Nginx 高级配置
四 Nginx 高级配置
4.1 Nginx 状态页
- 基于nginx 模块 ngx_http_stub_status_module 实现,
- 在编译安装nginx的时候需要添加编译参数 --with-http_stub_status_module
- 否则配置完成之后监测会是提示法错误
注意: 状态页显示的是整个服务器的状态,而非虚拟主机的状态
\
#配置示例:
[root@nginx ~]# cd /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/
[root@nginx conf.d]# vi vhost.confserver{listen 80;server_name tomcat.gee.org;root /web/html;index index.html;location /status {stub_status;auth_basic "stauts page";auth_basic_user_file /usr/local/nginx/.htpasswd; #做认证,不允许所有人随意访问}}#状态页用于输出nginx的基本状态信息: #输出信息示例: Active connections: 291 server accepts handled requests 16630948 16630948 31070465 上面三个数字分别对应accepts,handled,requests三个值 Reading: 6 Writing: 179 Waiting: 106 Active connections: #当前处于活动状态的客户端连接数 #包括连接等待空闲连接数=reading+writing+waiting accepts: #统计总值,Nginx自启动后已经接受的客户端请求连接的总数。 handled: #统计总值,Nginx自启动后已经处理完成的客户端请求连接总数 #通常等于accepts,除非有因worker_connections限制等被拒绝的 连接 requests: #统计总值,Nginx自启动后客户端发来的总的请求数Reading: #当前状态,正在读取客户端请求报文首部的连接的连接数 #数值越大,说明排队现象严重,性能不足 Writing: #当前状态,正在向客户端发送响应报文过程中的连接数,数值越大,说明 访问量很大 Waiting: #当前状态,正在等待客户端发出请求的空闲连接数 开启 keep-alive的情况下,这个值等于active – (reading+writing)

4.2 Nginx 压缩功能
Nginx支持对指定类型的文件进行压缩然后再传输给客户端,而且压缩还可以设置压缩比例,压缩后的文 件大小将比源文件显著变小,样有助于降低出口带宽的利用率,降低企业的IT支出,不过会占用相 应的CPU资源。
Nginx对文件的压缩功能是依赖于模块 ngx_http_gzip_module,默认是内置模块
配置指令如下:
#启用或禁用gzip压缩,默认关闭
gzip on | off;
#压缩比由低到高从1到9,默认为1,值越高压缩后文件越小,但是消耗cpu比较高。基本设定未4或者5
gzip_comp_level 4;
#禁用IE6 gzip功能,早期的IE6之前的版本不支持压缩
gzip_disable "MSIE [1-6]\.";
#gzip压缩的最小文件,小于设置值的文件将不会压缩
gzip_min_length 1k;
#启用压缩功能时,协议的最小版本,默认HTTP/1.1
gzip_http_version 1.0 | 1.1;
#指定Nginx服务需要向服务器申请的缓存空间的个数和大小,平台不同,默认:32 4k或者16 8k;
gzip_buffers number size;
#指明仅对哪些类型的资源执行压缩操作;默认为gzip_types text/html,不用显示指定,否则出错
gzip_types mime-type ...;
#如果启用压缩,是否在响应报文首部插入“Vary: Accept-Encoding”,一般建议打开
gzip_vary on | off;
#预压缩,即直接从磁盘找到对应文件的gz后缀的式的压缩文件返回给用户,无需消耗服务器CPU
#注意: 来自于ngx_http_gzip_static_module模块
gzip_static on | off;
示例:
#重启nginx并进行访问测试压缩功能[root@Nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
@@@@省略内容@@@@
gzip on;
gzip_comp_level 5;
gzip_min_length 5k;:
gzip_vary on;
#重启Nginx并访问测试:
[root@nginx ~]# curl --head --compressed tomcat.gee.org/small.html
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.24.0
Date: Tue, 12 Aug 2025 12:23:15 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 6
Last-Modified: Tue, 12 Aug 2025 12:16:17 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
ETag: "689b3091-6"
Accept-Ranges: bytes[root@nginx ~]# curl --head --compressed lee.timinglee.org/data/data.txt
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.26.1
Date: Sun, 21 Jul 2024 15:43:17 GMT
Content-Type: text/plain
