【Diffusion Model】IDDPM代码详解
注:Diffusion Model 最重要的三篇文章DDPM,DDIM,IDDPM请大家务必按照顺序读懂搞透!!
注:在明白了上述这些模型的原理之后,我们就需要开始接下来的实践部分了, IDDPM的代码是三者的集大成之作,所以我们只需要搞懂这个代码就可以了,剩下的这些代码都是在这个代码的基础上进行修改的
这个代码是很有难度的,建议大家先看论文!!!,然后配合 !!!up注deep_thoughts的视频链接!!!! 进行理解。
IDDPM论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.09672
IDDPM代码:https://github.com/openai/improved-diffusion
在讲解代码之前我们先来看一下思维导图,方便大家对于整个框架和结构的了解。如果大家觉得太小看不清的话,可以看我的飞书上的版本:
https://acnk4tpmnqlg.feishu.cn/wiki/P9EcwF0UXiV9eIkTnblcexOxnQg?from=from_copylink
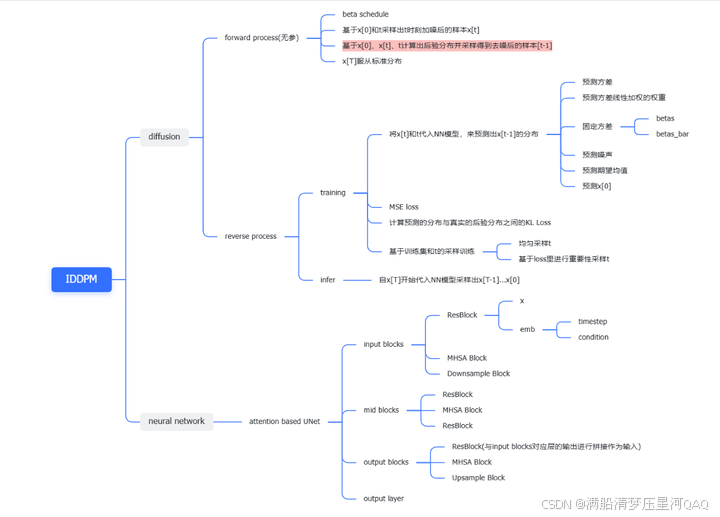
IDDPM对于diffusion的实现分为两部分,一部分是diffusion这个框架,另一部分是neural network。
diffusion包含两个过程forward processs和reverse process,forward process 是加噪过程不含学习参数,reverse process 是反向去噪过程,包含神经网络需要拟合的参数,在forward process中,需要设置一些超参数,然后由此将公式推导中需要的超参数全部计算出来,reverse process就是通过神经网络拟合出一些值,带入到公式中按逐步进行迭代,反向过程需要分为训练阶段和预测阶段,这两个阶段是有差异的。在DDPM论文中,作者为了简化处理只是用神经网络去预测噪声,在IDDPM论文中,作者进行了更加详细的实验,对神经网络可以拟合的内容进行了扩充(比如直接预测 x 0 x_0 x0 ,但是还是需要代回到公式中求均值,不然效果太差),同时在采样方面也进行了一些补充,在思维导图中都有详细的罗列出来。up主deep_thoughts讲解得很详细,我这里就不啰嗦了。下面来看代码。
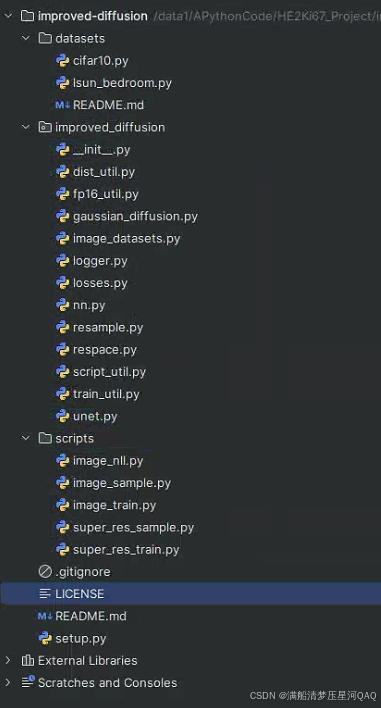
我下载代码的时间是2025.6.22,下面是代码的结构目录,该代码目录分为三部分:datasets,improved_diffusion,scripts。
- datasets:存放的是数据集相关的一些处理,
- improved_diffusion:是整个框架的实现核心
- scripts:中是一些训练和测试的脚本
接下来我们会根据代码的整体逻辑进行有详有略的讲解。
scripts/image_train.py
首先来看image_train.py文件 ,该文件中包主函数main和参数生成器函数create_argparser,create_argparser函数首先包含一个默认的训练参数字典,该字典中有常见的训练所需的参数比如:
- data_dir:数据集路径
- lr:学习率
- batch_size:大批量大小
- schedule_sampler:采样策略,默认uniform均匀采样
- weight_decay=0.0,
- lr_anneal_steps=0,
- microbatch=-1, # -1 disables microbatches
- ma_rate=“0.9999”, # comma-separated list of EMA values
- log_interval:日志打印间隔
- save_interval:保存间隔
- resume_checkpoint:断点续训
- use_fp16:是否使用fp16精度
- fp16_scale_growth
然后通过 defaults.update(model_and_diffusion_defaults())这行代码,将model和diffusion的字典也加载进来,组成一个大的字典,随后生成一个总的参数解析器parser
def create_argparser():defaults = dict(data_dir="",schedule_sampler="uniform",lr=1e-4,weight_decay=0.0,lr_anneal_steps=0,batch_size=1,microbatch=-1, # -1 disables microbatchesema_rate="0.9999", # comma-separated list of EMA valueslog_interval=10,save_interval=10000,resume_checkpoint="",use_fp16=False,fp16_scale_growth=1e-3,)defaults.update(model_and_diffusion_defaults()) #将模型和diffusion的框架的参数也加载进来parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() #参数解析器add_dict_to_argparser(parser, defaults) #将字典转化为参数解析器的参数return parser
接下来我们来看main函数,首先生成参数解析器parser,并通过parse_args()得到所有的参数,然后是分布式训练以及日志打印,接下来这行很关键
model, diffusion = create_model_and_diffusion(** args_to_dict(args, model_and_diffusion_defaults().keys()))
从所有的参数中提取只和model以及difffusion相关的参数,也是就是其他一些杂七杂八的参数忽略掉,然后用这些参数创建neural network以及guassian diffusion.
schedule_sampler = create_named_schedule_sampler(args.schedule_sampler, diffusion) 这行代码决定了时间t采样器,也就是时间t以怎样的分布出现。
