栈与队列的泛型实现
文章目录
- ۞声明:本篇博客栈与队列都采用的是数组实现的形式, 同时所有方法最后都会在Test中检验
- 一. 栈
- (一) 特性
- (二) 方法实现
- (1) T push(T e)
- (2) T pop()
- (3) T peek()
- (4) int size()
- (5) boolean isEmpty()
- (6) void ensureCapacity()
- (三) 测试
- 二. 普通队列
- (一) 特性
- (二) 方法实现
- (1) T offer(T e)
- (2) T poll()
- (3) T peek()
- (4) int size()
- (5) boolean isEmpty()
- (6) grow()
- (三) 测试
- 三. 循环队列
- (一) 特性
- (二) 方法实现
- (1) T enQueue(T e)
- (2) boolean deQueue()
- (3) T peek()
- (4) int size()
- (5) boolean isEmpty()
- (三) 测试
- 四. 双端队列
- (一) 特性
- (二) 方法实现
- (1) void offerFirst(T e)
- (2) void offerLast(T e)
- (3) boolean pollFirst()
- (4) boolean pollLast()
- (5) boolean isEmpty()
- (6) T peekFirst()
- (7) T peekLast()
- (8) int size()
- (9) grow()
- (三) 测试
- (五) 优先级队列(堆)
- (一) 特性
- (二) 方法实现
- (1) void siftUp(int child)
- (2) void siftDown(int parent, int k)
- (3) int poll()
- (4) void offer(int e)
- (5) int peek()
- (三) 测试
- (六) 小结
۞声明:本篇博客栈与队列都采用的是数组实现的形式, 同时所有方法最后都会在Test中检验
一. 栈
(一) 特性
栈在计算机学习中是一种重要的数据结构,拥有先进后出, 只在固定的的一端进行插入和删除操作, 插入数据在栈顶, 删除数据也在栈顶 的特性, 有非常多的应用:
- 内存管理:系统栈作为CPU与内存交互的媒介,存储临时数据和指令地址
- 虚拟机执行:JVM的栈帧存储局部变量表和操作数栈,支持字节码执行
- 文档撤销操作: 编辑软件(如Word、Photoshop)将用户操作记录存入栈,每次撤销时按反向顺序撤回最近的修改,支持多级撤销…
- 弹匣装弹时, 开出去的第一发子弹永远是最后加入弹匣的那颗
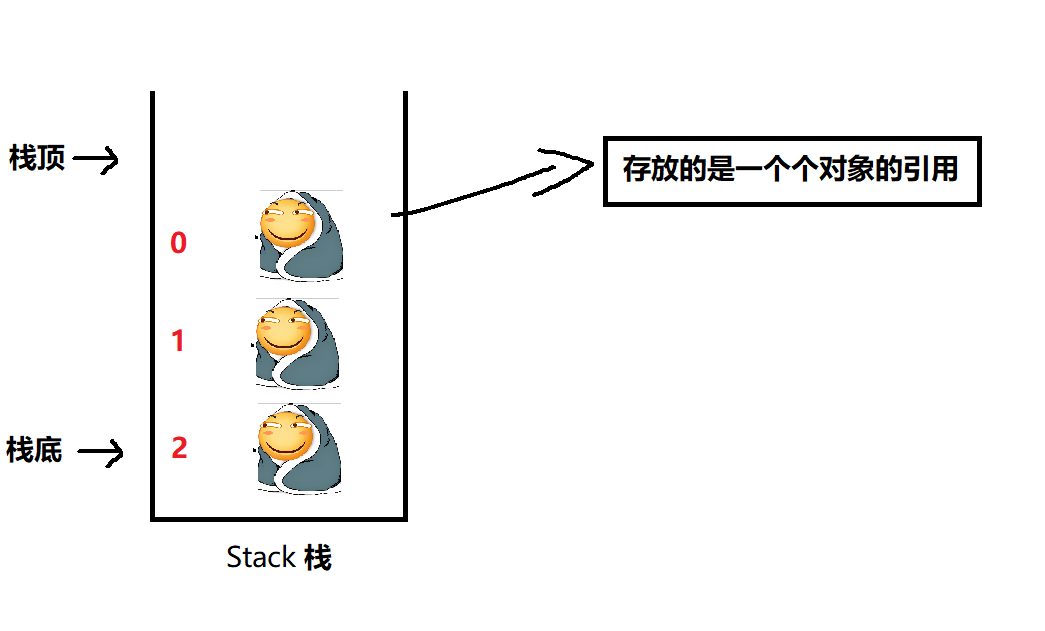
(二) 方法实现
栈的主要方法是:
push 入栈
pop 出栈
peek 查看栈顶元素
size 获取栈中有效元素个数
isEmpty 栈是否为空
我将模版放到下方, 想挑战的可以拿去自己实现~
import java.util.Arrays;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: ran* Date: 2025-07-31* Time: 20:24*/
public class MyStack<T> {private Object[] stack;private int size;public MyStack(int init) {if (init <= 0) {stack = new Object[100];}else {stack = new Object[init];}}public MyStack() {stack = new Object[100];}// 入栈public T push(T e){}// 出栈public T pop() {}// 查看栈顶元素public T peek(){}// 查看当前栈的元素个数public int size(){}// 查看栈是否为空public boolean isEmpty(){}// 栈的扩容private void ensureCapacity(){}}(1) T push(T e)
入栈操作, 重点是要从栈顶入栈
// 入栈public T push(T e){ensureCapacity();stack[size++] = e;return e;}
(2) T pop()
出栈, 也是在栈顶
// 出栈public T pop() {if (isEmpty()) {throw new RuntimeException("栈为空,⽆法删除元素");}return (T) stack[--size];}
(3) T peek()
查看栈顶元素
// 查看栈顶元素public T peek(){if(isEmpty()){throw new RuntimeException("栈为空,⽆法获取栈顶元素");}return (T)stack[size - 1];}
(4) int size()
获取栈中有效元素个数
// 查看当前栈的元素个数public int size(){return size;}
(5) boolean isEmpty()
查看栈是否为空
// 查看栈是否为空public boolean isEmpty(){return 0 == size;}
(6) void ensureCapacity()
栈的扩容
// 栈的扩容private void ensureCapacity(){if(size == stack.length){stack = Arrays.copyOf(stack, size*2);}}
(三) 测试

import java.util.Queue;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: ran* Date: 2025-07-31* Time: 16:14*/
public class Test {public static void main(String[] args) {MyStack<Integer> stack = new MyStack<>(10);stack.push(1);stack.push(2);stack.push(3);stack.push(4);stack.push(5);System.out.println("获取MyStack<Integer>的栈顶: " + stack.peek());System.out.println("删除MyStack<Integer>的栈顶: " + stack.pop());System.out.println("查看MyStack<Integer>是否空: " +stack.isEmpty());System.out.println("查看MyStack<Integer>栈的长度: " +stack.size());System.out.println("------------");MyStack<String> stringMyStack = new MyStack<>();stringMyStack.push("hello");stringMyStack.push("我");stringMyStack.push("是");stringMyStack.push("❀");System.out.println("获取MyStack<String>的栈顶: " + stringMyStack.peek());System.out.println("删除MyStack<String>的栈顶: " + stringMyStack.pop());System.out.println("查看MyStack<String>是否空: " +stringMyStack.isEmpty());System.out.println("查看MyStack<String>栈的长度: " +stringMyStack.size());}
}
二. 普通队列
(一) 特性
- 只允许在⼀端进⾏插⼊数据操作,在另⼀端进⾏删除数据操作的特殊线性表
- 插入/入队的一端是队尾, 删除/出队的一端是队头
- 队列拥有先进先出的特性, 与生活中的排队买票类似
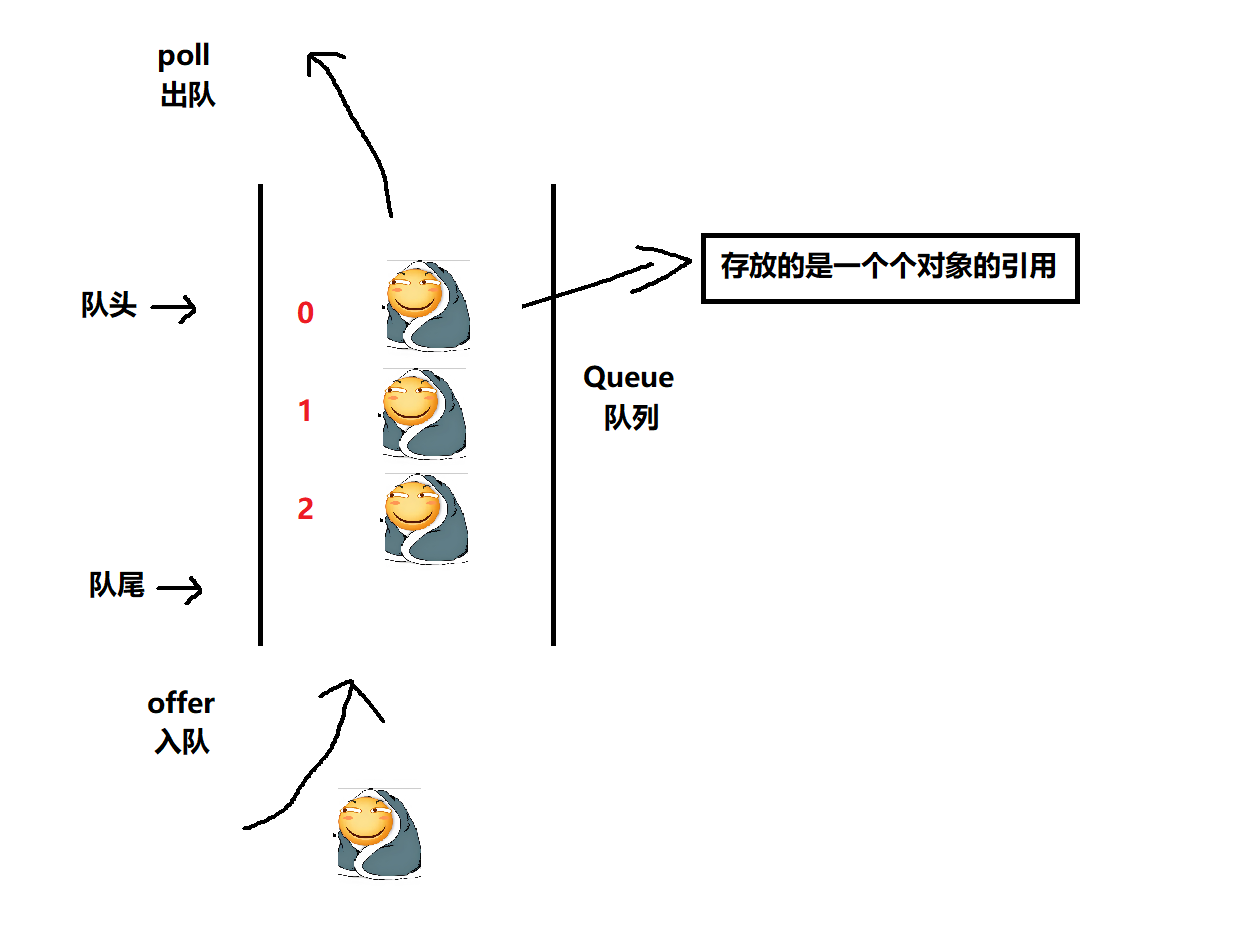
(二) 方法实现
offer 入队列
poll 出队列
peek 获取队头元素
size获取队列有效元素个数
isEmpty 检测队列是否为空
模版依旧放到下方~
/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: ran* Date: 2025-07-31* Time: 21:42*/
public class MyQueue<T> {private Object[] queue;private int front;private int rear;public MyQueue() {queue = new Object[100];}// 入队列public T offer(T e) {}// 出队列public T poll() {}// 获取队头元素public T peek() {}// 获取队列有效元素个数public int size() {}// 检测队列是否为空public boolean isEmpty() {}}(1) T offer(T e)
入队列, 只能从队尾入队列, 入队列之前要判断队列是否满
// 入队列public T offer(T e) {grow();queue[rear++] = e;return e;}
(2) T poll()
出队列, 只能从队头出队, 出之前要判断队列是否空
// 出队列public T poll() {if (isEmpty()) {throw new RuntimeException("队列没有元素!");}return (T) queue[front++];}
(3) T peek()
获取队头元素, 获取之前要判断队列是否空
// 获取队头元素public T peek() {if (isEmpty()) {throw new RuntimeException("队列没有元素!");}return (T) queue[front];}
(4) int size()
获取队列有效元素个数, 直接返回rear - font
// 获取队列有效元素个数public int size() {int size = rear - front;return size >= 0 ? size : -1;}
(5) boolean isEmpty()
检测队列是否为空, 判断rear是否等于front
// 检测队列是否为空public boolean isEmpty() {return rear == front;}
(6) grow()
队列扩容之前要判断是否已满
private void grow() {if (rear == queue.length) {queue = Arrays.copyOf(queue,size *2);}}
(三) 测试
public static void main(String[] args) {MyQueue<Integer> queue = new MyQueue<>();queue.offer(1);queue.offer(2);queue.offer(3);queue.offer(4);queue.offer(5);System.out.println("获取 MyQueue<Integer>的队头: " + queue.peek());System.out.println("删除 MyQueue<Integer>的队头: " + queue.poll());System.out.println("查看 MyQueue<Integer>是否空: " +queue.isEmpty());System.out.println("查看 MyQueue<Integer>队列的长度: " +queue.size());System.out.println("------------");MyQueue<String> stringMyQueue = new MyQueue<>();stringMyQueue.offer("hello");stringMyQueue.offer("我");stringMyQueue.offer("是");stringMyQueue.offer("❀");System.out.println("获取 MyQueue<String>的队头: " + stringMyQueue.peek());System.out.println("删除 MyQueue<String>的队头: " + stringMyQueue.poll());System.out.println("查看 MyQueue<String>是否空: " +stringMyQueue.isEmpty());System.out.println("查看 MyQueue<String>队列的长度: " +stringMyQueue.size());}
三. 循环队列
(一) 特性
观察上面的队列实现我们可以发现, 基于数组实现的普通队列空间利用率很低, 于是一种新的队列模型->循环队列诞生了, 通常我们去一个固定大小的数组, 队列满了则不能进队, 队列空了不能出队, 不再像之前扩容, 循环往复利用队列的空间
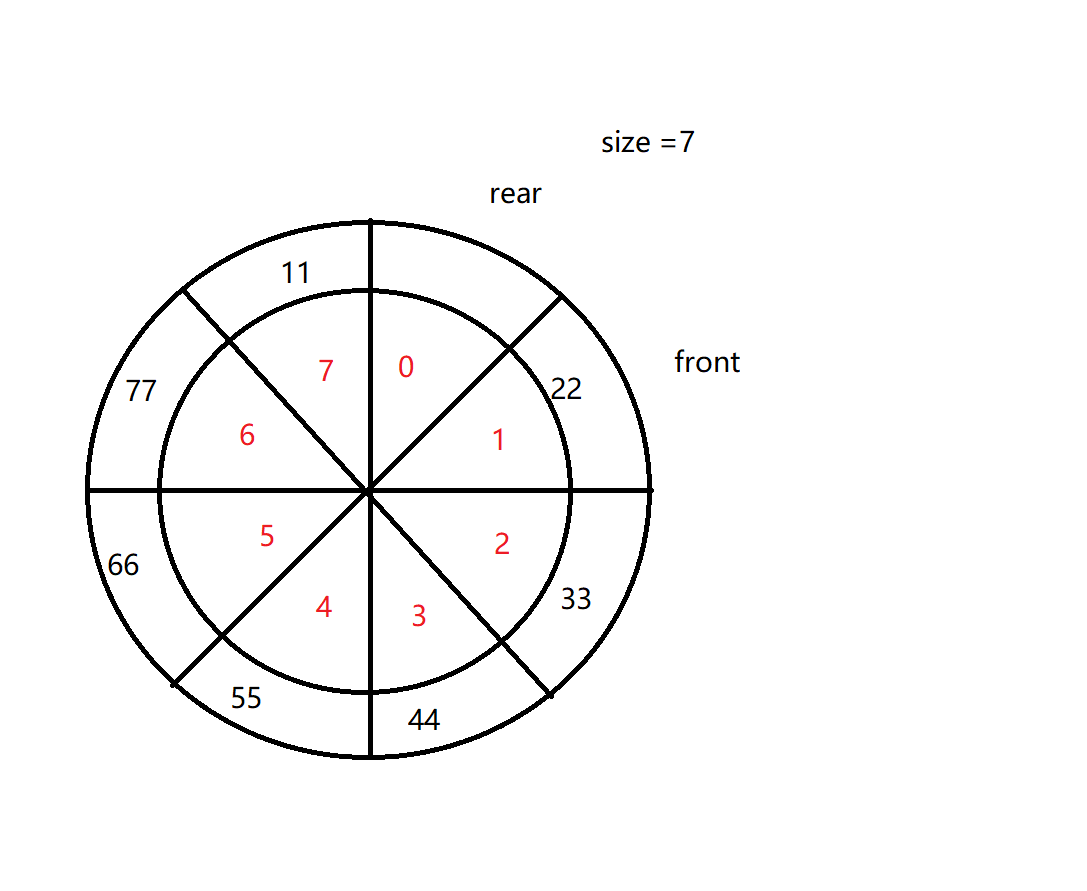
(二) 方法实现
在实现之前我们要用到头指针front 和 尾指针rear 以及标志位size, 分别用来表示头尾位置与有效元素个数
方法模版放在下方
/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: ran* Date: 2025-08-01* Time: 9:50*/
public class MyCycleQueue<T> {private Object[] deque;private int front;private int rear;private int size;public MyCycleQueue() {queue = new Object[5];}// 入队列public boolean enQueue(T e) {}// 出队列public boolean deQueue() {}// 获取队头元素public T peek() {}// 获取队列有效元素个数public int size() {}// 检测队列是否为空public boolean isEmpty() {}
}(1) T enQueue(T e)
入队列,先要判断队列是否已满, 注意: front 的移动方式是从0到尾再到0, 所以可以将front=front%length, 确保front可以回归0位置, 并且不越界
// 入队列public boolean enQueue(T e) {if (size() == queue.length) {return false;}queue[rear++] = e;rear = rear % queue.length;size++;return true;}
(2) boolean deQueue()
出队列前先判断队列是否是空的, rear的移动方式和dront相同
// 出队列public boolean deQueue() {if (isEmpty()) {return false;}front++;front = front % queue.length;size--;return true;}
(3) T peek()
获取队头元素之前先判断队列是否为空
// 获取队头元素public T peek() {if (isEmpty()) {throw new RuntimeException("队列是空的!!!");}return (T) queue[front];}
(4) int size()
获取队列有效元素个数, 返回size
// 获取队列有效元素个数public int size() {return size;}
(5) boolean isEmpty()
判断队列是否为空, 判断size是否为0
// 检测队列是否为空public boolean isEmpty() {return size == 0;}
(三) 测试
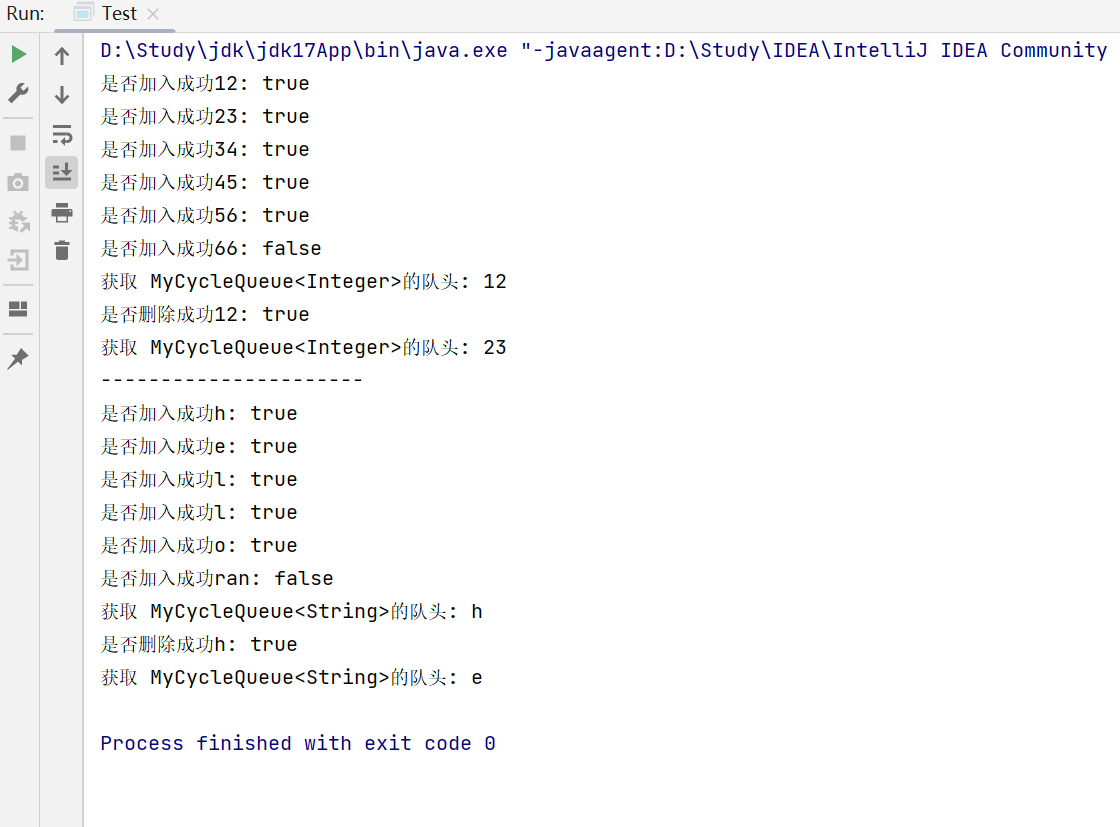
public static void main(String[] args) {MyCycleQueue<Integer> queue = new MyCycleQueue<>();System.out.println("是否加入成功12: " +queue.enQueue(12));System.out.println("是否加入成功23: " +queue.enQueue(23));System.out.println("是否加入成功34: " +queue.enQueue(34));System.out.println("是否加入成功45: " +queue.enQueue(45));System.out.println("是否加入成功56: " +queue.enQueue(56));System.out.println("是否加入成功66: " +queue.enQueue(66));System.out.println("获取 MyCycleQueue<Integer>的队头: " + queue.peek());System.out.println("是否删除成功12: " +queue.deQueue());System.out.println("获取 MyCycleQueue<Integer>的队头: " + queue.peek());System.out.println("----------------------");MyCycleQueue<String> stringMyCycleQueue = new MyCycleQueue<>();System.out.println("是否加入成功h: " + stringMyCycleQueue.enQueue("h"));System.out.println("是否加入成功e: " + stringMyCycleQueue.enQueue("e"));System.out.println("是否加入成功l: " + stringMyCycleQueue.enQueue("l"));System.out.println("是否加入成功l: " + stringMyCycleQueue.enQueue("l"));System.out.println("是否加入成功o: " + stringMyCycleQueue.enQueue("o"));System.out.println("是否加入成功ran: " + stringMyCycleQueue.enQueue("ran"));System.out.println("获取 MyCycleQueue<String>的队头: " + stringMyCycleQueue.peek());System.out.println("是否删除成功h: " + stringMyCycleQueue.deQueue());System.out.println("获取 MyCycleQueue<String>的队头: " + stringMyCycleQueue.peek());}
四. 双端队列
(一) 特性
- 双端队列(deque)是指允许两端都可以进⾏⼊队和出队操作的队列,deque 是 “double endedqueue” 的简称。那就说明元素可以从队头出队和⼊队,也可以从队尾出队和⼊队。
- 双端队列与链表LinkedList十分相似, 基本大差不差, 除了不能中间插入和获取随机元素外基本没有差别, 有兴趣的小伙伴可以借鉴上篇博客的LinkedList, 这里不过多赘述,
- 这里主要用数组实现双端队列
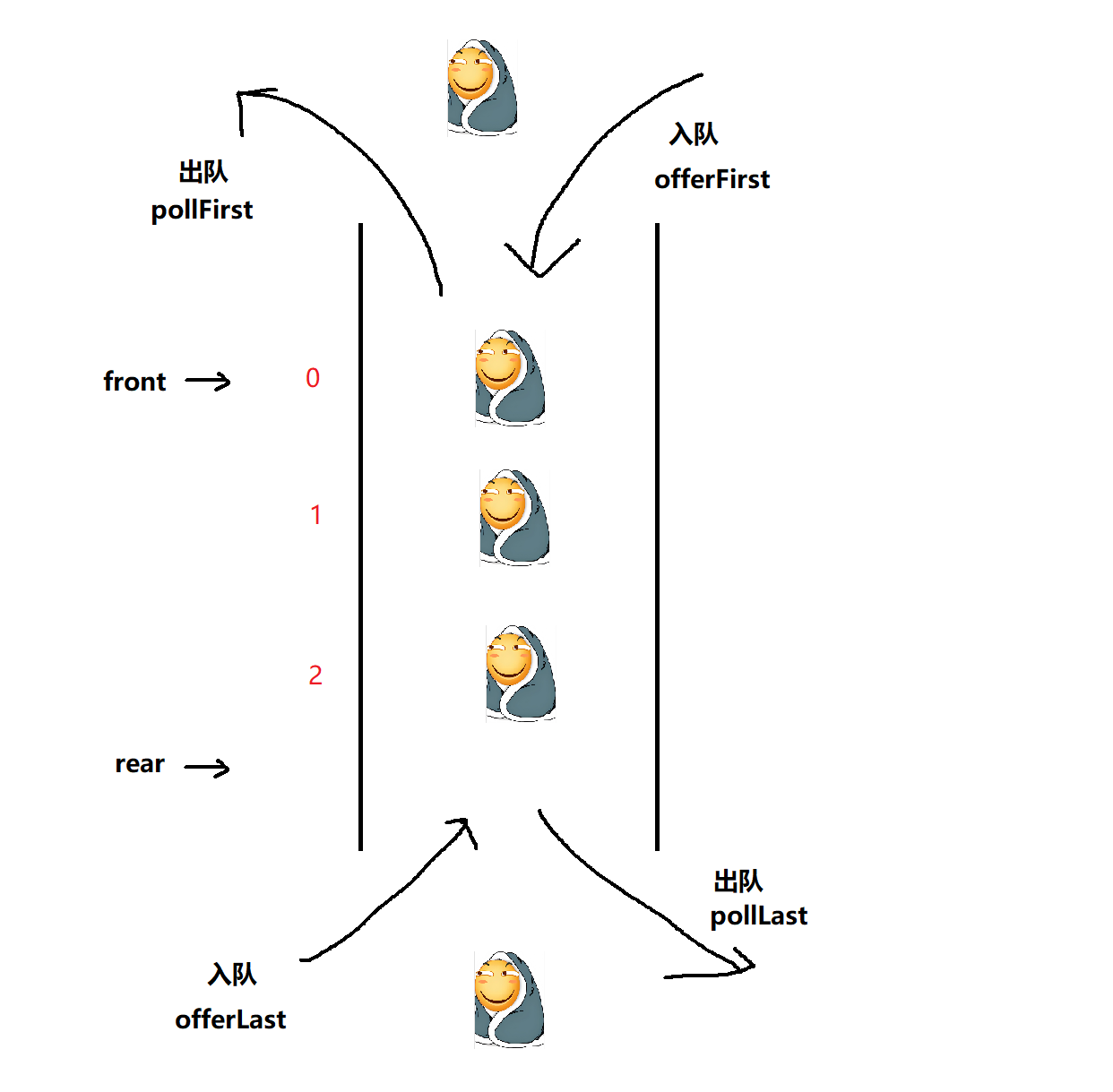
(二) 方法实现
需要三个属性, 头尾指针以及size
模版放在下方
import java.util.Deque;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: ran* Date: 2025-08-01* Time: 11:05*/
public class MyDque<T> {private Object[] deque;private int front;private int rear;private int size;public MyDque() {deque = new Object[5];}// 头插入队列public void offerFirst(T e) {}// 尾差入队列public void offerLast(T e) {}// 队头出队列public boolean pollFirst() {}// 队尾出队列public boolean pollLast() {}// 是否为空public boolean isEmpty() {}// 获取队头元素public T peekFirst() {}// 获取队尾元素public T peekLast() {}// 获取队列有效元素个数public int size() {}
}(1) void offerFirst(T e)
我们这里双端队列头插时可以采用类似于循环队列的方式, 即front可以左移, 充分利用空间
// 头插入队列public void offerFirst(T e) {grow();if (front > 0) {deque[--front] = e;size++;return;}if (front == 0 ) {for (int i = rear - 1; i >= 0; i--) {deque[i + 1] = deque[i];}}deque[0] = e;rear++;size++;}
(2) void offerLast(T e)
尾差法之前要判断是否满, 只需要移动rear即可
// 尾差入队列public void offerLast(T e) {grow();deque[rear++] = e;size++;}
(3) boolean pollFirst()
头删法, 先判断队列是否为空, 将front移动和置为null
// 队头出队列public boolean pollFirst() {if (isEmpty()) {return false;}deque[front++] = null;size--;return true;}
(4) boolean pollLast()
尾删法, 先判断队列是否为空, 移动rear和置为null
// 队尾出队列public boolean pollLast() {if (isEmpty()) {return false;}deque[--rear] = null;size--;return true;}
(5) boolean isEmpty()
判断对了是否为空, 判断size
// 是否为空public boolean isEmpty() {return size == 0;}
(6) T peekFirst()
获取队头元素, 先判断是否为空
// 获取队头元素public T peekFirst() {if (isEmpty()) {return null;}return (T) deque[front];}
(7) T peekLast()
获取队尾元素, 先判断队列空不空
// 获取队尾元素public T peekLast() {if (isEmpty()) {return null;}return (T) deque[rear - 1];}
(8) int size()
获取队列有效元素个数, 直接返回size即可
// 获取队列有效元素个数public int size() {return size;}
(9) grow()
队列满了就扩容
private void grow() {if (size == deque.length) {deque = Arrays.copyOf(deque, size * 2);}}
(三) 测试

public static void main(String[] args) {MyDque<Integer> deque = new MyDque<>();deque.offerFirst(1);deque.offerFirst(3);deque.offerFirst(2);deque.offerLast(0);deque.offerLast(9);System.out.println( "删除前: "+deque);System.out.println("删除头元素" +deque.pollFirst());System.out.println("删除尾元素" + deque.pollLast());System.out.println( "删除后: "+deque);System.out.println("------------------------");MyDque<String> stringMyDque = new MyDque<>();stringMyDque.offerFirst("h");stringMyDque.offerFirst("e");stringMyDque.offerFirst("l");stringMyDque.offerFirst("l");stringMyDque.offerFirst("0");stringMyDque.offerFirst("ran");System.out.println("删除前: " +stringMyDque);System.out.println("删除头元素" +stringMyDque.pollFirst());System.out.println("删除尾元素" +stringMyDque.pollLast());System.out.println("删除后: " +stringMyDque);}
(五) 优先级队列(堆)
(一) 特性
- 优先级队列在生活中也是极为常见的, 医院排队结账时, 会让孕妇, 老人, 和军人优先, 在这里, 我们可以让最小的/最大的优先出队列, 应该提供两个最基本的操作,⼀个是返回最⾼优先级对象,⼀个是添加新的对象。
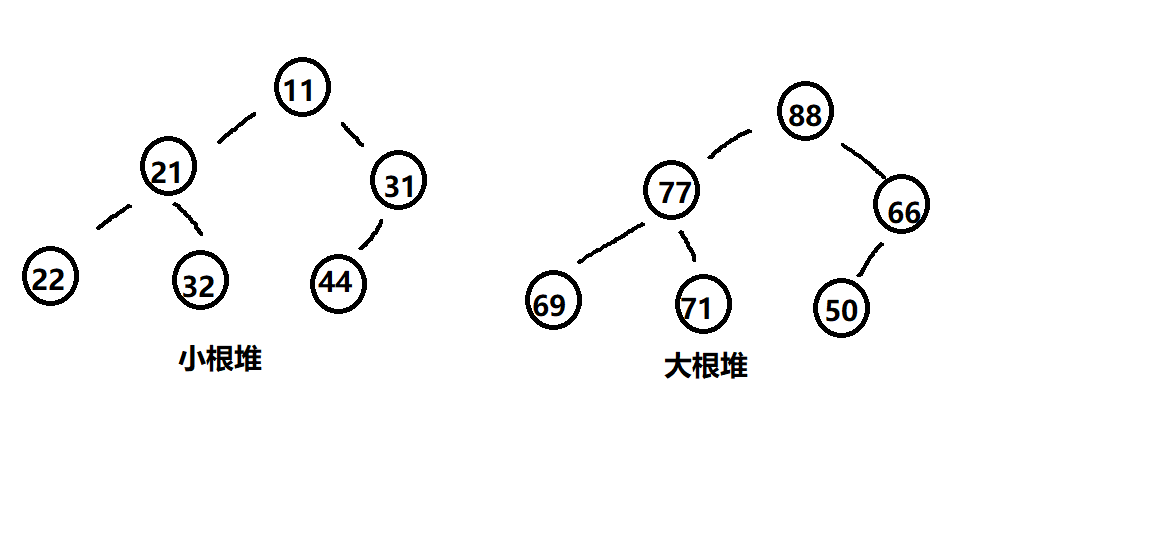
- 把它的所有元素按完全⼆叉树的顺序存储方式存储在⼀个⼀维数组中,
- 将根节点最⼤的堆叫做最⼤堆或⼤根堆,根节点最⼩的堆叫做最⼩堆或⼩根堆。
- 堆中某个节点的值总是不⼤于或不⼩于其⽗节点的值
- 堆总是⼀棵完全⼆叉树
(二) 方法实现
要知道向上调整 siftUp与向下调整 siftDown的概念, 以及应用场景
这里以大根堆为例, 采用int类型的数组实现, 不再用泛型(泛型难度有点大)
模版放在下方
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA.* Description:* User: ran* Date: 2025-08-01* Time: 12:33*/
public class MyPriorityQueue{int[] priorityQueue;int size;public MyPriorityQueue() {priorityQueue = new int[10];}// 入队列public void offer(int e) {}// 扩容private void grow() {}// 向上调整public void siftUp(int child) {}// 向下调整private void siftDown(int parent, int k) {}// 交换元素private void swap(int parent, int child) {}// 删除优先级最高的元素public int poll() {}// 获取优先级最高的元素public int peek() {}}(1) void siftUp(int child)
