快手开源 Kwaipilot-AutoThink 思考模型,有效解决过度思考问题

新闻
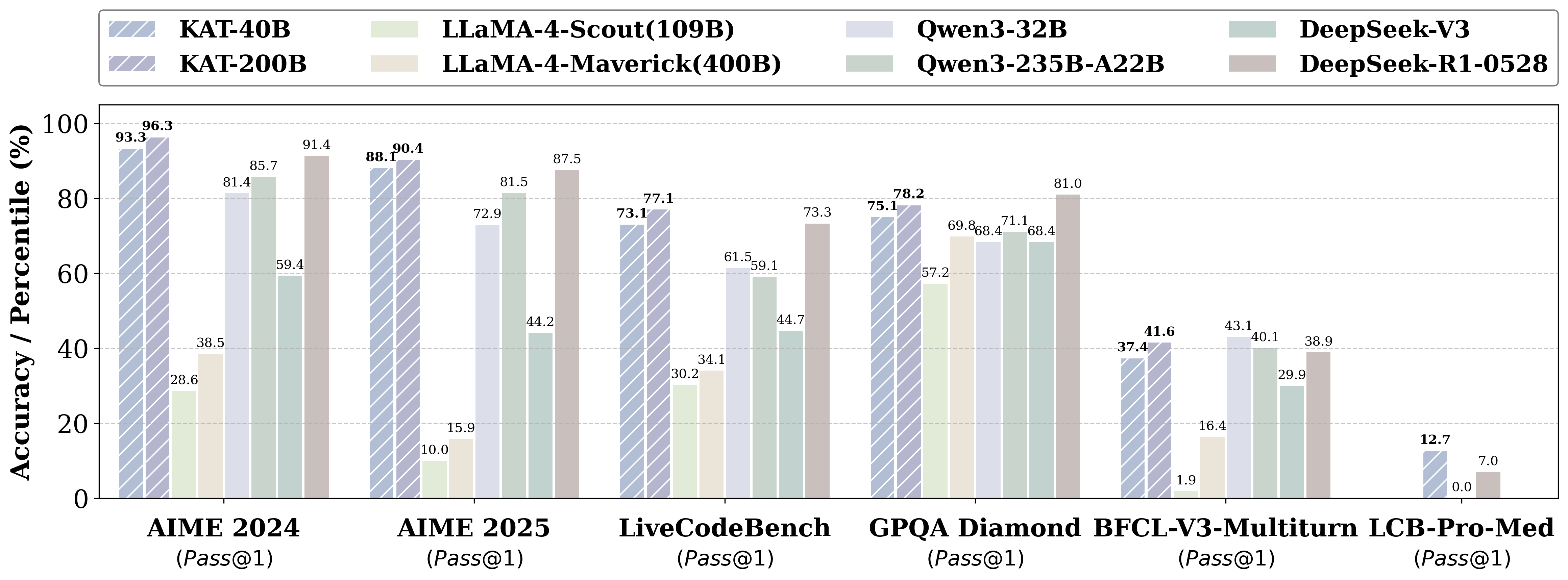
- 在专为防止数据泄露设计的挑战性基准测试LiveCodeBench Pro中,Kwaipilot-AutoThink位列所有开源模型榜首,甚至超越了Seed和o3-mini等强大的专有系统。
介绍
KAT(Kwaipilot-AutoThink) 是一个开源大语言模型,通过学习何时生成显式思维
链及何时直接作答,有效缓解过度思考问题。
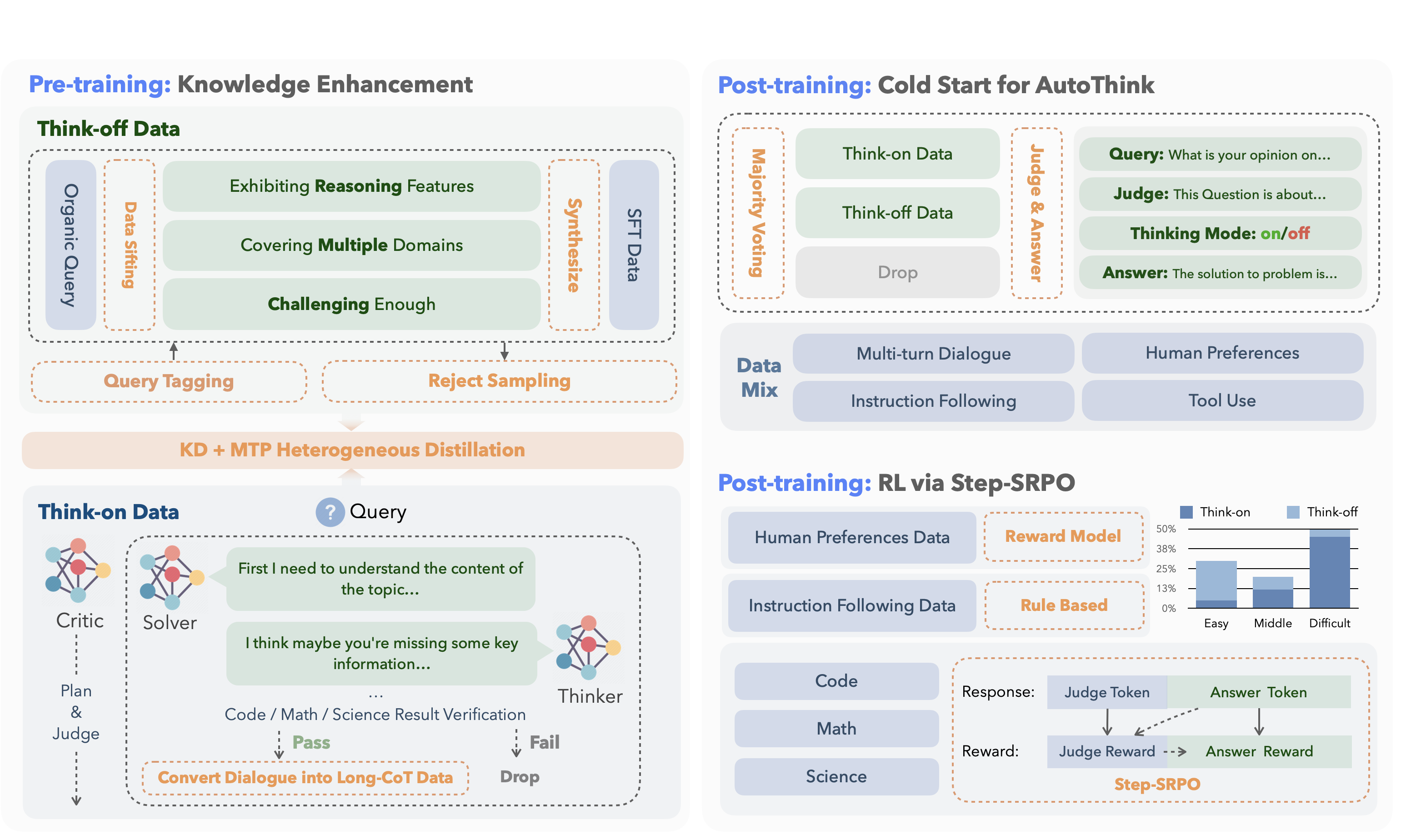
它的发展遵循简洁的两阶段训练流程:
| 阶段 | 核心思想 | 关键技术 | 成果 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. 预训练阶段 | 在分离"推理"与"直接回答"的同时注入知识 | 双机制数据 • 通过定制标签系统标注的非思考型查询 • 由多智能体求解器生成的思考型查询 知识蒸馏 + 多标记预测实现细粒度效用 | 基础模型在不承担完整预训练成本的情况下,获得强大的事实掌握和推理能力 |
| 2. 后训练阶段 | 使推理过程可选项且高效 | 冷启动自动思考 —— 多数表决设定初始思考模式 分步SRPO —— 中间监督机制奖励正确的模式选择及该模式下的答案准确性 | 模型仅在有益时触发思维链,减少标记使用并加速推理 |
数据格式
KAT生成的响应采用结构化模板,使推理路径清晰且机器可解析。
支持两种模式:
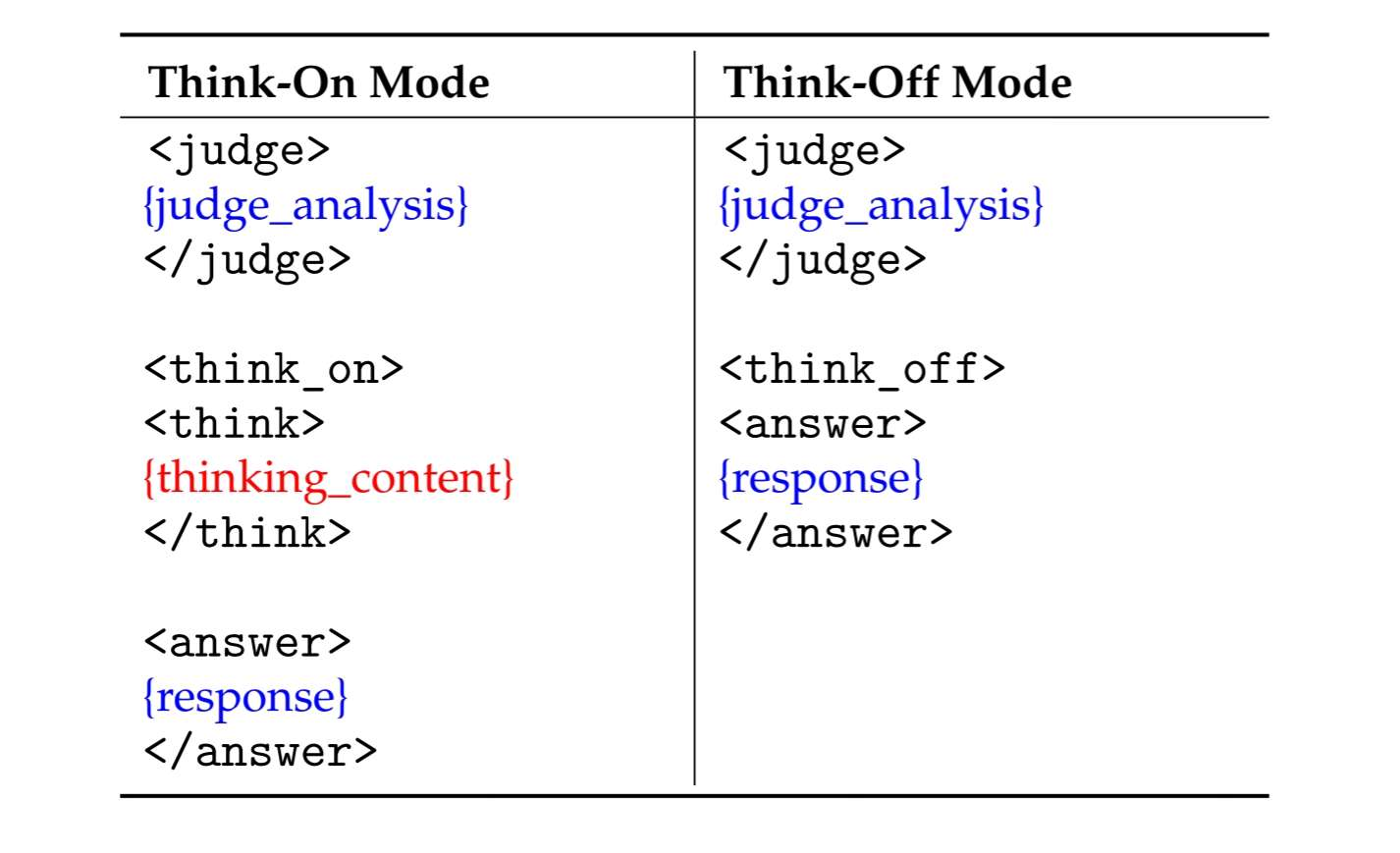
特殊标记
| 标记 | 描述 |
|---|---|
<judge> | 分析输入内容以判断是否需要显式推理。 |
<think_on> / <think_off> | 表示推理功能是否启用(“on”)或跳过(“off”)。 |
<think> | 当选择think_on时,标记思维链片段的开始。 |
<answer> | 标记最终面向用户答案的开始。 |
🔧 Quick Start
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForCausalLMmodel_name = "Kwaipilot/KAT-V1-40B"# load the tokenizer and the model
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name, trust_remote_code=True)
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name,torch_dtype="auto",device_map="auto"