def main():args = create_argparser().parse_args()dist_util.setup_dist() logger.configure()logger.log("creating model and diffusion...")model, diffusion = create_model_and_diffusion(**args_to_dict(args, model_and_diffusion_defaults().keys()))model.to(dist_util.dev()) #将模型放到相应的设备上schedule_sampler = create_named_schedule_sampler(args.schedule_sampler, diffusion) #创建时间t采样器,logger.log("creating data loader...") data = load_data(data_dir=args.data_dir,batch_size=args.batch_size,image_size=args.image_size,class_cond=args.class_cond,) #数据加载logger.log("training...") TrainLoop( #实例化类,并开始训练model=model,diffusion=diffusion,data=data,batch_size=args.batch_size,microbatch=args.microbatch,lr=args.lr,ema_rate=args.ema_rate,log_interval=args.log_interval,save_interval=args.save_interval,resume_checkpoint=args.resume_checkpoint,use_fp16=args.use_fp16,fp16_scale_growth=args.fp16_scale_growth,schedule_sampler=schedule_sampler,weight_decay=args.weight_decay,lr_anneal_steps=args.lr_anneal_steps,).run_loop()
improved_diffusion/script_utils.py
接下来我们来看一下create_model_and_diffusion,首先是传入一些参数,然后调用了两个子函数create_model和create_gaussian_diffusion
def create_model_and_diffusion(image_size,#图片大小class_cond, #是否是有条件的learn_sigma, #是否预测方差还是使用固定的方差sigma_small, num_channels,num_res_blocks,num_heads,num_heads_upsample,attention_resolutions, #在哪些位置使用attentiondropout,diffusion_steps,noise_schedule,timestep_respacing,use_kl,predict_xstart,rescale_timesteps,rescale_learned_sigmas,use_checkpoint,use_scale_shift_norm,
):model = create_model(image_size,num_channels,num_res_blocks,learn_sigma=learn_sigma,class_cond=class_cond,use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint,attention_resolutions=attention_resolutions,num_heads=num_heads,num_heads_upsample=num_heads_upsample,use_scale_shift_norm=use_scale_shift_norm,dropout=dropout,)diffusion = create_gaussian_diffusion(steps=diffusion_steps,learn_sigma=learn_sigma,sigma_small=sigma_small,noise_schedule=noise_schedule,use_kl=use_kl,predict_xstart=predict_xstart,rescale_timesteps=rescale_timesteps,rescale_learned_sigmas=rescale_learned_sigmas,timestep_respacing=timestep_respacing,)return model, diffusion
接下来我们先讲create_gaussian_diffusion,这个函数的主要目的是生成一个扩散模型的框架
def create_gaussian_diffusion(*,steps=1000,learn_sigma=False,sigma_small=False,noise_schedule="linear",use_kl=False,predict_xstart=False,rescale_timesteps=False,rescale_learned_sigmas=False,timestep_respacing="",
):betas = gd.get_named_beta_schedule(noise_schedule, steps)if use_kl:loss_type = gd.LossType.RESCALED_KLelif rescale_learned_sigmas:loss_type = gd.LossType.RESCALED_MSEelse:loss_type = gd.LossType.MSEif not timestep_respacing:timestep_respacing = [steps]return SpacedDiffusion(use_timesteps=space_timesteps(steps, timestep_respacing),betas=betas,model_mean_type=(gd.ModelMeanType.EPSILON if not predict_xstart else gd.ModelMeanType.START_X),model_var_type=((gd.ModelVarType.FIXED_LARGEif not sigma_smallelse gd.ModelVarType.FIXED_SMALL)if not learn_sigmaelse gd.ModelVarType.LEARNED_RANGE),loss_type=loss_type,rescale_timesteps=rescale_timesteps,)betas = gd.get_named_beta_schedule(noise_schedule, steps)这行代码用来生成一个前向加噪的方案,
在原始的DDPM中使用的是线性Linear加噪方案,而IDDPM中增加了余弦cosine的加噪方案。
def get_named_beta_schedule(schedule_name, num_diffusion_timesteps):"""Get a pre-defined beta schedule for the given name.The beta schedule library consists of beta schedules which remain similarin the limit of num_diffusion_timesteps.Beta schedules may be added, but should not be removed or changed oncethey are committed to maintain backwards compatibility."""if schedule_name == "linear":# Linear schedule from Ho et al, extended to work for any number of# diffusion steps.scale = 1000 / num_diffusion_timestepsbeta_start = scale * 0.0001beta_end = scale * 0.02return np.linspace(beta_start, beta_end, num_diffusion_timesteps, dtype=np.float64)elif schedule_name == "cosine": #余弦加噪方案return betas_for_alpha_bar(num_diffusion_timesteps,lambda t: math.cos((t + 0.008) / 1.008 * math.pi / 2) ** 2,)else:raise NotImplementedError(f"unknown beta schedule: {schedule_name}")
create_gaussian_diffusion最终返回的是一个SpaceDiffusion匿名对象,下面我们来看一下SpaceDiffusion类
improved_diffusion/respace.py
class SpacedDiffusion(GaussianDiffusion):"""A diffusion process which can skip steps in a base diffusion process.:param use_timesteps: a collection (sequence or set) of timesteps from theoriginal diffusion process to retain.:param kwargs: the kwargs to create the base diffusion process."""def __init__(self, use_timesteps, **kwargs):self.use_timesteps = set(use_timesteps)self.timestep_map = []self.original_num_steps = len(kwargs["betas"])base_diffusion = GaussianDiffusion(**kwargs) # pylint: disable=missing-kwoalast_alpha_cumprod = 1.0new_betas = []for i, alpha_cumprod in enumerate(base_diffusion.alphas_cumprod):if i in self.use_timesteps:new_betas.append(1 - alpha_cumprod / last_alpha_cumprod)last_alpha_cumprod = alpha_cumprodself.timestep_map.append(i)kwargs["betas"] = np.array(new_betas)super().__init__(**kwargs)def p_mean_variance(self, model, *args, **kwargs): # pylint: disable=signature-differsreturn super().p_mean_variance(self._wrap_model(model), *args, **kwargs)def training_losses(self, model, *args, **kwargs): # pylint: disable=signature-differsreturn super().training_losses(self._wrap_model(model), *args, **kwargs)def _wrap_model(self, model):if isinstance(model, _WrappedModel):return modelreturn _WrappedModel(model, self.timestep_map, self.rescale_timesteps, self.original_num_steps)def _scale_timesteps(self, t):# Scaling is done by the wrapped model.return t
