C++学习:C++类型转换专栏
对于C/C++这种强类型语言而言,类型转换是常态。
但是对于C++而言,类型转换又比C语言麻烦一些。
本期我们就来简单学习一下C++类型转换相关的知识
相关代码已经上传至作者个人gitee:楼田莉子/CPP代码学习喜欢请支持一下谢谢
目录
C语言类型转换
C++的类型转换
核心组件概览
智能指针(Smart Pointers)
std::unique_ptr - 独占所有权指针
std::weak_ptr - 弱引用指针
内存分配器(Allocators)
自定义内存分配
工具函数(Utility Functions)
std::addressof - 获取对象地址
std::align - 内存对齐
工厂函数
智能指针对比总结
应用场景
资源管理(RAII)
避免循环引用
C++中的强制显式类型转换
内存安全
C++中4种强制类型转换运算符
RAII
C语言类型转换
在C语⾔中,如果赋值运算符左右两侧类型不同,或者形参与实参类型不匹配,或者返回值类型与 接收返回值类型不⼀致时等场景,就需要发⽣类型转化。
C语⾔中总共有两种形式的类型转换:隐 式类型转换和显式强制类型转换。
隐式类型转化:编译器在编译阶段⾃动进⾏,能转就转,不能转就编译失败
显式强制类型转化:需要⽤⼾⾃去显⽰在变量前⽤括号指定要转换的类型。
并不是任意类型之前都⽀持转换,两个类型⽀持转换需要有⼀定关联性,也就是说转换后要有⼀定 的意义,两个毫⽆关联的类型是不⽀持转换的。
举例说明:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{int i = 1;// 隐式类型转换// 隐式类型转换主要发⽣在整形和整形之间,整形和浮点数之间,浮点数和浮点数之间double d = i;printf("%d, %.2f\n", i, d);int* p = &i;// 显⽰的强制类型转换// 强制类型转换主要发⽣在指针和整形之间,指针和指针之间int address = (int)p;printf("%p, %d\n", p, address);// malloc返回值是void*,被强转成int*int* ptr = (int*)malloc(8);// 编译报错:类型强制转换:⽆法从“int* ”转换为“double”// 指针是地址的编号,也是⼀种整数,所以可以和整形互相转换// 但是指针和浮点数毫⽆关联,强转也是不⽀持的// d = (double)p;return 0;
}C++的类型转换
C++兼容C,所以C⽀持的隐式类型转换和显式强制类型转换C++都⽀持。
单参数类型转换。下图所示的为隐式类型转换
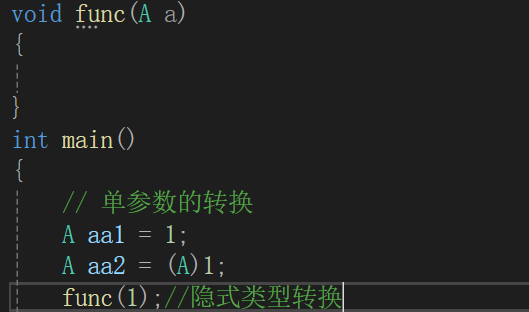
C++还⽀持内置类型到⾃定义类型之间的转换,内置类型转成⾃定义类型需要构造函数的⽀持,⾃定义类型转成内置类型,需要⼀个operator类型()的函数去⽀持。
C++还⽀持⾃定义类型到⾃定义类型之间的转换,需要对应类型的构造函数⽀持即可,⽐如A类型对 象想转成B类型,则⽀持⼀个形参为A类型的B构造函数即可⽀持。
自定义类型转换示例:
//test.cpp
#include"list.h"
using namespace std;
void test2()
{Boogiepop::list<int> lt = { 1,2,3,4,5 };//权限缩⼩?权限缩⼩和放⼤,仅限于const的指针和引⽤//这⾥不是权限缩⼩,这⾥是⾃定义类型=⾃定义类型之间的类型转换//具体实现看下⾯ListIterator中对应的构造函数的实现Boogiepop::list<int>::const_iterator cit = lt.begin();while (cit != lt.end()){cout << *cit << " ";++cit;}cout << endl;
}
int main()
{test2();return 0;
}
//list.h
#pragma once
#include <assert.h>
#include <initializer_list>
using namespace std;
namespace Boogiepop
{template<class T>struct ListNode{ListNode<T>* _next;ListNode<T>* _prev;T _data;ListNode(const T& data = T()):_next(nullptr), _prev(nullptr), _data(data){}};template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>struct ListIterator{typedef ListNode<T> Node;typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;Node* _node;ListIterator(Node* node):_node(node){}// typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;// typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;// ListIterator实例化为iterator时,这个函数是拷⻉构造// ListIterator实例化为const_iterator时,// 