【Java】认识String类
文章目录
- 一、String类的重要性
- 二、String类中的常用方法
- 1.字符串构造
- 2.String对象的比较
- 3.字符串查找
- 4.转换
- 5.字符串替换
- 6.字符串拆分
- 7.字符串截取
- 8.其他操作方法
- 9.字符串的不可变性
- 10.字符串修改
- 三、StringBuilder和StringBuffer
一、String类的重要性
在C语言中已经涉及到字符串了,但是在C语言中要表示字符串只能使用字符数组或者字符指针,可以使用标准库提供的字符串系列函数完成大部分操作,但是这种将数据和操作数据方法分离开的方式不符合面相对象的思想,而字符串应用又非常广泛,因此Java语言专门提供了String类
二、String类中的常用方法
1.字符串构造
String类提供的构造方式非常多,常用的有以下三种:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
System.out.println(s);
String s1 = new String("hello");
System.out.println(s1);
char[] s3 = {'h','e','l','l','o'};
System.out.println(s3);
}
}

注意:
1.String类是引用类型,内部并不存储字符串本身
2.在Java中""引起来的也是String类型对象
2.String对象的比较
Java中提供了四种比较方式:
1.==比较是否引用同一对象
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
int c = 10;
System.out.println(a==b);
System.out.println(a==c);
System.out.println("********");
String s = new String("hello");
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("word");
String s3 = s;
System.out.println(s==s1);
System.out.println(s1==s2);
System.out.println(s==s3);
}
}

注意: 对于内置类型,== 比较的是变量中的值;对于引用类型==比较的是引用中的地址
2.boolean equals(Object anObject) 方法:按照字典序比较
字典序:字符大小的顺序
String类重写了父类Object中equals方法,Object中equals默认按照==比较,String重写equals方法后,按照如下规则进行比较
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = new String("hello");
String s1 = new String("hello");
String s2 = new String("Hello");
// equals比较:String对象中的逐个字符
// s与s2引用的不是同一个对象,而且两个对象中内容也不同,因此输出false
// s与s1引用的不是同一个对象,但是两个对象中放置的内容相同,因此输出true
System.out.println(s.equals(s2));
System.out.println(s.equals(s1));
}
}

3.int compareTo(String s) 方法: 按照字典序进行比较
与equals不同的是,equals返回的是boolean类型,而compareTo返回的是int类型。具体比较方式:
1.先按照字典次序大小比较,如果出现不等的字符,直接返回这两个字符的大小差值
2.如果前k个字符相等(k为两个字符长度最小值),返回值两个字符串长度差值
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = new String("abc");
String s1 = new String("ac");
String s2 = new String("abc");
String s3 = new String("abcde");
System.out.println(s.compareTo(s1));//不同输出字符的差值为-1
System.out.println(s.compareTo(s2));//输出字符相同为0
System.out.println(s.compareTo(s3));//前几个字符相同,输出长度差值为-2
}
}
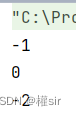
4. int compareToIgnoreCase(String str) 方法:与compareTo方式相同,但是忽略大小写比较
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = new String("abc");
String s1 = new String("ac");
String s2 = new String("ABc");
String s3 = new String("abcde");
System.out.println(s.compareToIgnoreCase(s1));//不同输出字符的差值为-1
System.out.println(s.compareToIgnoreCase(s2));//输出字符相同为0
System.out.println(s.compareToIgnoreCase(s3));//前几个字符相同,输出长度差值为-2
}
}
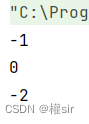
3.字符串查找
字符串查找也是字符串中非常常见的操作,String类提供的常用查找的方法:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| char charAt(int index) | 返回index位置上字符,如果index为负数或者越界,抛出IndexOutOfBoundsException异常 |
| int indexOf(int ch) | 返回ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
| int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
| int indexOf(String str) | 返回str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
| int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
| int lastIndexOf(int ch) | 从后往前找,返回ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
| int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找,从后往前找ch第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
| :int lastIndexOf(String str) | 从后往前找,返回str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1: |
| int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找,从后往前找str第一次出现的位置,没有返回-1 |
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "aaabbbcccaaabbbccc";
System.out.println(s.charAt(3));
System.out.println(s.indexOf('c'));
System.out.println(s.indexOf('c', 10));
System.out.println(s.indexOf("bbb"));
System.out.println(s.indexOf("bbb", 10));
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf('c'));
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf('c', 10));
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("bbb"));
System.out.println(s.lastIndexOf("bbb", 10));
}
}
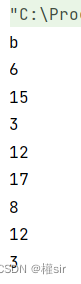
4.转换
1.数值和字符串转换化
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = String.valueOf(1234);
String s2 = String.valueOf(12.34);
String s3 = String.valueOf(true);
System.out.println(s1);
System.out.println(s2);
System.out.println(s3);
System.out.println("=================================");
// 字符串转数字
// 注意:Integer、Double等是Java中的包装类型
int data1 = Integer.parseInt("1234");
double data2 = Double.parseDouble("12.34");
System.out.println(data1);
System.out.println(data2);
}
}

