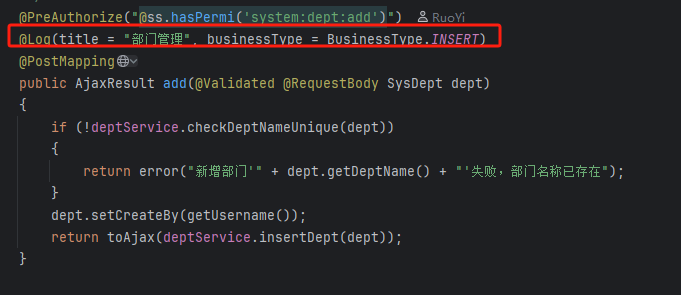
10.若依的自定义注解 Log
若依框架的自定义注解Log的含义是记录调用该api请求的请求参数、请求体、响应时间等信息
自定义注解的四个步骤:
1)开启Aop EnableAspectJAutoProxy
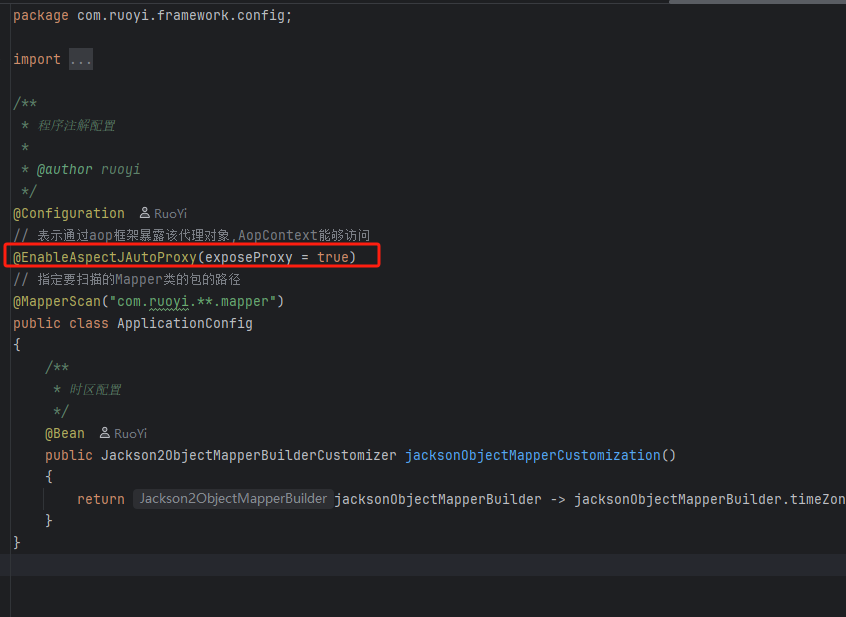
默认同一个类下的方法调用不会走代理,exposeProxy = true 的含义是让AopContext上下文能够获取该代理。
上面这句话太过于抽象,这里举个例子就明确了
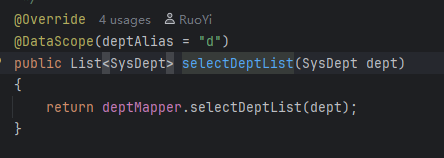
若依获取部门列表的方法,可以看出有个范围限制的注解
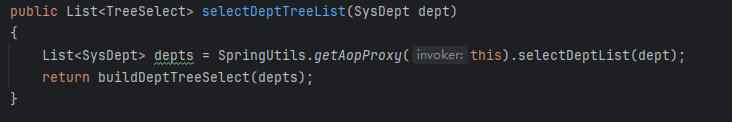
获取部门树结构,这里看出这里通过AopContext上下文获取代理,保证调用selectDeptList时DataScope注解生效,也就是只能查看自己权限范围内的部门树。
2. 定义注解
Target:指定注解可以用在方法上,也可以用在函数调用的参数上,还有Type、Field等。
Retention:包括三种,RetentionPolicy.SOURCE、RetentionPolicy.CLASS、RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME
Documented:javadoc文档
接口方法表示可设置参数
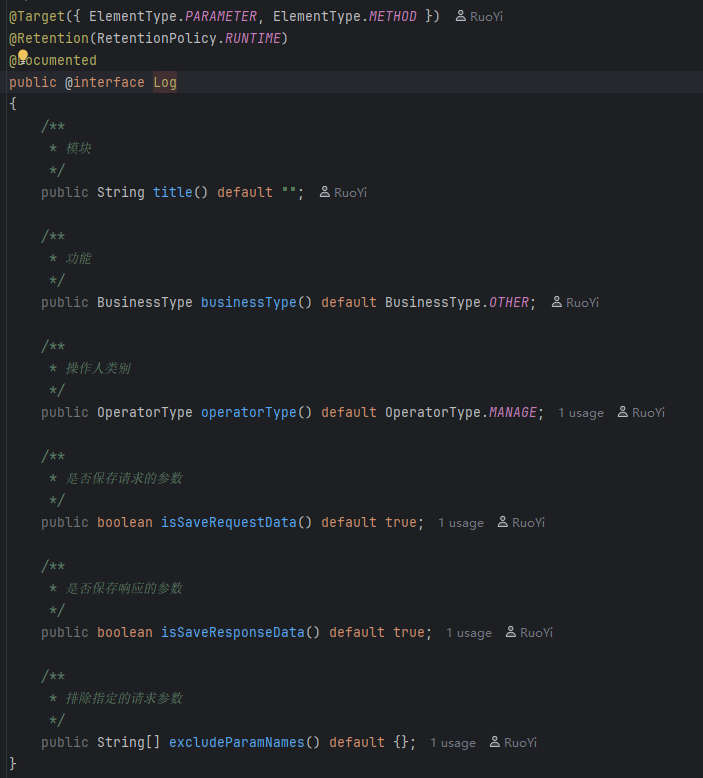
Target分类
TYPE
适用目标:类、接口(包括注解类型)、枚举
示例:@Controller, @Service
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Service {}@Service
public class UserService {}
FIELD
适用目标:字段(包括枚举常量)
示例:@Autowired, @Value
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface MaxLength {int value() default 100;
}public class User {@MaxLength(50)private String username;
}
METHOD
适用目标:方法
示例:@Override, @RequestMapping
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface LogExecutionTime {}public class OrderService {@LogExecutionTimepublic void placeOrder() {}
}
PARAMETER
适用目标:方法参数
示例:@RequestParam, @PathVariable
@Target(ElementType.PARAMETER)
public @interface NotNull {}public class ValidationService {public void validateUser(@NotNull String username) {}
}
CONSTRUCTOR
适用目标:构造方法
示例:@Autowired (用于构造方法)
@Target(ElementType.CONSTRUCTOR)
public @interface Inject {}public class PaymentService {@Injectpublic PaymentService() {}
}
LOCAL_VARIABLE
适用目标:局部变量
注意:很少用于自定义注解,通常用于静态分析工具
@Target(ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE)
public @interface SuppressWarning {}public class Example {public void demo() {@SuppressWarningString temp = "test";}
}
ANNOTATION_TYPE
适用目标:注解类型(用于元注解)
示例:@Target, @Retention 本身
ANNOTATION_TYPE 是 ElementType
中的一个特殊值,它表示注解可以用在其他注解上(即修饰注解的注解,称为元注解)。这种机制主要用于定义注解的元数据,例如控制注解的生命周期(@Retention)、作用目标(@Target)等。
PACKAGE
适用目标:包
示例:@Package-info 中的注解
@Target(ElementType.PACKAGE)
public @interface PackageInfo {}@PackageInfo
package com.example;
TYPE_PARAMETER (Java 8+)
适用目标:类型参数(泛型参数)
示例:class MyClass<@MyAnnotation T>
