快速上手大模型:机器学习4(特征缩放、学习率选择)
1 特征缩放
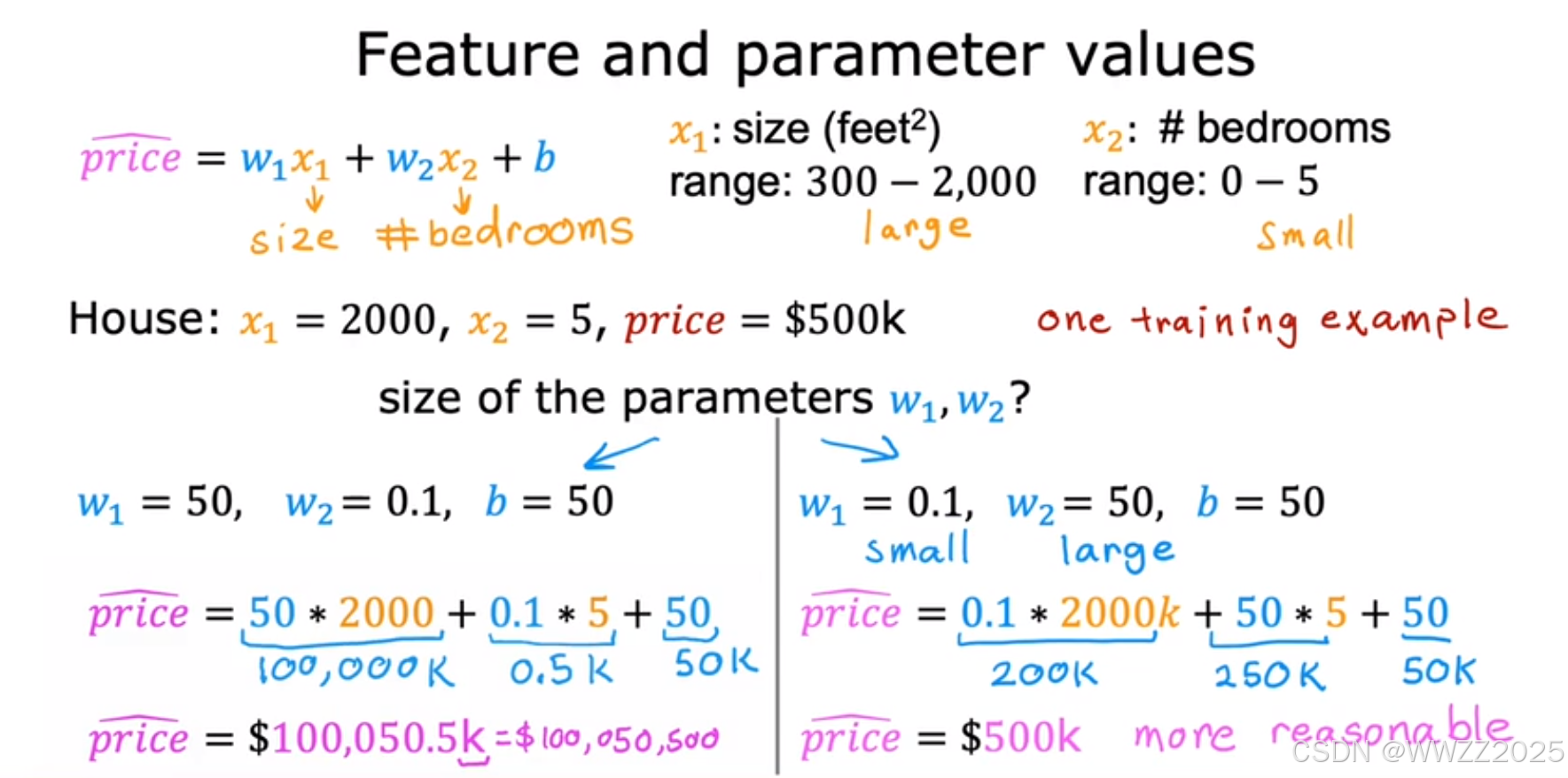
1.1 引子
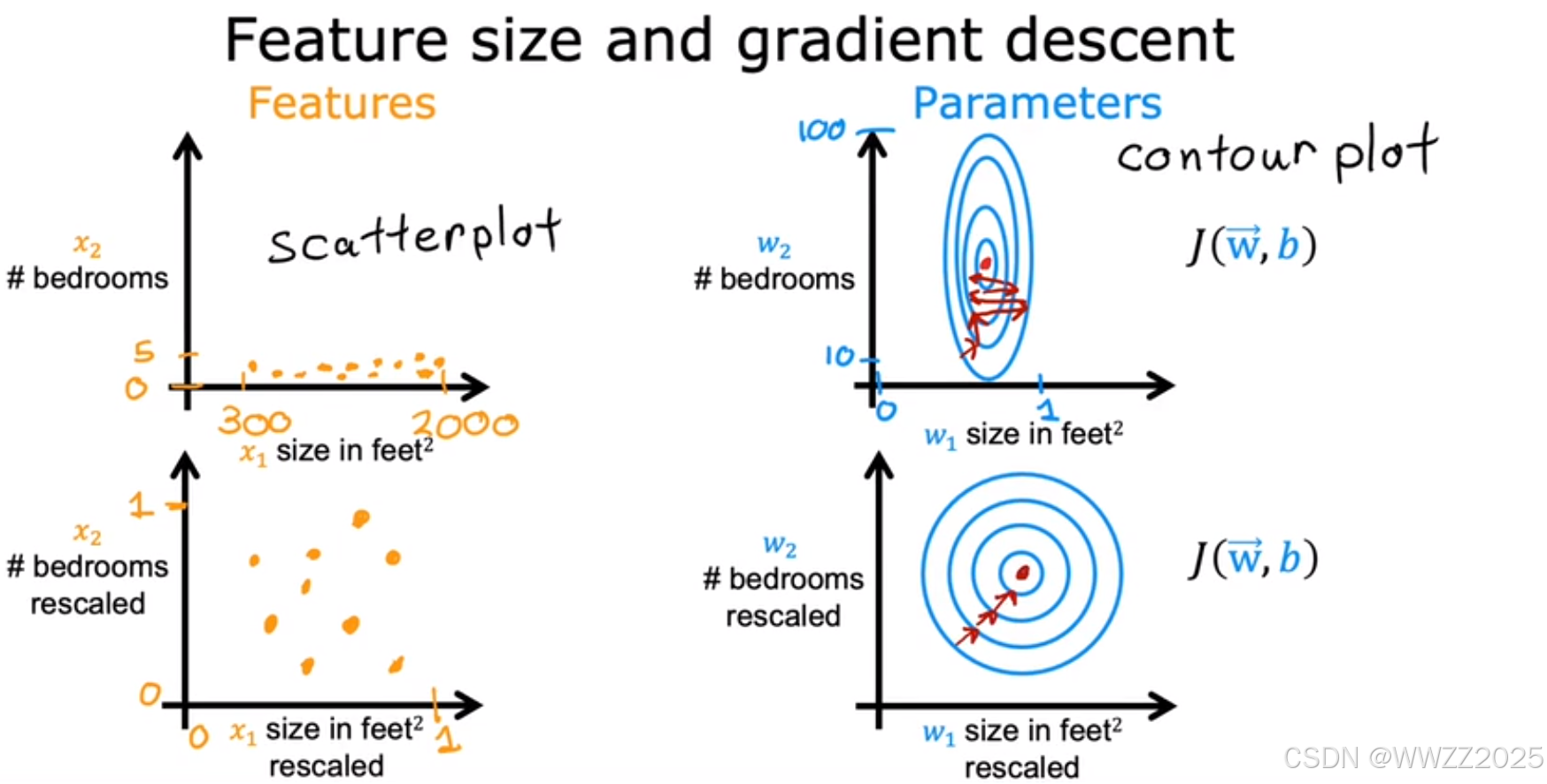
结论:通过缩放w1*x1、w2*x2使其数值差接近,使用转换后的数据运行梯度下降算法,等高线类似于圆,梯度下降可以找到一条更直接的路径到达全局最小值。
1.2 缩放方法
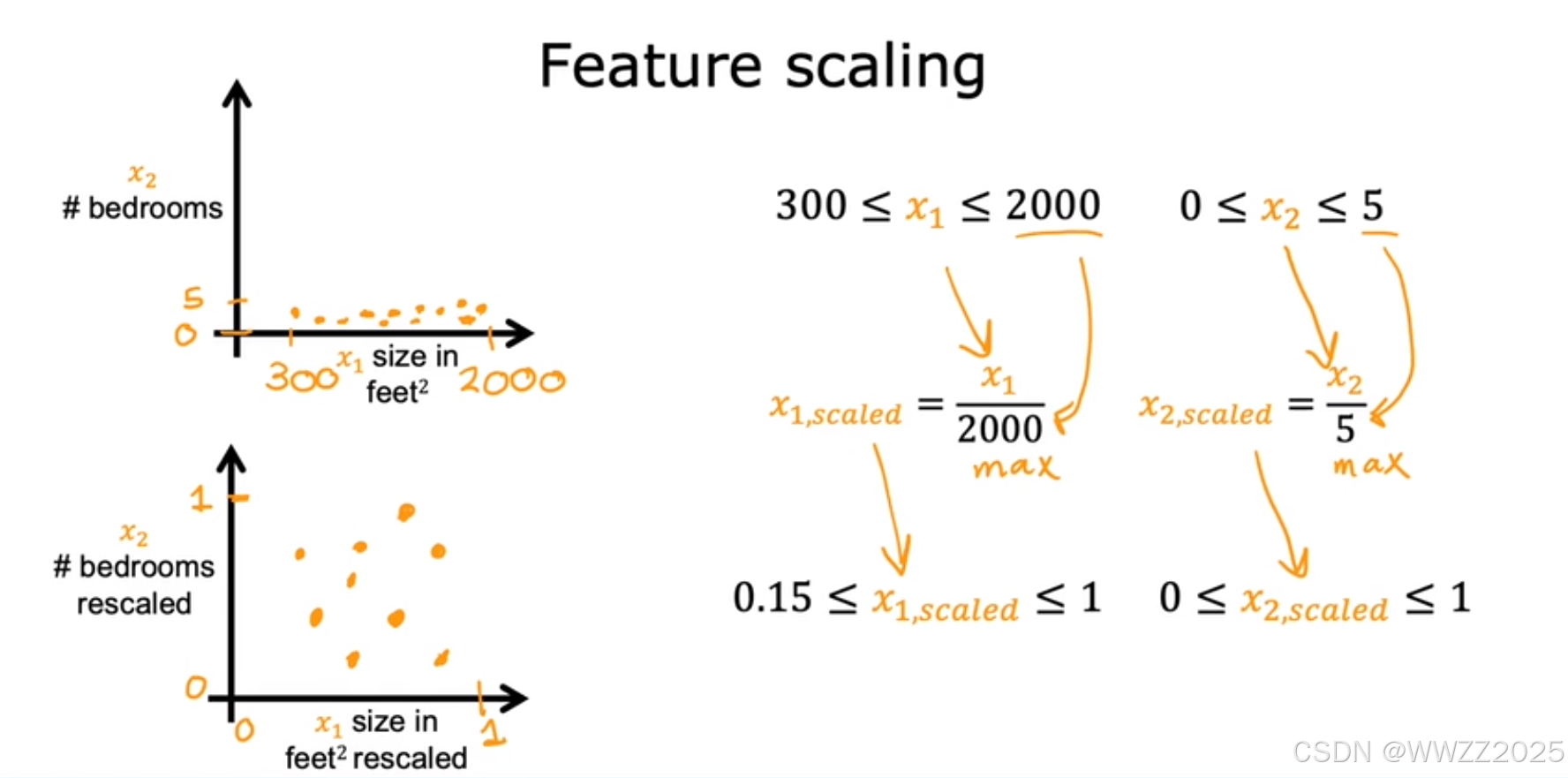
1.2.1 除以最大值法
除以区间最大值,使缩放后的点落在一个近圆上。
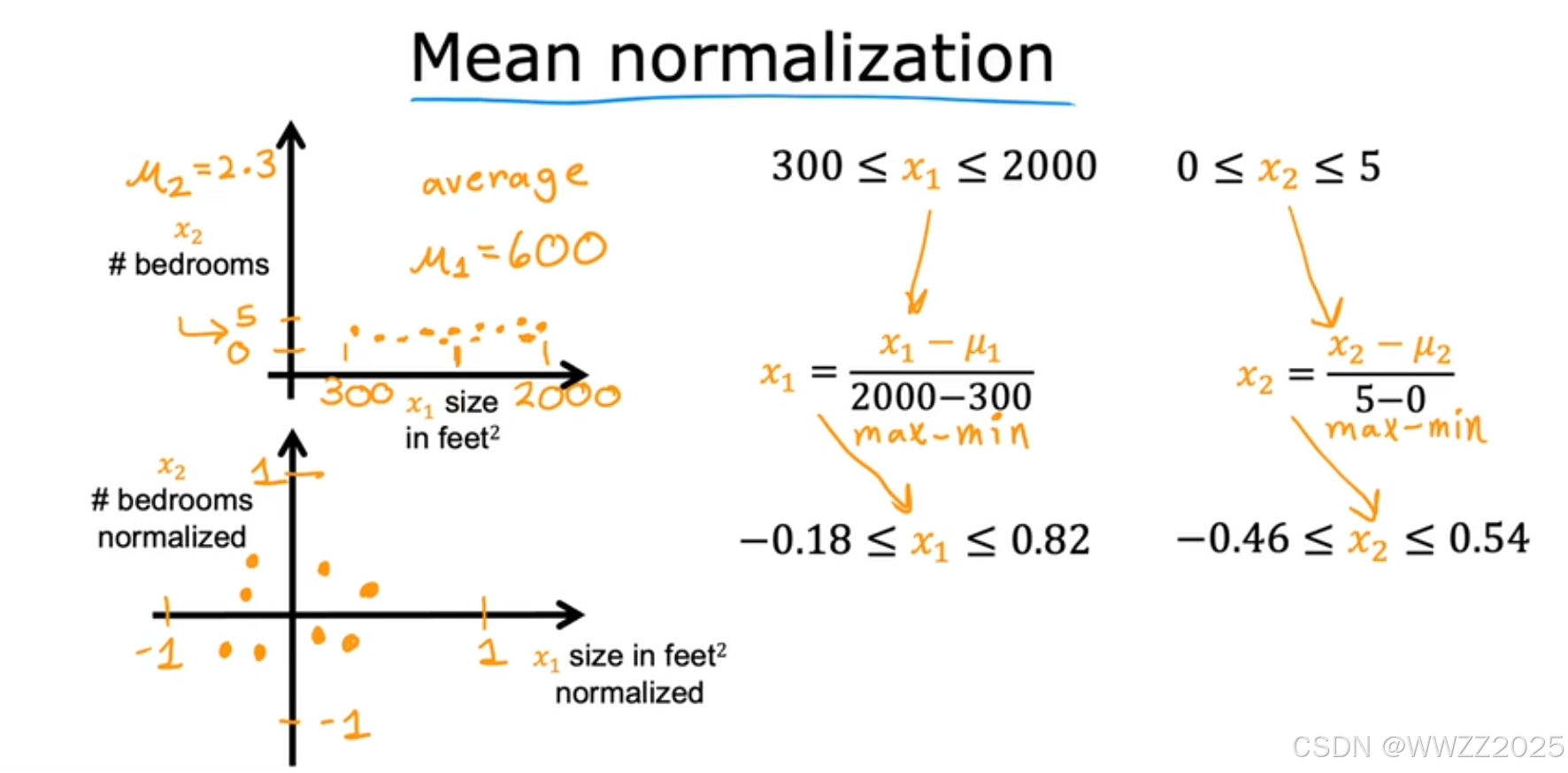
1.2.2 均值归一化(Mean normalization)
缩放后使x1、x2在-1~1之间分布。
、
分别是x1、x2在训练集上的均值,然后用每个x1、x2算放缩后的值,找出放缩后的范围。
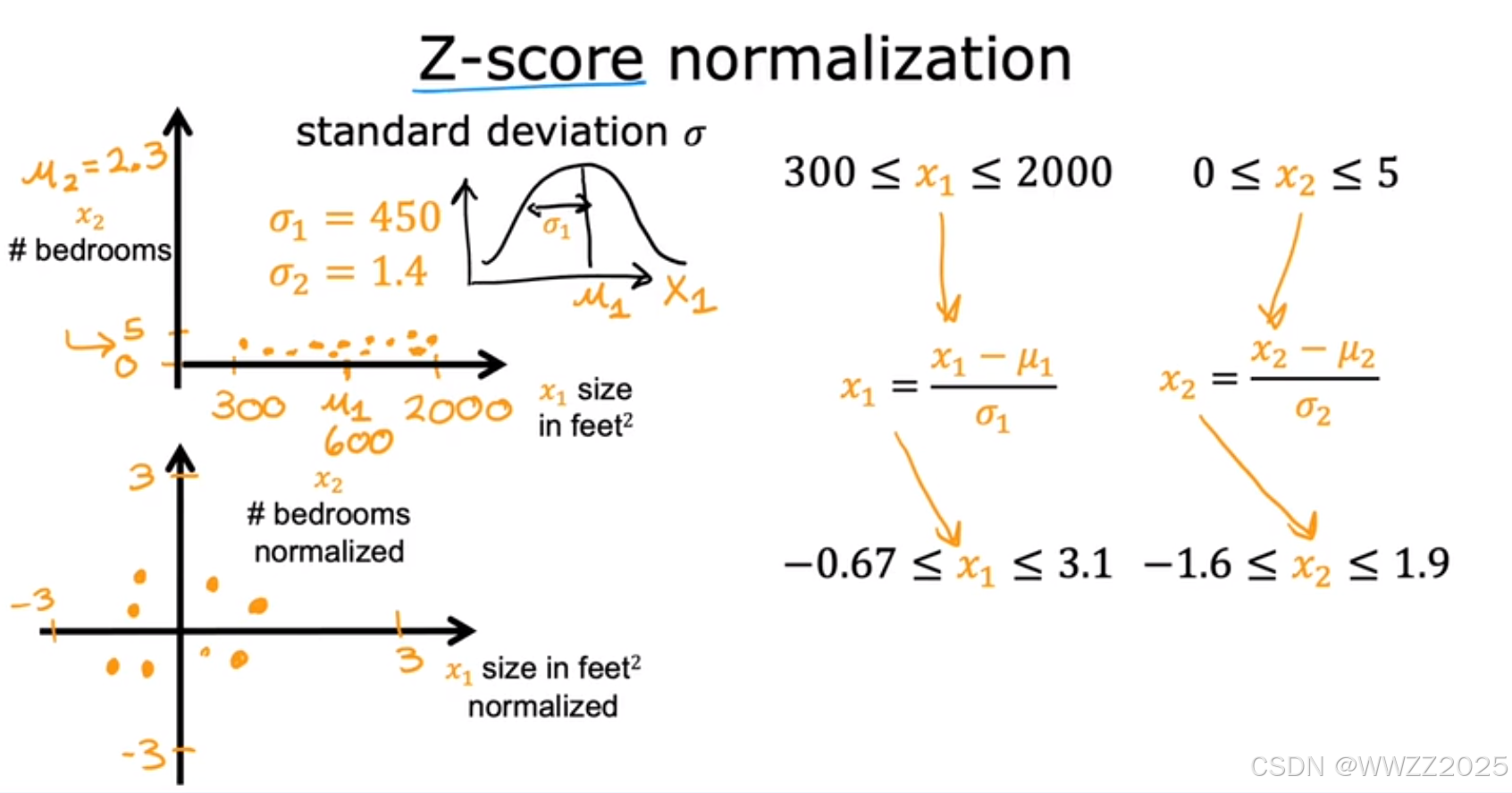
1.2.3 Z-score归一化(Z-score normalization)
