事件结束后,剔除outboundQueue队首的dispatchEntry,并保存在dispatchEntry中, 随即再把该dispatchEntry 放到 该connection 对应的waitQueue
- 为该次dispatchEntry的分发添加一个AnrTracker记录,用于追踪该事件可能产生的超时anr
- todo trace
status_t InputPublisher::publishMotionEvent(uint32_t seq, int32_t eventId, int32_t deviceId, int32_t source, int32_t displayId,std::array<uint8_t, 32> hmac, int32_t action, int32_t actionButton, int32_t flags,int32_t edgeFlags, int32_t metaState, int32_t buttonState,MotionClassification classification, const ui::Transform& transform, float xPrecision,float yPrecision, float xCursorPosition, float yCursorPosition,const ui::Transform& rawTransform, nsecs_t downTime, nsecs_t eventTime,uint32_t pointerCount, const PointerProperties* pointerProperties,const PointerCoords* pointerCoords) {.....// 填充InputMessageInputMessage msg;msg.header.type = InputMessage::Type::MOTION;msg.header.seq = seq;msg.body.motion.eventId = eventId;msg.body.motion.deviceId = deviceId;msg.body.motion.source = source;msg.body.motion.displayId = displayId;msg.body.motion.hmac = std::move(hmac);msg.body.motion.action = action;msg.body.motion.actionButton = actionButton;msg.body.motion.flags = flags;msg.body.motion.edgeFlags = edgeFlags;msg.body.motion.metaState = metaState;msg.body.motion.buttonState = buttonState;msg.body.motion.classification = classification;msg.body.motion.dsdx = transform.dsdx();msg.body.motion.dtdx = transform.dtdx();msg.body.motion.dtdy = transform.dtdy();msg.body.motion.dsdy = transform.dsdy();msg.body.motion.tx = transform.tx();msg.body.motion.ty = transform.ty();msg.body.motion.xPrecision = xPrecision;msg.body.motion.yPrecision = yPrecision;msg.body.motion.xCursorPosition = xCursorPosition;msg.body.motion.yCursorPosition = yCursorPosition;msg.body.motion.dsdxRaw = rawTransform.dsdx();msg.body.motion.dtdxRaw = rawTransform.dtdx();msg.body.motion.dtdyRaw = rawTransform.dtdy();msg.body.motion.dsdyRaw = rawTransform.dsdy();msg.body.motion.txRaw = rawTransform.tx();msg.body.motion.tyRaw = rawTransform.ty();msg.body.motion.downTime = downTime;msg.body.motion.eventTime = eventTime;msg.body.motion.pointerCount = pointerCount;for (uint32_t i = 0; i < pointerCount; i++) {msg.body.motion.pointers[i].properties.copyFrom(pointerProperties[i]);msg.body.motion.pointers[i].coords.copyFrom(pointerCoords[i]);}// 通过mChannel发送给app// core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp handleEvent()return mChannel->sendMessage(&msg);
}
上文提到,在窗口建立的过程中会生成一对建立了连接的SocketPair,一个被InputDispatcher端的InputChannel持有,另一个被App端的InputChannel持有,在app端得到这个InputChannel会通过如下类InputEventReceiver的子类来监听客户端InputChannel,接收来自InputDispatcher的事件:
public abstract class InputEventReceiver {private static final String TAG = "InputEventReceiver";private final CloseGuard mCloseGuard = CloseGuard.get();private long mReceiverPtr;// We keep references to the input channel and message queue objects here so that// they are not GC'd while the native peer of the receiver is using them.private InputChannel mInputChannel;private MessageQueue mMessageQueue;....../*** Creates an input event receiver bound to the specified input channel.