十八、k8s细粒度流量管理:服务网格
十八、k8s细粒度流量管理:服务网格
文章目录
- 十八、k8s细粒度流量管理:服务网格
- 1、服务网格
- 1.1 服务网格初识
- 1.2 服务网格核心功能
- 2、Istio初识
- 2.1 什么是Istio?
- 2.2 Istio功能
- 2.3 Istio架构平台
- 2.4 Istio Sidecar和Ambient模式对比
- 2.5 Istio控制平面组件介绍
- 2.6 Istio数据平面组件介绍
- 2.7 Istio核心资源DestinationRule介绍
- 2.8 Istio核心资源VirtualService介绍
- 2.9 Istio核心资源Gateway介绍
- 2.10 Istio核心资源关系总结
- 3、Istio 安装
- 3.1 使用 istioctl 部署 Istio
- 3.2 Istio 自动注入 Sidecar
- 3.2.1 Namespace 级别
- 3.2.2 Pod 级别
- 3.3 可视化工具 Kiali
- 3.4 Prometheus 和 Grafana
- 4、Istio 流量治理实践
- 4.1 部署 Istio 测试用例
- 4.2 使用 Istio 发布项目
- 4.3 Istio 地址重写和重定向
- 4.4 Istio 实现灰度部署
- 4.5 Istio 实现 AB 测试
- 4.6 Istio 负载均衡算法
- 4.7 Istio 熔断
- 4.8 Istio 注入延迟故障
- 4.9 Istio 注入中断故障
- 5、企业内项目接入 Istio 流程
- 5.1 部署企业测试项目
- 5.1.1 部署 mysql 服务
- 5.1.2 部署 order 服务
- 5.1.3 部署 handler 服务
- 5.1.4 部署 receive 服务
- 5.1.5 部署 前端ui 服务
- 5.2 Istio 南北流量网关改造
- 5.2.1 创建Gateway
- 5.2.2 改造 order 服务的 Ingress 为 VirtualService
- 5.2.3 改造 receive 服务的 Ingress 为 VirtualService
- 5.2.4 改造 前端ui 服务的 Ingress 为 VirtualService
- 5.3 Istio 东西流量改造
1、服务网格
1.1 服务网格初识
Service Mesh(服务网格)是由Buoyant公司的CEO William Morgan发起,目标为解决微服务之间复杂的链路关系。
Service Mesh将程序开发的网络功能和程序本身解耦,网络功能下沉到基础架构,由服务网格实现服务之间的负载均衡等功能,并且除网络功能外,也提供了其他更高级的功能,比如全链路加密、监控、链路追踪等。
1.2 服务网格核心功能
- 负载均衡
- 服务发现
- 熔断降级
- 动态路由
- 故障注入
- 错误重试
- 安全通信
- 语言无关
2、Istio初识
2.1 什么是Istio?
Istio是一个开源的服务网格(Service Mesh)产品,专为微服务架构设计,用于透明地管理服务间通信、安全、监控和流量策略。Istio通过Sidecar拦截并控制服务间的所有流量,将复杂的微服务治理(如流量管理、安全策略)从业务代码中剥离,并下沉到基础设施层,使开发者更专注于业务逻辑,以提升开发效率。
2.2 Istio功能
Istio几乎无需修改任何代码就可以实现如下功能:
- 双向TLS加密
- HTTP、gRPC、WebSocket和TCP流量的自动负载均衡
- 错误重试、故障转移和故障注入等
- 访问控制、限流、认证、鉴权等
- 可观测性指标、链路追踪、日志等
- 集群内入口和出口的流量管理
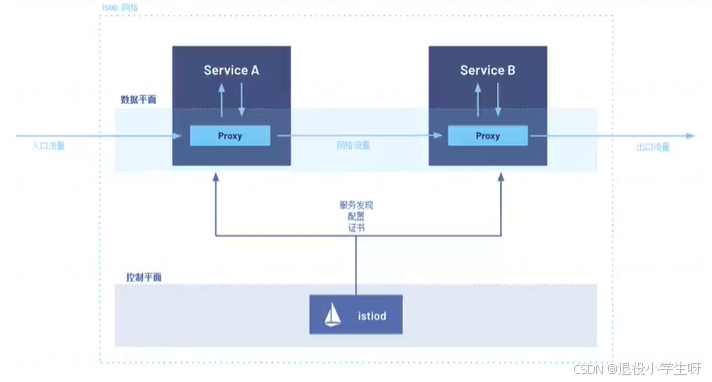
2.3 Istio架构平台
Istio从逻辑上分数据平面和控制平面:
- 控制平面:Control Plane负责管理和配置数据平面的流量策略,由管理员创建的Istio资源会解析成相关的配置下发到数据平面
- 数据平面:Data Plane负责拦截并处理所有入站(Inbound)和出站(Outbound)流量,用来执行由控制平台下发的策略,比如路由、负载均衡、重试、熔断、TLS加密等,同时数据平台还可以收集流量目标、日志和追踪数据,并发送给监控系统。
- Sidecar模式:此模式会为集群中启动的每个pod都部署一个Envoy代理,或者为在虚拟机上运行的服务运行一个Envoy代理
- Ambient模式:此模式在每个节点上启动一个四层代理,也可以为每个命名空间启动一个Envoy代理实现七层功能(1.22版本之后新加入的)
2.4 Istio Sidecar和Ambient模式对比
| 对比项 | 对比维度 | Sidecar模式 | Ambient模式 |
| 核心架构 | |||
| 代理部署方式 | 每个Pod注入一个Envoy Sidecar容器 | 分层部署: L4:每个阶段部署一个Ztunnel代理 L7:每个空间部署一个或多个Waypoint代理 | |
| 流量管理 | 通过iptables/IPVS规则劫持Pod的进出流量 | 四层由Ztunnel处理,七层由Waypoint处理 | |
| 覆盖范围 | 所有注入Sidecar的Pod | 默认纳入所有Pod,无需添加任何注解 | |
| 故障可用性 | 只影响某个故障的Pod | 影响当前节点或当前空间下的所有服务 | |
| 资源开销 | |||
| 代理数量 | 每一个Pod一个Envoy | Ztunnel:每一个节点一个代理 Waypoint:通常每个命名空间一个或多个 | |
| 内存/CPU消耗 | 较高 | 较低 | |
| 启动延迟 | Pod启动需等待Sidecar就绪 | Pod启动无需等待代理,延迟更低 | |
| 性能对比 | 调用延迟 | 每个请求经过两次Ztunnel代理 | L4经过Ztunnel,L7经过由Waypoint,可能更多 |
2.5 Istio控制平面组件介绍
Istiod为Istio的控制平面,提供服务发现、配置、证书管理、加密通信和认证。早期的Istio控制平台并没有Istiod这个容器,而是由Mixer(新版本已废弃)、Pilot、Citadel共同组成,后来为了简化Istio的架构,将其合并为Istiod,所有对新版本的Istio(V1.5+),部署后仅能看见Istiod一类Pod。
- Pilot:主要用于监听APIServer,动态获取集群中Service和Endpoints信息,并将配置的路由规则、负载均衡策略转换为Envoy可理解的配置,并下发至各个Sidecar中
- Citadel:主要用于提供强大的服务与服务之间的最终用户身份验证,可用于升级服务网格中未加密的流量,实现双向TLS加密
- Galley:负责配置管理的组件,用于验证配置信息的格式和正确性。galley使用网格配置协议(Mesh Configuration Protocol)和其它组件进行配置的交互
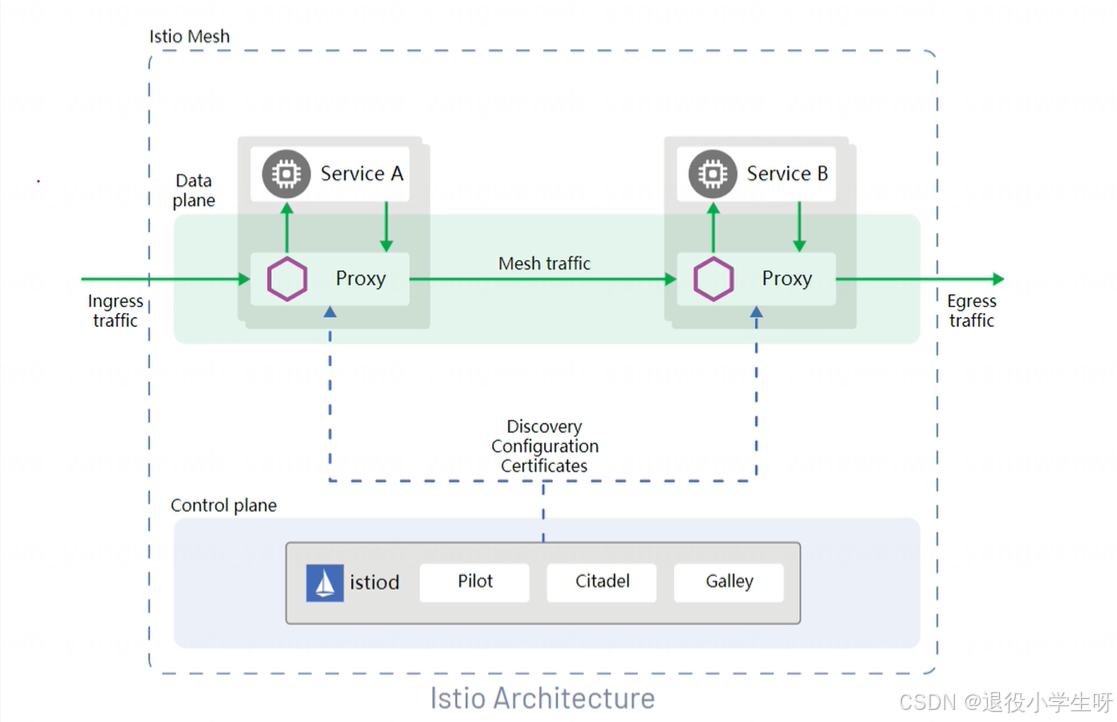
2.6 Istio数据平面组件介绍
Istio的数据平面使用的是Envoy,Envoy是用C++开发的高性能代理,用于调解服务网格中所有服务的所有入站和出站流量。Envoy代理是唯一一个与数据平面流量交互的Istio组件,并以Sidecar的方式注入到网格中的每一个Pod中。
主要提供如下功能:
- 动态服务发现
- 负载均衡
- HTTP/2 & gRPC代理
- 熔断器
- 健康检查
- 基于百分比流量拆分的灰度发布
- 故障注入
- 丰富的度量指标
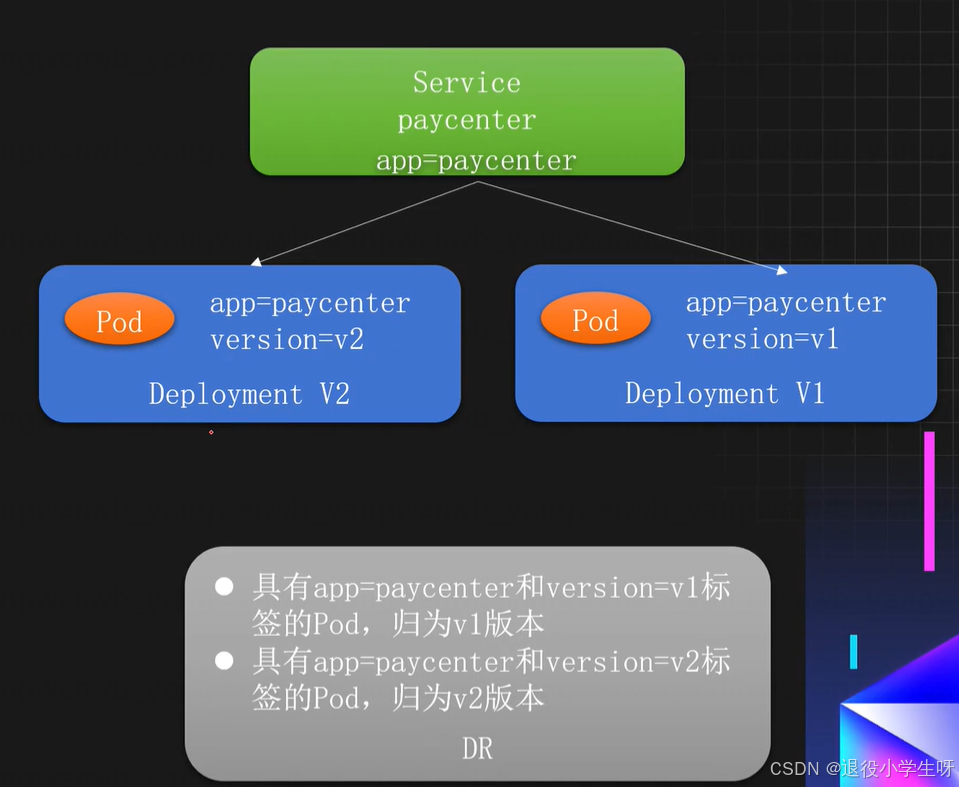
2.7 Istio核心资源DestinationRule介绍
DestinationRule:目标规划,主要用于将服务划分为多个版本(子集),同时可以对不同的版本进行配置负载均衡和连接池等策略。
使用场景:
- 版本划分:根据标签划分同一个服务的不同版本
- 负载均衡策略:支持配置各种负载均衡算法(如轮询、随机、最少连接)
- 熔断器:支持配置最大连接数、熔断等
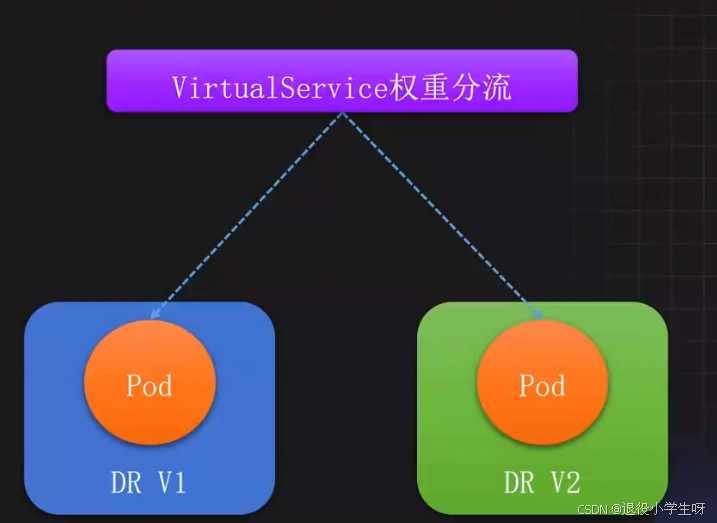
2.8 Istio核心资源VirtualService介绍
VirtualService:虚拟主机,是Istio路由规则的核心,用于控制流量走向,和Ingress类似,支持HTTP、gRPC、TCP等协议。通常和DestinationRule结合实现更细粒度的流量分配。
主要应用场景:
- 灰度发布:支持基于比例的流量分配
- A/B测试:支持基于请求头、URI、权重等条件的流量分配
- 重试:支持错误重试、故障注入、链接超时等策略
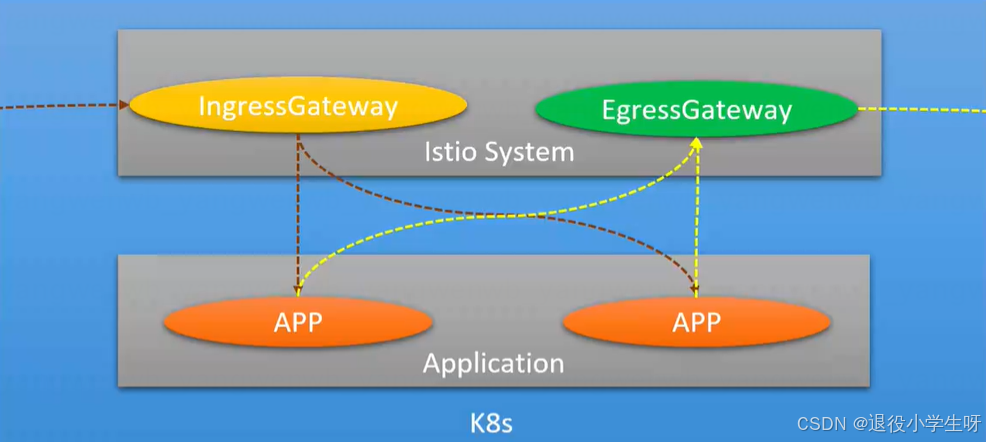
2.9 Istio核心资源Gateway介绍
Gateway:网关,Istio集群的出入口网关,主要用于处理对外的流量。通常和VirtualService结合实现内外流量的统一治理。
主要应用场景:
- 端口监听:可根据协议指定对外暴露的端口
- TLS:可以添加域名证书提供http访问
- 域名:可以根据域名进行路由分发
- 出口管控:可以将出口的流量固定从EgressGateway的服务中代理出去
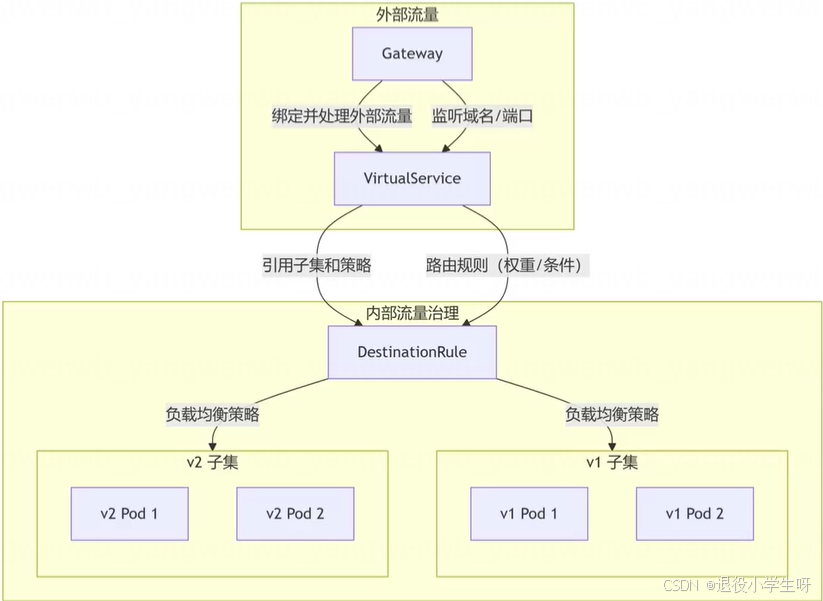
2.10 Istio核心资源关系总结
- DestinationRule:定义服务子集和流量策略,路由的最终目标。
- VirtualService:路由规则的核心,控制流量去向。
- Gateway:管理外部流量入口和出口,与VirtualService协同实现内外流量统一治理
3、Istio 安装
版本选择: https://istio.io/latest/docs/releases/supported-releases/#support-status-of-istioreleases
3.1 使用 istioctl 部署 Istio
首先下载 Istio 的安装包:
# 下载 Istio 的安装包
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# wget https://github.com/istio/istio/releases/download/1.26.0/istio-1.26.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz# 解压后,将 Istio 的客户端工具 istioctl,移动到/usr/local/bin 目录下:
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# tar xf istio-1.26.0-linux-amd64.tar.gz
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# mv istio-1.26.0/bin/istioctl /usr/local/bin/# 查看安装版本,这个报错是因为还没有安装istio-system
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# istioctl version
Istio is not present in the cluster: no running Istio pods in namespace "istio-system"
client version: 1.26.0
之后通过定义 IstioOperator 资源,在 Kubernetes 中安装 Istio:
[root@k8s-master01 ~]# cd istio-1.26.0
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# vim istio-operator.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# cat istio-operator.yaml
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
metadata:name: example-istionamespace: istio-system
spec:components:base:enabled: truecni:enabled: falseegressGateways:- enabled: falsename: istio-egressgatewaypilot:k8s:hpaSpec:minReplicas: 2 # 默认为 1maxReplicas: 5 # 默认为 5resources: # 注意资源配置,练习环境可以把 requests 调小limits:cpu: "2"memory: 2Girequests:cpu: "100m" # 生产环境调整为 2Gimemory: 512Mi # 生产环境调整为 2Gi ingressGateways:- enabled: truename: istio-ingressgatewayk8s:hpaSpec:minReplicas: 2 # 默认为 1maxReplicas: 5 # 默认为 5resources: # 注意资源配置,练习环境可以把 requests 调小limits:cpu: "2"memory: 2Girequests:cpu: "100m" # 生产环境调整为 2Gimemory: 512Mi # 生产环境调整为 2Giservice:type: NodePort # 将 Service 类型改成 NodePortports:- port: 15020nodePort: 30520name: status-port- port: 80 # 流量入口 80 端口映射到 NodePort 的 30080,之后通过节点IP+30080 即可访问 Istio 服务nodePort: 30080name: http2targetPort: 8080- port: 443nodePort: 30443name: httpstargetPort: 8443hub: m.daocloud.io/docker.io/istiomeshConfig:accessLogEncoding: JSONaccessLogFile: /dev/stdoutprofile: default
更多 Istio 安装配置:https://istio.io/latest/docs/setup/additional-setup/customize-installation/
安装 Istio:
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# istioctl install -f istio-operator.yaml |\ | \ | \ | \ /|| \ / || \ / || \ / || \ / || \ / || \
/______||__________\
____________________\__ _____/ \_____/ This will install the Istio 1.26.0 profile "default" into the cluster. Proceed? (y/N) y
✔ Istio core installed ⛵️
✔ Istiod installed 🧠
✔ Ingress gateways installed 🛬
✔ Installation complete
查看创建的 Service 和 Pod:
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl get pod,svc -n istio-system
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/istio-ingressgateway-d97b99d5d-czzp7 1/1 Running 0 103s
pod/istio-ingressgateway-d97b99d5d-wtbjl 1/1 Running 0 88s
pod/istiod-554d99f48b-7xfhs 1/1 Running 0 111s
pod/istiod-554d99f48b-wz7kn 1/1 Running 0 97sNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/istio-ingressgateway NodePort 10.103.74.144 <none> 15020:30520/TCP,80:30080/TCP,443:30443/TCP 103s
service/istiod ClusterIP 10.101.187.27 <none> 15010/TCP,15012/TCP,443/TCP,15014/TCP 112s
3.2 Istio 自动注入 Sidecar
Istio 注入 Sidecar 的常用方式有两种:
- Namespace 级别:添加
istio-injection=enabled(disabled关闭自动注入)的标签到指
定的 Namespace,那么该 Namespace 下的 Pod 都会被自动注入一个 Sidecar- Pod 级别:添加
sidecar.istio.io/inject=true(false 关闭自动注入)的标签到指定的 Pod,那么该 Pod 会被注入一个 Sidecar
3.2.1 Namespace 级别
接下来创建一个测试的 Namespace,并添加一个 istio-injection=enabled 的标签,之后在该 Namespace 下创建 Pod,测试 Istio Sidecar 的自动注入。
# 创建 Namespace 并添加 Label:
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl create ns istio-test
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl label namespace istio-test istio-injection=enabled
切换目录至 istio 的安装包,然后创建测试应用,此时创建的 Pod 会被自动注入一个istioproxy 的容器:
# 更改测试服务的镜像地址
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# sed -i 's|image: curlimages|image: crpi-q1nb2n896zwtcdts.cn-beijing.personal.cr.aliyuncs.com/ywb01|' samples/sleep/sleep.yaml[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# grep -rn "image:" samples/sleep/sleep.yaml
55: image: crpi-q1nb2n896zwtcdts.cn-beijing.personal.cr.aliyuncs.com/ywb01/curl# 创建测试服务
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl create -f samples/sleep/sleep.yaml -n istio-test
# 查看部署的容器:
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl get po -n istio-test
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
sleep-85fb677ff-57n27 2/2 Running 0 43s
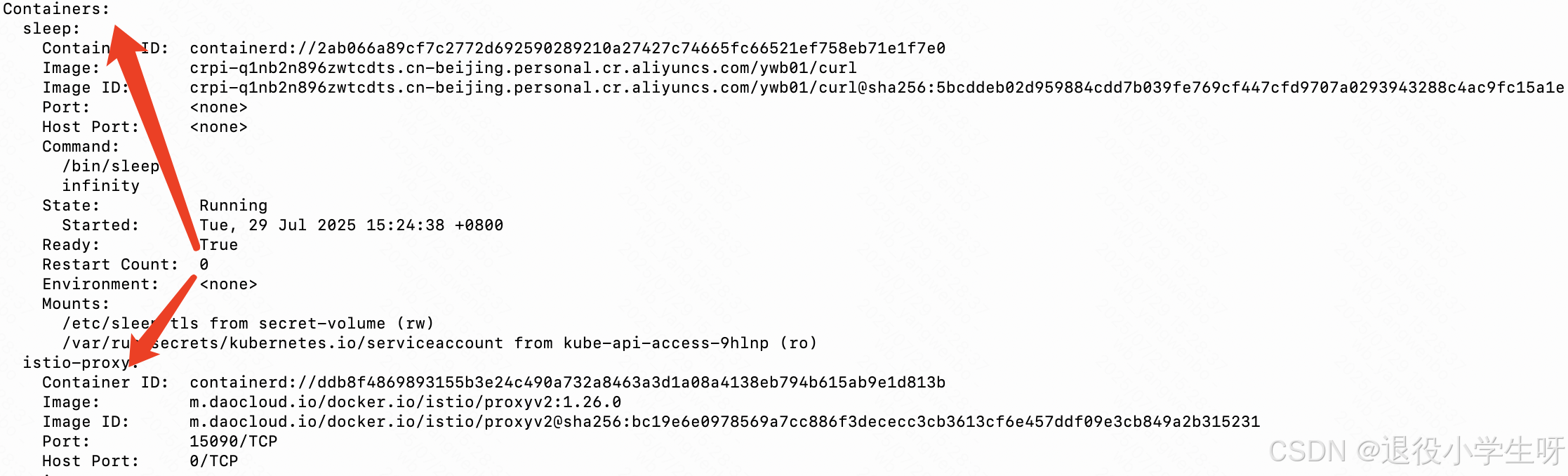
查看 Pod 详情:
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl describe po sleep-85fb677ff-57n27 -n istio-test
如果想要关闭该 Namespace 的自动注入,直接去除标签即可(已注入的 Pod 不受影响, 下次重建后,不再有 isito-proxy 的容器):
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl label namespace istio-test istio-injection-# 此时 Pod 不受影响:
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl get po -n istio-test
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
sleep-85fb677ff-57n27 2/2 Running 0 30m# 重建后不会再有 istio-proxy:
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl delete po sleep-85fb677ff-57n27 -n istio-test[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl get po -n istio-test
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
sleep-85fb677ff-bjjdg 1/1 Running 0 11s
如果某个服务不想被 istio 注入,可以添加 sidecar.istio.io/inject=false 的标签即可:
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# cat samples/sleep/sleep.yaml
....template:metadata:labels:app: sleepsidecar.istio.io/inject: "false"spec:terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0serviceAccountName: sleep
....
3.2.2 Pod 级别
如果需要给 Pod 单独添加 istio-proxy,可以给 Pod 添加 sidecar.istio.io/inject=true 标签即可:
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# vim samples/sleep/sleep.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# cat samples/sleep/sleep.yaml
....template:metadata:labels:app: sleepsidecar.istio.io/inject: "true"spec:terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 0serviceAccountName: sleep
....[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl replace -f samples/sleep/sleep.yaml -n istio-test[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl get po -n istio-test
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
sleep-774748f5b-tnvhh 2/2 Running 0 30s
3.3 可视化工具 Kiali
Kiali 为 Istio 提供了可视化的界面,可以在 Kiali 上进行观测流量的走向、调用链,同时还可以使用 Kiali 进行配置管理,给用户带来了很好的体验。
接下来在 Kubernetes 中安装 Kiali 工具:
# 修改 kiali 的 Service 类型为 NodePor
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# vim samples/addons/kiali.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# cat samples/addons/kiali.yaml
....
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:name: kialinamespace: "istio-system"
....annotations:
spec:type: NodePort
....# 安装Kiali服务
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl create -f samples/addons/kiali.yaml# 查看部署状态:
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl get po,svc -n istio-system -l app=kiali
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/kiali-6d774d8bb8-ckszt 1/1 Running 0 110sNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/kiali NodePort 10.106.203.41 <none> 20001:31365/TCP,9090:32392/TCP 110s
之后可以通过 任意IP+31365 访问 Kiali 服务:
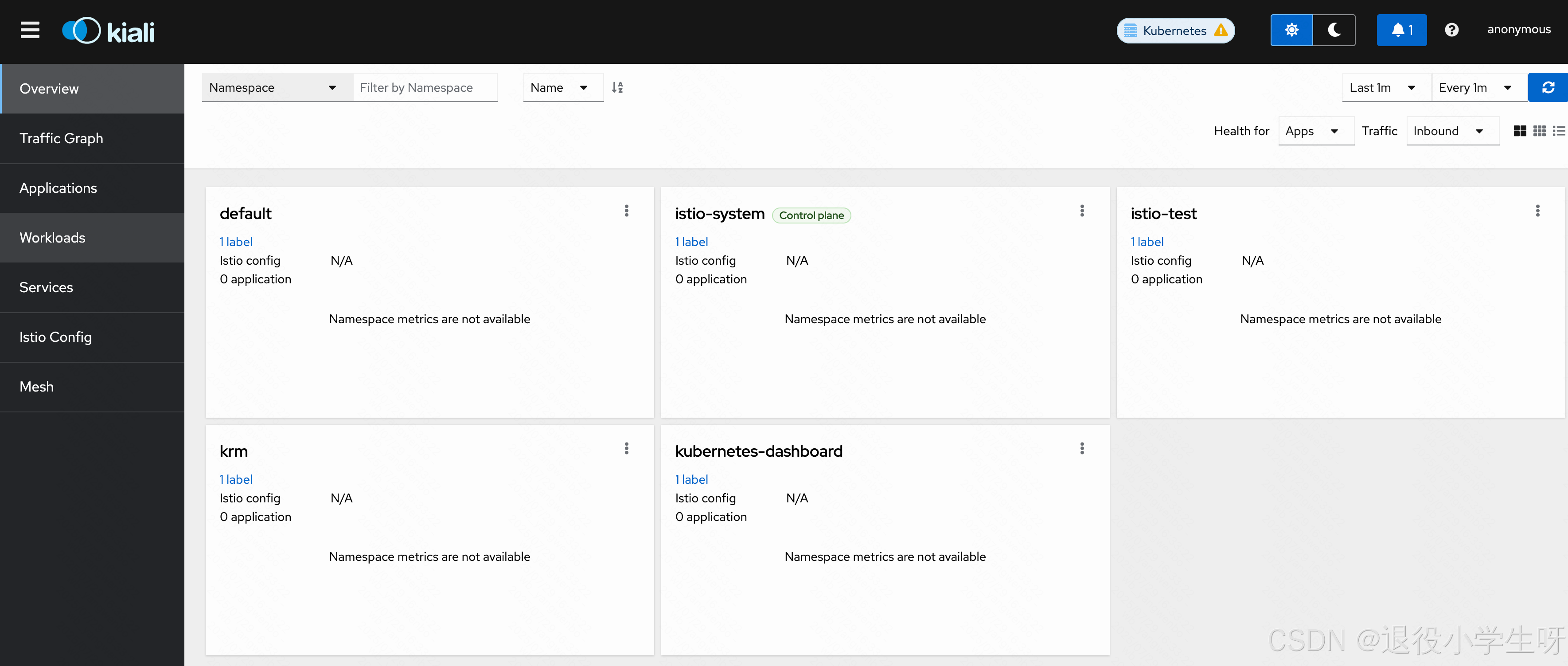
除了 Kiali 之外,还可以安装一个链路追踪的工具,安装该工具可以在 Kiali 的 Workloads 页面,查看某个服务的 Traces 信息:
# 首先更改镜像地址
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# sed -i 's|docker.io/jaegertracing|crpi-q1nb2n896zwtcdts.cn-beijing.personal.cr.aliyuncs.com/ywb01|' samples/addons/jaeger.yaml [root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# grep -rn "image:" samples/addons/jaeger.yaml
23: image: "crpi-q1nb2n896zwtcdts.cn-beijing.personal.cr.aliyuncs.com/ywb01/all-in-one:1.67.0"# 创建服务
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl create -f samples/addons/jaeger.yaml
# 查看部署状态:
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl get po,svc -n istio-system -l app=jaeger
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/jaeger-6498f6596f-tcbq8 1/1 Running 0 73sNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/jaeger-collector ClusterIP 10.98.59.72 <none> 14268/TCP,14250/TCP,9411/TCP,4317/TCP,4318/TCP 73s
service/tracing ClusterIP 10.96.238.231 <none> 80/TCP,16685/TCP 73s
3.4 Prometheus 和 Grafana
Istio 默认暴露了很多监控指标,比如请求数量统计、请求持续时间以及 Service 和工作负载的指标,这些指标可以使用 Prometheus 进行收集,Grafana 进行展示。
Istio内置了Prometheus 和Grafana的安装文件,直接安装即可(也可以使用外置的 Prometheus 和 Grafana):
# 同样需要修改镜像地址
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# sed -i 's|image: "prom|image: "crpi-q1nb2n896zwtcdts.cn-beijing.personal.cr.aliyuncs.com/ywb01|' samples/addons/prometheus.yaml [root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# sed -i 's|docker.io/grafana|crpi-q1nb2n896zwtcdts.cn-beijing.personal.cr.aliyuncs.com/ywb01|' samples/addons/grafana.yaml[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# grep -rn "image:" samples/addons/prometheus.yaml samples/addons/grafana.yaml
samples/addons/prometheus.yaml:487: image: "ghcr.io/prometheus-operator/prometheus-config-reloader:v0.81.0"
samples/addons/prometheus.yaml:515: image: "crpi-q1nb2n896zwtcdts.cn-beijing.personal.cr.aliyuncs.com/ywb01/prometheus:v3.2.1"
samples/addons/grafana.yaml:142: image: "crpi-q1nb2n896zwtcdts.cn-beijing.personal.cr.aliyuncs.com/ywb01/grafana:11.3.1"
# 将 Service 类型改成 NodePort
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# sed -i "s|ClusterIP|NodePort|" samples/addons/prometheus.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# sed -i "s|ClusterIP|NodePort|" samples/addons/grafana.yaml [root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# grep -rn NodePort samples/addons/prometheus.yaml samples/addons/grafana.yaml
samples/addons/prometheus.yaml:445: type: "NodePort"
samples/addons/grafana.yaml:93: type: NodePort
# 修改时区
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# sed -i 's/"timezone":"utc"/"timezone": "Asia\/Shanghai"/g' samples/addons/grafana.yaml
# 创建服务
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl create -f samples/addons/prometheus.yaml -f samples/addons/grafana.yaml# 查看部署状态:
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl get po,svc -n istio-system | egrep "prometheus|grafana"
pod/grafana-5574c54c77-wf6zh 1/1 Running 0 36s
pod/prometheus-687c9cbcd7-kbdsj 2/2 Running 0 36s
service/grafana NodePort 10.102.66.151 <none> 3000:31875/TCP 36s
service/prometheus NodePort 10.108.187.88 <none> 9090:31225/TCP 36s
同样的方式,将 Grafana 的 Service 改成 NodePort 或者添加 Ingress,之后访问即可:
默认监控模版
4、Istio 流量治理实践
4.1 部署 Istio 测试用例
Bookinfo 项目介绍:https://istio.io/latest/docs/examples/bookinfo/
首先在 Kubernetes 集群中,部署 Bookinfo 项目。
Istio 提供了用于测试功能的应用程序 Bookinfo,可以直接通过下述命令创建 Bookinfo:
# 创建 Namespace 并添加 Label:
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl create ns bookinfo
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl label ns bookinfo istio-injection=enabled
# 修改镜像地址
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# sed -i 's|docker.io/istio|crpi-q1nb2n896zwtcdts.cn-beijing.personal.cr.aliyuncs.com/ywb01|' samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml [root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# grep "image:" samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml image: crpi-q1nb2n896zwtcdts.cn-beijing.personal.cr.aliyuncs.com/ywb01/examples-bookinfo-details-v1:1.20.3image: crpi-q1nb2n896zwtcdts.cn-beijing.personal.cr.aliyuncs.com/ywb01/examples-bookinfo-ratings-v1:1.20.3image: crpi-q1nb2n896zwtcdts.cn-beijing.personal.cr.aliyuncs.com/ywb01/examples-bookinfo-reviews-v1:1.20.3image: crpi-q1nb2n896zwtcdts.cn-beijing.personal.cr.aliyuncs.com/ywb01/examples-bookinfo-reviews-v2:1.20.3image: crpi-q1nb2n896zwtcdts.cn-beijing.personal.cr.aliyuncs.com/ywb01/examples-bookinfo-reviews-v3:1.20.3image: crpi-q1nb2n896zwtcdts.cn-beijing.personal.cr.aliyuncs.com/ywb01/examples-bookinfo-productpage-v1:1.20.3# 创建Bookinfo服务
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl apply -f samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml -n bookinfo# 查看部署的 Pod 和 Service:
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl get po,svc -n bookinfo
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/details-v1-859dcddd6d-lxxlm 2/2 Running 0 87s
pod/productpage-v1-5f8d8bf969-tdfqn 2/2 Running 0 87s
pod/ratings-v1-68dcbc5d5b-dk47p 2/2 Running 0 87s
pod/reviews-v1-874fd588-kkwz9 2/2 Running 0 87s
pod/reviews-v2-cb8778f48-5gglc 2/2 Running 0 87s
pod/reviews-v3-5998b9d9dd-g49vt 2/2 Running 0 87sNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/details ClusterIP 10.96.115.151 <none> 9080/TCP 87s
service/productpage ClusterIP 10.98.96.114 <none> 9080/TCP 87s
service/ratings ClusterIP 10.106.215.139 <none> 9080/TCP 87s
service/reviews ClusterIP 10.100.32.85 <none> 9080/TCP 87s
# 之后可以通过 productpage Service 的 ClusterIP 访问 Bookinfo 项目:
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# curl 10.98.96.114:9080<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1">
....
4.2 使用 Istio 发布项目
接下来创建 Istio 的 Gateway 和 VirtualService 实现域名访问 Bookinfo 项目。
首先创建 Gateway,假设发布的域名是 bookinfo.kubeasy.com
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# vim samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# cat samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1 # Gateway 配置如下所示
kind: Gateway
metadata:name: bookinfo-gateway
spec:selector:istio: ingressgateway # use istio default controllerservers:- port:number: 80name: httpprotocol: HTTPhosts:- "bookinfo.kubeasy.com" # 发布域名
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1 # 接下来配置 VirtualService,实现对不同微服务的路由
kind: VirtualService
metadata:name: bookinfo
spec:hosts:- "bookinfo.kubeasy.com" # 发布域名gateways:- bookinfo-gatewayhttp:- match:- uri:exact: /productpage- uri:prefix: /static- uri:exact: /login- uri:exact: /logout- uri:prefix: /api/v1/productsroute:- destination:host: productpageport:number: 9080
# 创建资源
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl create -f samples/bookinfo/networking/bookinfo-gateway.yaml -n bookinfo# 查看资源:
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl get gw,vs -n bookinfo
NAME AGE
gateway.networking.istio.io/bookinfo-gateway 58sNAME GATEWAYS HOSTS AGE
virtualservice.networking.istio.io/bookinfo ["bookinfo-gateway"] ["bookinfo.kubeasy.com"] 58s
接下来将域名 bookinfo.kubeasy.com 解析至集群任意一个安装了 kube-proxy 的节点 IP 上,然后通过 ingressgateway 的 Service 的 NodePort 即可访问到 Bookinfo:
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl get svc -n istio-system istio-ingressgateway
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
istio-ingressgateway NodePort 10.103.74.144 <none> 15020:30520/TCP,80:30080/TCP,443:30443/TCP 5h1m
绑定 hosts 后,通过 bookinfo.kubeasy.com+ingressgateway 80 端口的 NodePort 即可访问该服务,比如本次示例的 http://bookinfo.kubeasy.com:30080/productpage:
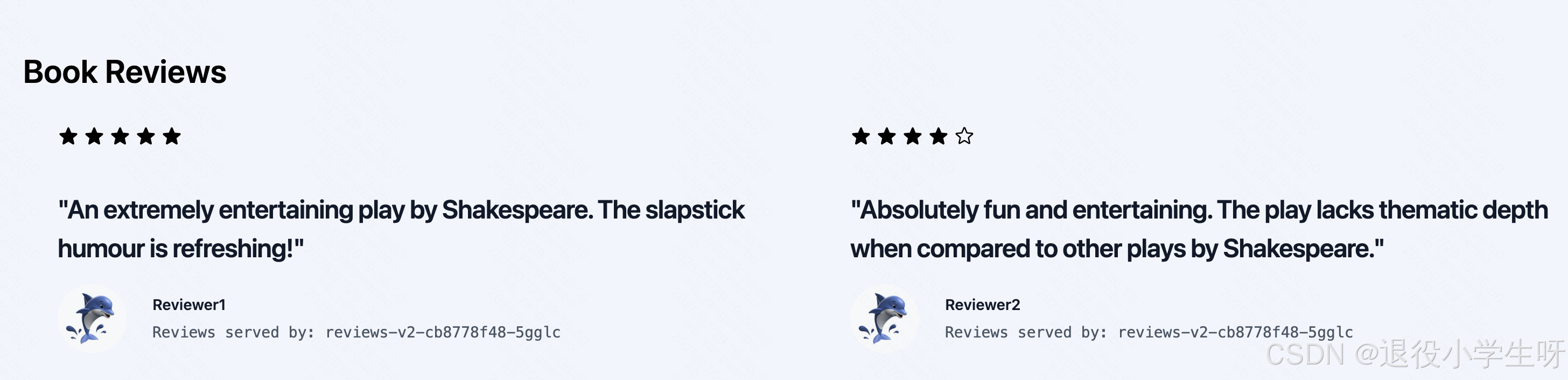

多次刷新可以看到 Reviewer 处的星星会在黑色、红色和消失之间来回替换,是因为之前部署了三个不同版本的 reviews,每个版本具有不同的显示效果.
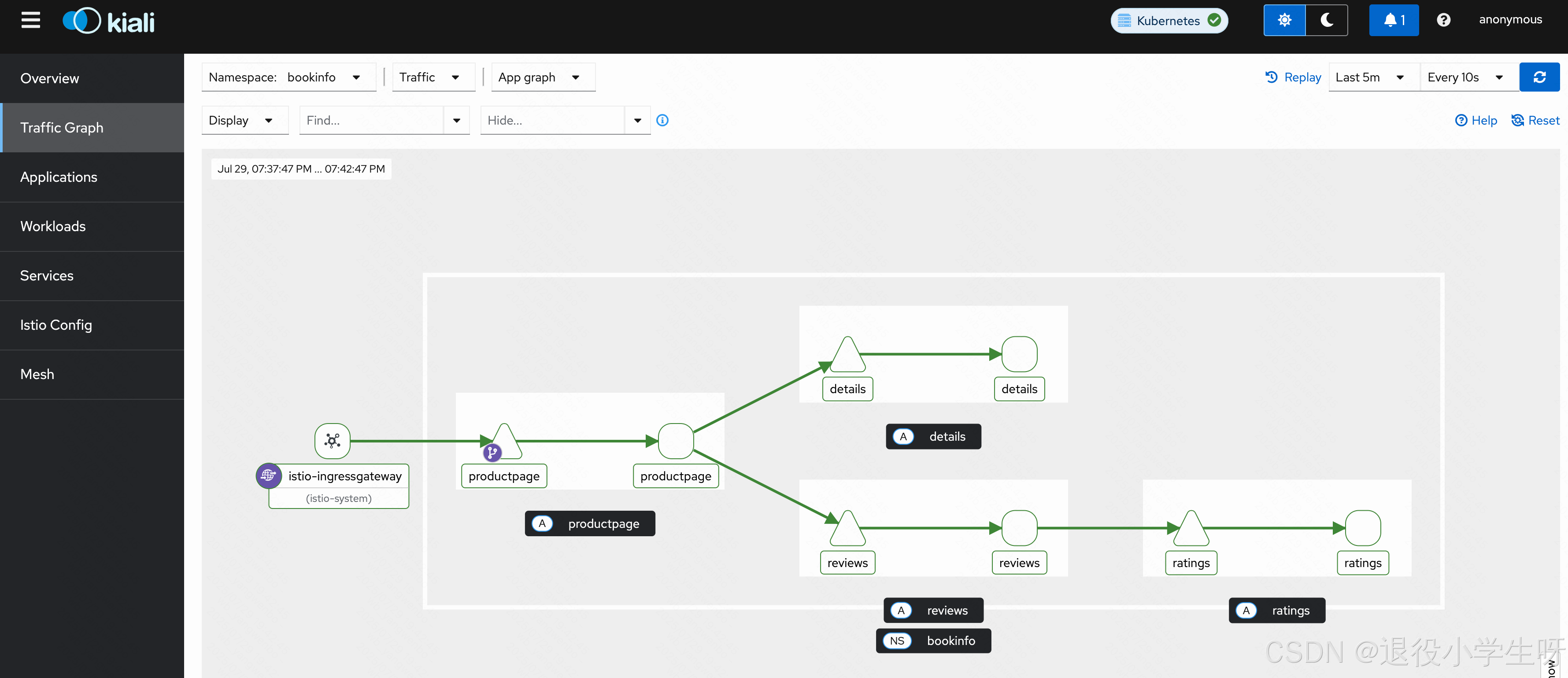
此时通过 Kiali 页面可以看到 Bookinfo 的调用链路:
4.3 Istio 地址重写和重定向
Istio 同样支持访问地址的重写和重定向,详细配置->:
比如将 bookinfo.kubeasy.com/yunwei,跳转到 blog.csdn.net/weixin_43279138?type=blog:
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl edit vs bookinfo -n bookinfo
....
spec:gateways:- bookinfo-gatewayhosts:- bookinfo.kubeasy.comhttp:- match:- uri:prefix: /yunwei # 匹配/yunweiredirect:authority: blog.csdn.net # 跳转的域名uri: /weixin_43279138?type=blog # 跳转的路径- match:- uri:exact: /productpage
....
通过浏览器访问 http://bookinfo.kubeasy.com:30080/yunwei(如果是学习环境需要加上端口号)即可跳转
到 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43279138?type=blog。当然也可以用 curl 进行测试:
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# curl -H "Host:bookinfo.kubeasy.com" 192.168.200.50:30080/yunwei -I
HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently
location: http://blog.csdn.net/weixin_43279138?type=blog
date: Tue, 29 Jul 2025 12:08:22 GMT
server: istio-envoy
transfer-encoding: chunked
Istio 地址重写可用于多个后端的路由,比如将/paymentapi/重写为/,此时就可以通过 VirtualService 实现。
Istio 地址重写配置方式和重定向类似,假如将/重写为/productpage,配置如下:
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# kubectl edit vs bookinfo -n bookinfo
....
spec:gateways:- bookinfo-gatewayhosts:- bookinfo.kubeasy.comhttp:- match:- uri:exact: / # 匹配根路径rewrite:uri: /productpage # 重写为/productpageroute:- destination:host: productpageport:number: 9080
....
保存退出后,访问 bookinfo.kubeasy.com 即可打开 bookinfo 的页面(未配置地址重写前,访问根路径会限制 404 错误)。
4.4 Istio 实现灰度部署
使用 Istio 进行细粒度的流量管理,需要使用 DestinationRule 资源对不同标签的 Pod 划分版本。
首先通过 DestinationRule 将 reviews 分成三个版本:
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# mkdir bookinfo
[root@k8s-master01 istio-1.26.0]# cd bookinfo/
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# vim reviews-dr.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# cat reviews-dr.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:name: reviews
spec:host: reviewssubsets:- name: v1labels:version: v1 # subset v1 指向具有 version=v1 的 Pod- name: v2labels:version: v2 # subset v2 指向具有 version=v2 的 Pod- name: v3labels:version: v3 # subset v3 指向具有 version=v3 的 Pod# 创建并查看该 DestinationRule:
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# kubectl create -f reviews-dr.yaml -n bookinfo# 查看资源:
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# kubectl get dr -n bookinfo
NAME HOST AGE
reviews reviews 20s
此时只是创建了 DestinationRule,并没有做任何限制,所以通过浏览器访问该服务时,并没有什么变化。但是 Kiali 中可以看到 reviews 变成了三个版本:
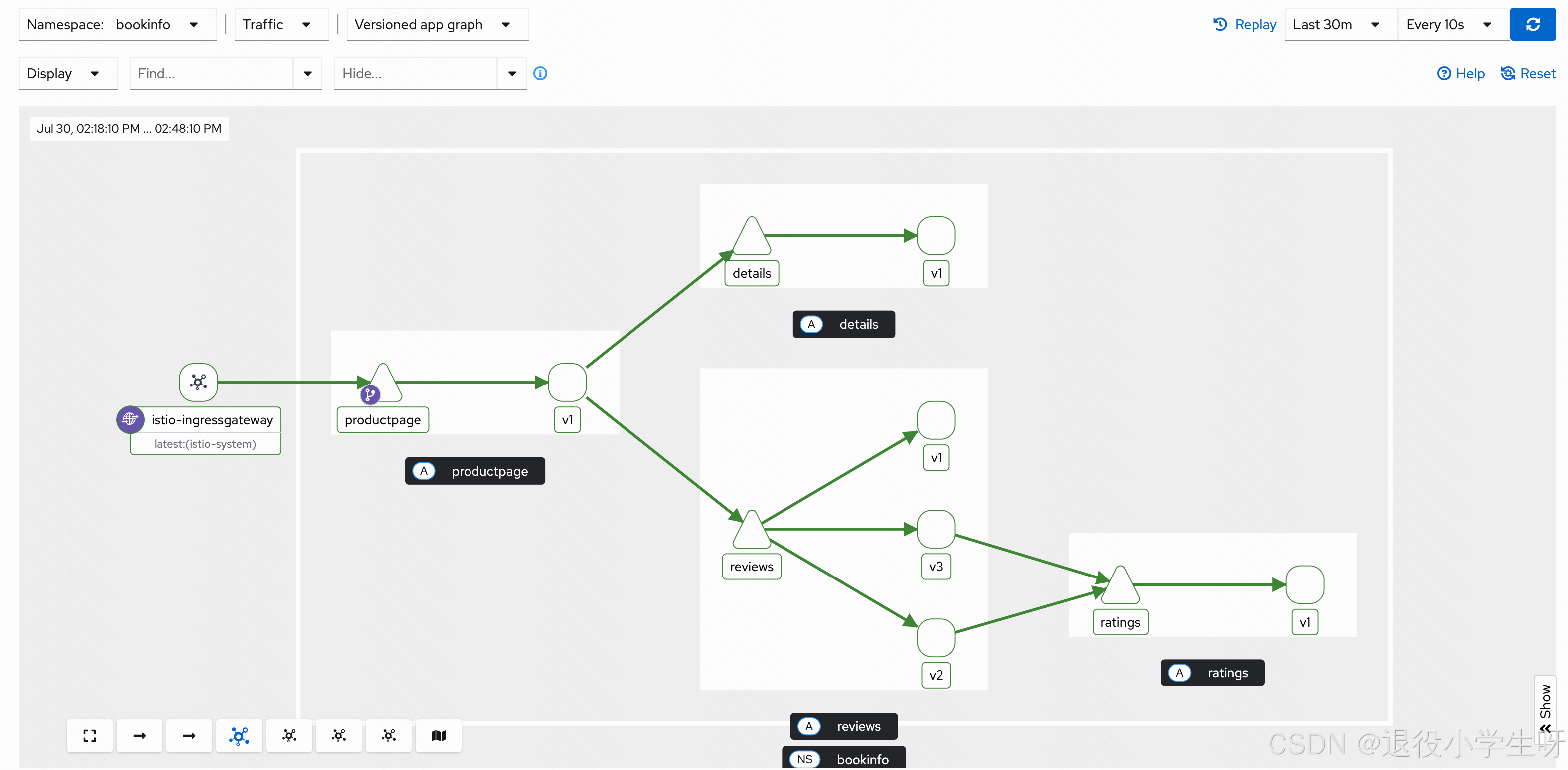
接下来使用 VirtualService 将所有访问 reviews 服务的流量指向 reviews 的 v1 版本:
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# vim reviews-v1-all.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# cat reviews-v1-all.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:name: reviews
spec:hosts:- reviewshttp:- route:- destination:host: reviewssubset: v1 # 将流量指向 v1# 创建该 VirtualService
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# kubectl create -f reviews-v1-all.yaml -n bookinfo
此时再次刷新浏览器,Reviews 处不再显示评分:

同时 Kiali 也不再显示 reviews 服务调用 ratings 服务:
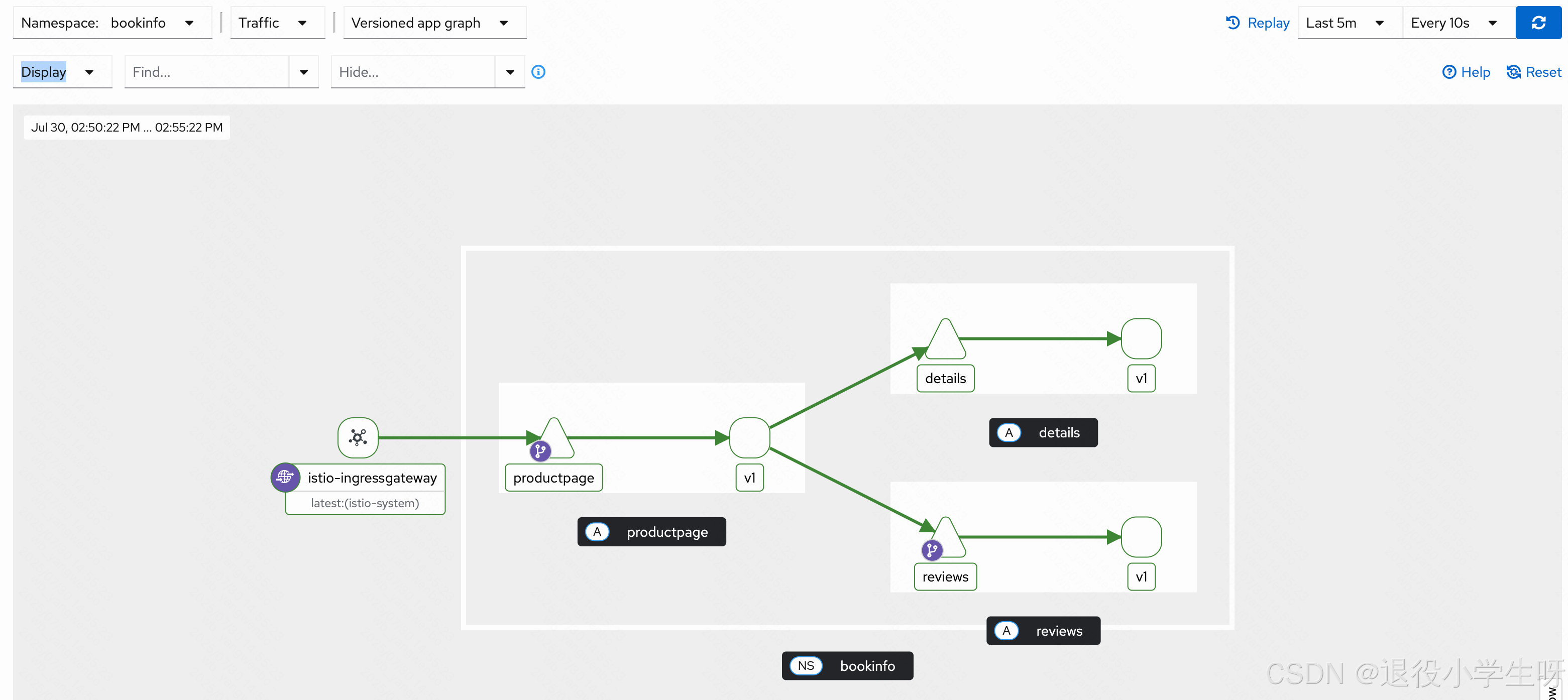
假如有新版本上线,不想直接接入所有流量,可以使用 VirtualService 控制流量分配比例,比如将 20%的流量路由到 v2 版本,其余的流量依旧路由到 v1 版本:
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# vim reviews-80v1-20v2.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# cat reviews-80v1-20v2.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:name: reviews
spec:hosts:- reviewshttp:- route:- destination:host: reviewssubset: v1weight: 80 # 将 80%流量指向 v1- destination:host: reviewssubset: v2 weight: 20 # 将 20%流量指向 v2# 更新该 VirtualService
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# kubectl replace -f reviews-80v1-20v2.yaml -n bookinfo
再次使用浏览器访问时,会有 20%的访问会出现评分(仅有黑色):

此时从 Kiali 页面即可看到 v2 版本的 review 调用 ratings:
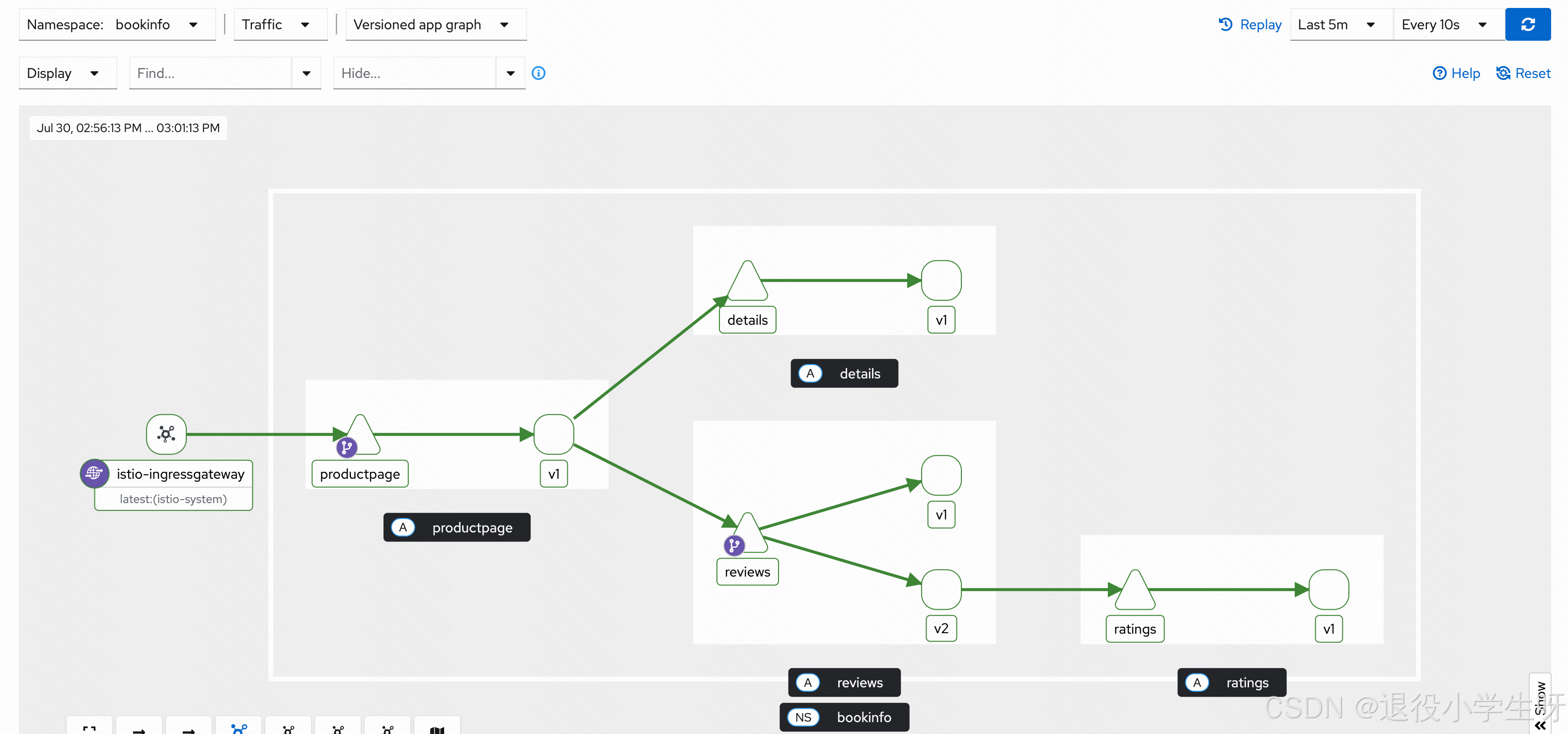
假设新版本已经没有任何问题,可以将流量全部指向新版本
4.5 Istio 实现 AB 测试
stio 也支持基于请求头、uri、schema 等方式的细粒度流量管理,这种路由方式比较适用于新版本上线时的 AB 测试。
Istio 请求头匹配介绍:
假如又开发了一个新版,此时只想要公司内部先进行测试,可以配置 VirtualService 指定部分用户访问新版本。
再次修改 reviews 的 VirtualService,将 jason 用户指向 v3,其他用户依旧使用 v2 版本:
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# vim reviews-jasonv3.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# cat reviews-jasonv3.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:name: reviews
spec:hosts:- reviewshttp:- match:- headers:end-user:exact: jasonroute:- destination:host: reviewssubset: v3- route:- destination:host: reviewssubset: v2# 更新该 VirtualService
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# kubectl replace -f reviews-jasonv3.yaml -n bookinfo
接下来首先登录 非 jason 用户, 可以看到页面只显示黑色五角星:
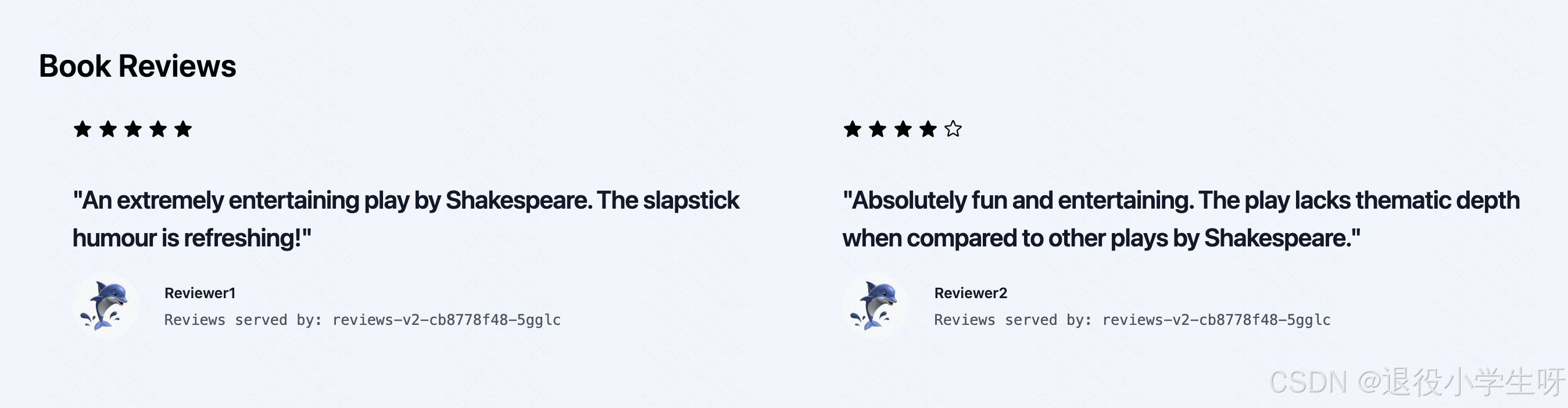
接下来登录 jason 用户,登录后页面评分只显示红色:
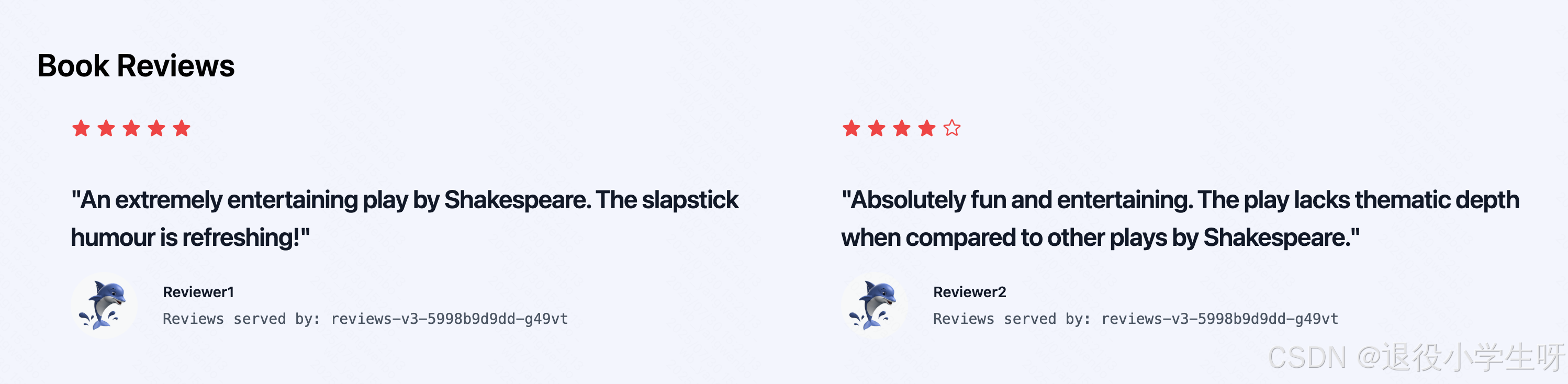
4.6 Istio 负载均衡算法
Istio 原生支持多种负载均衡算法,比如 ROUND_ROBIN、LEAST_REQUEST、LEAST_CONN、RANDOM 等。假如一个应用存在多个副本(Pod),可以使用上述算法对多个 Pod 进行定制化的负载均衡配置
常见的负载均衡策略如下:
- ROUND_ROBIN:轮询算法,将请求依次分配给每一个实例,不推荐使用;
- LEAST_REQUEST:最小链接算法,从池中随机选择两个实例,并将请求路由给当前活跃请求数较少的那个主机;
- RANDOM:随机算法,将请求随机分配给其中一个实例;
- PASSTHROUGH:将连接转发到调用者请求的原始 IP 地址,而不进行任何形式的负载均衡,目前不推荐使用;
- UNSPECIFIED:未指定负载均衡算法,Istio 将选择一个合适的默认算法,不推荐使用。
首先去除之前配置的一些路由策略,之后观看 Kiali 中 reviews 的流量分配:
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# kubectl delete vs -n bookinfo reviews
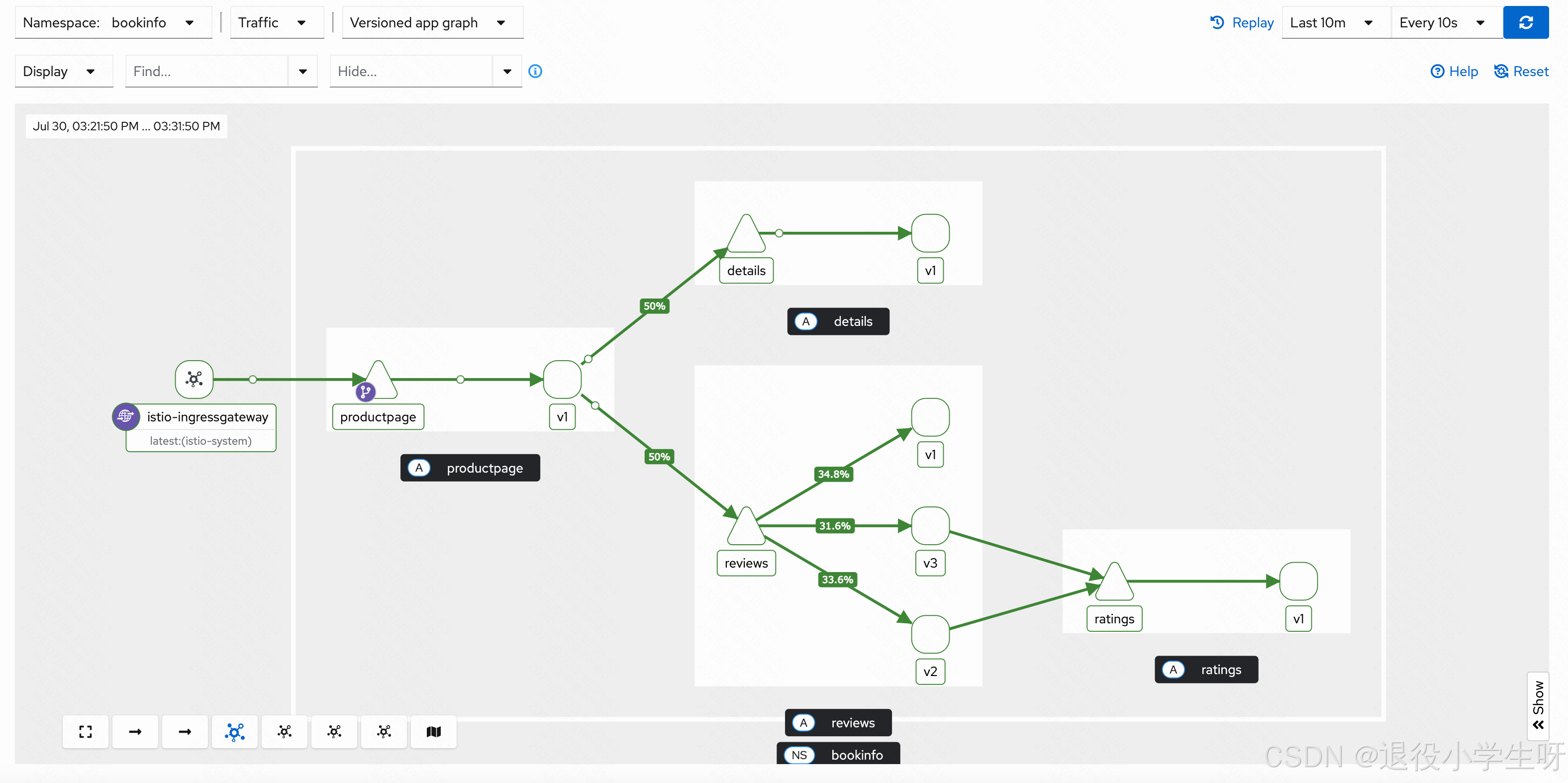
此时可以看到流量分配比较低的实例多次访问会慢慢提高,符合最小连接数的算法。接下来将算法改成 RANDOM(生产环境建议使用 LEAST_REQUEST):
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# vim reviews-dr.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# cat reviews-dr.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:name: reviews
spec:trafficPolicy: # 添加路由策略,在 spec 下对所有的 subset 生效,也可以在 subset 中配置loadBalancer: # 配置负载均衡simple: RANDOM # 策略为 RANDOMhost: reviewssubsets:- name: v1labels:version: v1- name: v2labels:version: v2- name: v3labels:version: v3[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# kubectl replace -f reviews-dr.yaml -n bookinfo
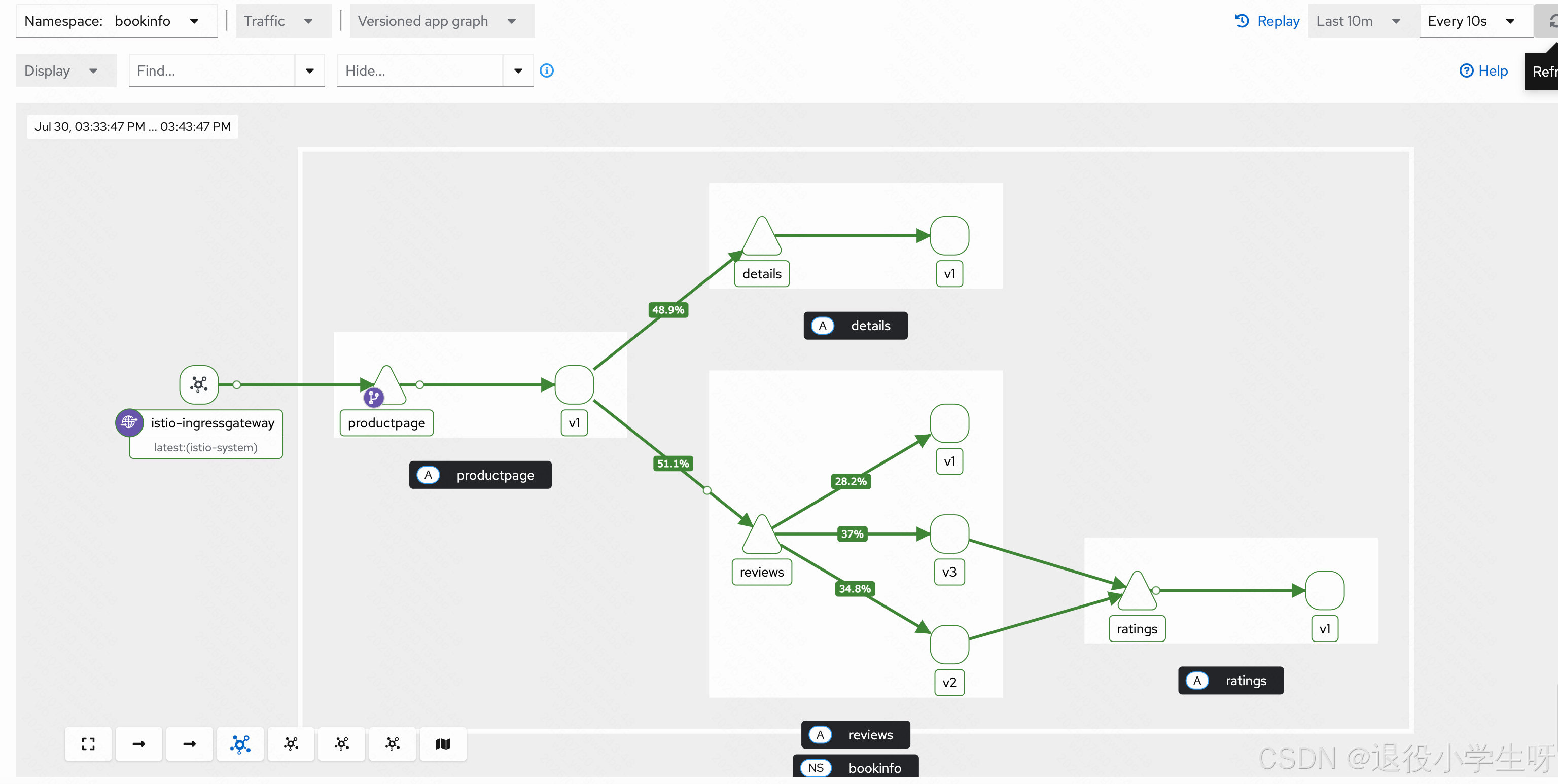
4.7 Istio 熔断
Istio 支持熔断机制,可以实现在高并发时对服务进行过载保护。
假设对 ratings 进行熔断,希望在并发请求数超过 3,并且存在 1 个以上的待处理请求,就触发熔断,此时可以配置 ratings 的 DestinationRule 如下所示:
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# vim ratings-dr.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# cat ratings-dr.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:name: ratingsnamespace: bookinfo
spec:host: ratingstrafficPolicy: # trafficPolicy 配置,可以配置在 subsets 级别connectionPool: # 连接池配置,可以单独使用限制程序的并发数tcp:maxConnections: 3 # 最大并发数为 3http:http1MaxPendingRequests: 1 # 最大的待处理请求outlierDetection: # 熔断探测配置consecutive5xxErrors: 1 # 如果连续出现的错误超过 1 次,就会被熔断interval: 10s # 每 10 秒探测一次后端实例baseEjectionTime: 3m # 熔断的时间maxEjectionPercent: 100 # 被熔断实例最大的百分比subsets:- labels:version: v1name: v1[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# kubectl create -f ratings-dr.yaml -n bookinfo
保存退出后,部署测试工具 fortio,用于对容器业务进行压力测试:
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# kubectl apply -f ../samples/httpbin/sample-client/fortio-deploy.yaml -n bookinfo
等待 fortio 容器启动后,获取 fortio 容器 id:
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# kubectl get po -n bookinfo | grep fortio
fortio-deploy-74ffb9b4d6-j28bh 2/2 Running 0 55s
发送一个请求,可以看到当前状态码为 200,即连接成功:
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# kubectl exec -ti fortio-deploy-74ffb9b4d6-j28bh -n bookinfo -- fortio load -curl http://ratings:9080/ratings/0
....
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
....
接下来更改为两个并发连接(-c 2),发送 20 请求(-n 20):
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# kubectl exec -ti fortio-deploy-74ffb9b4d6-j28bh -n bookinfo -- fortio load -c 2 -qps 0 -n 20 -loglevel Warning http://ratings:9080/ratings/0 | grep Code
Code 200 : 20 (100.0 %)
可以看到 503 的结果为 12,说明触发了熔断。如果提高并发量,会触发更高的熔断:
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# kubectl exec -ti fortio-deploy-74ffb9b4d6-j28bh -n bookinfo -- fortio load -c 20 -qps 0 -n 20 -loglevel Warning http://ratings:9080/ratings/0 | grep Code
Code 200 : 8 (40.0 %)
Code 503 : 12 (60.0 %)
4.8 Istio 注入延迟故障
Istio 支持为服务添加延迟和中断,可以用于测试链路的可靠性,添加延迟只需要在 VirtualService 添加 fault 字段即可。
首先不添加任何延迟,看一下访问速度如何
# 创建一个用于测试的工具
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# kubectl create deploy -n bookinfo debug-tools --image=crpi-q1nb2n896zwtcdts.cn-beijing.personal.cr.aliyuncs.com/ywb01/debug-tools -- sleep 36000# 查看pod
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# kubectl get po -n bookinfo | grep debug-tools
debug-tools-6447995767-bq2hd 2/2 Running 0 99s[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# kubectl exec -it debug-tools-6447995767-bq2hd -n bookinfo -- bash
(08:23 debug-tools-6447995767-bq2hd:/) time curl -I -s details:9080
....real 0m0.095s
user 0m0.003s
sys 0m0.009s
不添加任何故障延迟时,095 秒左右就会返回结果。接下来注入一个 5s 的延迟:
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# vim details-delay.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# cat details-delay.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:name: details
spec:hosts:- detailshttp:- fault: # 添加一个错误delay: # 添加类型为 delay 的故障percentage: # 故障注入的百分比value: 100 # 对所有请求注入故障fixedDelay: 5s # 注入的延迟时间route:- destination:host: details[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# kubectl create -f details-delay.yaml -n bookinfo
再次进行测试,返回时间已经达到了五秒:
(08:31 debug-tools-6447995767-bq2hd:/) time curl -I -s details:9080
....real 0m5.022s
user 0m0.003s
sys 0m0.007s
4.9 Istio 注入中断故障
中断故障注入只需要将 fault 的 delay 更改为 abort 即可:
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# vim details-abort.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# cat details-abort.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:name: details
spec:hosts:- detailshttp:- fault:abort: # 更改为 abort 类型的故障percentage:value: 100httpStatus: 400 # 故障状态码route:- destination:host: details# 替换该 VirtualService,再次访问测试:
[root@k8s-master01 bookinfo]# kubectl replace -f details-abort.yaml -n bookinfo# 直接返回 400 错误
(08:40 debug-tools-6447995767-bq2hd:/) curl -I -s details:9080
HTTP/1.1 400 Bad Request
content-length: 18
content-type: text/plain
date: Wed, 30 Jul 2025 08:40:13 GMT
server: envoy
connection: close
5、企业内项目接入 Istio 流程
企业内项目接入 Istio 常见的有两种情况:
- 需要注入 Istio Sidecar 进行流量管理的
- 不需要 Sidecar,只需要使用 ingressgateway
针对第一种情况,在建立服务时,最好配置 version 标签,第二种情况一般无需特殊处理。
同时也需要考虑项目是否已经部署在 Kubernetes 集群内:
- 新项目还未部署:按照 Istio 的规范创建 Deployment 及 Service,及 Istio 的核心资源
- 已部署在集群中的:需要修改 Deployment、Service,以及按需转为 Istio IngressGateway 对外提供服务
接下来以一个 Demo 项目为例,用于接入 Istio 并测试。
项目架构:
5.1 部署企业测试项目
5.1.1 部署 mysql 服务
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl create ns demo# 部署数据库
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl create -f mysql.yaml -f mysql-svc.yaml -f mysql-pvc.yaml -n demo# 查看部署pod
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl get po -n demo
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
mysql-6d698b4676-75g2x 1/1 Running 0 66s# 创建数据库、用户/密码
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl exec -it mysql-6d698b4676-75g2x -n demo -- bash
root@mysql-6d698b4676-75g2x:/# mysql -uroot -p
....