向上调整, 已知子节点来求父节点
// 向上调整public void siftUp(int child) {int parent = (child - 1) / 2;while (parent >= 0) {if (priorityQueue[child] > priorityQueue[parent]) {swap(parent, child);child = parent;parent = (child - 1) / 2;}else {break;}}}
(2) void siftDown(int parent, int k)
向下调整, 知道父节点后来求子节点, 并且有限制条件 k
// 向下调整private void siftDown(int parent, int k) {int child = parent * 2 + 1;while (child < k) {if (child + 1 < k && priorityQueue[child + 1] > priorityQueue[child]) {child++;}if (priorityQueue[child] > priorityQueue[parent]) {swap(parent,child);parent = child;child = parent * 2 + 1;}else {break;}}}
(3) int poll()
删除优先级最高的元素, 先判断是否为空, 交换收尾元素位置后向下调整
// 删除优先级最高的元素public int poll() {if (size == 0) {throw new RuntimeException("空队列!!!");}int ret = priorityQueue[0];swap(0, size - 1);size--;siftDown(0, size);return ret;}
(4) void offer(int e)
入队列, 从末尾入队列, 先判断队列是否, 后采用向上调整
// 入队列public void offer(int e) {grow();priorityQueue[size] = e;siftUp(size - 1);}
(5) int peek()
获取优先级最高的元素, 就是获取0下标的元素, 先判断是否为空
// 获取优先级最高的元素public int peek() {if (size == 0) {throw new RuntimeException("空队列!!!");}return priorityQueue[0];}
(三) 测试
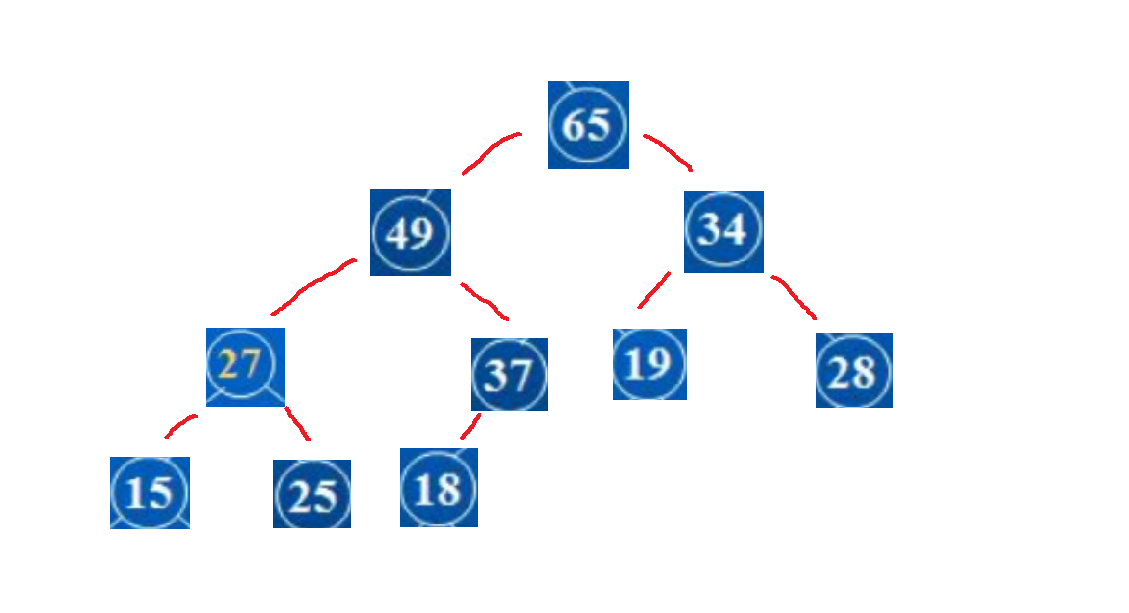
public static void main(String[] args) {MyPriorityQueue priorityQueue = new MyPriorityQueue();priorityQueue.offer(27);priorityQueue.offer(15);priorityQueue.offer(19);priorityQueue.offer(18);priorityQueue.offer(28);priorityQueue.offer(34);priorityQueue.offer(65);priorityQueue.offer(49);priorityQueue.offer(25);priorityQueue.offer(37);System.out.println("删除前: ");priorityQueue.display();System.out.println( "删除最大元素: " + priorityQueue.poll());System.out.println( "删除最大元素: " + priorityQueue.poll());System.out.println("删除后: ");priorityQueue.display();}
(六) 小结
希望本篇博客能对你有所帮助, 喜欢的话不妨互三一下☺