SpaceDiffusion继承自GaussianDiffusion,该类主要是为了对timesteps进行一系列的优化,该类实现了多个函数,p_mean_variance函数用来计算神经网络预测出来的均值和方差,该方法调用的是父类的方法,training_losses根据传入的超参数的不同得到不同的损失函数。
improved_diffusion/gaussian_diffusion.py
首先我们来看一下init函数,代码比较长,我会直接将注释卸载代码后面
def __init__(self,*,betas,model_mean_type,model_var_type,loss_type,rescale_timesteps=False,):self.model_mean_type = model_mean_type #确定预测的mean类型,具体看思维导图 self.model_var_type = model_var_type #确定预测的方差类型,具体看思维导图self.loss_type = loss_type #确定损失函数的计算方式self.rescale_timesteps = rescale_timesteps #确定时间步# Use float64 for accuracy.betas = np.array(betas, dtype=np.float64)self.betas = betasassert len(betas.shape) == 1, "betas must be 1-D"assert (betas > 0).all() and (betas <= 1).all()self.num_timesteps = int(betas.shape[0])alphas = 1.0 - betasself.alphas_cumprod = np.cumprod(alphas, axis=0) self.alphas_cumprod_prev = np.append(1.0, self.alphas_cumprod[:-1])self.alphas_cumprod_next = np.append(self.alphas_cumprod[1:], 0.0)assert self.alphas_cumprod_prev.shape == (self.num_timesteps,)# calculations for diffusion q(x_t | x_{t-1}) and othersself.sqrt_alphas_cumprod = np.sqrt(self.alphas_cumprod)self.sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod = np.sqrt(1.0 - self.alphas_cumprod)self.log_one_minus_alphas_cumprod = np.log(1.0 - self.alphas_cumprod)self.sqrt_recip_alphas_cumprod = np.sqrt(1.0 / self.alphas_cumprod)self.sqrt_recipm1_alphas_cumprod = np.sqrt(1.0 / self.alphas_cumprod - 1)# calculations for posterior q(x_{t-1} | x_t, x_0)self.posterior_variance = ( #后验分布方差betas * (1.0 - self.alphas_cumprod_prev) / (1.0 - self.alphas_cumprod))# log calculation clipped because the posterior variance is 0 at the# beginning of the diffusion chain.self.posterior_log_variance_clipped = np.log(np.append(self.posterior_variance[1], self.posterior_variance[1:]))self.posterior_mean_coef1 = ( #后验均值的第一个系数betas * np.sqrt(self.alphas_cumprod_prev) / (1.0 - self.alphas_cumprod))self.posterior_mean_coef2 = ( #后验均值的第二个系数(1.0 - self.alphas_cumprod_prev)* np.sqrt(alphas)/ (1.0 - self.alphas_cumprod))下面介绍一下这个类中的其他一些函数
def q_mean_variance(self, x_start, t):"""Get the distribution q(x_t | x_0).:param x_start: the [N x C x ...] tensor of noiseless inputs.:param t: the number of diffusion steps (minus 1). Here, 0 means one step.:return: A tuple (mean, variance, log_variance), all of x_start's shape.`在这里插入代码片`"""mean = (_extract_into_tensor(self.sqrt_alphas_cumprod, t, x_start.shape) * x_start)variance = _extract_into_tensor(1.0 - self.alphas_cumprod, t, x_start.shape)log_variance = _extract_into_tensor(self.log_one_minus_alphas_cumprod, t, x_start.shape)return mean, variance, log_variance
q_mean_variance 计算先验分布的均值和方差,得到在给定 x 0 x_0 x0的情况下,q(x_t|x_0)的分布。对应IDDPM文章中的公式8.
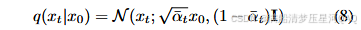
这里的self.sqrt_alphas_cumprod是所有时间步的,_extract_into_tensor函数的作用是将第t个时间步的给取出来,并且形状与输入形状相同
def q_sample(self, x_start, t, noise=None):"""Diffuse the data for a given number of diffusion steps.In other words, sample from q(x_t | x_0).:param x_start: the initial data batch.:param t: the number of diffusion steps (minus 1). Here, 0 means one step.:param noise: if specified, the split-out normal noise.:return: A noisy version of x_start."""if noise is None:noise = th.randn_like(x_start)assert noise.shape == x_start.shapereturn (_extract_into_tensor(self.sqrt_alphas_cumprod, t, x_start.shape) * x_start+ _extract_into_tensor(self.sqrt_one_minus_alphas_cumprod, t, x_start.shape)* noise)
q_sample函数的作用是重参数化,得到 x t x_t xt,对应文章中的公式9。
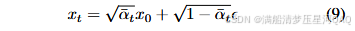
def q_posterior_mean_variance(self, x_start, x_t, t):"""Compute the mean and variance of the diffusion posterior:q(x_{t-1} | x_t, x_0)"""assert x_start.shape == x_t.shapeposterior_mean = (_extract_into_tensor(self.posterior_mean_coef1, t, x_t.shape) * x_start+ _extract_into_tensor(self.posterior_mean_coef2, t, x_t.shape) * x_t)posterior_variance = _extract_into_tensor(self.posterior_variance, t, x_t.shape)posterior_log_variance_clipped = _extract_into_tensor(self.posterior_log_variance_clipped, t, x_t.shape)assert (posterior_mean.shape[0]== posterior_variance.shape[0]== posterior_log_variance_clipped.shape[0]== x_start.shape[0])return posterior_mean, posterior_variance, posterior_log_variance_clipped
逆扩散过程中后验分布的真实均值和方差
def p_mean_variance(self, model, x, t, clip_denoised=True, denoised_fn=None, model_kwargs=None):"""Apply the model to get p(x_{t-1} | x_t), as well as a prediction ofthe initial x, x_0.:param model: the model, which takes a signal and a batch of timestepsas input.:param x: the [N x C x ...] tensor at time t.:param t: a 1-D Tensor of timesteps.:param clip_denoised: if True, clip the denoised signal into [-1, 1].:param denoised_fn: if not None, a function which applies to thex_start prediction before it is used to sample. Applies beforeclip_denoised.:param model_kwargs: if not None, a dict of extra keyword arguments topass to the model. This can be used for conditioning.:return: a dict with the following keys:- 'mean': the model mean output.- 'variance': the model variance output.- 'log_variance': the log of 'variance'.- 'pred_xstart': the prediction for x_0."""if model_kwargs is None:model_kwargs = {}B, C = x.shape[:2]assert t.shape == (B,)model_output = model(x, self._scale_timesteps(t), **model_kwargs)#得到方差和对数方差if self.model_var_type in [ModelVarType.LEARNED, ModelVarType.LEARNED_RANGE]:#可学习的方差assert model_output.shape == (B, C * 2, *x.shape[2:])model_output, model_var_values = th.split(model_output, C, dim=1)if self.model_var_type == ModelVarType.LEARNED:#直接预测方差model_log_variance = model_var_valuesmodel_variance = th.exp(model_log_variance)else:#预测方差插值的系数#预测的范围是[-1,1]min_log = _extract_into_tensor(self.posterior_log_variance_clipped, t, x.shape)max_log = _extract_into_tensor(np.log(self.betas), t, x.shape)# The model_var_values is [-1, 1] for [min_var, max_var].frac = (model_var_values + 1) / 2model_log_variance = frac * max_log + (1 - frac) * min_logmodel_variance = th.exp(model_log_variance)else:#固定的方差model_variance, model_log_variance = {# for fixedlarge, we set the initial (log-)variance like so# to get a better decoder log likelihood.ModelVarType.FIXED_LARGE: (np.append(self.posterior_variance[1], self.betas[1:]),np.log(np.append(self.posterior_variance[1], self.betas[1:])),),ModelVarType.FIXED_SMALL: (self.posterior_variance,self.posterior_log_variance_clipped,),}[self.model_var_type]model_variance = _extract_into_tensor(model_variance, t, x.shape)model_log_variance = _extract_into_tensor(model_log_variance, t, x.shape)def process_xstart(x):if denoised_fn is not None:x = denoised_fn(x)if clip_denoised:return x.clamp(-1, 1)return x#case1:预测x[t-1]的期望值if self.model_mean_type == ModelMeanType.PREVIOUS_X:pred_xstart = process_xstart(self._predict_xstart_from_xprev(x_t=x, t=t, xprev=model_output))model_mean = model_outputelif self.model_mean_type in [ModelMeanType.START_X, ModelMeanType.EPSILON]:if self.model_mean_type == ModelMeanType.START_X:#case2:预测x[0]的期望值pred_xstart = process_xstart(model_output)else:#case3:预测eps的期望值pred_xstart = process_xstart(self._predict_xstart_from_eps(x_t=x, t=t, eps=model_output))model_mean, _, _ = self.q_posterior_mean_variance(x_start=pred_xstart, x_t=x, t=t)else:raise NotImplementedError(self.model_mean_type)assert (model_mean.shape == model_log_variance.shape == pred_xstart.shape == x.shape)return {"mean": model_mean,"variance": model_variance,"log_variance": model_log_variance,"pred_xstart": pred_xstart,}
神经网络拟合的均值和方差
def _predict_xstart_from_eps(self, x_t, t, eps):assert x_t.shape == eps.shapereturn (_extract_into_tensor(self.sqrt_recip_alphas_cumprod, t, x_t.shape) * x_t- _extract_into_tensor(self.sqrt_recipm1_alphas_cumprod, t, x_t.shape) * eps)
从噪声 ϵ \epsilon ϵ预测 x 0 x_0 x0,公式8变形。
def p_sample(self, model, x, t, clip_denoised=True, denoised_fn=None, model_kwargs=None):"""Sample x_{t-1} from the model at the given timestep.:param model: the model to sample from.:param x: the current tensor at x_{t-1}.:param t: the value of t, starting at 0 for the first diffusion step.:param clip_denoised: if True, clip the x_start prediction to [-1, 1].:param denoised_fn: if not None, a function which applies to thex_start prediction before it is used to sample.:param model_kwargs: if not None, a dict of extra keyword arguments topass to the model. This can be used for conditioning.:return: a dict containing the following keys:- 'sample': a random sample from the model.- 'pred_xstart': a prediction of x_0."""out = self.p_mean_variance(model,x,t,clip_denoised=clip_denoised,denoised_fn=denoised_fn,model_kwargs=model_kwargs,)noise = th.randn_like(x)nonzero_mask = ((t != 0).float().view(-1, *([1] * (len(x.shape) - 1)))) # no noise when t == 0sample = out["mean"] + nonzero_mask * th.exp(0.5 * out["log_variance"]) * noisereturn {"sample": sample, "pred_xstart": out["pred_xstart"]}
推理时从 x t x_t xt采样出 x t − 1 x_{t-1} xt−1
def p_sample_loop(self,model,shape,noise=None,clip_denoised=True,denoised_fn=None,model_kwargs=None,device=None,progress=False,):"""Generate samples from the model.:param model: the model module.:param shape: the shape of the samples, (N, C, H, W).:param noise: if specified, the noise from the encoder to sample.Should be of the same shape as `shape`.:param clip_denoised: if True, clip x_start predictions to [-1, 1].:param denoised_fn: if not None, a function which applies to thex_start prediction before it is used to sample.:param model_kwargs: if not None, a dict of extra keyword arguments topass to the model. This can be used for conditioning.:param device: if specified, the device to create the samples on.If not specified, use a model parameter's device.:param progress: if True, show a tqdm progress bar.:return: a non-differentiable batch of samples."""final = Nonefor sample in self.p_sample_loop_progressive(model,shape,noise=noise,clip_denoised=clip_denoised,denoised_fn=denoised_fn,model_kwargs=model_kwargs,device=device,progress=progress,):final = samplereturn final["sample"]
循环多次采样
def _vb_terms_bpd(self, model, x_start, x_t, t, clip_denoised=True, model_kwargs=None):"""Get a term for the variational lower-bound.The resulting units are bits (rather than nats, as one might expect).This allows for comparison to other papers.:return: a dict with the following keys:- 'output': a shape [N] tensor of NLLs or KLs.- 'pred_xstart': the x_0 predictions."""# 真实的x[0],x[t]和t去计算出x[t-1]的均值与方差true_mean, _, true_log_variance_clipped = self.q_posterior_mean_variance(x_start=x_start, x_t=x_t, t=t)#x[t],t和预测的x[0]去计算出x[t-1]的均值和方差out = self.p_mean_variance(model, x_t, t, clip_denoised=clip_denoised, model_kwargs=model_kwargs)#p_theta与q分布之间的KL散度# 对应着L(t-1)损失函数kl = normal_kl(true_mean, true_log_variance_clipped, out["mean"], out["log_variance"])kl = mean_flat(kl) / np.log(2.0)#对应着L[0]损失函数decoder_nll = -discretized_gaussian_log_likelihood(x_start, means=out["mean"], log_scales=0.5 * out["log_variance"])assert decoder_nll.shape == x_start.shapedecoder_nll = mean_flat(decoder_nll) / np.log(2.0)# At the first timestep return the decoder NLL,# otherwise return KL(q(x_{t-1}|x_t,x_0) || p(x_{t-1}|x_t))output = th.where((t == 0), decoder_nll, kl)return {"output": output, "pred_xstart": out["pred_xstart"]}
_vb_terms_bpd损失计算,对应公式4-7
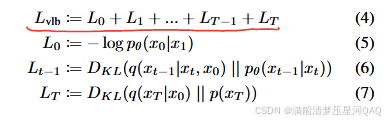
接下来是DDIM这篇文章中介绍的DDIM采样
improved_diffusion/gaussian_diffusion.py
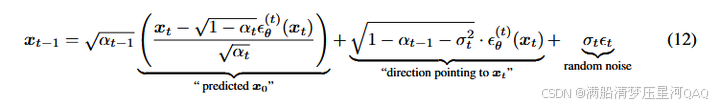
根据公式12编写采样代码
def ddim_sample(self,model,x,t,clip_denoised=True,denoised_fn=None,model_kwargs=None,eta=0.0,):"""Sample x_{t-1} from the model using DDIM.Same usage as p_sample()."""out = self.p_mean_variance(model,x,t,clip_denoised=clip_denoised,denoised_fn=denoised_fn,model_kwargs=model_kwargs,)# Usually our model outputs epsilon, but we re-derive it# in case we used x_start or x_prev prediction.eps = self._predict_eps_from_xstart(x, t, out["pred_xstart"])alpha_bar = _extract_into_tensor(self.alphas_cumprod, t, x.shape)alpha_bar_prev = _extract_into_tensor(self.alphas_cumprod_prev, t, x.shape)sigma = (eta* th.sqrt((1 - alpha_bar_prev) / (1 - alpha_bar))* th.sqrt(1 - alpha_bar / alpha_bar_prev))# Equation 12.noise = th.randn_like(x)mean_pred = (out["pred_xstart"] * th.sqrt(alpha_bar_prev)+ th.sqrt(1 - alpha_bar_prev - sigma ** 2) * eps)nonzero_mask = ((t != 0).float().view(-1, *([1] * (len(x.shape) - 1)))) # no noise when t == 0sample = mean_pred + nonzero_mask * sigma * noisereturn {"sample": sample, "pred_xstart": out["pred_xstart"]}
先算出 ϵ 然后根据公式16进行计算
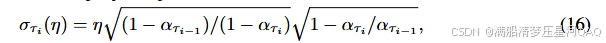
注python 需要注意的是DDIM算法本身和DDPM一样,是没有加速的,DDIM和DDPM只是分布不同,加速采样是用到了respace的技术在respace.py文件中实现 !!!
improved_diffusion/respace.py
space_timesteps有两个参数,第一个参数num_timesteps是采样步数,section_counts是分几部分采样。
def space_timesteps(num_timesteps, section_counts):"""Create a list of timesteps to use from an original diffusion process,given the number of timesteps we want to take from equally-sized portionsof the original process.For example, if there's 300 timesteps and the section counts are [10,15,20]then the first 100 timesteps are strided to be 10 timesteps, the second 100are strided to be 15 timesteps, and the final 100 are strided to be 20.If the stride is a string starting with "ddim", then the fixed stridingfrom the DDIM paper is used, and only one section is allowed.:param num_timesteps: the number of diffusion steps in the originalprocess to divide up.:param section_counts: either a list of numbers, or a string containingcomma-separated numbers, indicating the step countper section. As a special case, use "ddimN" where Nis a number of steps to use the striding from theDDIM paper.:return: a set of diffusion steps from the original process to use."""if isinstance(section_counts, str):if section_counts.startswith("ddim"):desired_count = int(section_counts[len("ddim") :])for i in range(1, num_timesteps):if len(range(0, num_timesteps, i)) == desired_count:return set(range(0, num_timesteps, i))raise ValueError(f"cannot create exactly {num_timesteps} steps with an integer stride")section_counts = [int(x) for x in section_counts.split(",")]size_per = num_timesteps // len(section_counts)extra = num_timesteps % len(section_counts)start_idx = 0all_steps = []for i, section_count in enumerate(section_counts):size = size_per + (1 if i < extra else 0)if size < section_count:raise ValueError(f"cannot divide section of {size} steps into {section_count}")if section_count <= 1:frac_stride = 1else:frac_stride = (size - 1) / (section_count - 1)cur_idx = 0.0taken_steps = []for _ in range(section_count):taken_steps.append(start_idx + round(cur_idx))cur_idx += frac_strideall_steps += taken_stepsstart_idx += sizereturn set(all_steps)
SpaceDiffusion继承了GaussianDiffusion
class SpacedDiffusion(GaussianDiffusion):"""A diffusion process which can skip steps in a base diffusion process.:param use_timesteps: a collection (sequence or set) of timesteps from theoriginal diffusion process to retain.:param kwargs: the kwargs to create the base diffusion process."""def __init__(self, use_timesteps, **kwargs):self.use_timesteps = set(use_timesteps) #可用时间步序列,步长可以为1,也可以大于1self.timestep_map = []self.original_num_steps = len(kwargs["betas"])base_diffusion = GaussianDiffusion(**kwargs) # pylint: disable=missing-kwoalast_alpha_cumprod = 1.0#重新定义betas序列new_betas = []for i, alpha_cumprod in enumerate(base_diffusion.alphas_cumprod):if i in self.use_timesteps:new_betas.append(1 - alpha_cumprod / last_alpha_cumprod)last_alpha_cumprod = alpha_cumprodself.timestep_map.append(i)kwargs["betas"] = np.array(new_betas) #super().__init__(**kwargs)def p_mean_variance(self, model, *args, **kwargs): # pylint: disable=signature-differsreturn super().p_mean_variance(self._wrap_model(model), *args, **kwargs)def training_losses(self, model, *args, **kwargs): # pylint: disable=signature-differsreturn super().training_losses(self._wrap_model(model), *args, **kwargs)def _wrap_model(self, model):if isinstance(model, _WrappedModel):return modelreturn _WrappedModel(model, self.timestep_map, self.rescale_timesteps, self.original_num_steps)def _scale_timesteps(self, t):# Scaling is done by the wrapped model.return t