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.mysql> create database orders;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.03 sec)mysql> CREATE USER 'order'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'password';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.04 sec)mysql> GRANT ALL ON orders.* TO 'order'@'%';
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
5.1.2 部署 order 服务
# 创建Ingress
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl label node k8s-node02 ingress=true
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl create -f ingress-nginx-daemonset.yaml# 添加 Version 字段
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# vim demo-order-deploy.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# cat demo-order-deploy.yaml
....template:metadata:creationTimestamp: nulllabels:app: demo-orderversion: v1spec:containers:
....# 启动 order 服务
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl create -f demo-order-deploy.yaml -f demo-order-svc.yaml -f demo-order-ingress.yaml -n demo# 查看资源信息
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl get po,svc,ingress -n demo
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/demo-order-7c6ccb7865-b8btq 1/1 Running 0 83s
pod/mysql-6d698b4676-75g2x 1/1 Running 0 10mNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/mysql NodePort 10.102.167.87 <none> 3306:32541/TCP 10m
service/order ClusterIP 10.98.35.104 <none> 80/TCP 83sNAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
ingress.networking.k8s.io/demo-order nginx demo.test.com 192.168.200.52 80 82s# 测试访问:
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# echo "192.168.200.52 demo.test.com" >> /etc/hosts
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# curl demo.test.com/orders
[{"id":1,"name":"Order 1","price":10},{"id":2,"name":"Order 2","price":20}]
5.1.3 部署 handler 服务
# 添加 Version 字段
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# vim demo-handler-deploy.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# cat demo-handler-deploy.yaml
....template:metadata:creationTimestamp: nulllabels:app: demo-handlerversion: v1spec:containers:
....# 启动 handler 服务
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl create -f demo-handler-deploy.yaml -f demo-handler-svc.yaml -n demo
5.1.4 部署 receive 服务
# 添加 Version 字段
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# vim demo-receive-deploy.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# cat demo-receive-deploy.yaml
....template:metadata:creationTimestamp: nulllabels:app: demo-receiveversion: v1spec:volumes:
....# 启动 receive 服务
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl create -f demo-receive-deploy.yaml -f demo-receive-svc.yaml -f demo-receive-ingress.yaml -n demo
5.1.5 部署 前端ui 服务
# 添加 Version 字段
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# vim demo-ui-deploy.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# cat demo-ui-deploy.yaml
....template:metadata:creationTimestamp: nulllabels:app: demo-uiversion: v1spec:containers:
....# 启动 前端ui 服务
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl create -f demo-ui-deploy.yaml -f demo-ui-svc.yaml -f demo-ui-ingress.yaml -n demo
# 部署完毕后,最终的服务如下:
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl get po,svc -n demo
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/demo-handler-775df45c67-gc55g 1/1 Running 0 32m
pod/demo-order-7c6ccb7865-b8btq 1/1 Running 0 75m
pod/demo-receive-6cf94f6d9f-6b6lh 1/1 Running 0 5m33s
pod/demo-ui-88c9b5f76-jmjb4 1/1 Running 0 43s
pod/mysql-6d698b4676-75g2x 1/1 Running 0 84mNAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/demo-receive ClusterIP 10.96.97.54 <none> 8080/TCP 5m32s
service/demo-ui ClusterIP 10.98.249.2 <none> 80/TCP 43s
service/handler ClusterIP 10.99.3.59 <none> 80/TCP 32m
service/mysql NodePort 10.102.167.87 <none> 3306:32541/TCP 84m
service/order ClusterIP 10.98.35.104 <none> 80/TCP 75m
接下来通过浏览器访问:

5.2 Istio 南北流量网关改造
如果想要使用 Istio 管理流量,建议服务的入口使用 IngressGateway 进行管理,也就是需要把之前由其他控制器管理的 Ingress 改造为由 Istio Gateway 管理(新项目直接创建即可,无需改造)。
5.2.1 创建Gateway
首先确认当前项目的 Ingress 配置有哪些:
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl get ingress -n demo
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE
demo-order nginx demo.test.com 192.168.200.52 80 108m
demo-receive nginx demo.test.com 192.168.200.52 80 38m
demo-ui nginx demo.test.com 192.168.200.52 80 33m
接下来为该项目创建一个 Gateway:
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# vim demo-gateway.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# cat demo-gateway.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:name: demo-gateway
spec:selector:istio: ingressgateway # 使用默认的 istio ingress gatewayservers:- port:number: 80name: httpprotocol: HTTPhosts:- "demo.test.com" # 发布域名# 创建资源
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl create -f demo-gateway.yaml -n demo
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl get gw -n demo
NAME AGE
demo-gateway 14s
5.2.2 改造 order 服务的 Ingress 为 VirtualService
查看 order 服务的配置详情:
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# cat demo-order-ingress.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:name: demo-ordernamespace: demo
spec:ingressClassName: nginxrules:- host: demo.test.comhttp:paths:- backend:service:name: orderport:number: 80path: /orderspathType: ImplementationSpecific
改造后的 VirtualService:
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# vim demo-order-vs.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# cat demo-order-vs.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:name: demo-order
spec:hosts:- "demo.test.com"gateways:- demo-gatewayhttp:- match:- uri:prefix: /ordersroute:- destination:host: orderport:number: 80# 创建资源
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl create -f demo-order-vs.yaml -n demo
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl get vs -n demo
NAME GATEWAYS HOSTS AGE
demo-order ["demo-gateway"] ["demo.test.com"] 7s
接下来通过浏览器访问:

5.2.3 改造 receive 服务的 Ingress 为 VirtualService
查看 receive 服务的配置详情:
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# cat demo-receive-ingress.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:annotations:nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: /$2name: demo-receivenamespace: demo
spec:ingressClassName: nginxrules:- host: demo.test.comhttp:paths:- backend:service:name: demo-receiveport:number: 8080path: /receiveapi(/|$)(.*)pathType: ImplementationSpecific
改造后的 VirtualService:
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# vim demo-receive-vs.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# cat demo-receive-vs.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:name: demo-receive
spec:hosts:- "demo.test.com"gateways:- demo-gatewayhttp:- match:- uri:prefix: /receiveapi/rewrite:uri: /route:- destination:host: demo-receiveport:number: 8080# 创建资源
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl create -f demo-receive-vs.yaml -n demo
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl get vs -n demo
NAME GATEWAYS HOSTS AGE
demo-order ["demo-gateway"] ["demo.test.com"] 78m
demo-receive ["demo-gateway"] ["demo.test.com"] 7s
5.2.4 改造 前端ui 服务的 Ingress 为 VirtualService
查看 前端ui 服务的配置详情:
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# cat demo-ui-ingress.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:name: demo-uinamespace: demo
spec:ingressClassName: nginxrules:- host: demo.test.comhttp:paths:- backend:service:name: demo-uiport:number: 80path: /pathType: ImplementationSpecific
改造后的 VirtualService:
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# vim demo-ui-vs.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# cat demo-ui-vs.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:name: demo-ui
spec:hosts:- "demo.test.com"gateways:- demo-gatewayhttp:- match:- uri:prefix: /route:- destination:host: demo-uiport:number: 80# 创建资源
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl create -f demo-ui-vs.yaml -n demo
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl get vs -n demo
NAME GATEWAYS HOSTS AGE
demo-order ["demo-gateway"] ["demo.test.com"] 83m
demo-receive ["demo-gateway"] ["demo.test.com"] 5m13s
demo-ui ["demo-gateway"] ["demo.test.com"] 7s
接下来即可通过 http://demo.test.com:30080 访问该服务:

5.3 Istio 东西流量改造
如果需要 Istio 管理东西流量,需要注入 Istio 的 Sidecar。首先向 demo 的空间添加 Istio 注入的标签:
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl label ns demo istio-injection=enabled
接下来重建所有 Pod,注入 Sidecar:
# 删除所有pod
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl delete po -n demo --all# 查看重新建立的pod
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl get po -n demo
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
demo-handler-775df45c67-f42pv 2/2 Running 2 (52s ago) 2m47s
demo-order-7c6ccb7865-5gnw7 2/2 Running 3 (91s ago) 2m47s
demo-receive-6cf94f6d9f-d7794 2/2 Running 0 2m47s
demo-ui-88c9b5f76-l4qsx 2/2 Running 0 2m47s
mysql-6d698b4676-ns6qw 2/2 Running 0 2m48s
之后给需要管理东西流量的 Service 创建 VirtualService 和 DestinationRule,比如给 handler服务创建 VirtualService 和 DestinationRule:
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# vim demo-handler-dr.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# cat demo-handler-dr.yaml
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: DestinationRule
metadata:name: handler
spec:host: handlersubsets:- name: v1labels:version: v1
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1
kind: VirtualService
metadata:name: handlernamespace: demo
spec:hosts:- handlerhttp:- route:- destination:host: handlerport:number: 80subset: v1# 创建资源
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl create -f demo-handler-dr.yaml
[root@k8s-master01 demo]# kubectl get -f demo-handler-dr.yaml
NAME HOST AGE
destinationrule.networking.istio.io/handler handler 8sNAME GATEWAYS HOSTS AGE
virtualservice.networking.istio.io/handler ["handler"] 8s
访问测试后,查看 kiali 流量:
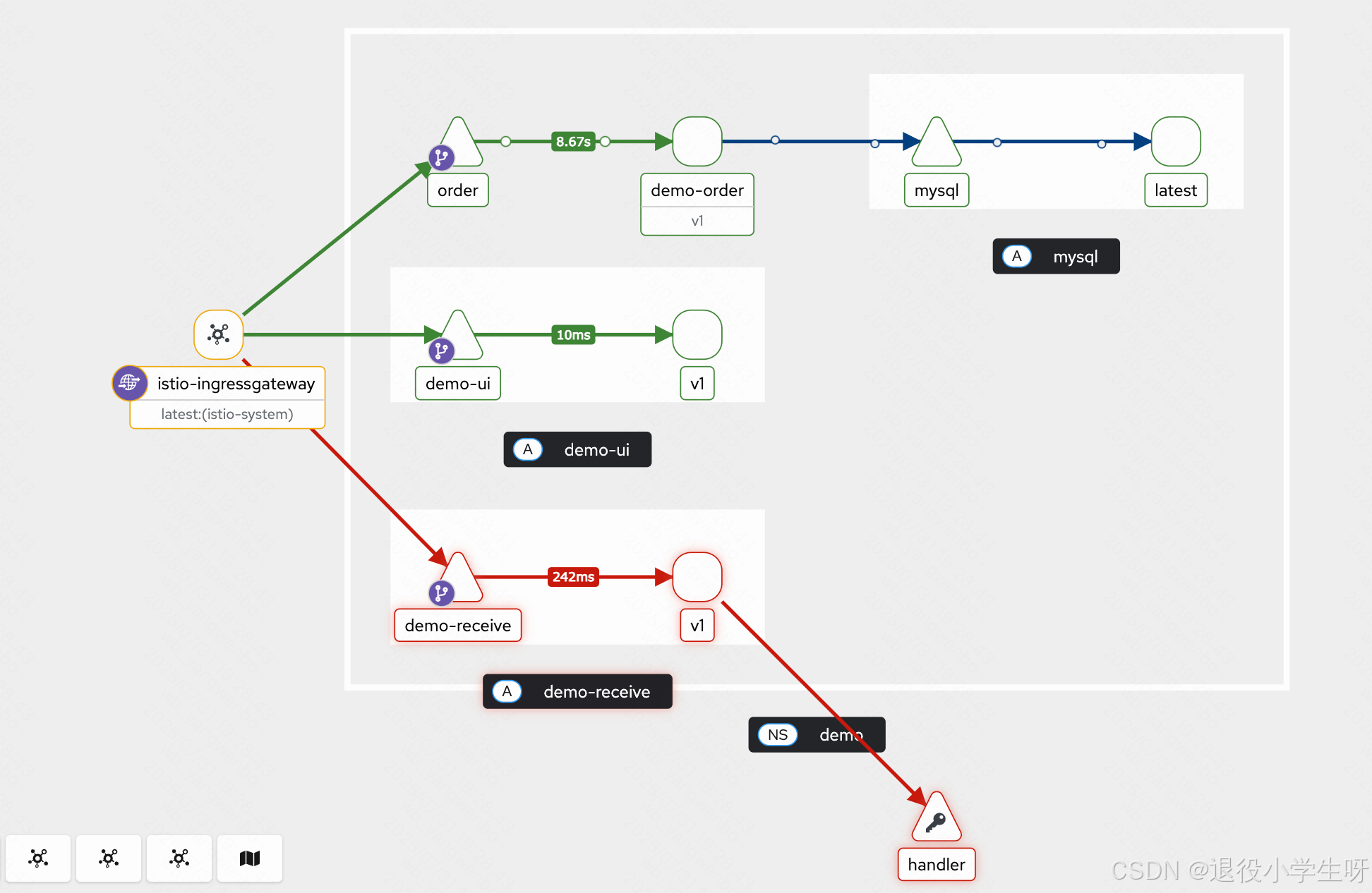
此博客来源于:https://edu.51cto.com/lecturer/11062970.html