** @param inputChannel The input channel.* @param looper The looper to use when invoking callbacks.*/// InputEventReceiver的构造函数中会在Native层建立对象,监听inputChannelpublic InputEventReceiver(InputChannel inputChannel, Looper looper) {if (inputChannel == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("inputChannel must not be null");}if (looper == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("looper must not be null");}mInputChannel = inputChannel;mMessageQueue = looper.getQueue();// 建立native层的对象,会对inputChannel中的socket进行监听mReceiverPtr = nativeInit(new WeakReference<InputEventReceiver>(this),inputChannel, mMessageQueue);mCloseGuard.open("InputEventReceiver.dispose");}// Called from native code.@SuppressWarnings("unused")/** 事件分发 调用到这里 WindowInputEventReceiver* */@UnsupportedAppUsage(maxTargetSdk = Build.VERSION_CODES.R, trackingBug = 170729553)private void dispatchInputEvent(int seq, InputEvent event) {mSeqMap.put(event.getSequenceNumber(), seq);// 普通应用调用到 onInputEvent的内部类onInputEvent(event);}/** 应用处理完毕 event 会调用到这里* */public final void finishInputEvent(InputEvent event, boolean handled) {if (event == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("event must not be null");}if (mReceiverPtr == 0) {Log.w(TAG, "Attempted to finish an input event but the input event "+ "receiver has already been disposed.");} else {int index = mSeqMap.indexOfKey(event.getSequenceNumber());if (index < 0) {Log.w(TAG, "Attempted to finish an input event that is not in progress.");} else {int seq = mSeqMap.valueAt(index);mSeqMap.removeAt(index);// 调用到nativenativeFinishInputEvent(mReceiverPtr, seq, handled);}}event.recycleIfNeededAfterDispatch();}}
当监听到事件后,会通过JNI调用到dispatchInputEvent,随即触发事件在应用层的分发过程,该文章关注于事件在framework层的流转,应用层的分发不再展开
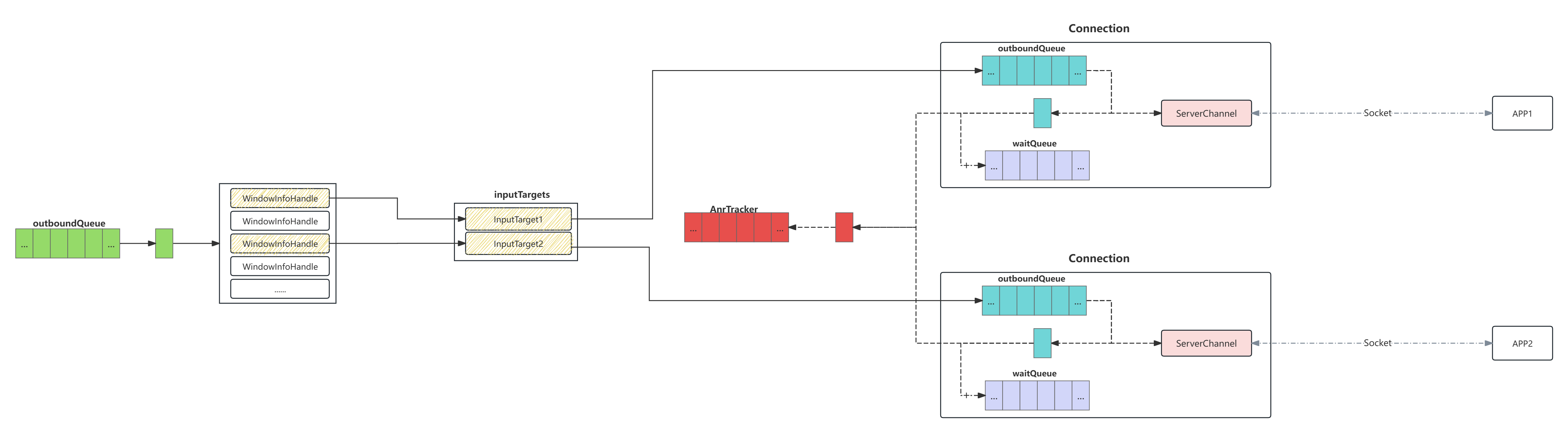
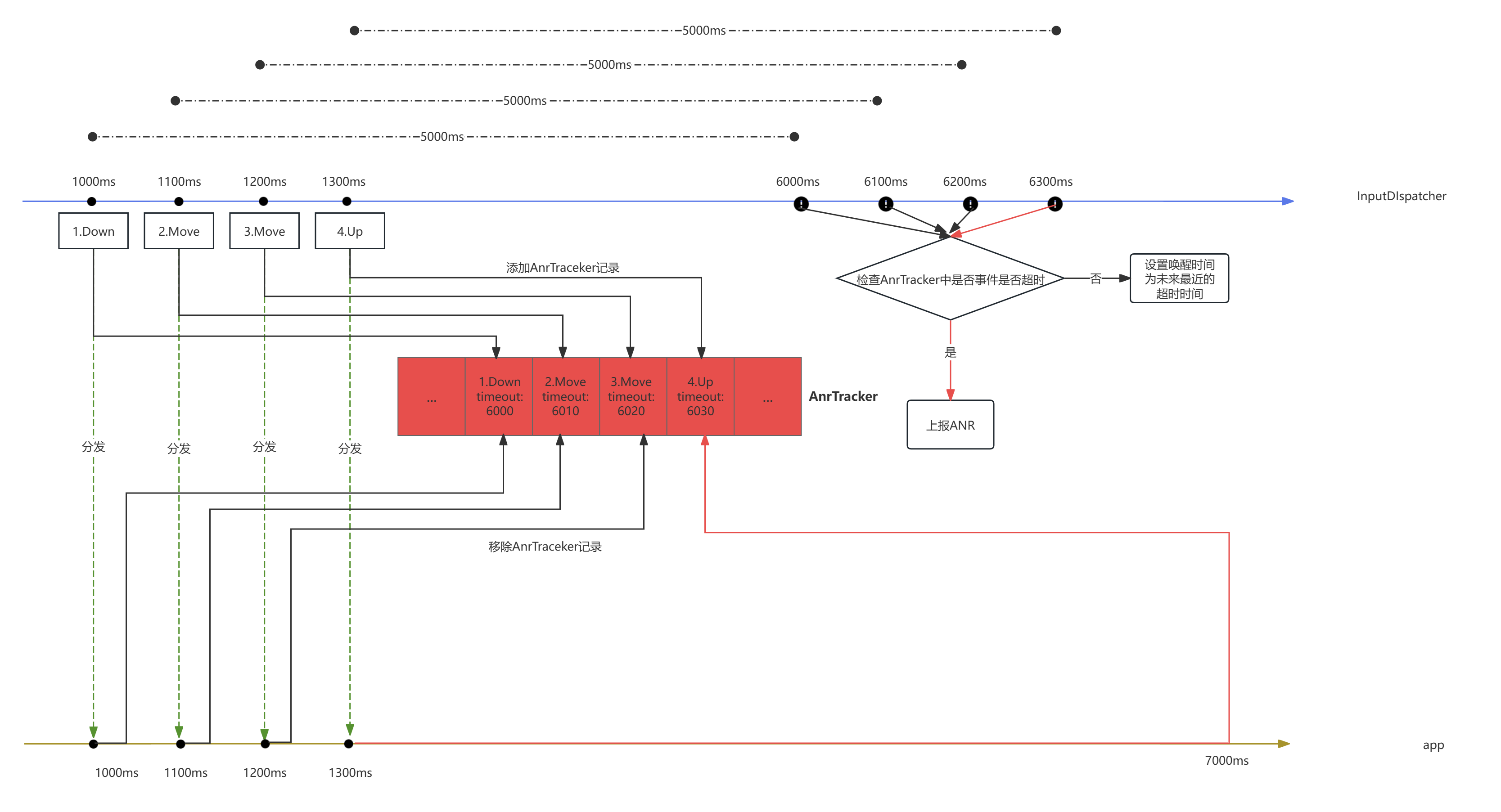
2.AnrTracker
事件的分发暂时按下不表,上文中提到 在inputDispatcher把一个事件发送给应用端后,随后为该次dispatchEntry的分发添加一个AnrTracker记录,用于追踪该事件可能产生的超时anr:
void InputDispatcher::startDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,const sp<Connection>& connection) {.....// 把一个事件发送给应用端status = connection->inputPublisher.publishMotionEvent(....);break;}.....// Re-enqueue the event on the wait queue.// 发送事件结束剔除outboundQueue队首的事件记录,并保存在dispatchEntry中connection->outboundQueue.erase(std::remove(connection->outboundQueue.begin(),connection->outboundQueue.end(),dispatchEntry));traceOutboundQueueLength(*connection);// 把刚才分发了的 dispatchEntry 放到 该connection 对应的waitQueueconnection->waitQueue.push_back(dispatchEntry);// 然后向AnrTracker添加一条该dispatchEntry相关的记录if (connection->responsive) {// 随后把该 dispatchEntry 放到 mAnrTracker 用于跟踪事件相关的anrmAnrTracker.insert(dispatchEntry->timeoutTime,// 获取之前设置的timeoutTime时间connection->inputChannel->getConnectionToken());}//traceWaitQueueLength(*connection);}
}
AnrTracker,正如该类的注释描述:
记录每个连接发生 ANR 的时间。提供快速查找即将导致 ANR 的连接的能力
该类被InputDispatcher拥有,该类中维护multiset类型的容器,名为mAnrTimeouts,容器中的一条记录保存着一个被分发的事件的超时时间和对应的Connection,如上文描述每分发一个事件,就是通过AnrTracker.insert向mAnrTimeouts插入一条记录,记录着事件的超时时间和对应Connection的Token,一般情况下超时时间为当前时间 + 5000ms
