python -基础(5)组合数据类型

一:序列和索引
1:属于序列结构:字符串,列表,元组,集合和字典
2:有序序列:列表,元组
3:无序序列:集合,字典
4:组合数据类型:列表,字典,集合,元组
5:只要有序列就会有索引
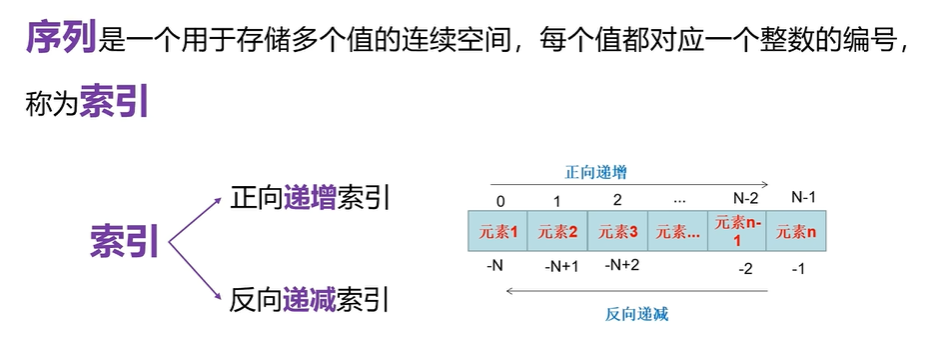
#获取字符串中某个元素 变量[索引]
#1:正向递增
word = 'helloword'
for i in range(1,10):print(i,word[i],end='\t\t')
print()#2:反向递减
for i in range(-9,0):print(i,word[i],end='\t\t')
print('\n',word[0],word[-9])1.2:序列的相关操作
1: 切片操作的语法结构
1:切片可以适用于所有的序列类型
2:切片是访问序列元素的一种方法,但是访问的不是一个,而是一定范围的元素
3:通过切片操作可以生成一个新的序列
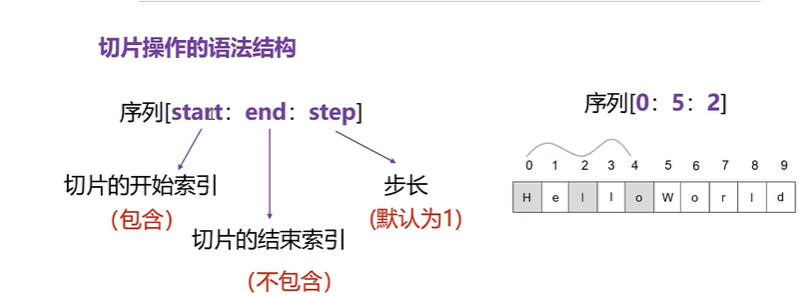
word = 'helloword'
#1:切片操作
# 索引从0开始,到5结束(不包含5)步长为2
word_01 = word[0:5:2]
print(word_01) #hlo#2:省略开始位置,start默认从0开始
print(word[:5:1]) #hello#3:省略开始位置start,省略步长step (默认为1)
print(word[:5:]) #hello#4:省略结束位置
#stop,默认到序列的最后一个元素(包含最后一个元素)
print(word[0::1]) #helloword#5:省略结尾,步长
print(word[5::1])
print(word[5::]) #这两结果一样#6:更改步长
print(word[0:5:2])#7:省略开始,结束位置,只写步长
print(word[::2]) #hlood#8:省略开始,结束位置,步长为负数
print(word[::-1]) #drowolleh
#替换
print(word[-1:-11:-1]) #drowolleh2:序列的其他操作
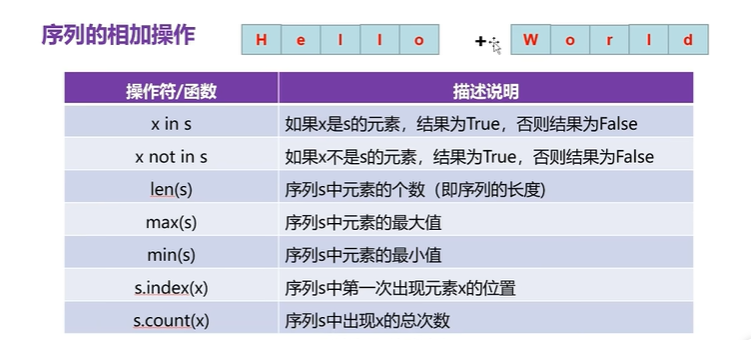
# 序列的相加操作
a = 'hello'
b = 'word'
print(a+b)#2:序列的相乘操作
print(a*5)
print('-'*40)#3:in
c = 'helloword'
print('e在hellowolrd中存在吗',('e' in c))
print('e在hellowolrd中存在吗',('a'in c))#4:not in
print('e在hellowolrd中存在吗',('e' not in c))
print('e在hellowolrd中存在吗',('a' not in c))#5:内置函数
print('len()',len(c))
print('max()',max(c)) #按照ascii码计算的
print('max()',min(c))#6:序列对象的方法,使用序列(对象的名称;打点调用的称为方法
print('c.index():',c.index('o')) #o在c中第一次出现的索引位置# print('c.index():',c.index('a')) #ValueError:substring not found ,报错的原因是v在字符串中根本不存在,不存在所以找不到
print('c.count():',c.count('o'))二:列表类型(组合数据类型)
1:列表是指一系列的按特定顺序排序的元素组成
2:是Python中内置的可变序列
3:是Python中使用【】定义列表,元素与元素之间使用英文的逗号分隔
4:列表中的元素可以是任意的数据类型(多个)
不可变的数据类型(可变序列):字符串,整数,元组,浮点数
可变数据类型(序列):列表
1:列表的创建,删除,函数使用

#1:直接使用[]创建列表
lst = ['hello','word',98,100.5]
print(lst)#2:使用内置函数list()创建列表
lst2 = list('hello')
lst3 = list(range(1,10,2)) #从1开始,到10结束,步长2
print(lst2)
print(lst3)#列表是序列中的一种,对序列的操作符,运算符,函数均可使用
print(lst+lst2+lst3) #序列中的相加操作
print(lst*3) #序列中的相乘操作
print(len(lst))
print(max(lst2))
print(min(lst3))print(lst2.count('l')) #统计个数
print(lst2.index('o')) #o在列表中第一次出现的位置#3:列表的删除操作
lst5 = [10,20,30]
print(lst5)del lst5
print(lst5)2:enumerate函数的使用语法结构
1:for index,item in enumerate(lst):
输出index和item
2: index是序号,不是索引,默认从0开始,可以指定位置
3:item(元素)
列表的遍历操作:
1:for循环
2:for + 索引
3:enumerate