这个函数⽀持iterator转换为const_iterator构造函数ListIterator(const ListIterator<T, T&, T*>& it):_node(it._node){}// ++it;Self& operator++(){_node = _node->_next;return *this;}// --it;Self& operator--(){_node = _node->_prev;return *this;}// it++Self operator++(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_next;return tmp;}// 修正2:后置递减运算符返回Self而不是Self&Self operator--(int){Self tmp(*this);_node = _node->_prev;return tmp;}Ref operator*(){return _node->_data;}Ptr operator->(){return &_node->_data;}bool operator!=(const Self& it){return _node != it._node;}bool operator==(const Self& it){return _node == it._node;}};template<class T>class list{typedef ListNode<T> Node;public://同⼀个类模板给不同参数会实例化出不同的类型typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator;iterator begin(){return iterator(_head->_next);}const_iterator begin() const{return const_iterator(_head->_next);}iterator end(){return iterator(_head);}const_iterator end() const{return const_iterator(_head);}void empty_init(){_head = new Node();_head->_next = _head;_head->_prev = _head;}list(){empty_init();}// 修正3:添加std::命名空间限定list(std::initializer_list<T> il){empty_init();for (const auto& e : il){push_back(e);}}void push_back(const T& x){insert(end(), x);}// 没有iterator失效iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x){Node* cur = pos._node;Node* newnode = new Node(x);Node* prev = cur->_prev;// prev newnode curprev->_next = newnode;newnode->_prev = prev;newnode->_next = cur;cur->_prev = newnode;return iterator(newnode);}private:Node* _head;};
}C++头文件<memory>
<memory> 头文件是 C++ 标准库中用于智能内存管理的核心头文件,提供了自动内存管理的工具,避免手动内存管理带来的问题。
核心组件概览
| 组件 | 功能 | 特点 |
|---|---|---|
| 智能指针 | 自动内存管理 | 防止内存泄漏,自动释放资源 |
| 内存分配器 | 自定义内存分配 | 控制内存分配策略 |
| 工具函数 | 内存操作辅助 | 提供安全的内存操作工具 |
<memory> 头文件中常见函数的主要作用
| 函数名 | 主要作用 | 引入版本 | 特点 | 使用示例 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
std::make_unique | 创建 std::unique_ptr 智能指针 | C++14 | 异常安全,避免直接使用 new | auto ptr = make_unique<MyClass>(args); |
std::make_shared | 创建 std::shared_ptr 智能指针 | C++11 | 单次内存分配,效率更高 | auto ptr = make_shared<MyClass>(args); |
std::make_shared_for_overwrite | 创建未初始化的 shared_ptr | C++20 | 避免值初始化开销 | auto ptr = make_shared_for_overwrite<T>(); |
std::make_unique_for_overwrite | 创建未初始化的 unique_ptr | C++20 | 避免值初始化开销 | auto ptr = make_unique_for_overwrite<T>(); |