归一化公式:
,
其中,
分别是x1、x2在训练集上的均值;
是标准差(
)
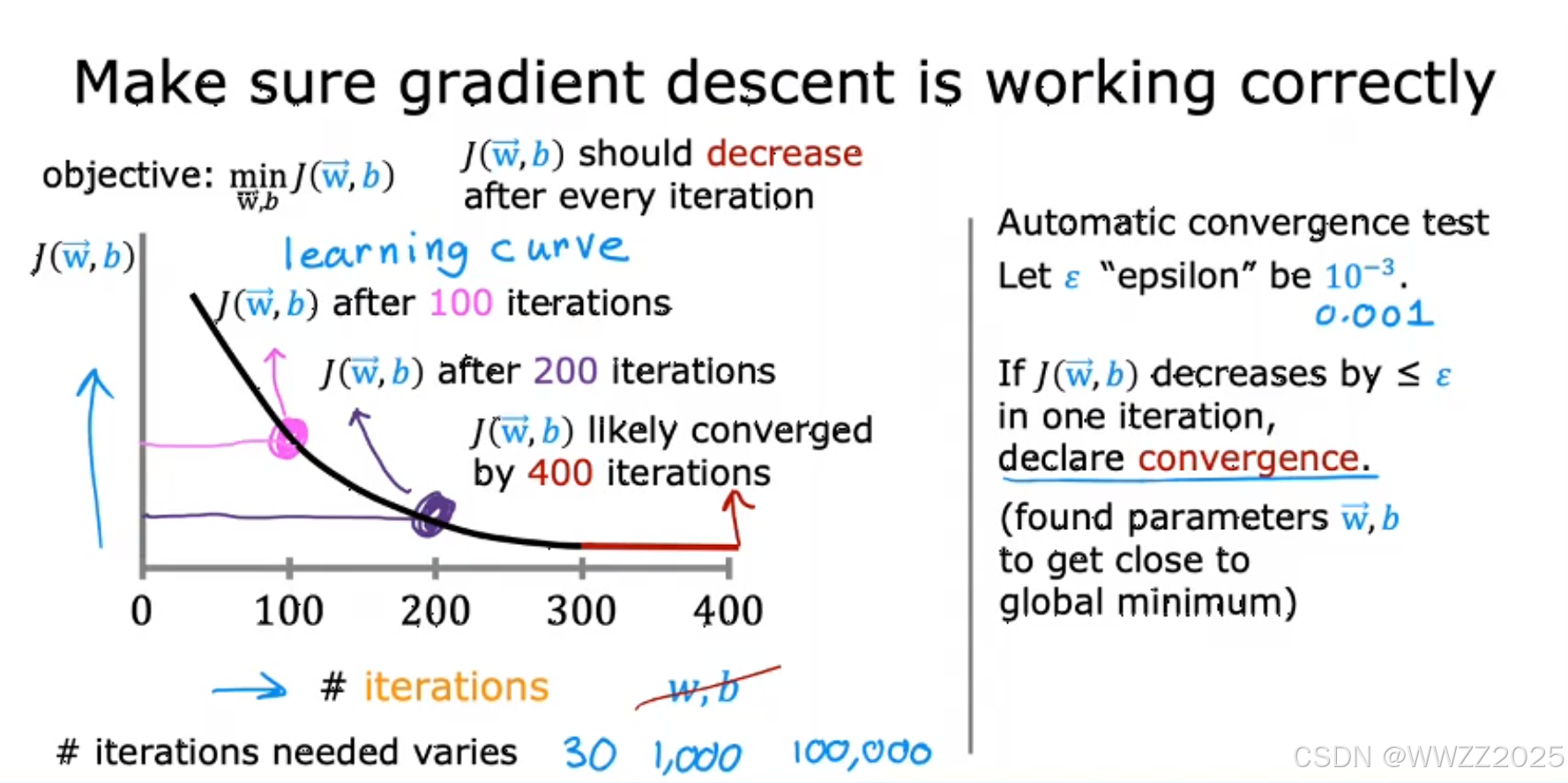
2 梯度下降收敛判断
法1:
观察左侧曲线图,迭代至一定次数后基本不再下降,此时即认为收敛。
法2:
自动收敛测试,当J<
时认为收敛,
为设定值,实际使用时不好找,常用法1。
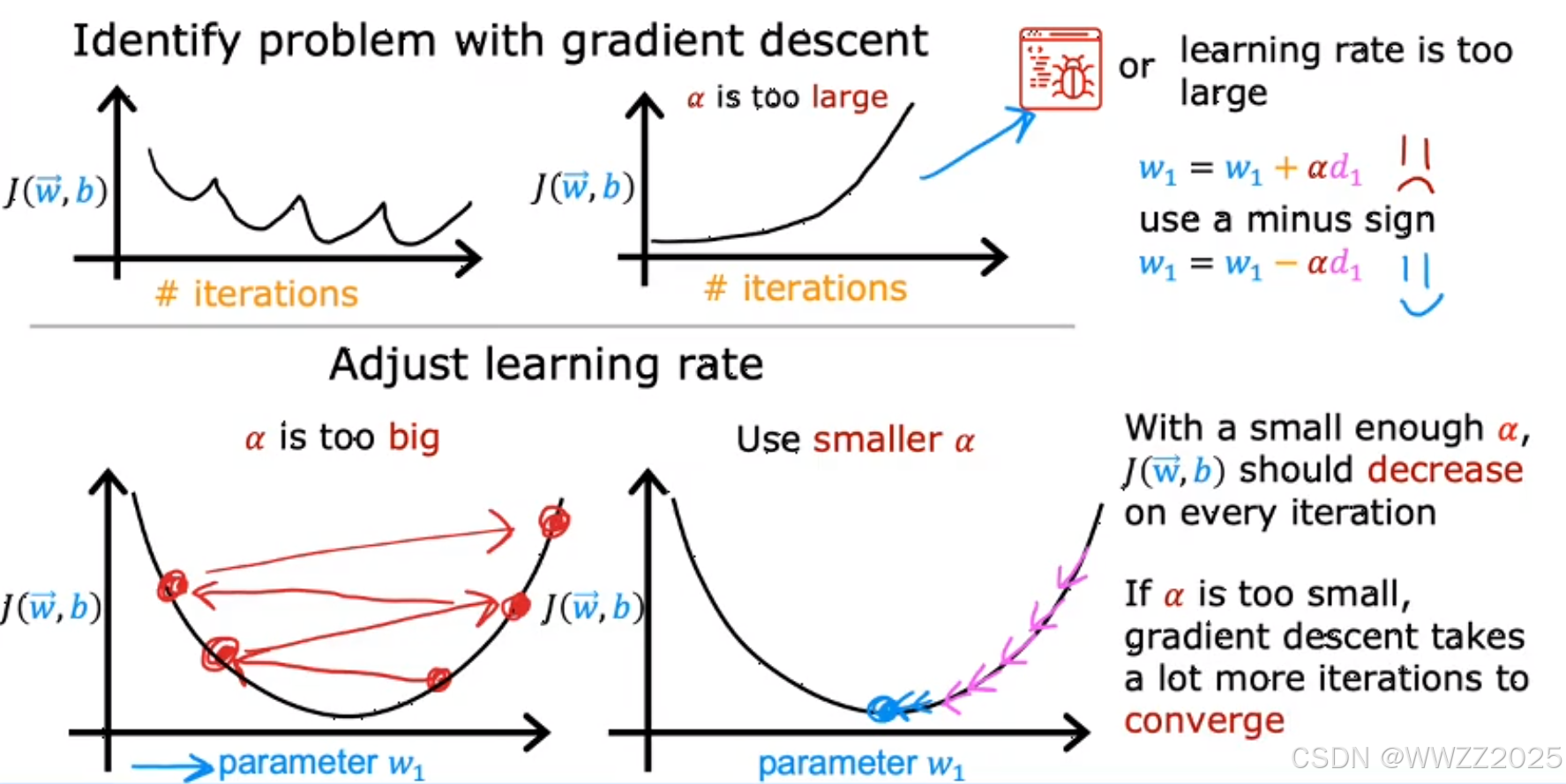
3 学习率选择(步长)
3.1 理论
结论:学习率不宜过大或过小,过大出现发散,过小则需要通过更多的迭代次数才能达到收敛。
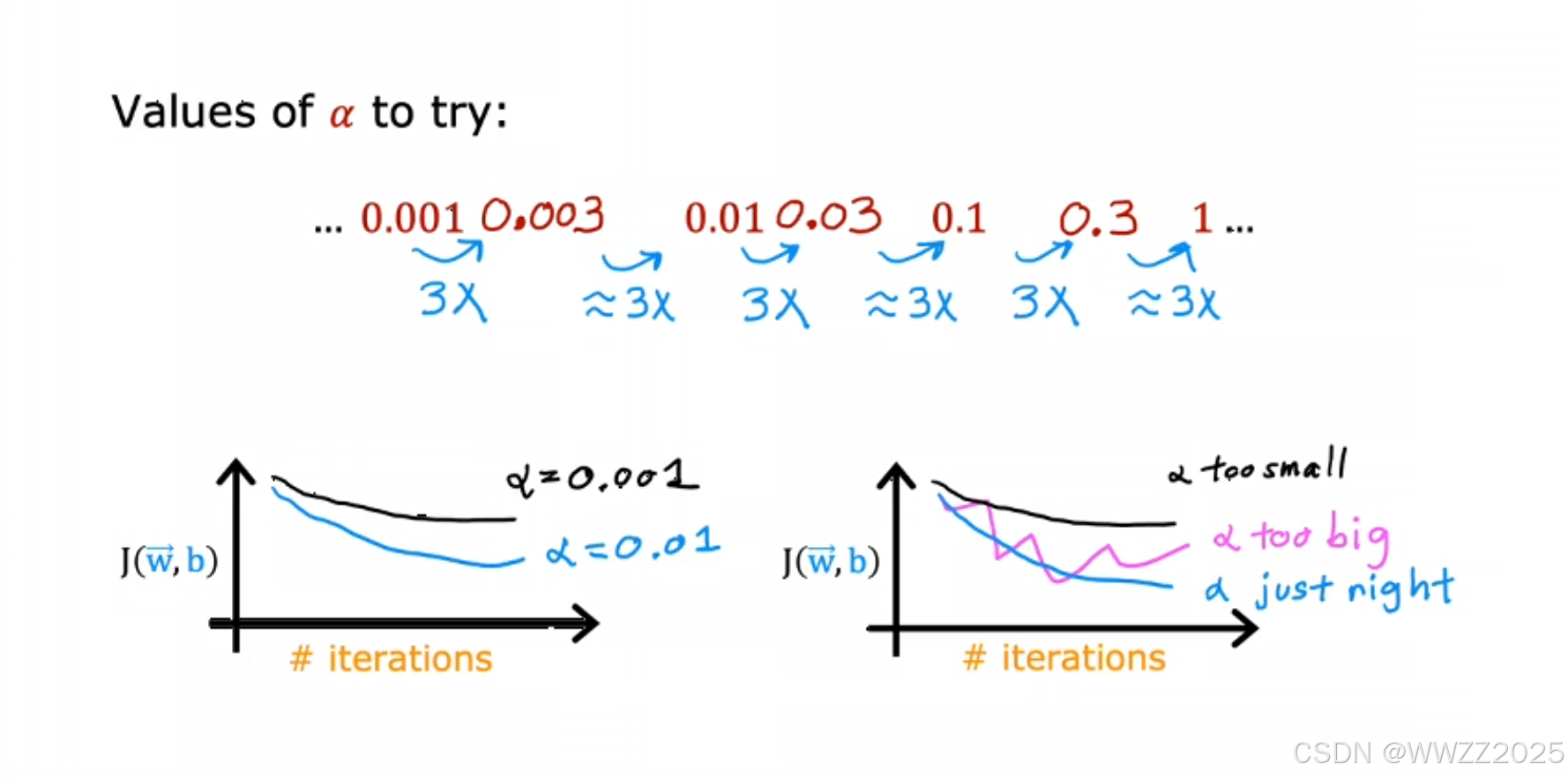
学习率选择:
从0.001开始,0.01、0.1、1进行选择,十倍频程,直至找到蓝色曲线。
3.2 代码实现
3.2.1 代价函数及参数运算
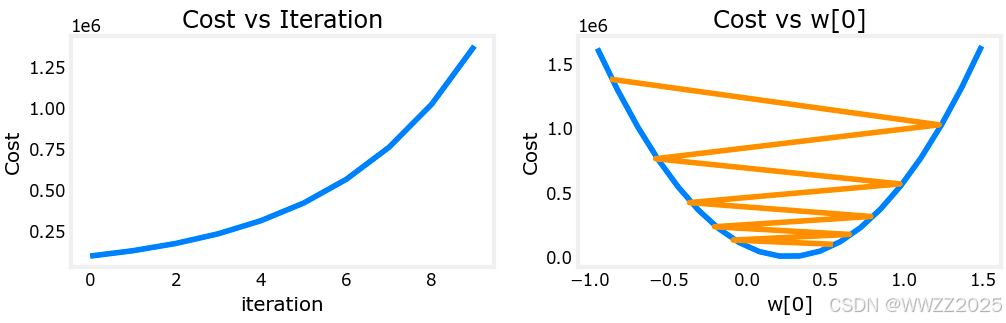
#set alpha to 9.9e-7 _, _, hist = run_gradient_descent(X_train, y_train, 10, alpha = 9.9e-7)输出:
Iteration Cost w0 w1 w2 w3 b djdw0 djdw1 djdw2 djdw3 djdb ---------------------|--------|--------|--------|--------|--------|--------|--------|--------|--------|--------|0 9.55884e+04 5.5e-01 1.0e-03 5.1e-04 1.2e-02 3.6e-04 -5.5e+05 -1.0e+03 -5.2e+02 -1.2e+04 -3.6e+021 1.28213e+05 -8.8e-02 -1.7e-04 -1.0e-04 -3.4e-03 -4.8e-05 6.4e+05 1.2e+03 6.2e+02 1.6e+04 4.1e+022 1.72159e+05 6.5e-01 1.2e-03 5.9e-04 1.3e-02 4.3e-04 -7.4e+05 -1.4e+03 -7.0e+02 -1.7e+04 -4.9e+023 2.31358e+05 -2.1e-01 -4.0e-04 -2.3e-04 -7.5e-03 -1.2e-04 8.6e+05 1.6e+03 8.3e+02 2.1e+04 5.6e+024 3.11100e+05 7.9e-01 1.4e-03 7.1e-04 1.5e-02 5.3e-04 -1.0e+06 -1.8e+03 -9.5e+02 -2.3e+04 -6.6e+025 4.18517e+05 -3.7e-01 -7.1e-04 -4.0e-04 -1.3e-02 -2.1e-04 1.2e+06 2.1e+03 1.1e+03 2.8e+04 7.5e+026 5.63212e+05 9.7e-01 1.7e-03 8.7e-04 1.8e-02 6.6e-04 -1.3e+06 -2.5e+03 -1.3e+03 -3.1e+04 -8.8e+027 7.58122e+05 -5.8e-01 -1.1e-03 -6.2e-04 -1.9e-02 -3.4e-04 1.6e+06 2.9e+03 