【C++】二叉搜索树(图码详解)
一. 概念
又称二叉排序树、二叉查找树
性质、判定:
1. 若它的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值都小于根节点的值
2. 若它的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有节点的值都大于根节点的值
3. 它的左右子树都是二叉搜索树
二. 实现
BinarySearchTree.h
template<class K>
struct BSTreeNode
{BSTreeNode<K>* _left;BSTreeNode<K>* _right;K _key;BSTreeNode(const K& key):_left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _key(key){ }
};template<class K>
class BSTree
{typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:BSTree():_root(nullptr){ }bool Insert(const K& key) {}bool Find(const K& key) {}bool Erase(const K& key) {}void InOrder() {}private:void _InOrder(Node* root) {}private:Node* _root;
};void TestBSTree1()
{int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 };BSTree<int> t;for (auto e : a){t.Insert(e);}t.InOrder();t.Erase(4);t.InOrder();t.Erase(6);t.InOrder();t.Erase(7);t.InOrder();t.Erase(3);t.InOrder();for (auto e : a){t.Erase(e);}t.InOrder();
}1. 查找
从根开始比较,查找,比根大则往右边走查找,比根小则往左边走查找
最多找高度次:O(N)
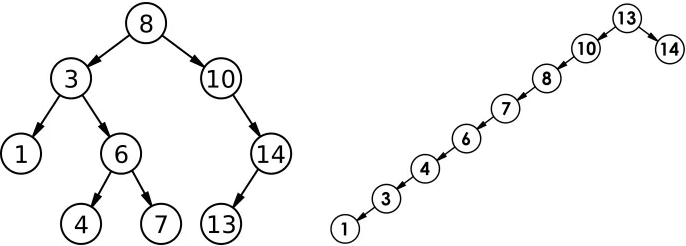
红黑树、AVL树:O(logN)
bool Find(const K& key)
{Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_key < key){cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_key > key){cur = cur->_left;}else{return true;}}return false;
}2. 插入
树为空,则直接新增节点,赋值给 root 指针
树不空,按二叉搜索树性质查找插入位置,插入新节点
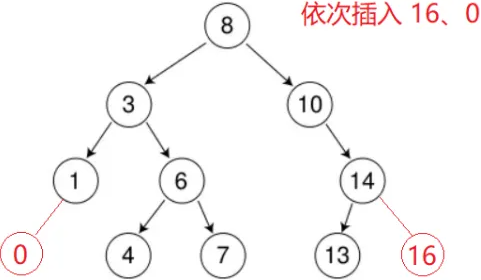
bool Insert(const K& key)
{if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(key);return true;}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_key < key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_key > key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return false;}}cur = new Node(key);if (parent->_key < key){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}return true;
}3. 中序遍历
中序遍历(左子树、根、右子树)二叉搜索树的结果是排序的结果
void InOrder(Node* root)
{if (root == nullptr){return;}InOrder(root->_left);cout << root->_key << " ";InOrder(root->_right);
}有问题,我们在外面用对象调用中序遍历要传私有成员变量 _root,但是私有我们不能在类外面用
BSTree<int> t;
t.InOrder();可以这样解决:
void InOrder()
{_InOrder(_root);cout << endl;
}void _InOrder(Node* root)
{if (root == nullptr){return;}_InOrder(root->_left);cout << root->_key << " ";_InOrder(root->_right);
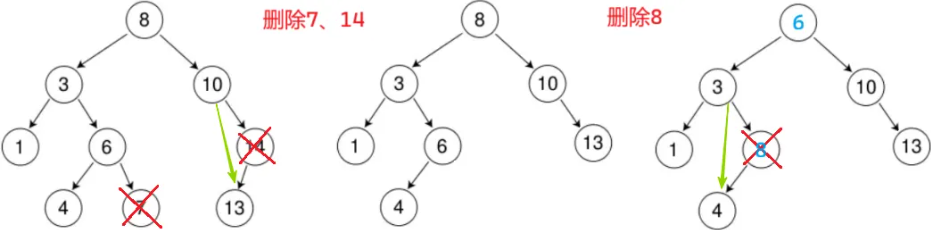
}4. 删除
要删的节点有3种情况:
1. 没有孩子:托孤
2. 有1个孩子:托孤
3. 有2个孩子:和左子树的最大节点(左子树的最右节点) 或 右子树的最小节点(右子树的最左节点) 替换
bool Erase(const K& key){Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_key < key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_key > key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else // 树中找到了要删除的节点cur{// ......delete cur;return true;}}return false;}cur 左为空(也解决了没有孩子,左右都为空):
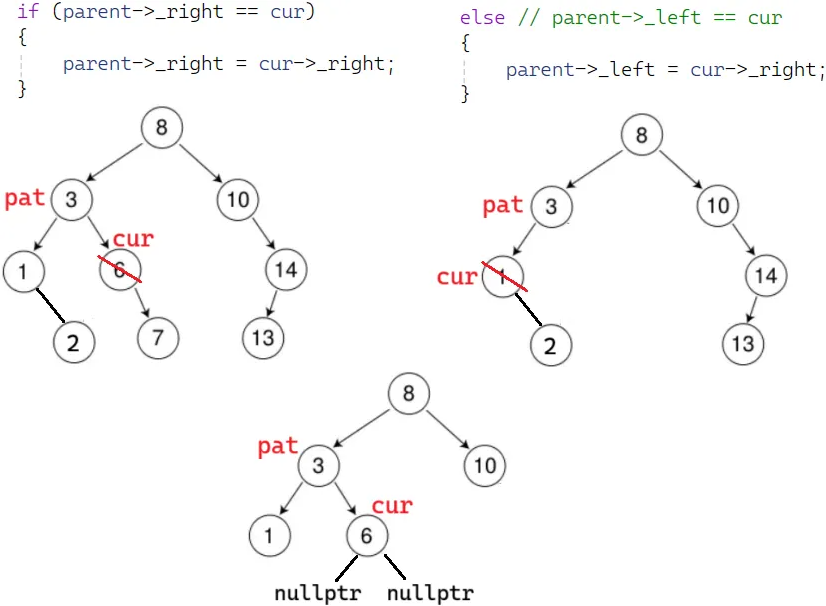
else // 树中找到了要删除的节点cur
{// cur左为空if (cur->_left == nullptr){if (parent->_right == cur){parent->_right = cur->_right;}else{parent->_left = cur->_right;}}// ......delete cur;return true;
}但有这种特殊情况:
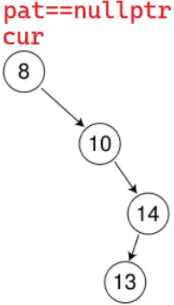
else // 树中找到了要删除的节点cur
{// cur左为空if (cur->_left == nullptr){if (cur == _root){_root = cur->_right;}else{if (parent->_right == cur){parent->_right = cur->_right;}else{parent->_left = cur->_right;}}}// ......delete cur;return true;
}cur 右为空:同理
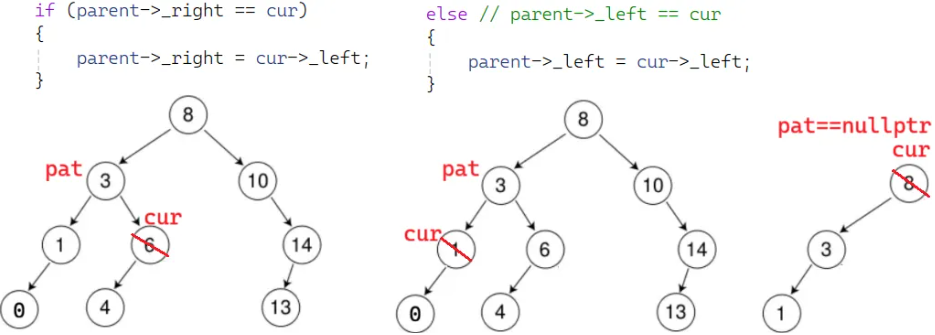
else // 树中找到了要删除的节点cur
{// cur左为空if (cur->_left == nullptr) { }// cur右为空else if (cur->_right == nullptr){if (cur == _root){_root = cur->_left;}else{if (parent->_right == cur){parent->_right = cur->_left;}else // parent->_left == cur{parent->_left = cur->_left;}}}// ......delete cur;return true;
}cur 左右都不为空:替换 以左子树的最大节点(左子树的最右节点)为例
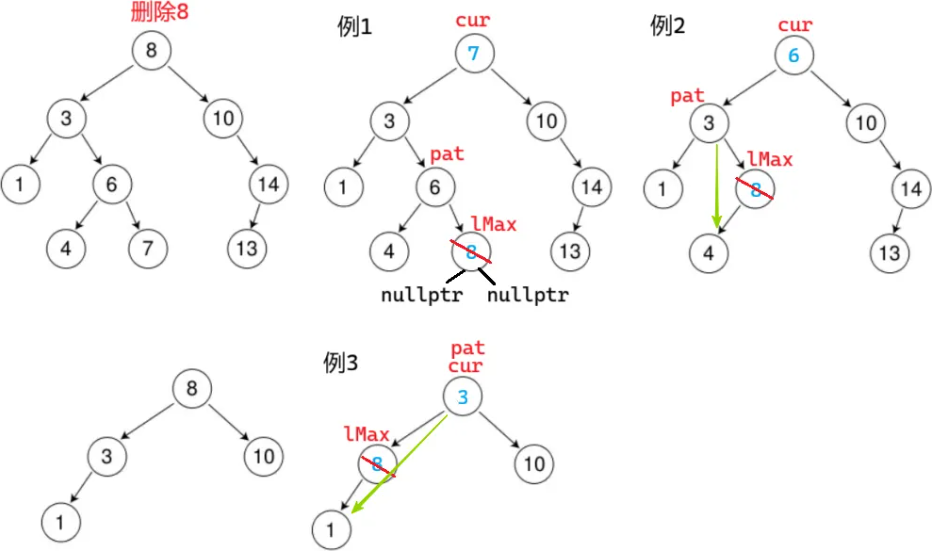
注意:leftMax 是左子树的最右节点,leftMax 这个节点一定不会有右子树,可能有左子树
注意:
这里是左右都不为空的情况,而且我们要去左子树找最右节点,所以 leftMax 可直接定义为 cur->_left;parent 可直接定义为 cur
如果 leftMax 定义为 cur,parent 定义为 nullptr,例3会坑

注意:替换后要通过找到父亲直接删(一定可以直接删,因为 leftMax 右一定为空)。不能递归删(7 < 8,在右子树找,找不到,删不了)。因为搜索树的结构变了,而且无法传根,无法控制;进而导致不满足二叉搜索树的性质
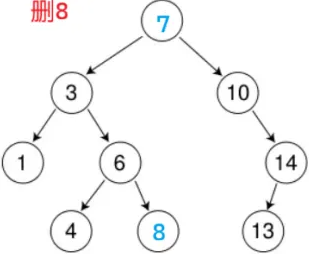
else // 树中找到了要删除的节点cur
{// cur左为空if (cur->_left == nullptr) { }// cur右为空else if (cur->_right == nullptr) { }// cur左右都不为空else{// 找替代节点Node* parent = cur;Node* leftMax = cur->_left;while (leftMax->_right){parent = leftMax;leftMax = leftMax->_right;}swap(cur->_key, leftMax->_key);if (parent->_left == leftMax){parent->_left = leftMax->_left;}else // parent->_right == leftMax{parent->_right = leftMax->_left;}cur = leftMax;}delete cur;return true;
}三. 递归版实现
C++里,凡是树形结构递归,都要单独写子函数。因为递归是子问题,要控制子树
BinarySearchTree.h
template<class K>
struct BSTreeNode
{BSTreeNode<K>* _left;BSTreeNode<K>* _right;K _key;BSTreeNode(const K& key):_left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _key(key){ }
};template<class K>
class BSTree
{typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:BSTree():_root(nullptr){ }void InOrder(){_InOrder(_root);cout << endl;}bool FindR(const K& key){return _FindR(_root, key);}bool InsertR(const K& key){return _InsertR(_root, key);}bool EraseR(const K& key){return _EraseR(_root, key);}private:bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key) {}bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key) {}bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key) {}void _InOrder(Node* root) {}private:Node* _root;
};1. 查找
比根大,在右子树找;比根小,在左子树找;到空还没找到,则不存在
bool FindR(const K& key)
{return _FindR(_root, key);
}bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key)
{if (root == nullptr)return false;if (root->_key < key){return _FindR(root->_right, key);}else if (root->_key > key){return _FindR(root->_left, key);}else{return true;}
}2. 插入
插入的值 < 根:往左子树去插入
插入的值 > 根:往右子树去插入
插入的值 == 根:插入失败
走到空的地方就可以插入
怎么插入?new Node(key),但还要找父亲,怎么解决?加引用成为 Node*& root
这里指针的作用:链接树
这里引用的作用:下一层改变影响上一层
bool InsertR(const K& key)
{return _InsertR(_root, key);
}bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{if (root == nullptr){root = new Node(key);return true;}if (root->_key < key){return _InsertR(root->_right, key);}else if (root->_key > key){return _InsertR(root->_left, key);}else{return false;}
}如果是空树,root 是 _root 的别名,new 的第一个节点刚好给 _root
如果不是空树,层层往下递归,前面的引用不起作用,每一层(每一个栈帧)都有一个引用
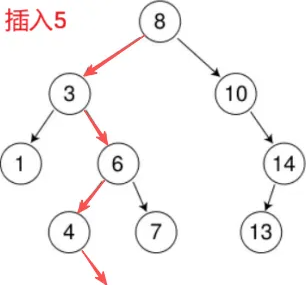
6 是对象,把左指针这个成员传给下一层,下一层的 root 是 6 的左指针的别名(引用此时不发挥作用)
5 > 4,把 4 的右指针往下传,root 是 4 的右指针的别名
4 的右指针为空 ==> 插入
new节点,给 root,对 root 修改,就是对 4 的右指针修改
这一句赋值,直接就链接上了,不用找父亲,不用比较大小

3. 删除
先找有没有要删的节点,找到了就删,同样分3种情况:左为空、右为空、左右都为空
bool EraseR(const K& key)
{return _EraseR(_root, key);
}bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key)
{if (root == nullptr) // 树里没有return false;if (root->_key < key){return _EraseR(root->_right, key);}else if (root->_key > key){return _EraseR(root->_left, key);}else // 找到了,准备删{Node* del = root;if (root->_left == nullptr) // 1.左为空{root = root->_right;}else if (root->_right == nullptr) // 2.右为空{root = root->_left;}else // 3. 左右都不为空{ }delete del;return true;}
}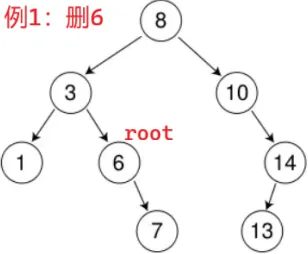
3 < 6,3 的右指针往下传,root 是 3 的右指针的别名
此时 root 是 6,找到了,开始删:root 左为空,把 root(3的右指针)赋值为 root 的右指针
root 的右指针指向 7 ==> 3 的右指针指向 7,完成了链接关系
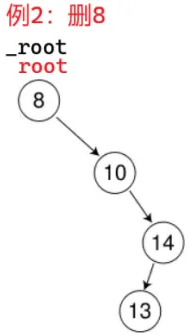
root 是 _root 的别名,上来就找到了,开始删:
root 不为空,root = root->_right 就是 _root = _root->_right;
左右都为空:找替代节点(以找左树的最右节点为例,最右节点的右一定为空)
以刚开始就找到要删的 8 为例:
转化为删红圈的节点。非递归实现一定可以找父亲,直接删;不能递归删
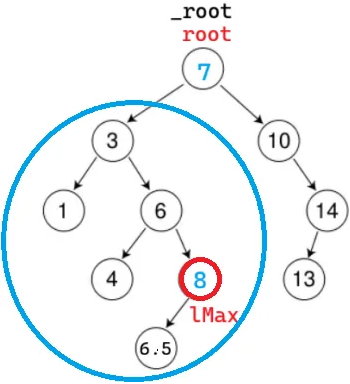
我们现在有了引用,root 是 _root 的别名
但在 root 当前位置发挥不了作用,因为不需要改 _root,所以不能直接在最大的树删除
可以转化为在蓝圈的树中删,递归往下走,一定是右为空的情况。那时,root 是 6 的右指针的别名
走这个情形:

else // 3. 左右都不为空
{Node* leftMax = root->_left;while (leftMax->_right){leftMax = leftMax->_right;}swap(root->_key, leftMax->_key);return _EraseR(root->_left, key);
}这种方法在替换后,会在左子树再找一遍要删除的节点,但代价不大
第11行递归进去之后,不会再次走这个左右都不为空的 else
4. 析构、拷贝、赋值
析构:析构也得写子函数,因为要递归,析构函数都没有参数
二叉树:用后序遍历删除,循环不好用
拷贝:不能调 Insert,会改变树的形状
走前序遍例赋值
默认的拷贝构造是浅拷贝,会出错,要自己实现深拷贝
赋值:现代写法
BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t)
{_root = Copy(t._root);
}BSTree<K>& operator=(BSTree<K> t)
{swap(_root, t._root);return *this;
}~BSTree()
{Destroy(_root);
}void Destroy(Node*& root)
{if (root == nullptr)return;Destroy(root->_left);Destroy(root->_right);delete root;root = nullptr; // 这就是传引用的原因
}Node* Copy(Node* root)
{if (root == nullptr)return nullptr;Node* copyroot = new Node(root->_key);copyroot->_left = Copy(root->_left);copyroot->_right = Copy(root->_right);return copyroot;
}非递归+递归整体代码
template<class K>
struct BSTreeNode
{BSTreeNode<K>* _left;BSTreeNode<K>* _right;K _key;BSTreeNode(const K& key):_left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _key(key){ }
};template<class K>
class BSTree
{typedef BSTreeNode<K> Node;
public:BSTree():_root(nullptr){ }BSTree(const BSTree<K>& t){_root = Copy(t._root);}BSTree<K>& operator=( BSTree<K> t){swap(_root, t._root);return *this;}~BSTree(){Destroy(_root);}bool Insert(const K& key){if (_root == nullptr){_root = new Node(key);return true;}Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_key < key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_key > key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else{return false;}}cur = new Node(key);if (parent->_key < key){parent->_right = cur;}else{parent->_left = cur;}return true;}bool Find(const K& key){Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_key < key){cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_key > key){cur = cur->_left;}else{return true;}}return false;}bool Erase(const K& key){Node* parent = nullptr;Node* cur = _root;while (cur){if (cur->_key < key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_right;}else if (cur->_key > key){parent = cur;cur = cur->_left;}else // 树中找到了要删除的节点cur{// cur左为空if (cur->_left == nullptr){if (cur == _root){_root = cur->_right;}else{if (parent->_right == cur){parent->_right = cur->_right;}else // parent->_left == cur{parent->_left = cur->_right;}}}// cur右为空else if (cur->_right == nullptr){if (cur == _root){_root = cur->_left;}else{if (parent->_right == cur){parent->_right = cur->_left;}else // parent->_left == cur{parent->_left = cur->_left;}}}// cur左右都不为空 else{// 找替代节点Node* parent = cur;Node* leftMax = cur->_left;while (leftMax->_right){parent = leftMax;leftMax = leftMax->_right;}swap(cur->_key, leftMax->_key);if (parent->_left == leftMax){parent->_left = leftMax->_left;}else // parent->_right == leftMax{parent->_right = leftMax->_left;}cur = leftMax;}delete cur;return true;}}return false;}void InOrder(){_InOrder(_root);cout << endl;}bool FindR(const K& key){return _FindR(_root, key);}bool InsertR(const K& key){return _InsertR(_root, key);}bool EraseR(const K& key){return _EraseR(_root, key);}private:void Destroy(Node*& root){if (root == nullptr)return;Destroy(root->_left);Destroy(root->_right);delete root;root = nullptr; // 这就是传引用的原因}Node* Copy(Node* root){if (root == nullptr)return nullptr;Node* copyroot = new Node(root->_key);copyroot->_left = Copy(root->_left);copyroot->_right = Copy(root->_right);return copyroot;}bool _FindR(Node* root, const K& key){if (root == nullptr)return false;if (root->_key < key){return _FindR(root->_right, key);}else if (root->_key > key){return _FindR(root->_left, key);}else{return true;}}bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key){if (root == nullptr){root = new Node(key);return true;}if (root->_key < key){return _InsertR(root->_right, key);}else if (root->_key > key){return _InsertR(root->_left, key);}else{return false;}}bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key){if (root == nullptr) // 树里没有return false;if (root->_key < key){return _EraseR(root->_right, key);}else if (root->_key > key){return _EraseR(root->_left, key);}else // 找到了,准备删{Node* del = root;if (root->_left == nullptr) // 1.左为空{root = root->_right;}else if (root->_right == nullptr) // 2.右为空{root = root->_left;}else // 3. 左右都不为空{Node* leftMax = root->_left;while (leftMax->_right){leftMax = leftMax->_right;}swap(root->_key, leftMax->_key);return _EraseR(root->_left, key);}delete del;return true;}}void _InOrder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return;}_InOrder(root->_left);cout << root->_key << " ";_InOrder(root->_right);}private:Node* _root;
};void TestBSTree1()
{int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 };BSTree<int> t;for (auto e : a){t.InsertR(e);}t.InOrder();t.EraseR(4);t.InOrder();t.EraseR(6);t.InOrder();t.EraseR(7);t.InOrder();t.EraseR(3);t.InOrder();for (auto e : a){t.EraseR(e);}t.InOrder();
}void TestBSTree2()
{int a[] = { 8, 3, 1, 10, 6, 4, 7, 14, 13 };BSTree<int> t;for (auto e : a){t.InsertR(e);}BSTree<int> t1(t);t.InOrder();t1.InOrder();
}四. 应用模型
1. key 的搜索模型
快速判断在不在的场景
门禁系统、小区车辆出入系统 ……
2. key_value 的搜索模型
通过一个值找另一个值
商场的车辆出入系统、高铁实名制车票系统 ……
namespace key_value
{template<class K, class V>struct BSTreeNode{BSTreeNode<K, V>* _left;BSTreeNode<K, V>* _right;K _key;V _value;BSTreeNode(const K& key, const V& value):_left(nullptr), _right(nullptr), _key(key), _value(value){ }};template<class K, class V>class BSTree{typedef BSTreeNode<K, V> Node;public:BSTree():_root(nullptr){ }void InOrder(){_InOrder(_root);cout << endl;}Node* FindR(const K& key){return _FindR(_root, key);}bool InsertR(const K& key, const V& value){return _InsertR(_root, key, value);}bool EraseR(const K& key){return _EraseR(_root, key);}private:Node* _FindR(Node* root, const K& key){if (root == nullptr)return nullptr;if (root->_key < key){return _FindR(root->_right, key);}else if (root->_key > key){return _FindR(root->_left, key);}else{return root;}}bool _InsertR(Node*& root, const K& key, const V& value){if (root == nullptr){root = new Node(key, value);return true;}if (root->_key < key){return _InsertR(root->_right, key, value);}else if (root->_key > key){return _InsertR(root->_left, key, value);}else{return false;}}bool _EraseR(Node*& root, const K& key){if (root == nullptr) // 树里没有return false;if (root->_key < key){return _EraseR(root->_right, key);}else if (root->_key > key){return _EraseR(root->_left, key);}else // 找到了,准备删{Node* del = root;if (root->_left == nullptr) // 1.左为空{root = root->_right;}else if (root->_right == nullptr) // 2.右为空{root = root->_left;}else // 3. 左右都不为空{Node* leftMax = root->_left;while (leftMax->_right){leftMax = leftMax->_right;}swap(root->_key, leftMax->_key);return _EraseR(root->_left, key);}delete del;return true;}}void _InOrder(Node* root){if (root == nullptr){return;}_InOrder(root->_left);cout << root->_key << ":" << root->_value << endl;_InOrder(root->_right);}private:Node* _root;};
}拼写检查:读取词库放到一颗搜索树;读取单词,看在不在树中,不在则拼写错误
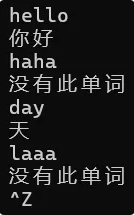
void TestBSTree1()
{BSTree<string, string> dict;dict.InsertR("hello", "你好");dict.InsertR("tree", "树");dict.InsertR("apple", "苹果");dict.InsertR("day", "天");string str;while (cin >> str){BSTreeNode<string, string>* ret = dict.FindR(str);if (ret != nullptr){cout << ret->_value << endl;}else{cout << "没有此单词" << endl;}}
}
统计出现次数
void TestBSTree2()
{string arr[] = { "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "西瓜", "苹果","苹果", "西瓜", "苹果", "香蕉", "苹果", "香蕉" };BSTree<string, int> countTree;for (auto& str : arr){BSTreeNode<string, int>* ret = countTree.FindR(str);if (ret == nullptr){countTree.InsertR(str, 1);}else{ret->_value++;}}countTree.InOrder();
}
本篇的分享就到这里了,感谢观看,如果对你有帮助,别忘了点赞+收藏+关注。
小编会以自己学习过程中遇到的问题为素材,持续为您推送文章
