网站开发工程师岗位职责要求厦门制作网站企业
Elasticsearch 作为一种高效的全文搜索引擎,广泛应用于实时搜索、日志分析等场景。而 openGauss,作为一款企业级关系型数据库,强调事务处理与数据一致性。那么,当这两者的应用场景和技术架构发生交集时,如何实现它们之间的平滑迁移呢?
本文将探讨 Elasticsearch 基础数据数据迁移至 openGauss 的解决方案,在此,我们首先根据等价实例来看一下 Elasticsearch 和关系型数据库(如 openGauss)的基础数据结构:
关系型数据库操作:
CREATE TABLE products (id INT PRIMARY KEY,name VARCHAR(100),price DECIMAL(10,2));INSERT INTO products VALUES (1, 'Laptop', 999.99);
Elasticsearch等价操作:
PUT /products{"mappings": {"properties": {"id": { "type": "integer" },"name": { "type": "text" },"price": { "type": "double" }}}}POST /products/_doc/1{"id": 1,"name": "Laptop","price": 999.99}
数据组织层级:
-
关系型数据库:
Database → Table → Row/Column
-
Elasticsearch:
6.x之前:Index → Type → Document (类似Database → Table → Row)
7.x之后:Index → Document (Type被移除,强化了Index≈Table的对应关系)
| Elasticsearch 概念 | 关系型数据库(如openGauss)概念 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 索引(Index) | 库-表(Table) | 对应关系 |
| 类型(Type) | (已弃用,7.x后无对应) | 早期版本中类似表分区 |
| 文档(Document) | 行(Row) | 一条记录 |
| 字段(Field) | 列(Column) | 数据属性 |
| 映射(Mapping) | 表结构定义(Schema) | 定义字段类型等 |
| 索引别名(Alias) | 视图(View) | 虚拟索引/表 |
| 分片(Shard) | 分区(Partition) | 数据水平拆分 |
检索方式
1、向量检索
Elasticsearch 向量检索
# 1. 创建包含向量字段的索引PUT /image_vectors{"mappings": {"properties": {"image_name": {"type": "text"},"image_vector": {"type": "dense_vector","dims": 512}}}}# 2. 插入向量数据POST /image_vectors/_doc{"image_name": "sunset.jpg","image_vector": [0.12, 0.34, ..., 0.56] // 512维向量}# 3. 精确向量检索 (script_score)GET /image_vectors/_search{"query": {"script_score": {"query": {"match_all": {}},"script": {"source": "cosineSimilarity(params.query_vector, 'image_vector') + 1.0","params": {"query_vector": [0.23, 0.45, ..., 0.67] // 查询向量}}}}}# 4. 近似最近邻搜索 (kNN search)GET /image_vectors/_search{"knn": {"field": "image_vector","query_vector": [0.23, 0.45, ..., 0.67],"k": 10,"num_candidates": 100}}
openGauss 向量检索(openGauss 从 7.0 版本开始支持向量检索功能)
# 1. 创建包含向量字段的表-- 创建表CREATE TABLE image_vectors (id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,image_name TEXT,image_vector VECTOR(512) -- 512维向量);#2. 插入向量数据INSERT INTO image_vectors (image_name, image_vector)VALUES ('sunset.jpg', '[0.12, 0.34, ..., 0.56]');# 3. 精确向量检索 (余弦相似度)-- 使用余弦相似度SELECT id, image_name,1 - (image_vector <=> '[0.23, 0.45, ..., 0.67]') AS cosine_similarityFROM image_vectorsORDER BY cosine_similarity DESCLIMIT 10;# 4. 近似最近邻搜索 (使用IVFFLAT索引)-- 创建IVFFLAT索引CREATE INDEX idx_image_vector ON image_vectorsUSING IVFFLAT(image_vector) WITH (lists = 100);-- 近似最近邻查询SELECT id, image_name,image_vector <=> '[0.23, 0.45, ..., 0.67]' AS distanceFROM image_vectorsORDER BY distanceLIMIT 10;
2、全文检索
es全文检索 相当于 openGauss的LIKE和正则表达式