2.大小写转换
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
String s1 = "HELLO";
System.out.println(s.toUpperCase());//小写转大写
System.out.println(s1.toLowerCase());//大写转小写
}
}

这两个函数只转换字母
3.字符串转数组
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
// 字符串转数组
char[] ch = s.toCharArray();
for (int i = 0; i < ch.length; i++) {
System.out.print(ch[i]);
}
System.out.println();
// 数组转字符串
String s2 = new String(ch);
System.out.println(s2);
}
}

4.格式化
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = String.format("%d-%d-%d", 2019, 9,14);
System.out.println(s);
}
}

5.字符串替换
使用一个指定的新的字符串替换掉已有的字符串数据,可用的方法如下:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| String replaceAll(String regex, String replacement) | 替换所有的指定内容 |
| String replaceFirst(String regex, String replacement) | 替换收个内容 |
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hellohello";
System.out.println(s.replaceAll("l", "z"));
System.out.println(s.replaceFirst("l", "z"));
}
}

注意事项: 由于字符串是不可变对象, 替换不修改当前字符串, 而是产生一个新的字符串
6.字符串拆分
可以将一个完整的字符串按照指定的分隔符划分为若干个子字符串
方法如下:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| String[] split(String regex) | 将字符串全部拆分 |
| String[] split(String regex, int limit) | 将字符串以指定的格式,拆分为limit组 |
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello word is you";
String[] s = str.split(" ");//按照空格拆分
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
System.out.println(s[i]);
}
}
}

public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "hello word is you";
String[] s = str.split(" ",2);//按照空格拆分成两份
for (int i = 0; i < s.length; i++) {
System.out.println(s[i]);
}
}
}

拆分是特别常用的操作. 一定要重点掌握. 另外有些特殊字符作为分割符可能无法正确切分, 需要加上转义
注意事项:
1.字符"|“,”*“,”+“都得加上转义字符,前面加上 “\”
2.而如果是 “” ,那么就得写成 “\\”
3.如果一个字符串中有多个分隔符,可以用”|"作为连字符
多次拆分:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "name=zhagnsan&age=10";
String[] s = str.split("&");
for (String ss:s) {
String[] ret = ss.split("=");
for (String sss:ret) {
System.out.println(sss);
}
}
}
}

7.字符串截取
从一个完整的字符串之中截取出部分内容
方法如下:
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| String substring(int beginIndex) | 从指定索引截取到结尾 |
| String substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) | 截取部分内容 |
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "helloword";
System.out.println(str.substring(5));
System.out.println(str.substring(0, 5));
}
}