std::allocate_shared | 使用自定义分配器创建 shared_ptr | C++11 | 控制内存分配策略 | auto ptr = allocate_shared<T>(alloc, args); |
std::addressof | 获取对象的真实地址 | C++11 | 绕过 operator& 重载 | T* p = addressof(obj); |
std::align | 内存对齐调整 | C++11 | 在缓冲区中对齐指针 | align(alignment, size, ptr, space); |
智能指针(Smart Pointers)
std::unique_ptr - 独占所有权指针
#include <memory>
#include <iostream>class MyClass {
public:MyClass(int value) : data(value) {std::cout << "MyClass constructed: " << data << std::endl;}~MyClass() {std::cout << "MyClass destroyed: " << data << std::endl;}void print() { std::cout << "Value: " << data << std::endl; }
private:int data;
};void unique_ptr_example() {// 创建 unique_ptrstd::unique_ptr<MyClass> ptr1 = std::make_unique<MyClass>(42);ptr1->print();// 所有权转移(移动语义)std::unique_ptr<MyClass> ptr2 = std::move(ptr1);if (!ptr1) {std::cout << "ptr1 现在为空" << std::endl;}ptr2->print();// 自动释放内存,无需手动 delete
} std::shared_ptr - 共享所有权指针
#include <memory>void shared_ptr_example() {// 创建 shared_ptrstd::shared_ptr<MyClass> ptr1 = std::make_shared<MyClass>(100);{std::shared_ptr<MyClass> ptr2 = ptr1; // 共享所有权std::cout << "引用计数: " << ptr1.use_count() << std::endl; // 2ptr2->print();} // ptr2 离开作用域,引用计数减1std::cout << "引用计数: " << ptr1.use_count() << std::endl; // 1ptr1->print();// 当最后一个 shared_ptr 销毁时,对象自动释放
} std::weak_ptr - 弱引用指针
#include <memory>void weak_ptr_example() {std::shared_ptr<MyClass> shared = std::make_shared<MyClass>(200);std::weak_ptr<MyClass> weak = shared;std::cout << "引用计数: " << shared.use_count() << std::endl; // 1// 使用 weak_ptr 前需要转换为 shared_ptrif (auto temp = weak.lock()) {temp->print(); // 对象还存在} else {std::cout << "对象已被释放" << std::endl;}shared.reset(); // 释放对象if (auto temp = weak.lock()) {temp->print();} else {std::cout << "对象已被释放" << std::endl; // 这里会执行}
}内存分配器(Allocators)
自定义内存分配
#include <memory>
#include <vector>template<typename T>
class CustomAllocator {
public:using value_type = T;CustomAllocator() = default;template<typename U>constexpr CustomAllocator(const CustomAllocator<U>&) noexcept {}T* allocate(std::size_t n) {std::cout << "分配 " << n << " 个元素" << std::endl;return static_cast<T*>(::operator new(n * sizeof(T)));}void deallocate(T* p, std::size_t n) noexcept {std::cout << "释放 " << n << " 个元素" << std::endl;::operator delete(p);}
};void allocator_example() {// 使用自定义分配器的 vectorstd::vector<int, CustomAllocator<int>> vec;vec.push_back(1);vec.push_back(2);vec.push_back(3);
}工具函数(Utility Functions)
std::addressof - 获取对象地址
#include <memory>class WeirdClass {
public:WeirdClass* operator&() { // 重载了 & 运算符return nullptr;}
};void addressof_example() {WeirdClass obj;WeirdClass* p1 = &obj; // 使用重载的 &,得到 nullptrWeirdClass* p2 = std::addressof(obj); // 得到真实地址std::cout << "重载&: " << p1 << std::endl; // 0std::cout << "addressof: " << p2 << std::endl; // 真实地址
} std::align - 内存对齐
#include <memory>void align_example() {char buffer[100];std::size_t space = sizeof(buffer);void* ptr = buffer;// 尝试在 buffer 中寻找对齐到 16 字节边界的地址if (std::align(16, 50, ptr, space)) {std::cout << "对齐成功: " << ptr << std::endl;std::cout << "剩余空间: " << space << std::endl;}
}工厂函数
std::make_unique 和 std::make_shared
#include <memory>class Resource {
public:Resource(int a, int b, int c) : x(a), y(b), z(c) {}void show() {std::cout << "Resource: " << x << ", " << y << ", " << z << std::endl;}
private:int x, y, z;
};void factory_functions_example() {// C++14 引入 make_uniqueauto unique = std::make_unique<Resource>(1, 2, 3);unique->show();// C++11 引入 make_shared(更高效,引用计数和对象在同一内存块)auto shared = std::make_shared<Resource>(4, 5, 6);shared->show();// 对比传统 newstd::shared_ptr<Resource> old_way(new Resource(7, 8, 9)); // 不推荐
}智能指针对比总结
| 特性 | unique_ptr | shared_ptr | weak_ptr |
|---|---|---|---|
| 所有权 | 独占 | 共享 | 无所有权 |
| 拷贝 | 不允许 | 允许 | 允许 |
| 移动 | 允许 | 允许 | 允许 |
| 引用计数 | 无 | 有 | 观察计数 |
| 性能 | 接近裸指针 | 有额外开销 | 有额外开销 |
| 适用场景 | 独占资源 | 共享资源 | 打破循环引用 |
应用场景
资源管理(RAII)
#include <memory>
#include <fstream>class FileHandler {
private:std::unique_ptr<std::fstream> file;
public:FileHandler(const std::string& filename) : file(std::make_unique<std::fstream>(filename)) {if (!file->is_open()) {throw std::runtime_error("无法打开文件");}}// 自动关闭文件,无需手动调用 close()
};void raii_example() {try {FileHandler handler("data.txt");// 使用文件...} catch (const std::exception& e) {std::cout << "错误: " << e.what() << std::endl;}// 文件自动关闭
}避免循环引用
#include <memory>class Node {
public:std::string name;std::shared_ptr<Node> parent;std::weak_ptr<Node> child; // 使用 weak_ptr 避免循环引用Node(const std::string& n) : name(n) {}~Node() {std::cout << "销毁节点: " << name << std::endl;}
};void cycle_reference_example() {auto node1 = std::make_shared<Node>("父节点");auto node2 = std::make_shared<Node>("子节点");node1->child = node2; // 弱引用node2->parent = node1; // 强引用// 可以正常释放,不会内存泄漏