Last-Modified: Sun, 21 Jul 2024 15:40:13 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
Vary: Accept-Encoding
ETag: W/"669d2bdd-3e25b5"
Content-Encoding: gzip


4.3 Nginx的版本隐藏
用户在访问nginx的时候,我们可以从报文中获得nginx的版本,相对于裸漏版本号的nginx,我们把其隐 藏起来更安全
[root@Nginx nginx-1.26.1]# vim src/core/nginx.h
#define nginx_version 1026001
#define NGINX_VERSION "1.0"
#define NGINX_VER "HAHA/" NGINX_VERSION
4.4 Nginx 变量使用
- nginx的变量可以在配置文件中引用,作为功能判断或者日志等场景使用
- 变量可以分为内置变量和自定义变量
- 内置变量是由nginx模块自带,通过变量可以获取到众多的与客户端访问相关的值。
#echo插件需要重新编译才能使用,把之前编译好的nginx-1.24.0的文件删除,重新编译
./configure--prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_v2_module --with-http_realip_module --with-http_stub_status_module --with-http_gzip_static_module --with-pcre --with-stream --with-stream_ssl_module --with-stream_realip_module --add-module=/root/echo-nginx-module-0.63 #写解压的真死

4.4.1 内置变量
官方文档:http://nginx.org/en/docs/varindex.html
常用内置变量
$remote_addr;
#存放了客户端的地址,注意是客户端的公网IP
$args;
#变量中存放了URL中的所有参数
#例如:https://search.jd.com/Search?keyword=手机&enc=utf-8
#返回结果为: keyword=手机&enc=utf-8
$is_args
#如果有参数为? 否则为空
$document_root;
#保存了针对当前资源的请求的系统根目录,例如:/webdata/nginx/timinglee.org/lee。
$document_uri;
#保存了当前请求中不包含参数的URI,注意是不包含请求的指令
#比如:http://lee.timinglee.org/var?\id=11111会被定义为/var
#返回结果为:/var
$host;
#存放了请求的host名称
limit_rate 10240;
echo $limit_rate;
#如果nginx服务器使用limit_rate配置了显示网络速率,则会显示,如果没有设置, 则显示0
$remote_port;
#客户端请求Nginx服务器时随机打开的端口,这是每个客户端自己的端口
$remote_user;
#已经经过Auth Basic Module验证的用户名
$request_body_file;
#做反向代理时发给后端服务器的本地资源的名称
$request_method;
#请求资源的方式,GET/PUT/DELETE等
$request_filename;
#当前请求的资源文件的磁盘路径,由root或alias指令与URI请求生成的文件绝对路径,
#如:webdata/nginx/timinglee.org/lee/var/index.html
$request_uri;
#包含请求参数的原始URI,不包含主机名,相当于:$document_uri?$args,
#例如:/main/index.do?id=20190221&partner=search
$scheme;
#请求的协议,例如:http,https,ftp等
$server_protocol;
#保存了客户端请求资源使用的协议的版本,例如:HTTP/1.0,HTTP/1.1,HTTP/2.0等
$server_addr;
#保存了服务器的IP地址
$server_name;
#虚拟主机的主机名
$server_port;
#虚拟主机的端口号
$http_user_agent;
#客户端浏览器的详细信息
$http_cookie;
#客户端的所有cookie信息
$cookie_<name>
#name为任意请求报文首部字部cookie的key名
$http_<name>
#name为任意请求报文首部字段,表示记录请求报文的首部字段,name的对应的首部字段名需要为小写,如果有
横线需要替换为下划线
#示例:
echo $http_user_agent;
echo $http_host;
$sent_http_<name>
#name为响应报文的首部字段,name的对应的首部字段名需要为小写,如果有横线需要替换为下划线,此变量有
问题
echo $sent_http_server;
$arg_<name>
#此变量存放了URL中的指定参数,name为请求url中指定的参数
echo $arg_id;
示例:
[root@Nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {listen 80;server_name tomcat.gee.org;root /web/html;index index.html;location /var {default_type text/html;echo $remote_addr;echo $args;echo $document_root;echo $document_uri;echo $host;echo $http_user_agent;echo $request_filename;echo $scheme;echo $scheme://$host$document_uri?$args;echo $http_cookie;echo $cookie_key2;echo $http_Accept;}
}[root@nginx conf.d]# curl -b "title=gee;key1=gee,key2=gee" tomcat.gee.org/stats/
172.25.250.70/web
/stats/
tomcat.gee.org
curl/7.76.1
/web/stats/
http
title=gee;key1=gee,key2=gee
gee
*/*
4.4.2 自定义变量
假如需要自定义变量名称和值,使用指令set $variable value;
语法格式:
Syntax: set $variable value;
Default: —
Context: server, location, if
示例:
set $name timinglee;
echo $name;
set $my_port $server_port;
echo $my_port;
echo "$server_name:$server_port";
[root@Nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server{listen 80;server_name tomcat.gee.org;root /web/html;index index.html;location /stats/ {root /web/;set $name gee;echo $name;set $web_port $server_port;echo $web_port;}}测试输出
[root@nginx conf.d]# curl tomcat.gee.org/stats/
gee
80
五、Nginx Rewrite相关功能
Nginx服务器利用 ngx_http_rewrite_module 模块解析和处理rewrite请求,此功能依靠 PCRE(perl compatible regular expression),因此编译之前要安装PCRE库
rewrite是nginx服务器的重要功能之一,用于实现URL的重写,URL的重写是非常有用的功能,比如它可以在我们改变网站结构之后,不需要客户端修改原来的书签,也无需其他网站修改我们的链接,就可以设置为访问,另外还可以在一定程度上提高网站的安全性。
5.1 ngx_http_rewrite_module 模块指令
官方文档: https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_rewrite_module.html
5.1.1 if 指令
用于条件匹配判断,并根据条件判断结果选择不同的Nginx配置,可以配置在server或location块中进行配置,Nginx的if语法仅能使用if做单次判断,不支持使用if else或者if elif这样的多重判断,用法如下:
location /rewrite {if ($http_user_agent = gee) {echo gee;}if ($http_user_agent = minggee) {echo minggee;}
}
使用正则表达式对变量进行匹配,匹配成功时if指令认为条件为true,否则认为false,变量与表达式之间使用以下符号链接
= #比较变量和字符串是否相等,相等时if指令认为该条件为true,反之为false
!= #比较变量和字符串是否不相等,不相等时if指令认为条件为true,反之为false
~ #区分大小写字符,可以通过正则表达式匹配,满足匹配条件为真,不满足匹配条件为假
!~ #区分大小写字符,判断是否匹配,不满足匹配条件为真,满足匹配条件为假
~* #不区分大小写字符,可以通过正则表达式匹配,满足匹配条件为真,不满足匹配条件为假
!~* #不区分大小字符,判断是否匹配,满足匹配条件为假,不满足匹配条件为真
-f 和 !-f #判断请求的文件是否存在和是否不存在
-d 和 !-d #判断请求的目录是否存在和是否不存在
-x 和 !-x #判断文件是否可执行和是否不可执行
-e 和 !-e #判断请求的文件或目录是否存在和是否不存在(包括文件,目录,软链接)
#注意:
#如果$变量的值为空字符串或0,则if指令认为该条件为false,其他条件为true。
#nginx 1.0.1之前$变量的值如果以0开头的任意字符串会返回false
5.1.2 set 指令
指定key并给其定义一个变量,变量可以调用Nginx内置变量赋值给key
另外set定义格式为set $key value,value可以是text, variables和两者的组合。
[root@Nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server{listen 80;server_name tomcat.gee.org;root /web/html;index index.html;location /stats/ {root /web/;set $name gee;echo $name;set $web_port $server_port;echo $web_port;}}测试输出
[root@nginx conf.d]# curl tomcat.gee.org/stats/
gee
80
5.1.3 break 指令
用于中断当前相同作用域(location)中的其他Nginx配置
与该指令处于同一作用域的Nginx配置中,位于它前面的配置生效
位于后面的 ngx_http_rewrite_module 模块中指令就不再执行
Nginx服务器在根据配置处理请求的过程中遇到该指令的时候,回到上一层作用域继续向下读取配置
该指令可以在server块和locationif块中使用
注意: 如果break指令在location块中后续指令还会继续执行,只是不执行 ngx_http_rewrite_module模块的指令,其它指令还会执行
使用语法如下:
[root@Nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name lee.timinglee.org;
root /webdata/nginx/timinglee.org/lee;
location /break{
default_type text/html;
set $name lee;
echo $name;
break;
set $port $server_port;
echo $port;
}
}
[root@client ~]# curl lee.timinglee.org/break #当未添加break时
lee
80
[root@client ~]# curl lee.timinglee.org/break #添加break后
lee5.1.4 return 指令
return用于完成对请求的处理,并直接向客户端返回响应状态码,比如:可以指定重定向URL(对于特殊重定向状态码,301/302等) 或者是指定提示文本内容(对于特殊状态码403/500等),处于此指令后的所有配置都将不被执行,return可以在server、if 和 location块进行配置
语法格式:
return code; #返回给客户端指定的HTTP状态码
return code [text]; #返回给客户端的状态码及响应报文的实体内容
#可以调用变量,其中text如果有空格,需要用单或双引号
return code URL; #返回给客户端的URL地址server {
listen 80;
server_name lee.timinglee.org;
root /webdata/nginx/timinglee.org/lee;
location /return {
default_type text/html;
if ( !-e $request_filename){
return 301 http://www.baidu.com;
#return 666 "$request_filename is not exist";
}
echo "$request_filename is exist";
}
}
测试:
[root@client ~]# curl lee.timinglee.org/return
/webdata/nginx/timinglee.org/lee/return is exist
[root@client ~]# curl lee.timinglee.org/return1
/webdata/nginx/timinglee.org/lee/return1 is not exist
#测试return 301 http://www.baidu.com;
可在浏览器直接访问lee.timinglee.org/return15.2 rewrite指令
通过正则表达式的匹配来改变URI,可以同时存在一个或多个指令,按照顺序依次对URI进行匹配,rewrite主要是针对用户请求的URL或者是URI做具体处理
官方文档:https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_rewrite_module.html#rewrite
语法格式 :
rewrite regex replacement [flag];rewrite将用户请求的URI基于regex所描述的模式进行检查,匹配到时将其替换为表达式指定的新的URI
注意:如果在同一级配置块中存在多个rewrite规则,那么会自下而下逐个检查;被某条件规则替换完成后,会重新一轮的替换检查,隐含有循环机制,但不超过10次;如果超过,提示500响应码,[flag]所表示的标志位用于控制此循环机制
如果替换后的URL是以http://或https://开头,则替换结果会直接以重定向返回给客户端, 即永久重定向301
正则表达式格式
. #匹配除换行符以外的任意字符
\w #匹配字母或数字或下划线或汉字
\s #匹配任意的空白符
\d #匹配数字
\b #匹配单词的开始或结束
^ #匹配字付串的开始
$ #匹配字符串的结束
* #匹配重复零次或更多次
+ #匹配重复一次或更多次
? #匹配重复零次或一次
(n) #匹配重复n次
{n,} #匹配重复n次或更多次
{n,m} #匹配重复n到m次
*? #匹配重复任意次,但尽可能少重复
+? #匹配重复1次或更多次,但尽可能少重复
?? #匹配重复0次或1次,但尽可能少重复
{n,m}? #匹配重复n到m次,但尽可能少重复
{n,}? #匹配重复n次以上,但尽可能少重复
\W #匹配任意不是字母,数字,下划线,汉字的字符
\S #匹配任意不是空白符的字符
\D #匹配任意非数字的字符
\B #匹配不是单词开头或结束的位置
[^x] #匹配除了x以外的任意字符
[^lee] #匹配除了lee 这几个字母以外的任意字符5.2.1 rewrite flag 使用介绍
利用nginx的rewrite的指令,可以实现url的重新跳转,rewrite有四种不同的flag,分别是redirect(临时重定向302)、permanent(永久重定向301)、break和last。其中前两种是跳转型的flag,后两种是代理型
-
跳转型指由客户端浏览器重新对新地址进行请求
代理型是在WEB服务器内部实现跳转
rewrite 格式
Syntax: rewrite regex replacement [flag]; #通过正则表达式处理用户请求并返回替换后的数据
包。
Default: —
Context: server, location, ifflag说明
redirect;
#临时重定向,重写完成后以临时重定向方式直接返回重写后生成的新URL给客户端
#由客户端重新发起请求;使用相对路径,或者http://或https://开头,状态码:302
permanent;
#重写完成后以永久重定向方式直接返回重写后生成的新URL给客户端
#由客户端重新发起请求,状态码:301
break;
#重写完成后,停止对当前URL在当前location中后续的其它重写操作
#而后直接跳转至重写规则配置块之后的其它配置,结束循环,建议在location中使用
#适用于一个URL一次重写
last;
#重写完成后,停止对当前URI在当前location中后续的其它重写操作,
#而后对新的URL启动新一轮重写检查,不建议在location中使用
#适用于一个URL多次重写,要注意避免出现超过十次以及URL重写后返回错误的给用户5.2.2 rewrite案例:域名永久与临时重定向
域名的临时的调整,后期可能会变,之前的域名或者URL可能还用、或者跳转的目的域名和URL还会跳
转,这种情况浏览器不会缓存跳转,临时重定向不会缓存域名解析记录(A记录),但是永久重定向会缓存。
示例: 因业务需要,将访问源域名 www.timinglee.org 的请求永久重定向到 www.timinglee.com
location / {
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
index index.html;
rewrite / http://www.timinglee.com permanent;
#rewrite / http://www.timinglee.com redirect;
}
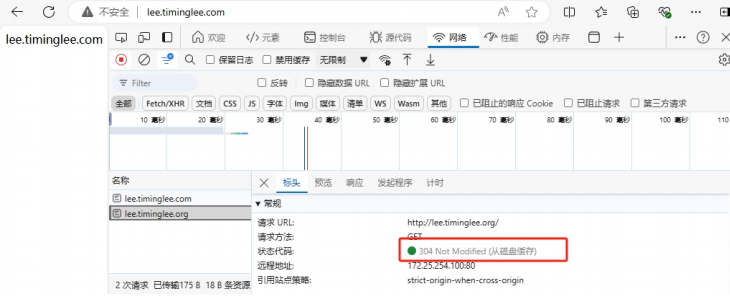
#重启Nginx并访问域名 http://www.timinglee.org 进行测试5.2.2.1 永久重定向301
域名永久型调整,即域名永远跳转至另外一个新的域名,之前的域名再也不使用,跳转记录可以缓存到客户端浏览器
永久重定向会缓存DNS解析记录, 浏览器中有 from disk cache 信息,即使nginx服务器无法访问,浏览器也会利用缓存进行重定向
比如: 京东早期的域名 www.360buy.com 由于与360公司类似,于是后期永久重定向到了 www.jd.com
[root@Nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name lee.timinglee.org;
root /webdata/nginx/timinglee.org/lee;
location / {
#rewrite / http://lee.timinglee.com redirect;
rewrite / http://lee.timinglee.com permanent;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name lee.timinglee.com;
root /webdata/nginx/timinglee.com/lee;
}
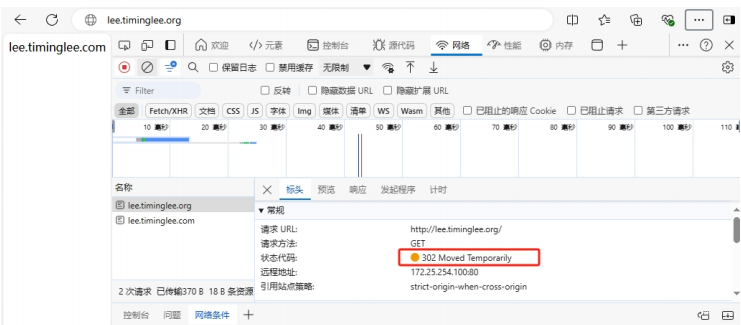
5.2.2.2 临时重定向302
域名临时重定向,告诉浏览器域名不是固定重定向到当前目标域名,后期可能随时会更改,因此浏览器不会缓存当前域名的解析记录,而浏览器会缓存永久重定向的DNS解析记录,这也是临时重定向与永久重定向最大的本质区别。
即当nginx服务器无法访问时,浏览器不能利用缓存,而导致重定向失败
[root@Nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name lee.timinglee.org;
root /webdata/nginx/timinglee.org/lee;
location / {
rewrite / http://lee.timinglee.com redirect;
#rewrite / http://lee.timinglee.com permanent;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name lee.timinglee.com;
root /webdata/nginx/timinglee.com/lee;
}
5.2.3 rewrite 案例: break与 last
测试:
访问break请求被rewrite至test1,而访问test1转递请求再次被rewrite发送至test2,此测试last和break分别有什么区别
5.2.3.1 break和last区别案例
[root@nginx]# mkdir /data/web/html/{test1,test2,break,last}
[root@nginx]# echo test1 > /data/web/html/test1/index.html
[root@nginx]# echo test2 > /data/web/html/test2/index.html
[root@nginx]# echo last > /data/web/html/last/index.html
[root@nginx]# echo break > /data/web/html/break/index.html
[root@nginx nginx]# vim conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.timinglee.org;
root /data/web/html;
index index.html;
location /break {
root /data/web/html;
rewrite ^/break/(.*) /test1/$1 break;
rewrite ^/test1/(.*) /test2/$1 ;
}
location /last {
root /data/web/html;
rewrite ^/last/(.*) /test1/$1 last;
rewrite ^/test1/(.*) /test2/$1 ;
}
location /test1 {
default_type text/html;
return 666 "new test1";
}
location /test2 {
root /data/web/html;
}
}
#测试:
[root@client ~]# curl -L www.timinglee.org/break/index.html
test1
[root@client ~]# curl -L www.timinglee.org/last/index.html
new test1[root@client ~]#5.2.4 rewrite案例:自动跳转 https
案例:基于通信安全考虑公司网站要求全站 https,因此要求将在不影响用户请求的情况下将http请求全部自动跳转至 https,另外也可以实现部分 location 跳转
[root@centos8 ~]#vim /apps/nginx/conf.d/pc.conf
server {
listen 443 ssl;
listen 80;
ssl_certificate /apps/nginx/certs/www.timinglee.org.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /apps/nginx/certs/www.timinglee.org.key;
ssl_session_cache shared:sslcache:20m;
ssl_session_timeout 10m;
server_name www.timniglee.org;
location / { #针对全站跳转
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
index index.html;
if ($scheme = http ){ #如果没有加条件判断,会导致死循环
rewrite / https://$host redirect;
}
}
location /login { #针对特定的URL进行跳转https
if ($scheme = http ){ #如果没有加条件判断,会导致死循环
rewrite / https://$host/login redirect;
}
}
}
#重启Nginx并访问测试
[root@centos7 ~]#curl -ikL www.timinglee.org
HTTP/1.1 302 Moved Temporarily
Server: nginx/1.18.0
Date: Thu, 08 Oct 2020 15:23:48 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 145
Connection: keep-alive
Location: https://www.timinglee.org
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Server: nginx/1.18.0
Date: Thu, 08 Oct 2020 15:23:48 GMT
Content-Type: text/html
Content-Length: 7
Last-Modified: Sat, 26 Sep 2020 01:18:32 GMT
Connection: keep-alive
ETag: "5f6e96e8-7"
Accept-Ranges: bytes
pc web5.2.5 rewrite 案例:判断文件是否存在
案例:当用户访问到公司网站的时输入了一个错误的URL,可以将用户重定向至官网首页
[root@centos8 ~]#vim /apps/nginx/conf.d/pc.conf
location / {
root /data/nginx/html/pc;
index index.html;
if (!-e $request_filename) {
rewrite .* http://www.timinglee.org/index.html; #实现客户端浏览器的302跳转
#rewrite .* /index.html; #web服务器内部跳转
}
}
#重启Nginx并访问测试5.3 Nginx 防盗链
防盗链基于客户端携带的referer实现,referer是记录打开一个页面之前记录是从哪个页面跳转过来的标记信息,如果别人只链接了自己网站图片或某个单独的资源,而不是打开了网站的整个页面,这就是盗链,referer就是之前的那个网站域名,正常的referer信息有以下几种:
none: #请求报文首部没有referer首部,
#比如用户直接在浏览器输入域名访问web网站,就没有referer信息。
blocked: #请求报文有referer首部,但无有效值,比如为空。
server_names: #referer首部中包含本主机名及即nginx 监听的server_name。
arbitrary_string: #自定义指定字符串,但可使用*作通配符。示例: *.timinglee.org
www.timinglee.*
regular expression: #被指定的正则表达式模式匹配到的字符串,要使用~开头,例如:
~.*\.timinglee\.com正常通过搜索引擎搜索web 网站并访问该网站的referer信息如下
172.25.254.1 - - [22/Jul/2024:09:27:36 +0800] "GET /favicon.ico HTTP/1.1" 404 149
"http://lee.timinglee.org/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64; rv:109.0)
Gecko/20100101 Firefox/115.0"
2024/07/22 09:27:36 [error] 34596#0: *205 open()
"/webdata/nginx/timinglee.org/lee/favicon.ico" failed (2: No such file or
directory), client: 172.25.254.1, server: lee.timinglee.org, request: "GET
/favicon.ico HTTP/1.1", host: "lee.timinglee.org", referrer:
"http://lee.timinglee.org/"5.3.1 实现盗链
在一个web 站点盗链另一个站点的资源信息,比如:图片、视频等
#新建一个主机172.25.254.20,盗取另一台主机lee.timinglee.org/images/lee.png的图片
[root@client ~]# yum install httpd -y
[root@client html]# vim /var/www/html/index.html
#准备盗链web页面:
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv=Content-Type content="text/html;charset=utf-8">
<title>盗链</title>
</head>
<body>
<img src="http://www.timinglee.org/images/lee.png" >
<h1 style="color:red">欢迎大家</h1>
<p><a href=http://www.timinglee.org>狂点老李</a>出门见喜</p>
</body>
</html>
~
#重启apache并访问http://172.25.254.20 测试
#验证两个域名的日志,是否会在被盗连的web站点的日志中出现以下盗链日志信息:
[root@Nginx ~]# cat /usr/local/nginx/logs/access.log
172.25.254.1 - - [22/Jul/2024:09:50:01 +0800] "GET /images/logo.png HTTP/1.1" 304
0 "http://172.25.254.20/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64)
AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/126.0.0.0 Safari/537.36
Edg/126.0.0.0"
172.25.254.1 - - [22/Jul/2024:09:50:18 +0800] "GET / HTTP/1.1" 304 0
"http://172.25.254.20/" "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/126.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 Edg/126.0.0.0"5.3.2 实现防盗链
基于访问安全考虑,nginx支持通过ngx_http_referer_module模块,检查访问请求的referer信息是否有效实现防盗链功能
官方文档:
https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_referer_module.html
[root@Nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.timinglee.org;
root /data/web/html;
index index.html;
location / {
valid_referers none blocked server_names *.timinglee.org ~/.baidu/.;
if ($invalid_referer){
return 404;
}
}
location /images {
valid_referers none blocked server_names *.timinglee.org ~/.baidu/.;
if ($invalid_referer){
rewrite ^/ http://www.timinglee.org/daolian.png permanent; #注意此图片
不能和正常图片放在一个目录中
}
}
}
#重启Nginx并访问测试
http://172.25.254.20
于访问安全考虑,nginx支持通过ngx_http_referer_module模块,检查访问请求的referer信息是否有效实现防盗链功能官方文档:https://nginx.org/en/docs/http/ngx_http_referer_module.html示例: 定义防盗链:```bash
[root@Nginx ~]# vim /usr/local/nginx/conf.d/vhosts.conf
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.timinglee.org;
root /data/web/html;
index index.html;
location / {
valid_referers none blocked server_names *.timinglee.org ~/.baidu/.;
if ($invalid_referer){
return 404;
}
}
location /images {
valid_referers none blocked server_names *.timinglee.org ~/.baidu/.;
if ($invalid_referer){
rewrite ^/ http://www.timinglee.org/daolian.png permanent; #注意此图片
不能和正常图片放在一个目录中
}
}
}
#重启Nginx并访问测试
http://172.25.254.20