string 类运算符重载
目录
一、赋值运算符 (=)
二、复合赋值运算符 (+=)
三、字符串连接运算符 (+)
四、流操作运算符 (>> 和 <<)
工作原理:
五、关系比较运算符
boolalpha 的基本作用
六、总结表
一、赋值运算符 (=)
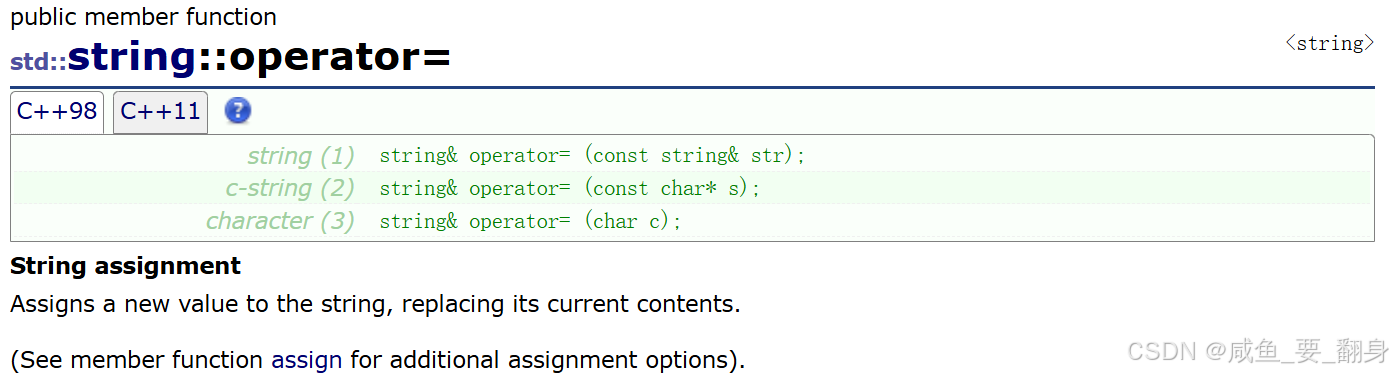
string 类重载了赋值运算符,支持多种类型的赋值操作。
string& operator=(const string& str); // string对象赋值
string& operator=(const char* s); // C风格字符串赋值
string& operator=(char c); // 单个字符赋值
string& operator=(initializer_list<char> il); // 初始化列表赋值 (C++11)示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
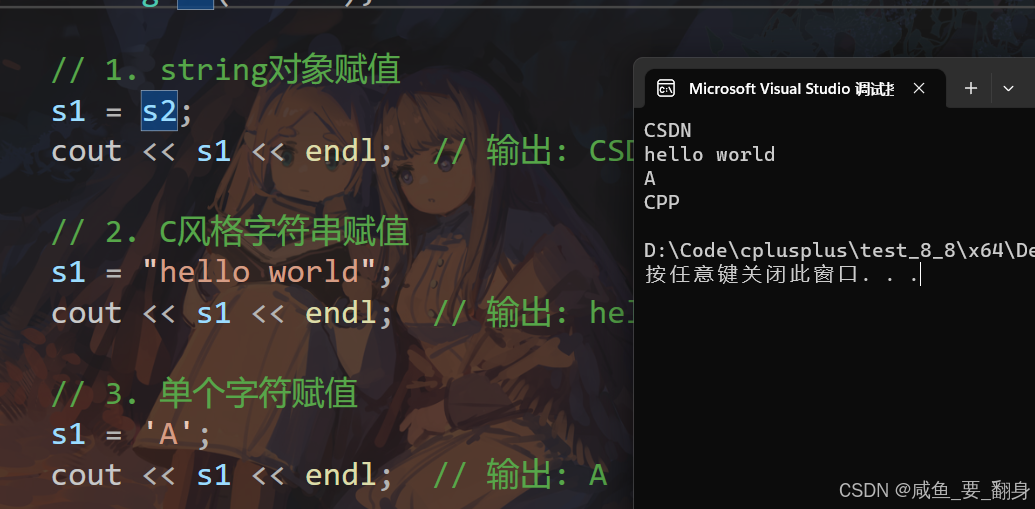
using namespace std;int main() {string s1;string s2("CSDN");// 1. string对象赋值s1 = s2;cout << s1 << endl; // 输出: CSDN// 2. C风格字符串赋值s1 = "hello world";cout << s1 << endl; // 输出: hello world// 3. 单个字符赋值s1 = 'A';cout << s1 << endl; // 输出: A// 4. 初始化列表赋值 (C++11)s1 = {'C', 'P', 'P'};cout << s1 << endl; // 输出: CPPreturn 0;
}
二、复合赋值运算符 (+=)
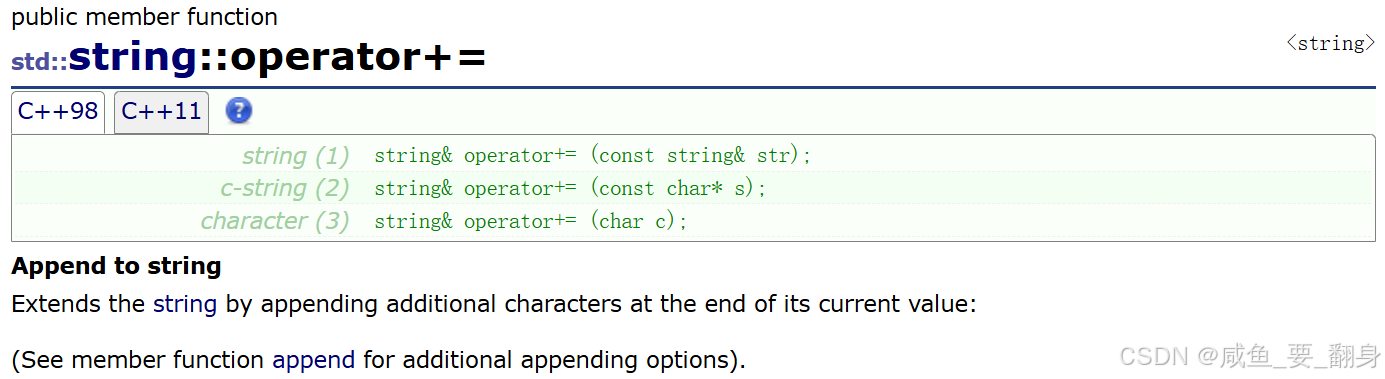
string 类重载了 += 运算符,支持多种类型的追加操作。
string& operator+=(const string& str); // 追加string对象
string& operator+=(const char* s); // 追加C风格字符串
string& operator+=(char c); // 追加单个字符
string& operator+=(initializer_list<char> il); // 追加初始化列表 (C++11)示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
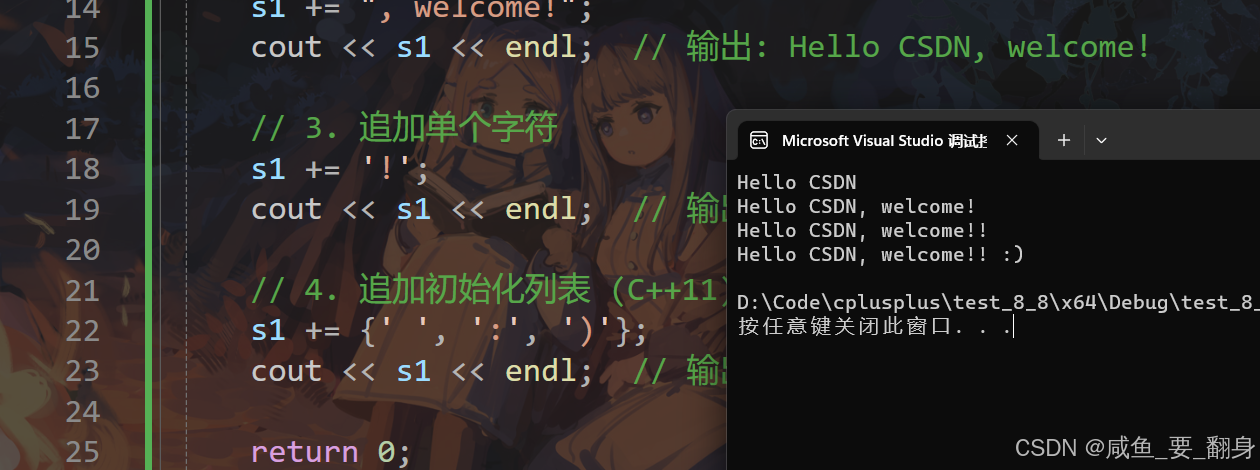
using namespace std;int main() {string s1("Hello");string s2(" CSDN");// 1. 追加string对象s1 += s2;cout << s1 << endl; // 输出: Hello CSDN// 2. 追加C风格字符串s1 += ", welcome!";cout << s1 << endl; // 输出: Hello CSDN, welcome!// 3. 追加单个字符s1 += '!';cout << s1 << endl; // 输出: Hello CSDN, welcome!!// 4. 追加初始化列表 (C++11)s1 += {' ', ':', ')'};cout << s1 << endl; // 输出: Hello CSDN, welcome!! :)return 0;
}
三、字符串连接运算符 (+)
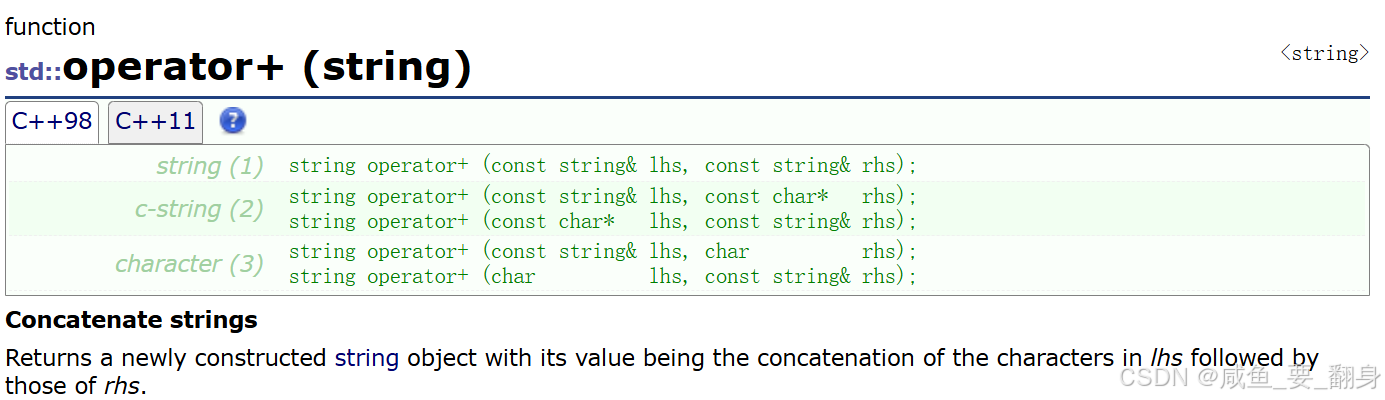
string 类重载了 + 运算符,支持多种字符串连接组合。
string operator+(const string& lhs, const string& rhs); // string + string
string operator+(const string& lhs, const char* rhs); // string + C字符串
string operator+(const char* lhs, const string& rhs); // C字符串 + string
string operator+(const string& lhs, char rhs); // string + 字符
string operator+(char lhs, const string& rhs); // 字符 + string
string operator+(string&& lhs, string&& rhs); // 右值引用版本C++ 中的 string 类的 + 运算符被设计为不修改原对象,而是返回一个新的 临时string 对象。
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
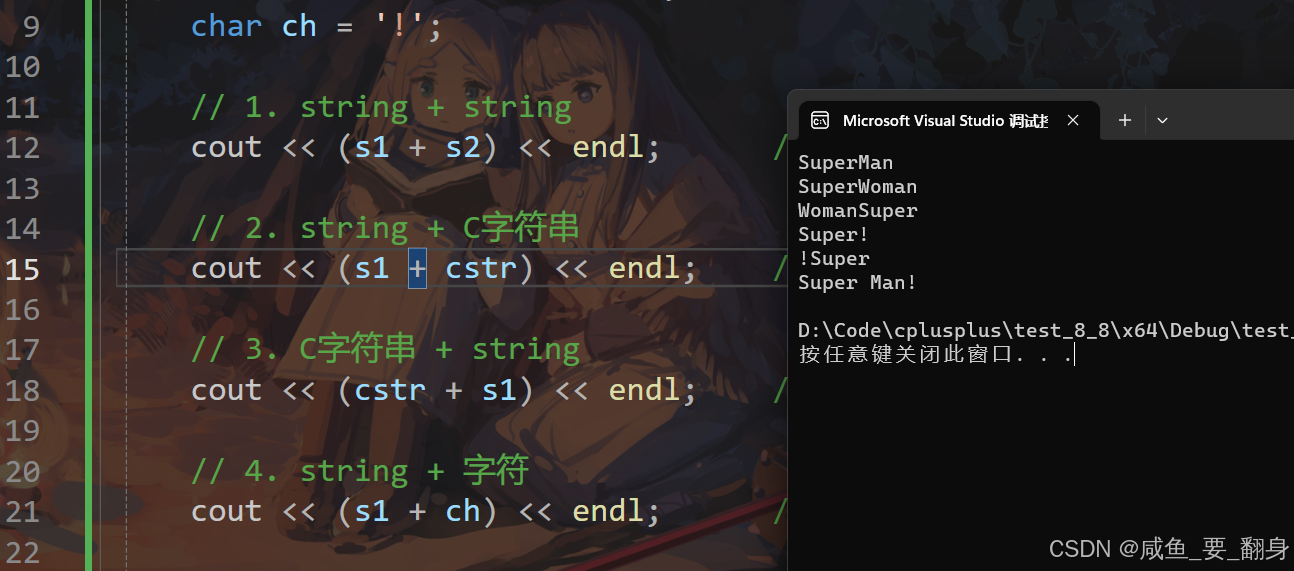
using namespace std;int main() {string s1("Super");string s2("Man");const char* cstr = "Woman";char ch = '!';// 1. string + stringcout << (s1 + s2) << endl; // 输出: SuperMan// 2. string + C字符串cout << (s1 + cstr) << endl; // 输出: SuperWoman// 3. C字符串 + stringcout << (cstr + s1) << endl; // 输出: WomanSuper// 4. string + 字符cout << (s1 + ch) << endl; // 输出: Super!// 5. 字符 + stringcout << (ch + s1) << endl; // 输出: !Super// 6. 链式连接cout << (s1 + " " + s2 + ch) << endl; // 输出: Super Man!return 0;
}
四、流操作运算符 (>> 和 <<)

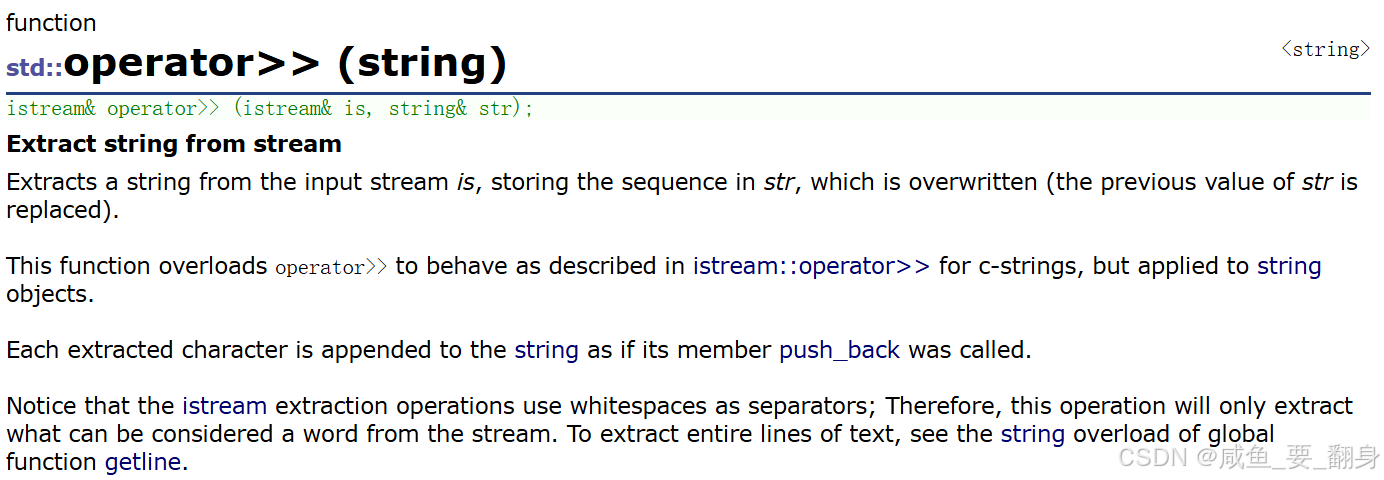
string 类重载了流操作运算符,支持直接的输入输出。
istream& operator>>(istream& is, string& str); // 输入运算符
ostream& operator<<(ostream& os, const string& str); // 输出运算符示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
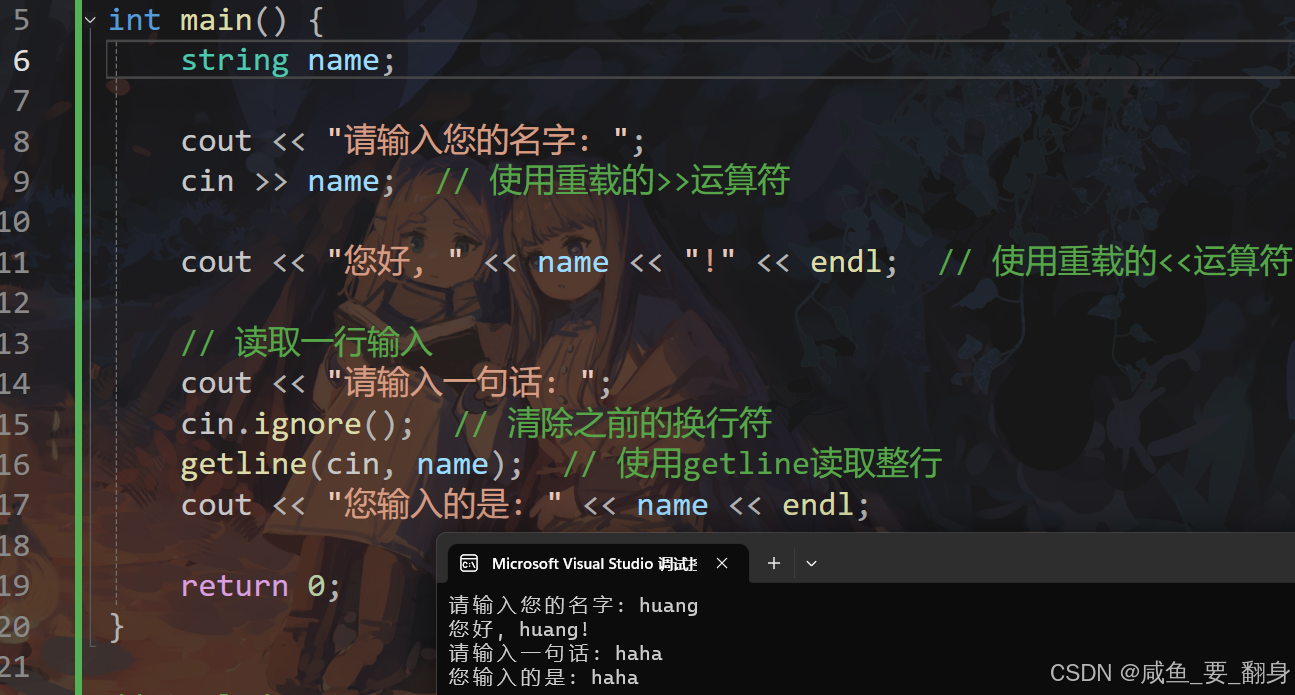
using namespace std;int main() {string name;cout << "请输入您的名字: ";cin >> name; // 使用重载的>>运算符cout << "您好, " << name << "!" << endl; // 使用重载的<<运算符// 读取一行输入cout << "请输入一句话: ";cin.ignore(); // 清除之前的换行符getline(cin, name); // 使用getline读取整行cout << "您输入的是: " << name << endl;return 0;
}工作原理:
-
cin.ignore():-
清除输入缓冲区中残留的换行符(
\n) -
这是因为之前的
cin >>操作会在缓冲区留下换行符 -
如果不调用,
getline会立即读取到空行
-
-
getline(cin, name):-
读取从当前光标到换行符之前的所有字符
-
包含空格
-
丢弃最后的换行符(不存入字符串)
-
五、关系比较运算符
string 类重载了完整的关系运算符,支持多种比较操作。