/*** Keeps track of the times when each connection is going to ANR.* Provides the ability to quickly find the connection that is going to cause ANR next.*/
class AnrTracker {
public:void insert(nsecs_t timeoutTime, sp<IBinder> token);void erase(nsecs_t timeoutTime, const sp<IBinder>& token);void eraseToken(const sp<IBinder>& token);void clear();bool empty() const;// If empty() is false, return the time at which the next connection should cause an ANR// If empty() is true, return LONG_LONG_MAXnsecs_t firstTimeout() const;// Return the token of the next connection that should cause an ANR.// Do not call this unless empty() is false, you will encounter undefined behaviour.const sp<IBinder>& firstToken() const;private:// Optimization: use a multiset to keep track of the event timeouts. When an event is sent// to the InputConsumer, we add an entry to this structure. We look at the smallest value to// determine if any of the connections is unresponsive, and to determine when we should wake// next for the future ANR check.// Using a multiset helps quickly look up the next timeout due.//// We must use a multi-set, because it is plausible (although highly unlikely) to have entries// from the same connection and same timestamp, but different sequence numbers.// We are not tracking sequence numbers, and just allow duplicates to exist.std::multiset<std::pair<nsecs_t /*timeoutTime*/, sp<IBinder> /*connectionToken*/>> mAnrTimeouts;
};
再回到上文中的InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce(),这里是事件在InputDispatcher开始分发的起点:
在dispatchOnceInnerLocked中我们刚刚分发了一个事件,接下来processAnrsLocked(),在processAnrsLocked中会对刚才在AnrTracker插入的记录做进一步的处理:
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {// 先把下次的唤醒事件是设置为无穷大nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;{ // acquire lockstd::scoped_lock _l(mLock);mDispatcherIsAlive.notify_all();// Run a dispatch loop if there are no pending commands.// The dispatch loop might enqueue commands to run afterwards.// 刚开始 haveCommandsLocked返回FALSE, 1.即进入该逻辑,进行事件分发if (!haveCommandsLocked()) {dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);}// Run all pending commands if there are any.// If any commands were run then force the next poll to wake up immediately.if (runCommandsLockedInterruptable()) {nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN;}// If we are still waiting for ack on some events,// we might have to wake up earlier to check if an app is anr'ing.// 2.处理anr相关 这一步骤关键, 算出 最近一次anr唤醒的超时时间,时间到了 就唤醒.const nsecs_t nextAnrCheck = processAnrsLocked();nextWakeupTime = std::min(nextWakeupTime, nextAnrCheck);// We are about to enter an infinitely long sleep, because we have no commands or// pending or queued eventsif (nextWakeupTime == LONG_LONG_MAX) {mDispatcherEnteredIdle.notify_all();}} // release lock// Wait for callback or timeout or wake. (make sure we round up, not down)nsecs_t currentTime = now();int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime);// 3.按照计算出的时间进行阻塞mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);
}
如下,暂时关注 窗口焦点anr相关逻辑,只关注事件超时的anr相关逻辑