}C++中的强制显式类型转换
内存安全
类型安全是指编程语⾔在编译和运⾏时提供保护机制,避免⾮法的类型转换和操作,导致出现⼀个 内存访问错误等,从⽽减少程序运⾏时的错误。
C语⾔不是类型安全的语⾔,C语⾔允许隐式类型转换,⼀些特殊情况下就会导致越界访问的内存错 误,其次不合理的使⽤强制类型转换也会导致问题,⽐如⼀个int*的指针强转成double*访问就会 出现越界。
C++兼容C语⾔,⽀持隐式类型转换和强制类型转换,C++也不是类型安全的语⾔,C++提出4个显 ⽰的命名强制类型转换
static_cast/reinterpret_cast/const_cast/dynamic_cast就是为了让类型转 换相对⽽⾔更安全。
void insert(size_t pos, char ch)
{//这⾥当pos == 0时,就会引发由于隐式类型转换// end跟pos⽐较时,提升为size_t导致判断结束逻辑出现问题// 在数组中访问挪动数据就会出现越界,经典的类型安全问题int end = 10;while (end >= pos){// ...cout << end << endl; --end;}
}
void test3()
{insert(5, 'x');//insert(0, 'x');// 这⾥会本质已经出现了越界访问,只是越界不⼀定能被检查出来int x = 100;double* p1 = (double*)&x;cout << *p1 << endl;const int y = 0;//可以利用关键字volatile来避免优化int* p2 = (int*)&y;(*p2) = 1;// 这⾥打印的结果是1和 0,也是因为我们类型转换去掉了const属性// 但是编译器认为 y是const的,不会被改变,所以会优化编译时放到// 寄存器或者直接替换y为0导致的volatile const int z = 0;int* p3 = (int*)&z;(*p3) = 1;// 这⾥打印的结果是1和 0,也是因为我们类型转换去掉了const属性cout << *p2 << endl;cout << y << endl;cout << *p3 << endl;cout << z << endl;
}C++中4种强制类型转换运算符
static_cast⽤于两个类型意义相近的转换,这个转换是具有明确定义的,只要底层不包含const, 都可以使⽤static_cast。
reinterpret_cast⽤于两个类型意义不相近的转换,reinterpret是重新解释的意思,通常为运算对 象的位模式提供较低层次上的重新解释,也就是说转换后对原有内存的访问解释已经完全改变了, ⾮常的⼤胆。所以我们要谨慎使⽤,清楚知道这样转换是没有内存访问安全问题的。
const_cast⽤于const类型到⾮const类型的转换,去掉了const属性,也是⼀样的我们要谨慎使 ⽤,否则可能会出现意想不到的结果。
dynamic_cast⽤于将基类的指针或者引⽤安全的转换成派⽣类的指针或者引⽤。如果基类的指针 或者引⽤时指向派⽣类对象的,则转换回派⽣类指针或者引⽤时可以成功的,如果基类的指针指向 基类对象,则转换失败返回nullptr,如果基类引⽤指向基类对象,则转换失败,抛出bad_cast异 常。
其次dynamic_cast要求基类必须是多态类型,也就是基类中必须有虚函数。因为dynamic_cast是 运⾏时通过虚表中存储的type_info判断基类指针指向的是基类对象还是派⽣类对象。
void test1()
{// 对应隐式类型转换--数据的解释意义没有改变double d = 12.34;int a = static_cast<int>(d);cout << a << endl;int&& ref = static_cast<int&&>(a);// 对应强制类型转换--数据的解释意义已经发⽣改变int* p1 = reinterpret_cast<int*>(a);// 对应强制类型转换中有⻛险的去掉const属性// 所以要注意加volatilevolatile const int b = 0;int* p2 = const_cast<int*>(&b);*p2 = 1;cout << b << endl;cout << *p2 << endl;// 对应类型名查询cout << typeid(d).name() << endl;cout<<typeid(a).name()<<endl;cout << typeid(ref).name() << endl;cout << typeid(p1).name() << endl;cout << typeid(p2).name() << endl;cout<<typeid(b).name()<<endl;
}结果为:

void fun1(A* pa)
{// 指向⽗类转换时有⻛险的,后续访问存在越界访问的⻛险// 指向⼦类转换时安全B* pb1 = (B*)pa;cout << "pb1:" << pb1 << endl;cout << pb1->_a << endl;cout << pb1->_b << endl;pb1->_a++;pb1->_b++;cout << pb1->_a << endl;cout << pb1->_b << endl;
