Heteroskedasticity
Heteroskedasticity come from


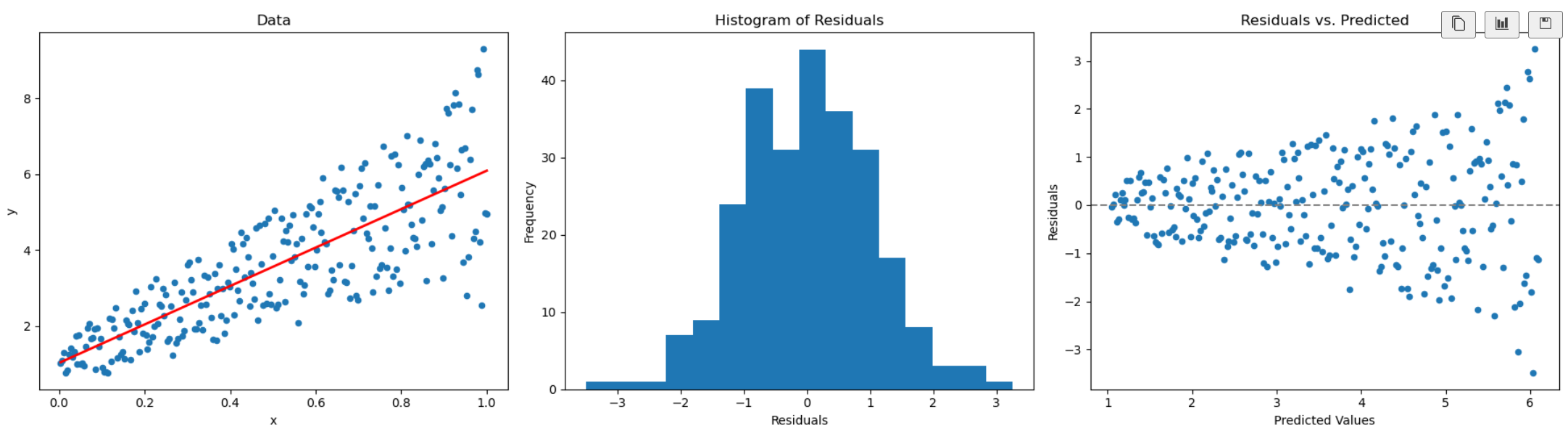
The passage is describing heteroskedasticity, a situation where the variance of the error term ( ϵ\epsilonϵ ) is not constant but depends on the explanatory variable (x).
In ordinary regression we usually assume homoskedasticity: (Var(ϵ)=σ2\text{Var}(\epsilon) = \sigma^2Var(ϵ)=σ2), the same for all values of (x)(x)(x). But here, the idea is that when (x) is large in magnitude, the spread (variance) of the errors is also larger. In probabilistic terms, if (Var(ϵ)\text{Var}(\epsilon)Var(ϵ)) grows with (x), then the probability that (ϵ\epsilonϵ) takes on large positive or negative values increases as (x) increases.
Consequences of heteroskedasticity

the equation (221) is ∑i=1n(xi−xˉ)2\sum_{i=1}^n(x_{i}-\bar{x})^2∑i=1n(xi−xˉ)2 in the denominator
the equation (222) is [∑i=1n(xi−xˉ)2]2[\sum_{i=1}^n(x_{i}-\bar{x})^2]^2[∑i=1n(xi−xˉ)2]2 in the denominator
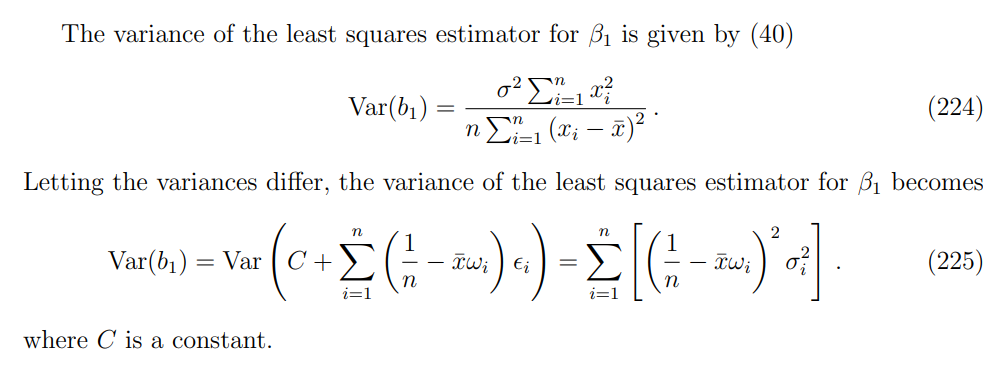
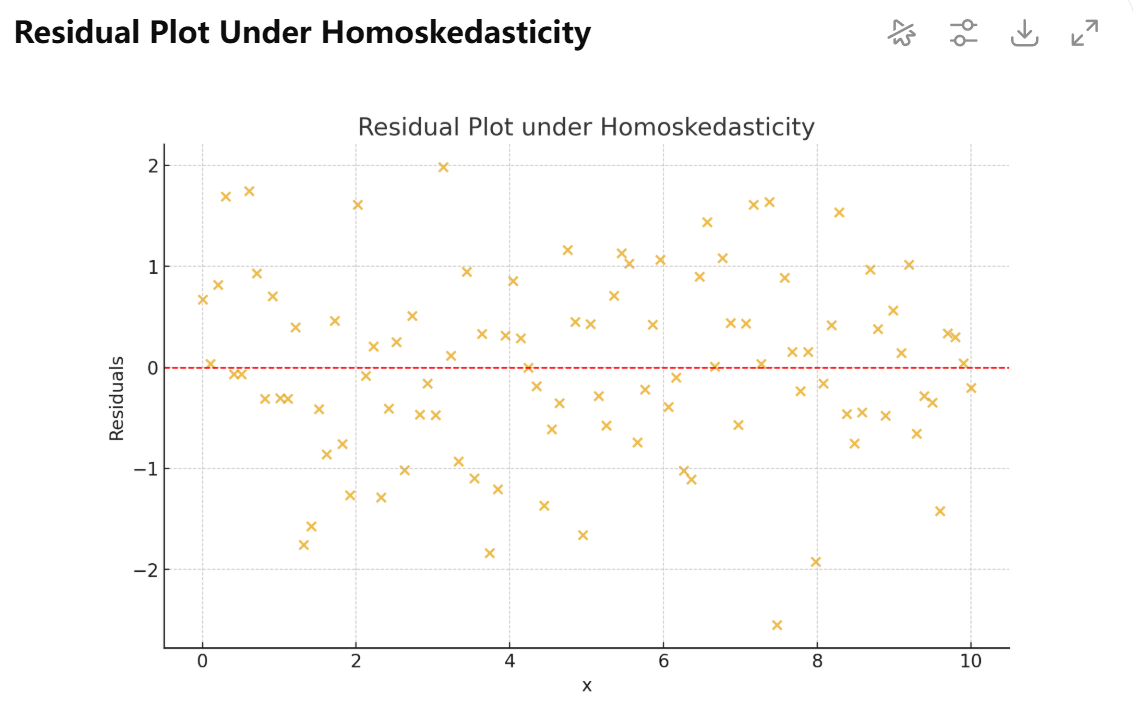
Detecting heteroskedasticity


Formal statistical tests

注意这里是对yiy_iyi的方差,也是error平方的期望.
下面这里是真实的error平方.

The White Test


1. White 检验的特点
-
不需要假设异方差的具体形式:
和 Breusch–Pagan 不同,BP 假设方差和解释变量的线性关系;White 则允许更一般的关系(比如平方项、交互项),所以更灵活。 -
不要求误差服从正态分布:
White 检验基于大样本渐近理论,不依赖于正态性假设。
2. 局限性
-
拒绝零假设 ≠ 一定有异方差:
White 检验本质上是在检验“模型是否被正确设定”。所以如果模型有遗漏变量、函数形式错了,它也可能拒绝零假设。
换句话说,它可能把“模型设定错误”当成“异方差”。 -
过于一般:
-
优点:几乎任何形式的异方差都能检测出来。
-
缺点:敏感度太高,有时会报“假阳性”,让人以为是异方差,实际上是模型设定的问题。
-