- 1. 通过AnrTracker.firstTimeout()在AnrTracker的mAnrTimeouts取出一个最早超时的记录
在上文中我们分发了一个down事件,那么取出的记录即为刚才插入的那条记录
- 2.如果当前时间比最早超时的记录的超时时间早,这说明对应的事件的ANR时间未到
上文中我们提到在dispatchOnceInnerLocked分发完事件后随即来到processAnrsLocked处理Anr相关,所以当前的时间点略微大于举例的down事件AnrTracker的插入时间,而down事件AnrTracker超时时间是插入时间 + 5000ms,故当前时间比最早超时的记录的超时时间早,肯定不会触发anr。
- 3.随后返回下次一个最早超时的记录的超时时间,用于下次InputDispatcher的唤醒时间,通过 mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis) 设置唤醒时间, 即下次再调用到的dispatchOnce的时间为最近一个分发了的事件的超时时间 唤醒后依旧通过processAnrsLocked检查时间是否anr
这样做的原因是确保每一个被分发出去的事件都能准确的检查anr超时
当然dispatchOnce并不是只能等到设置的唤醒时间到了才能被唤醒,期间他依旧可以因为其他业务 被唤醒
nsecs_t InputDispatcher::processAnrsLocked() {const nsecs_t currentTime = now();nsecs_t nextAnrCheck = LONG_LONG_MAX;// Check if we are waiting for a focused window to appear. Raise ANR if waited too long// 焦点anr相关if (mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime.has_value() && mAwaitedFocusedApplication != nullptr) {if (currentTime >= *mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime) {processNoFocusedWindowAnrLocked();mAwaitedFocusedApplication.reset();mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime = std::nullopt;return LONG_LONG_MIN;} else {// Keep waiting. We will drop the event when mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime comes.nextAnrCheck = *mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime;}}// Check if any connection ANRs are due// 事件超时的anr相关// 1.通过AnrTracker.firstTimeout()在AnrTracker的mAnrTimeouts取出一个最早超时的记录nextAnrCheck = std::min(nextAnrCheck, mAnrTracker.firstTimeout());// 2.如果当前时间比最早超时的记录的超时时间早,这说明对应的事件的ANR时间未到,3.随后返回下次一个最早超时的记录的超时时间,用于下次InputDispatcher的唤醒时间.if (currentTime < nextAnrCheck) { // most likely scenarioreturn nextAnrCheck; // everything is normal. Let's check again at nextAnrCheck}// 到这里说/说明 有 处理超时的事件,找出对应的 connection// If we reached here, we have an unresponsive connection.sp<Connection> connection = getConnectionLocked(mAnrTracker.firstToken());if (connection == nullptr) {ALOGE("Could not find connection for entry %" PRId64, mAnrTracker.firstTimeout());return nextAnrCheck;}connection->responsive = false;// Stop waking up for this unresponsive connection// 先清除 ,避免重复报anrmAnrTracker.eraseToken(connection->inputChannel->getConnectionToken());// 上报anronAnrLocked(connection);return LONG_LONG_MIN;
}3. 应用端消费完事件,回调InputDispatcher
回到事件分发流程,
当应用层处理完该事件后,最后调用到finishInputEvent,用于告知InputDispatcher该事件应用端处理完毕,该方法将通过JNI调用Native层,最终会调用到InputDispatcher的finishDispatchCycleLocked:
public abstract class InputEventReceiver {private static final String TAG = "InputEventReceiver";private final CloseGuard mCloseGuard = CloseGuard.get();private long mReceiverPtr;// We keep references to the input channel and message queue objects here so that// they are not GC'd while the native peer of the receiver is using them.private InputChannel mInputChannel;private MessageQueue mMessageQueue;....../*** Creates an input event receiver bound to the specified input channel.** @param inputChannel The input channel.* @param looper The looper to use when invoking callbacks.