1.5e+03 3.8e+04 1.0e+038 1.02068e+06 1.2e+00 2.2e-03 1.1e-03 2.3e-02 8.3e-04 -1.8e+06 -3.3e+03 -1.7e+03 -4.2e+04 -1.2e+039 1.37435e+06 -8.7e-01 -1.7e-03 -9.1e-04 -2.7e-02 -5.2e-04 2.1e+06 3.9e+03 2.0e+03 5.1e+04 1.4e+03 w,b found by gradient descent: w: [-0.87 -0. -0. -0.03], b: -0.00
3.2.2 图像绘制
plot_cost_i_w(X_train, y_train, hist)输出:
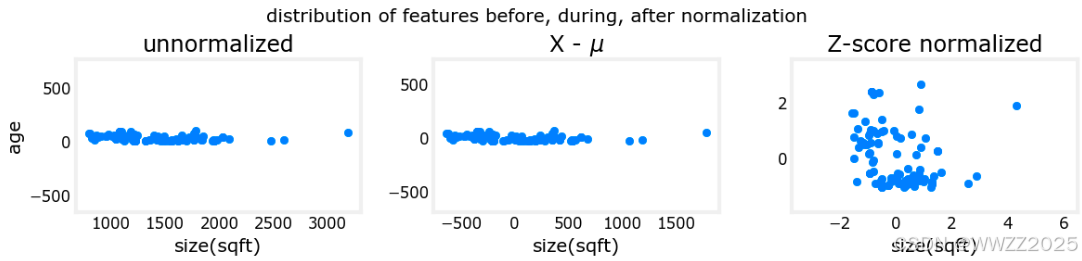
3.2.3 Z-score归一化
def zscore_normalize_features(X):"""computes X, zcore normalized by columnArgs:X (ndarray): Shape (m,n) input data, m examples, n featuresReturns:X_norm (ndarray): Shape (m,n) input normalized by columnmu (ndarray): Shape (n,) mean of each featuresigma (ndarray): Shape (n,) standard deviation of each feature"""# find the mean of each column/featuremu = np.mean(X, axis=0) # mu will have shape (n,)# find the standard deviation of each column/featuresigma = np.std(X, axis=0) # sigma will have shape (n,)# element-wise, subtract mu for that column from each example, divide by std for that columnX_norm = (X - mu) / sigma return (X_norm, mu, sigma)#check our work #from sklearn.preprocessing import scale #scale(X_orig, axis=0, with_mean=True, with_std=True, copy=True)mu = np.mean(X_train,axis=0) sigma = np.std(X_train,axis=0) X_mean = (X_train - mu) X_norm = (X_train - mu)/sigma fig,ax=plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(12, 3)) ax[0].scatter(X_train[:,0], X_train[:,3]) ax[0].set_xlabel(X_features[0]); ax[0].set_ylabel(X_features[3]); ax[0].set_title("unnormalized") ax[0].axis('equal')ax[1].scatter(X_mean[:,0], X_mean[:,3]) ax[1].set_xlabel(X_features[0]); ax[0].set_ylabel(X_features[3]); ax[1].set_title(r"X - $\mu$") ax[1].axis('equal')ax[2].scatter(X_norm[:,0], X_norm[:,3]) ax[2].set_xlabel(X_features[0]); ax[0].set_ylabel(X_features[3]); ax[2].set_title(r"Z-score normalized") ax[2].axis('equal') plt.tight_layout(rect=[0, 0.03, 1, 0.95]) fig.suptitle("distribution of features before, during, after normalization") plt.show()输出: