Leetcode 深度优先搜索 (11)
113. 路径总和 II
给你二叉树的根节点 root 和一个整数目标和 targetSum ,找出所有 从根节点到叶子节点 路径总和等于给定目标和的路径。
示例 1:
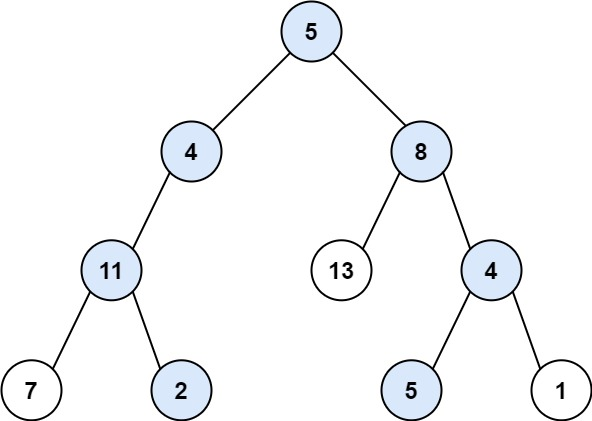
输入: root = [5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,5,1], targetSum = 22
输出: [[5,4,11,2],[5,8,4,5]]
深度优先搜索(DFS)递归回溯思路
- 从根节点出发,递归遍历每一条路径。
- 用一个列表记录当前路径上的节点值。
- 每到一个节点,将其值加入路径列表,并累加到当前路径和。
- 如果到达叶子节点且路径和等于目标和,则将当前路径的副本加入结果集。
- 递归返回时,需要将当前节点值从路径列表中移除(回溯)。
- 最终返回所有满足条件的路径。
public class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();dfs(root, targetSum, path, res);return res;}private void dfs(TreeNode node, int targetSum, List<Integer> path, List<List<Integer>> res) {if (node == null) return;path.add(node.val);targetSum -= node.val;if (node.left == null && node.right == null && targetSum == 0) {res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));}dfs(node.left, targetSum, path, res);dfs(node.right, targetSum, path, res);path.remove(path.size() - 1); // 回溯}
}
深度优先搜索(DFS)非递归(栈模拟)
深度优先搜索(DFS)非递归(栈模拟)方法利用栈来模拟递归过程。每次将当前节点、当前路径和、当前路径列表一起压入栈中。遍历时弹出栈顶元素,判断是否为叶子节点且路径和等于目标和,如果是则将路径加入结果集。否则,将左右子节点连同更新后的路径和路径列表压入栈中。这样可以避免递归带来的栈溢出风险。
class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null) return result;// 栈中存储:当前节点、当前路径和、当前路径Deque<Object[]> stack = new ArrayDeque<>();stack.push(new Object[]{root, root.val, new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(root.val))});while (!stack.isEmpty()) {Object[] tuple = stack.pop();TreeNode node = (TreeNode) tuple[0];int sum = (int) tuple[1];List<Integer> path = (List<Integer>) tuple[2];// 判断是否为叶子节点且路径和等于目标和if (node.left == null && node.right == null && sum == targetSum) {result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));}// 右子节点先入栈if (node.right != null) {List<Integer> newPath = new ArrayList<>(path);newPath.add(node.right.val);stack.push(new Object[]{node.right, sum + node.right.val, newPath});}// 左子节点后入栈if (node.left != null) {List<Integer> newPath = new ArrayList<>(path);newPath.add(node.left.val);stack.push(new Object[]{node.left, sum + node.left.val, newPath});}}return result;}
}
广度优先搜索(BFS)
广度优先搜索(BFS)用于本题时,通常用队列来存储节点、当前路径和路径和。每次从队列取出一个节点,判断是否为叶子节点且路径和等于目标和,如果是则将路径加入结果集。否则,将其左右子节点和对应的路径、路径和加入队列。
public class Solution {public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();if (root == null) return result;// 队列存储:当前节点、到该节点的路径、路径和Queue<TreeNode> nodeQueue = new LinkedList<>();Queue<List<Integer>> pathQueue = new LinkedList<>();Queue<Integer> sumQueue = new LinkedList<>();nodeQueue.offer(root);pathQueue.offer(new ArrayList<>(Arrays.asList(root.val)));sumQueue.offer(root.val);while (!nodeQueue.isEmpty()) {TreeNode node = nodeQueue.poll();List<Integer> path = pathQueue.poll();int sum = sumQueue.poll();// 如果是叶子节点且路径和等于目标和if (node.left == null && node.right == null && sum == targetSum) {result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));}// 左子节点if (node.left != null) {nodeQueue.offer(node.left);List<Integer> newPath = new ArrayList<>(path);newPath.add(node.left.val);pathQueue.offer(newPath);sumQueue.offer(sum + node.left.val);}// 右子节点if (node.right != null) {nodeQueue.offer(node.right);List<Integer> newPath = new ArrayList<>(path);newPath.add(node.right.val);pathQueue.offer(newPath);sumQueue.offer(sum + node.right.val);}}return result;}
}