*/// InputEventReceiver的构造函数中会在Native层建立对象,监听inputChannelpublic InputEventReceiver(InputChannel inputChannel, Looper looper) {if (inputChannel == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("inputChannel must not be null");}if (looper == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("looper must not be null");}mInputChannel = inputChannel;mMessageQueue = looper.getQueue();// 建立native层的对象,会对inputChannel中的socket进行监听mReceiverPtr = nativeInit(new WeakReference<InputEventReceiver>(this),inputChannel, mMessageQueue);mCloseGuard.open("InputEventReceiver.dispose");}// Called from native code.@SuppressWarnings("unused")/** 事件分发 调用到这里 WindowInputEventReceiver* */@UnsupportedAppUsage(maxTargetSdk = Build.VERSION_CODES.R, trackingBug = 170729553)private void dispatchInputEvent(int seq, InputEvent event) {mSeqMap.put(event.getSequenceNumber(), seq);// 普通应用调用到 onInputEvent的内部类onInputEvent(event);}/** 应用处理完毕 event 会调用到这里* */public final void finishInputEvent(InputEvent event, boolean handled) {if (event == null) {throw new IllegalArgumentException("event must not be null");}if (mReceiverPtr == 0) {Log.w(TAG, "Attempted to finish an input event but the input event "+ "receiver has already been disposed.");} else {int index = mSeqMap.indexOfKey(event.getSequenceNumber());if (index < 0) {Log.w(TAG, "Attempted to finish an input event that is not in progress.");} else {int seq = mSeqMap.valueAt(index);mSeqMap.removeAt(index);// 调用到nativenativeFinishInputEvent(mReceiverPtr, seq, handled);}}event.recycleIfNeededAfterDispatch();}}
如下在InputDispatcher::finishDispatchCycleLocked,创建了一个Lambda 匿名函数,函数中封装了对应事件的Connection信息和seq序号,然后通过postCommandLocked将该Lambda匿名函数入队
void InputDispatcher::finishDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,const sp<Connection>& connection, uint32_t seq,bool handled, nsecs_t consumeTime) {if (DEBUG_DISPATCH_CYCLE) {ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ finishDispatchCycle - seq=%u, handled=%s",connection->getInputChannelName().c_str(), seq, toString(handled));}if (connection->status == Connection::Status::BROKEN ||connection->status == Connection::Status::ZOMBIE) {return;}// Notify other system components and prepare to start the next dispatch cycle.// 生成一个 Lambda 匿名函数auto command = [this, currentTime, connection, seq, handled, consumeTime]() REQUIRES(mLock) {// 用于取消 事件的anr定时doDispatchCycleFinishedCommand(currentTime, connection, seq, handled, consumeTime);};// post了一个消息,用于取消该次事件的anr定时等, 在 dispatchOnce处理postCommandLocked(std::move(command));
}void InputDispatcher::postCommandLocked(Command&& command) {mCommandQueue.push_back(command);
}// mCommandQueue是容纳Lambda 匿名函数的容器
using Command = std::function<void()>;std::deque<Command> mCommandQueue GUARDED_BY(mLock);
再次回到InputDispatcher事件分发的开端:InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce(),上文中在分析分发流程中,直接介绍了dispatchOnceInnerLocked,但通过代码可以看到在分发后随即调用了runCommandsLockedInterruptable()
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;{ // acquire lockstd::scoped_lock _l(mLock);mDispatcherIsAlive.notify_all();// Run a dispatch loop if there are no pending commands.// The dispatch loop might enqueue commands to run afterwards.if (!haveCommandsLocked()) {dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);}// Run all pending commands if there are any.// If any commands were run then force the next poll to wake up immediately.if (runCommandsLockedInterruptable()) {nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN;}// If we are still waiting for ack on some events,// we might have to wake up earlier to check if an app is anr'ing.// 2.处理anr相关 这一步骤关键, 算出 最近一次anr唤醒的超时时间,时间到了 就唤醒.const nsecs_t nextAnrCheck = processAnrsLocked();nextWakeupTime = std::min(nextWakeupTime, nextAnrCheck);// We are about to enter an infinitely long sleep, because we have no commands or// pending or queued eventsif (nextWakeupTime == LONG_LONG_MAX) {mDispatcherEnteredIdle.notify_all();}} // release lock// Wait for callback or timeout or wake. (make sure we round up, not down)nsecs_t currentTime = now();int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime);// 3.按照计算出的时间进行阻塞mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);
}
在runCommandsLockedInterruptable中 ,mCommandQueue是容纳Lambda 匿名函数的容器,可见会遍历mCommandQueue中的所有Lambda 匿名函数,随后执行弹出的Lambda 匿名函数,上文中finishDispatchCycleLocked中向mCommandQueue添加函数 doDispatchCycleFinishedCommand, 在这里将执行该函数
bool InputDispatcher::runCommandsLockedInterruptable() {if (mCommandQueue.empty()) {return false;}do {auto command = std::move(mCommandQueue.front());mCommandQueue.pop_front();// Commands are run with the lock held, but may release and re-acquire the lock from within.command();} while (!mCommandQueue.empty());return true;
}
doDispatchCycleFinishedCommand中的处理如下:
- 1.根据seq从对应的Connection的WaitQueue中取出一个已经分发,待结束的DispatchEntry
- 2.从对应的Connection的WaitQueue中中移除该dispatchEntry
- 3. 清除该次事件在mAnrTracker中的记录
- 4. trace上更新WaitQueue
至此事件的分发整个全流程告一段落,
void InputDispatcher::doDispatchCycleFinishedCommand(nsecs_t finishTime,const sp<Connection>& connection, uint32_t seq,bool handled, nsecs_t consumeTime) {// Dequeue the event and start the next cycle.// Because the lock might have been released, it is possible that the// contents of the wait queue to have been drained, so we need to double-check// a few things.// 1.根据seq从对应的Connection的WaitQueue中取出一个已经分发,待结束的事件dispatchEntryIt = connection->findWaitQueueEntry(seq);if (dispatchEntryIt != connection->waitQueue.end()) {dispatchEntry = *dispatchEntryIt;// 2. 从对应的Connection的WaitQueue中中移除该dispatchEntryconnection->waitQueue.erase(dispatchEntryIt);const sp<IBinder>& connectionToken = connection->inputChannel->getConnectionToken();// 3. 清除该次事件在mAnrTracker中的记录mAnrTracker.erase(dispatchEntry->timeoutTime, connectionToken);...// 4. trace上更新WaitQueuetraceWaitQueueLength(*connection);...}// 继续分发// Start the next dispatch cycle for this connection.startDispatchCycleLocked(now(), connection);/*+++++*-
}
需要再重点关注下AnrTracker,回到InputDispatcher的开端:dispatchOnce
1.如果CommandQueue队列内没有任务则去分发事件
2.在检查anr前,执行CommandQueue队列中的任务,应用侧在处理完事件后,会回到InputDispatcher并向队列中添加一条移除事件在WaitQueue和AnrTracker中的对应记录
3.处理anr相关, 找出AnrTracker所有记录中最早超时的一个记录,并和当前时间比较,大于当前时间则上报anr,小于则返回该超时时间