bool operator==(const string& lhs, const string& rhs);
bool operator!=(const string& lhs, const string& rhs);
bool operator<(const string& lhs, const string& rhs);
bool operator<=(const string& lhs, const string& rhs);
bool operator>(const string& lhs, const string& rhs);
bool operator>=(const string& lhs, const string& rhs);比较规则:
-
按字典序逐个比较字符的ASCII码值
-
比较区分大小写
-
较短的字符串如果与较长字符串的前面部分相同,则认为较短字符串较小
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;int main() {string s1("apple");string s2("banana");string s3("Apple");string s4("app");// 1. 相等比较cout << boolalpha;cout << (s1 == "apple") << endl; // 输出: truecout << (s1 == s3) << endl; // 输出: false// 2. 不等比较cout << (s1 != s2) << endl; // 输出: true// 3. 小于比较cout << (s1 < s2) << endl; // 输出: true ('a' < 'b')cout << (s1 < s3) << endl; // 输出: false ('a' > 'A')cout << (s4 < s1) << endl; // 输出: true ("app" < "apple")// 4. 其他比较cout << (s1 <= s2) << endl; // 输出: truecout << (s1 > s3) << endl; // 输出: truecout << (s1 >= "apple") << endl; // 输出: truereturn 0;
}boolalpha 的基本作用
功能:将布尔值的输出从 0/1 格式转换为 true/false 文本格式
默认情况(不使用 boolalpha):
bool b = true;
cout << b; // 输出: 1使用 boolalpha 后:
cout << boolalpha;
bool b = true;
cout << b; // 输出: true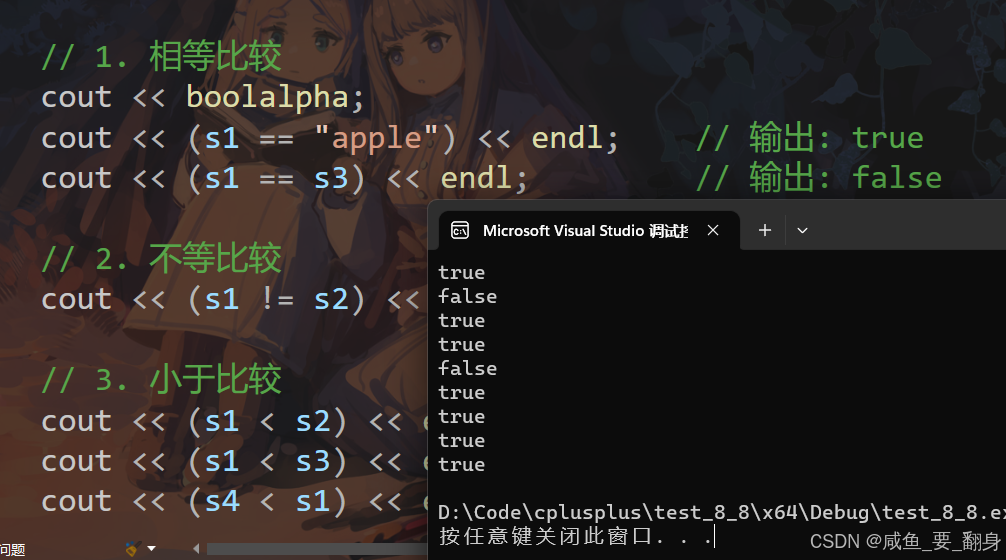
六、总结表
| 运算符 | 功能描述 | 支持的操作类型 |
|---|---|---|
| = | 赋值 | string, const char*, char, initializer_list |
| += | 追加 | string, const char*, char, initializer_list |
| + | 连接 | string + string, string + const char, const char + string, string + char, char + string |
| >> << | 流操作 | 输入输出流 |
| == != | 相等比较 | string与string, string与const char* |
| < <= > >= | 关系比较 | string与string, string与const char* |
| [] | 下标访问 | 非const和const版本 |
| bool | 空值检查 | 隐式转换为bool |
这些运算符重载使得string类的使用更加直观和方便,大大简化了字符串操作的代码编写。