注意事项:
1.索引从0开始
2.注意前闭后开区间的写法,substring(0,5)表示包含0下标的字符,不包含5下标的字符
8.其他操作方法
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| String trim() | 去掉字符串中的左右空格,保留中间空格 |
| String toUpperCase() | 字符串转大写 |
| String toLowerCase() | 字符串转小写 |
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = " hello word ";
System.out.println(str.trim());
}
}

trim 会去掉字符串开头和结尾的空白字符(空格, 换行, 制表符等)
9.字符串的不可变性
String是一种不可变对象. 字符串中的内容是不可改变。字符串不可被修改,是因为:
1.String类在设计时就是不可改变的,String类实现描述中已经说明了
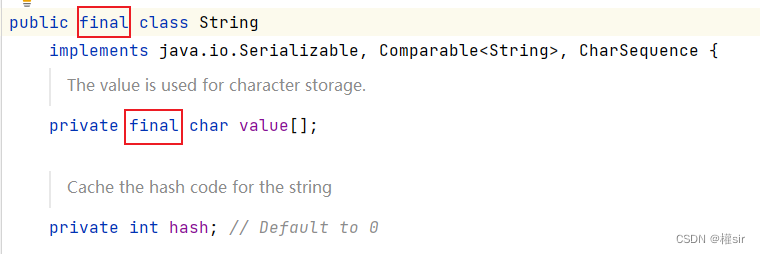
String类中的字符实际保存在内部维护的value字符数组中,从上图中可以看出:
1.String类被final修饰,表示该类不能被继承
2.value被final修饰,表明value自身的值不能改变,即不能引用其它字符数组,但是其引用空间中的内容可以修改
2. 所有涉及到可能修改字符串内容的操作都是创建一个新对象,改变的是新对象
字符串不可变是因为其内部保存字符的数组被final修饰了,因此不能改变。
这种说法是错误的,不是因为String类自身,或者其内部value被final修饰而不能被修改。
final修饰类表明该类不想被继承,final修饰引用类型表明该引用变量不能引用其他对象,但是其引用对象中的内容是可以修改的
10.字符串修改
注意: 尽量避免直接对String类型对象进行修改,因为String类是不能修改的,所有的修改都会创建新对象,效率非常低下
三、StringBuilder和StringBuffer
由于String的不可更改特性,为了方便字符串的修改,Java中又提供StringBuilder和StringBuffer类。这两个类大部分功能是相同的
| 方法 | 功能 |
|---|---|
| StringBuff append(String str) | 在尾部追加,相当于String的+=,可以追加:boolean、char、char[]、double、float、int、long、Object、String、StringBuff的变量 |
| char charAt(int index) | 获取index位置的字符 |
| int length() | 获取字符串的长度 |
| int capacity() | 获取底层保存字符串空间总的大小 |
| void ensureCapacity(int mininmumCapacity) | 扩容 |
| void setCharAt(int index,char ch) | 将index位置的字符设置为ch |
| int indexOf(String str) | 返回str第一次出现的位置 |
| int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始查找str第一次出现的位置 |
| int lastIndexOf(String str) | 返回最后一次出现str的位置 |
| int lastIndexOf(String str,int fromIndex) | 从fromIndex位置开始找str最后一次出现的位置 |
| StringBuff insert(int offset, String str) | 在offset位置插入:八种基类类型 & String类型 & Object类型数据 |
| StringBuffer deleteCharAt(int index) | 删除index位置字符 |
| StringBuffer delete(int start, int end) | 删除[start, end)区间内的字符 |
| StringBuffer replace(int start, int end, String str) | 将[start, end)位置的字符替换为str |
| String substring(int start) | 从start开始一直到末尾的字符以String的方式返回 |
| String substring(int start,int end) | 将[start, end)范围内的字符以String的方式返回 |
| StringBuffer reverse() | 反转字符串 |
| String toString() | 将所有字符按照String的方式返回 |
String和StringBuilder最大的区别在于String的内容无法修改,而StringBuilder的内容可以修改。频繁修改字符串的情况考虑使用StringBuilder
注意: String和StringBuilder类不能直接转换。如果要想互相转换,可以采用如下原则:
1.String变为StringBuilder: 利用StringBuilder的构造方法或append()方法
2.StringBuilder变为String: 调用toString()方法
String、StringBuffer、StringBuilder的区别
1.String的内容不可修改,StringBuffer与StringBuilder的内容可以修改.
2.StringBuffer与StringBuilder大部分功能是相似的
3.StringBuffer采用同步处理,属于线程安全操作;而StringBuilder未采用同步处理,属于线程不安全操作