# es 全文检索GET /products/_search{"query": {"match": {"description": "search term"}}}# openGauss 模糊查询SELECT * FROM productsWHERE description LIKE '%search term%';# openGauss 正则表达式匹配SELECT * FROM logsWHERE message ~ 'error|warning';
因此,根据数据层级及检索方式分析,迁移时将es的索引迁移到openGauss的一张表里。
环境准备
-
已部署7.3 及以上(支持向量)版本的ElasticSearch实例
-
已部署7.0.0-RC1 及以上版本(支持向量)的openGauss实例
-
已安装3.8 及以上版本的Python环境
-
已安装涉及的Python库
pip3 install psycopg2pip3 install requestspip3 install pyOpenSSL#如果安装失败,可以考虑在一个新的虚拟环境中重新安装所需的库,执行以下命令:python3 -m venv venvsource venv/bin/activatepip install requests pyOpenSSL
前置条件
远程连接权限:
openGauss端:
#修改openGauss配置文件。将迁移脚本所在机器IP地址加入白名单,修改openGauss监听地址。# 执行以下命令gs_guc set -D {DATADIR} -c " listen_addresses = '\*'"gs_guc set -D {DATADIR} -h "host all all x.x.x.x/32 sha256"# 修改完毕后重启openGauss。gs_ctl restart -D {DATADIR}
elasticsearch端:
vim /path/to/your_elasticsearch/config/elasticsearch.yml#修改network.hostnetwork.host: 0.0.0.0
openGauss端创建普通用户(赋权)、迁移的目标数据库:
create user mig_test identified by 'Simple@123';grant all privileges to mig_test;create database es_to_og with owner mig_test;
迁移操作
1、根据本地部署的elasticsearch与openGauss对脚本进行配置修改,需要修改的内容如下:
# Elasticsearch 配置信息es_url = 'http://ip:port' # Elasticsearch 服务器地址es_index = 'your_es_index' # Elasticsearch 索引名# openGauss 配置信息db_host = '127.0.0.1' # openGauss服务器地址db_port = 5432 # openGauss 端口号db_name = 'your_opengauss_db' # 迁移到openGauss的数据库名称db_user = 'user_name' # 连接openGauss的普通用户db_password = 'xxxxxx' # 连接openGauss的用户密码
elasticsearchToOpenGauss.py迁移脚本如下:
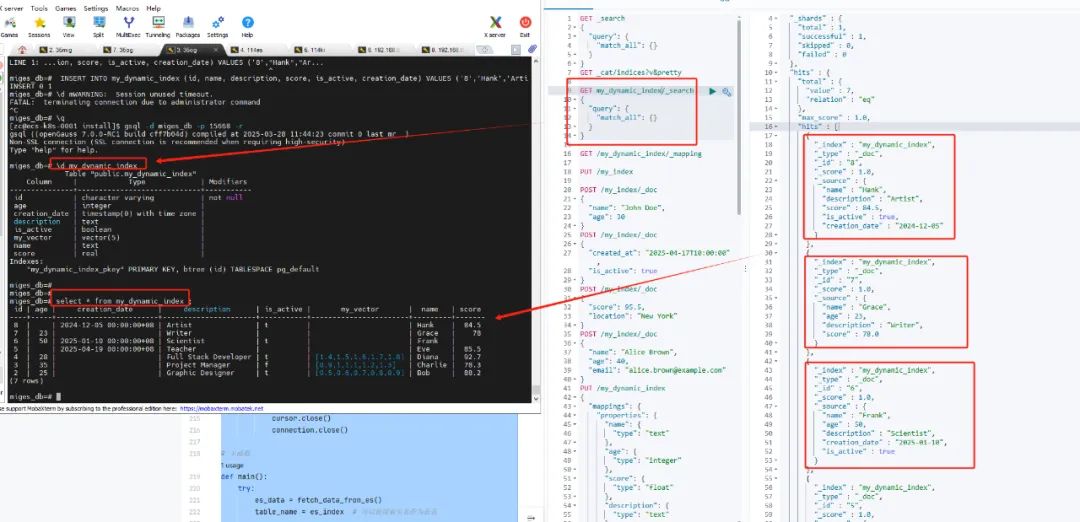
import requestsimport psycopg2import jsonimport refrom typing import List, Dict, Any, Optional, Union# Elasticsearch 配置信息es_url = 'http://192.168.0.114:9200' # Elasticsearch 服务器地址es_index = 'my_dynamic_index' # Elasticsearch 索引名# openGauss 配置信息db_host = '192.168.0.219' # openGauss服务器地址db_port = 15620 # openGauss 端口号db_name = 'es_to_og' # 迁移到openGauss的数据库名称db_user = 'mig_test' # 连接openGauss的普通用户db_password = 'xxxxxx' # 连接openGauss的用户密码RESERVED_KEYWORDS = {"select", "insert", "update", "delete", "drop", "table", "from", "where", "group","by", "having", "order", "limit", "join", "inner", "left", "right", "full", "union","all", "distinct", "as", "on", "and", "or", "not", "null", "true", "false", "case","when", "then", "else", "end", "exists", "like", "in", "between", "is", "like","references", "foreign", "primary", "key", "unique", "check", "default", "constraint","index", "unique", "varchar", "text", "int", "bigint", "smallint", "boolean", "timestamp"}# 从 Elasticsearch 获取数据def fetch_data_from_es():query = {"query": {"match_all": {}},"_source": True # 获取所有字段}response = requests.get(f'{es_url}/{es_index}/_search', json=query)if response.status_code == 200:return response.json()['hits']['hits']else:raise Exception(f"Failed to fetch data from Elasticsearch: {response.status_code}, {response.text}")# 获取索引映射信息def fetch_mapping(es_url, es_index):response = requests.get(f'{es_url}/{es_index}/_mapping')if response.status_code == 200:return response.json()else:raise Exception(f"Failed to fetch mapping: {response.status_code}, {response.text}")def get_field_type(es_url: str, es_index: str, field_name: str) -> str:""" 获取 Elasticsearch 字段的类型 """mappings = fetch_mapping(es_url, es_index)print(f"Field name: {field_name}")print(f"map: {mappings}")# 获取 properties 字段properties = mappings.get(es_index, {}).get('mappings', {}).get('properties', {})# 遍历并查找字段的类型field_type = 'text' # 默认类型为 'text'if field_name in properties:field_type = properties[field_name].get('type', 'text')elif 'fields' in properties.get(field_name, {}):# 如果字段有子字段(比如 keyword),获取 'keyword' 类型field_type = properties[field_name]['fields'].get('keyword', {}).get('type', 'text')return field_typedef convert_dict_to_jsonb(value):# 如果 value 是字典类型,递归调用该函数处理其中的每个元素if isinstance(value, dict):return json.dumps({k: convert_dict_to_jsonb(v) for k, v in value.items()})# 如果 value 是列表类型,递归处理其中的每个元素elif isinstance(value, list):return json.dumps([convert_dict_to_jsonb(v) for v in value])# 如果是其他类型(如字符串、数字),直接返回该值else:return value# 映射 Elasticsearch 数据类型到 openGauss 类型def map_to_opengauss_type(es_type: str, dim: Optional[int] = None) -> str:"""Map Elasticsearch types to openGauss types"""if isinstance(es_type, (dict, list)): # 如果 es_type 是字典类型,则需要特殊处理return 'JSONB'type_map = {"long": "BIGINT", # 大整数"integer": "INTEGER", # 整数"short": "SMALLINT", # 小整数"byte": "SMALLINT", # 小字节"float": "REAL", # 浮点数"double": "DOUBLE PRECISION", # 双精度浮点数"boolean": "BOOLEAN", # 布尔值"keyword": "VARCHAR", # 关键字(字符串类型)"text": "TEXT", # 长文本"date": "TIMESTAMP", # 日期类型"binary": "BYTEA", # 二进制数据"geo_point": "POINT", # 地理坐标(经纬度)"geo_shape": "GEOMETRY", # 复杂地理形状"nested": "JSONB", # 嵌套对象"object": "JSONB", # 对象"ip": "INET", # IP 地址"scaled_float": "REAL", # 扩展浮动类型(带缩放的浮动)"float_vector": f"VECTOR({dim})" if dim else "VECTOR", # 浮动向量类型"dense_vector": f"VECTOR({dim})" if dim else "VECTOR", # 稠密向量类型"binary_vector": f"BIT({dim})" if dim else "BIT", # 二进制向量类型"half_float": "REAL", # 半精度浮动"unsigned_long": "BIGINT", # 无符号长整数"date_nanos": "TIMESTAMP", # 高精度日期时间"alias": "TEXT", # 别名(通常是字段的别名)}# 如果 es_type 在映射表中,直接返回映射后的类型if es_type in type_map:print(f"es_type:{es_type} ----- og_type: {type_map[es_type]}")return type_map[es_type]else:print(f"Warning: Unsupported Elasticsearch type '{es_type}', defaulting to 'TEXT'")return 'TEXT' # 默认使用 TEXT 类型# 函数:将非法字符替换为下划线def sanitize_name(field_name: str) -> str:"""处理字段名,确保不会与保留字冲突,且将非字母数字字符替换为下划线"""# 将所有非字母数字字符替换为下划线sanitized_name = re.sub(r'[^a-zA-Z0-9_]', '_', field_name)# 如果是保留字,则加双引号if sanitized_name.lower() in RESERVED_KEYWORDS:return f'"{sanitized_name}"'return sanitized_name# 创建 openGauss 表def create_table_in_opengauss(es_url, es_index, table_name):columns_definition = ['id VARCHAR PRIMARY KEY'] # 增加 id 主键字段seen_fields = set() # 用于记录已经处理过的字段名# 获取 properties 字段properties = fetch_mapping(es_url, es_index).get(es_index, {}).get('mappings', {}).get('properties', {})# 遍历每个字段for field, field_info in properties.items():# 如果该字段已经处理过,跳过if field in seen_fields:continue# 获取字段的类型es_type = field_info.get('type', 'text')dim = field_info.get('dims', 0) if isinstance(field_info, dict) else 0field_type = map_to_opengauss_type(es_type, dim)sanitized_field_name = sanitize_name(field)seen_fields.add(field)columns_definition.append(f"{sanitized_field_name} {field_type}")# 生成表创建 SQLcolumns_str = ", ".join(columns_definition)create_table_sql = f"DROP TABLE IF EXISTS {sanitize_name(table_name)}; CREATE TABLE {sanitize_name(table_name)} ({columns_str});"try:# 建立数据库连接并执行创建表 SQLconnection = psycopg2.connect(host=db_host,port=db_port,dbname=db_name,user=db_user,password=db_password)cursor = connection.cursor()cursor.execute(create_table_sql)connection.commit()print(f"Table {sanitize_name(table_name)} created successfully.")except Exception as e:print(f"Error while creating table {sanitize_name(table_name)}: {e}")finally:if connection:cursor.close()connection.close()# 将数据插入到 openGauss 表中def insert_data_to_opengauss(table_name, es_source, es_id):try:# 建立数据库连接connection = psycopg2.connect(host=db_host,port=db_port,dbname=db_name,user=db_user,password=db_password)cursor = connection.cursor()# 动态生成插入 SQL 语句sanitized_columns = ['id'] + [sanitize_name(col) for col in es_source.keys()] # 清理列名values = [es_id]# 处理每一列的数据类型,必要时进行转换for column in es_source:value = es_source[column]if isinstance(value, (dict, list)):# 如果是字典类型,转换为 JSONBvalue = convert_dict_to_jsonb(value)values.append(value)columns_str = ', '.join(sanitized_columns)values_str = ', '.join(['%s'] * len(values))insert_sql = f"INSERT INTO {sanitize_name(table_name)} ({columns_str}) VALUES ({values_str})"cursor.execute(insert_sql, values)# 提交事务connection.commit()except Exception as e:print(f"Error while inserting data into {table_name}: {e}")finally:if connection:cursor.close()connection.close()# 主函数def main():try:es_data = fetch_data_from_es()table_name = es_index # 可以使用索引名作为表名create_table_in_opengauss(es_url, es_index, table_name)for record in es_data:es_source = record['_source'] # 获取 Elasticsearch 文档中的数据es_id = record['_id']insert_data_to_opengauss(table_name, es_source, es_id)print(f"Successfully inserted data into table {table_name}.")except Exception as e:print(f"Migration failed: {e}")if __name__ == "__main__":main()
2、执行脚本
python3 ./elasticsearchToOpenGauss.py3、openGauss端查看数据
#切换到迁移目标数据库openGauss=# \c es_to_og#查看迁移的表es_to_og=# \d#查看表结构es_to_og=# \d my_dynamic_index#查看表数据es_to_og=# select c
-END-