4.按照既定的时间休眠,时间到了后,唤醒继续执行dispatchOnce,会再次检查anr,检查事件的分发是否超时。
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {// 先把下次的唤醒事件是设置为无穷大nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;{ // acquire lockstd::scoped_lock _l(mLock);mDispatcherIsAlive.notify_all();// Run a dispatch loop if there are no pending commands.// The dispatch loop might enqueue commands to run afterwards.// 如果CommandQueue队列内没有任务则去分发事件if (!haveCommandsLocked()) {dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);}// Run all pending commands if there are any.// If any commands were run then force the next poll to wake up immediately.// 执行CommandQueue队列中的任务,应用侧在处理完事件后,会回到InputDispatcher并向队列中添加一条移除事件在WaitQueue和AnrTracker中的对应记录if (runCommandsLockedInterruptable()) {nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN;}// If we are still waiting for ack on some events,// we might have to wake up earlier to check if an app is anr'ing.// 处理anr相关, 找出AnrTracker所有记录中最早超时的一个记录,并和当前时间比较,大于当前时间则上报anr,小于则返回该超时时间const nsecs_t nextAnrCheck = processAnrsLocked();nextWakeupTime = std::min(nextWakeupTime, nextAnrCheck);// We are about to enter an infinitely long sleep, because we have no commands or// pending or queued eventsif (nextWakeupTime == LONG_LONG_MAX) {mDispatcherEnteredIdle.notify_all();}} // release lock// Wait for callback or timeout or wake. (make sure we round up, not down)nsecs_t currentTime = now();int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime);mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);
}
nsecs_t InputDispatcher::processAnrsLocked() {const nsecs_t currentTime = now();nsecs_t nextAnrCheck = LONG_LONG_MAX;// Check if we are waiting for a focused window to appear. Raise ANR if waited too long// 焦点anr相关if (mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime.has_value() && mAwaitedFocusedApplication != nullptr) {if (currentTime >= *mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime) {processNoFocusedWindowAnrLocked();mAwaitedFocusedApplication.reset();mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime = std::nullopt;return LONG_LONG_MIN;} else {// Keep waiting. We will drop the event when mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime comes.nextAnrCheck = *mNoFocusedWindowTimeoutTime;}}// Check if any connection ANRs are due// 事件超时的anr相关nextAnrCheck = std::min(nextAnrCheck, mAnrTracker.firstTimeout());// 如果当前时间比 最近的anr事小,这说明分发的事件的ANR时间都没到if (currentTime < nextAnrCheck) { // most likely scenarioreturn nextAnrCheck; // everything is normal. Let's check again at nextAnrCheck}// 到这里说/说明 有 处理超时的事件,找出对应的 connection// If we reached here, we have an unresponsive connection.sp<Connection> connection = getConnectionLocked(mAnrTracker.firstToken());if (connection == nullptr) {ALOGE("Could not find connection for entry %" PRId64, mAnrTracker.firstTimeout());return nextAnrCheck;}connection->responsive = false;// Stop waking up for this unresponsive connection// 先清除 ,避免重复报anrmAnrTracker.eraseToken(connection->inputChannel->getConnectionToken());// 上报anronAnrLocked(connection);return LONG_LONG_MIN;
}