@Target(ElementType.TYPE_PARAMETER)
public @interface NonNull {}public class Box<@NonNull T> {}
TYPE_USE (Java 8+)
适用目标:类型使用的任何地方
包括:类型声明、类型参数、throws子句等
@Target(ElementType.TYPE_USE)
public @interface NonNull {}public class Example {private List<@NonNull String> names;public @NonNull String getName() { return ""; }
}
Retention分类
RetentionPolicy.SOURCE
源码使用,不会被编译到class,典型应用Override
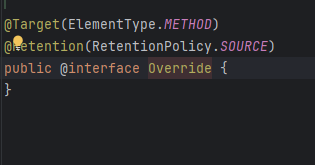
RetentionPolicy.CLASS
保留到编译后的 .class 文件中,不会被加载到JVM中,运行时无法通过反射获取,主要在类加载时或编译后处理阶段被工具处理。
也就是通过字节码可以看到该定义,一般用于静态工具使用。
RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME
我们一般定义的都是该类型,在运行过程中反射API,获取注解信息
3. 注解实现
ElementType.METHOD 切面位置
@Around
环绕通知,在目标方法执行前后都执行,可以控制方法是否执行。
@Before
前置通知,在目标方法执行前执行。
@After
后置通知,在目标方法执行后执行(无论是否抛出异常)。
@AfterReturning
返回通知,在目标方法正常返回后执行。
@AfterThrowing
异常通知,在目标方法抛出异常后执行。
@Pointcut
定义切点表达式,通常不直接标注在方法上,但可以引用方法作为切点。
举例:
// 定义切点:匹配 com.example.service 包下的所有方法
@Pointcut("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public void serviceLayer() {}// 环绕通知:记录方法执行时间
@Around("serviceLayer()") // 引用切点
public Object logExecutionTime(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();Object result = joinPoint.proceed(); // 执行目标方法long duration = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;System.out.println(joinPoint.getSignature() + " executed in " + duration + "ms");return result;
}
下面来看下Log实现了哪些方法:
- 当前线程记录调用方法开始的时间
@Before(value = "@annotation(controllerLog)")
public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint, Log controllerLog)
{TIME_THREADLOCAL.set(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
- 正常返回,没有抛异常执行
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "@annotation(controllerLog)", returning = "jsonResult")public void doAfterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint, Log controllerLog, Object jsonResult){handleLog(joinPoint, controllerLog, null, jsonResult);}
pointcut表示要匹配哪些注解,"@annotation(controllerLog)"表示匹配所有带有@controllerLog注解的方法
returning = "jsonResult"表示将返回值绑定到通知方法的jsonResult参数上
handleLog 的实现比较简单,获取当前用户、IP、请求参数等,将其记录到数据中。下面几个函数用法可以学习下
//通过joinPoint获取注解调用方法的所在类名、方法名
String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getName();
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
4. 应用注解
应用注解,会在操作记录表中插入一行数据