)# prepare the model input
prompt = "Give me a short introduction to large language model."
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": prompt}
]
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(messages,tokenize=False,add_generation_prompt=True
)
model_inputs = tokenizer([text], return_tensors="pt").to(model.device)# conduct text completion
generated_ids = model.generate(**model_inputs,max_new_tokens=65536,temperature=0.6,top_p=0.95,
)
output_ids = generated_ids[0][len(model_inputs.input_ids[0]):].tolist()
content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids, skip_special_tokens=True).strip("\n")
print("prompt:\n", prompt)
print("content:\n", content)
"""
prompt:
Give me a short introduction to large language model.
content:
<judge>
The user's request is to provide a concise factual introduction to large language models, which involves retrieving and summarizing basic information. This task is straightforward as it only requires recalling and presenting well-known details without deeper analysis. No complex reasoning is needed here—just a simple explanation will suffice.
</judge><think_off>
<answer>
A **Large Language Model (LLM)** is an advanced AI system trained on vast amounts of text data to understand, generate, and process human-like language. Here’s a concise introduction:### Key Points:
1. **Training**: Trained on diverse text sources (books, websites, etc.) using deep learning.
2. **Capabilities**: - Answer questions, generate text, summarize content, translate languages.- Understand context, sentiment, and nuances in language.
3. **Architecture**: Often based on **transformer models** (e.g., BERT, GPT, LLaMA).
4. **Scale**: Billions of parameters, requiring massive computational resources.
5. **Applications**: Chatbots, content creation, coding assistance, research, and more.### Examples:
- **OpenAI’s GPT-4**: Powers ChatGPT.
- **Google’s Gemini**: Used in Bard.
- **Meta’s LLaMA**: Open-source alternative.### Challenges:
- **Bias**: Can reflect biases in training data.
- **Accuracy**: May hallucinate "facts" not grounded in reality.
- **Ethics**: Raises concerns about misinformation and job displacement.LLMs represent a leap forward in natural language processing, enabling machines to interact with humans in increasingly sophisticated ways. 🌐🤖
</answer>
"""