}
void fun2(A* pa)
{// dynamic_cast会先检查是否能转换成功(指向⼦类对象),能成功则转换,// (指向⽗类对象)转换失败则返回nullptrB* pb1 = dynamic_cast<B*>(pa);if (pb1){cout << "pb1:" << pb1 << endl;cout << pb1->_a << endl;cout << pb1->_b << endl;pb1->_a++;pb1->_b++;cout << pb1->_a << endl;cout << pb1->_b << endl;}else{cout << "转换失败" << endl;}
}
void fun3(A& pa)
{// 转换失败,则抛出bad_cast异常try {B& pb1 = dynamic_cast<B&>(pa);cout << "转换成功" << endl;}catch (const exception& e){cout << e.what() << endl;}
}
void test2()
{A a;B b;//fun1(&a);//fun1(&b);fun2(&a);fun2(&b);fun3(a);fun3(b);
}RAII
RTTI的英⽂全称是"RuntimeTypeIdentification",中⽂称为"运⾏时类型识别",它指的是程序在 运⾏的时候才确定需要⽤到的对象是什么类型的。⽤于在运⾏时(⽽不是编译时)获取有关对象的 信息。
RTTI主要由两个运算符实现,typeid和dynamic_cast;typeid主要⽤于返回表达式的类型, dynamic_cast前⾯已经讲过了,主要⽤于将基类的指针或者引⽤安全的转换成派⽣类的指针或者 引⽤。
typeid(e)中e可以是任意表达式或类型的名字,typeid(e)的返回值是typeinfo或typeinfo派⽣类对 象的引⽤,typeinfo可以只⽀持⽐较等于和不等于,name成员函数可以返回C⻛格字符串表⽰对象 类型名字,typeinfo的精确定义随着编译器的不同⽽略有差异,也就以为着同⼀个e表达式,不同 编译器下,typeid(e).name()返回的名字可能是不⼀样的。
typeinfo的⽂档如下:<typeinfo> - C++参考
typeid(e)时,当运算对象不属于类类型或者是⼀个不包含任何虚函数的类时,typeid返回的是运算 对象的静态类型,当运算对象是定义了⾄少⼀个虚函数的类的左值时,typeid的返回结果直到运⾏ 时才会求得。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <typeinfo>
#include <exception>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
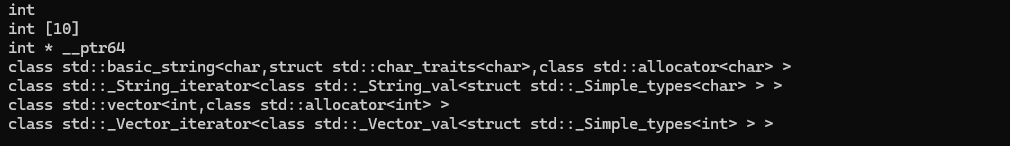
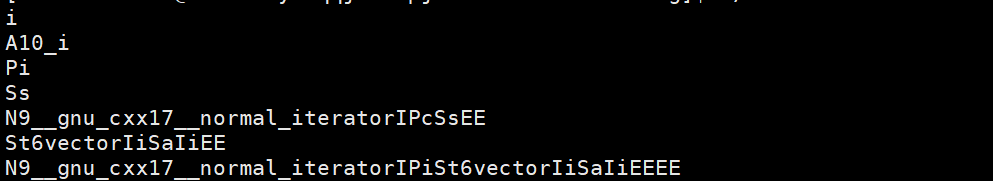
int main()
{int a[10];int* ptr = nullptr;cout << typeid(10).name() << endl;cout << typeid(a).name() << endl;cout << typeid(ptr).name() << endl;cout << typeid(string).name() << endl;cout << typeid(string::iterator).name() << endl;cout << typeid(vector<int>).name() << endl;cout << typeid(vector<int>::iterator).name() << endl;return 0;
}vs2022下结果为:
g++编辑器下运行结果为:
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:virtual void func(){}
protected:int _a1 = 1;
};
class B : public A
{
protected:int _b1 = 2;
};
int main()
{try{B* pb = new B;A* pa = (A*)pb;if (typeid(*pb) == typeid(B)){cout << "typeid(*pb) == typeid(B)" << endl;}// 如果 A 和 B不是继承关系,则会抛 bad_typeid异常if (typeid(*pa) == typeid(B)){cout << "typeid(*pa) == typeid(B)" << endl;}// 这⾥ pa 和 pb是 A* 和 B*,不是类类型对象,他会被当做编译是求值的静态类型运算// 所以这⾥始终是不相等的if (typeid(pa) == typeid(pb)){cout << "typeid(pa) == typeid(B)" << endl;}}catch (const std::exception& e){cout << e.what() << endl;}return 0;
}结果为:

本期内容就到这里了,喜欢请点个赞谢谢
封面图自取:

