篇章五 数据结构——链表(一)
目录
1.ArrayList的缺陷
2. 链表
2.1 链表的概念及结构
2.2 链表结构
1. 单向或者双向
2.带头或者不带头
3.循环或者非循环
2.3 链表的实现
1.完整代码
2.图解
3.显示方法
4.链表大小
5. 链表是否存在 key 值
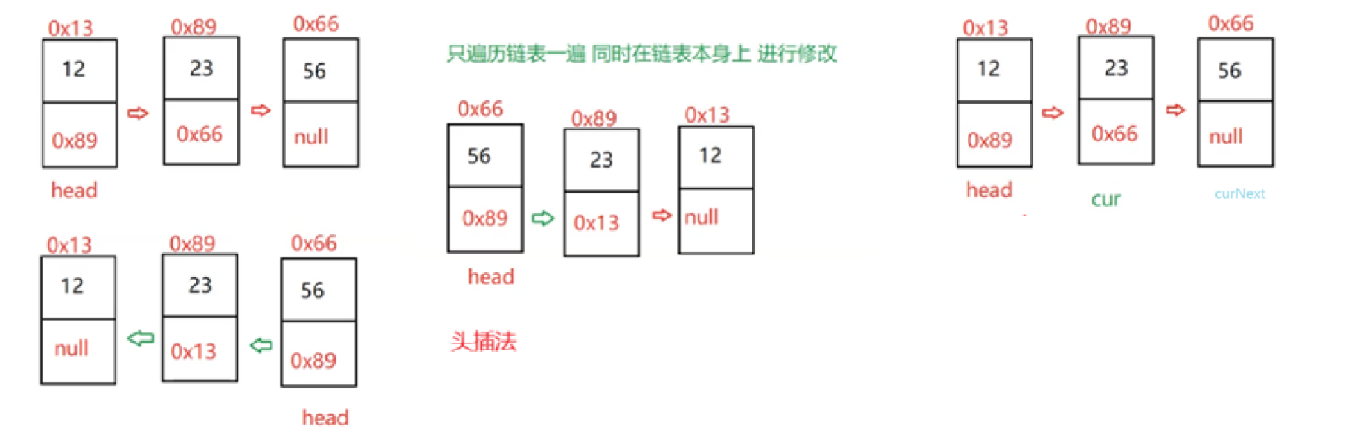
6.头插法
7.尾插法
8.中间插入
9.删除key值节点
10.删除所有key值节点
11.clear
3.练习
3.1 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点
3.2 反转一个单链表
3.3 给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点
3.4 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点
3.5 将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的
3.6 编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前
编辑
3.7 链表的回文结构
3.8 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点
3.9 给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环
3.10 给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 NULL
1.ArrayList的缺陷
通过篇章四,我们已经熟悉了ArrayList的使用,并且进行了简单模拟实现。通过源码知道,ArrayList底层使用数组来存储元素。
那这样会出现什么问题呢?
由于其底层是一段连续空间,当在ArrayList任意位置插入或者删除元素时,就需要将后序元素整体往前或者往后搬移,时间复杂度为O(n),效率比较低。因此ArrayList不适合做任意位置插入和删除比较多的场景。因此:java集合中又引入了LinkedList,即链表结构。
2. 链表
2.1 链表的概念及结构
链表是一种 物理存储结构上非连续 存储结构,数据元素的 逻辑顺序 是通过链表中的 引用链接 次序实现的。

注意:
1.从上图可看出,链式结构在逻辑上是连续的,但是在物理上不一定连续
2.现实中的结点一般都是从堆上申请出来的
3.从堆上申请的空间,是按照一定的策略来分配的,两次申请的空间可能连续,也可能不连续
2.2 链表结构
实际中链表的结构非常多样,以下情况组合起来就有8种链表结构:
1. 单向或者双向

什么是双向?

2.带头或者不带头
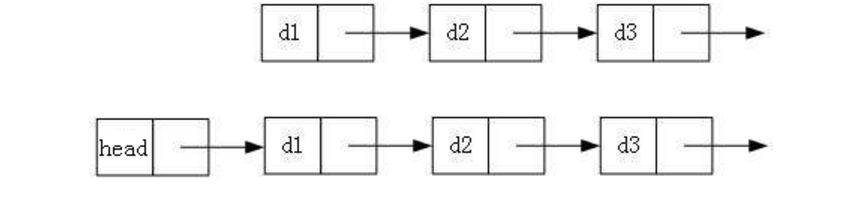
什么是带头?

什么是不带头?

3.循环或者非循环

什么是循环?

组合成的 8种链表结构:

虽然有这么多的链表的结构,但是我们重点掌握两种:
1. 无头单向非循环链表:结构简单,一般不会单独用来存数据。实际中更多是作为其他数据结构的子结构,如哈希桶、图的邻接表等等。

2. 无头双向非循环链表:在Java的集合框架库中LinkedList底层实现就是无头双向循环链表。
2.3 链表的实现
1.完整代码
/*** Created with IntelliJ IDEA* Description 无头单向非循环链表实现* User: 王杰* Date: 2025-05-26* Time: 20:33*/
public class MySingleList implements IList{static class ListNode {public int val;public ListNode next;public ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}}public ListNode head;// 创建链表public void createList() {ListNode node1 = new ListNode(12);ListNode node2 = new ListNode(23);ListNode node3 = new ListNode(34);ListNode node4 = new ListNode(45);ListNode node5 = new ListNode(56);node1.next = node2;node2.next = node3;node3.next = node4;node4.next = node5;this.head = node1;}// 显示方法@Overridepublic void display() {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {System.out.print(cur.val + " ");cur = cur.next;}}// 链表大小@Overridepublic int size() {int len = 0;ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {len++;cur = cur.next;}return len;}// 链表是否存在 key 值@Overridepublic boolean contains(int key) {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == key) {return true;}cur = cur.next;}return false;}// 头插法@Overridepublic void addFirst(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);node.next = head;head = node;}// 尾插法@Overridepublic void addLast(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);// 一个节点都没有if (head == null) {head = node;return;}// 找尾巴ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.next == null) {cur.next = node;return;}cur = cur.next;}}//中间插入@Overridepublic void addIndex(int index, int data) {int len = size();if (index < 0 || index > len) {System.out.println("index位置不存在");return;}if (index == 0) {addFirst(data);return;}if (index == len) {addLast(data);return;}// 中间插入ListNode cur = head;if (index - 1 != 0) {cur = cur.next;index--;}ListNode node = new ListNode(data);// 所有的插入 优先 绑定后边node.next = cur.next;cur.next = node;}// 删除 key值 节点@Overridepublic void remove(int key) {if (head == null) {return;}// 删除头节点if (head.val == key) {head = head.next;return;}ListNode cur = findNodeOfKey(key);if (cur == null) {return;}ListNode del = cur.next;cur.next = del.next;}private ListNode findNodeOfKey(int key) {ListNode cur = head;while (cur.next != null) {if (cur.next.val == key) {return cur;}cur = cur.next;}return null;}// 删除 所有key值 节点@Overridepublic void removeAllKey(int key) {if (head == null) {return;}ListNode prev = head;ListNode cur = head.next;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == key) {prev.next = cur.next;cur = cur.next;}else {prev = cur;cur = cur.next;}}if (head.val == key) {head = head.next;}}@Overridepublic void clear() {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {ListNode curNext = cur.next;cur.next = null;cur = curNext;}head = null;}}
2.图解
单向不带头非循环链表:

3.显示方法

// 显示方法
@Override
public void display() {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {System.out.print(cur.val + " ");cur = cur.next;}
}4.链表大小

// 链表大小@Overridepublic int size() {int len = 0;ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {len++;cur = cur.next;}return len;}实现到这里,我们需要掌握的是:
1.ListNode cur = head;
此处申请了临时变量,因为数据存储在堆空间,而且 cur 也指向链表,所以改变有效。同时 此处也是为了不改变 head 的位置,因为后续要用head找到该链表,如果head位置变动了,就找不到该链表了。
2.cur != null;
此处最后一个节点,是会运算的。最后,cur指向的是最后一个节点的下一个节点,也就是 null;
3.cur.next != null;
此处最后一个节点,是不会运算的。最后,cur指向的是最后一个节点。
5. 链表是否存在 key 值

// 链表是否存在 key 值@Overridepublic boolean contains(int key) {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == key) {return true;}cur = cur.next;}return false;}6.头插法

// 头插法@Overridepublic void addFirst(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);node.next = head;head = node;}7.尾插法

// 尾插法@Overridepublic void addLast(int data) {ListNode node = new ListNode(data);// 一个节点都没有if (head == null) {head = node;return;}// 找尾巴ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.next == null) {cur.next = node;return;}cur = cur.next;}}8.中间插入

//中间插入@Overridepublic void addIndex(int index, int data) {int len = size();if (index < 0 || index > len) {System.out.println("index位置不存在");return;}if (index == 0) {addFirst(data);return;}if (index == len) {addLast(data);}// 中间插入ListNode cur = head;if (index - 1 != 0) {cur = cur.next;index--;}ListNode node = new ListNode(data);// 所有的插入 优先 绑定后边node.next = cur.next;cur.next = node;}注意:
1.此处中间插入,关键是找到 要 插入的位置 的 前一个位置。
2.要牢记 所有的插入 优先 绑定后边
9.删除key值节点

// 删除 key值 节点@Overridepublic void remove(int key) {if (head == null) {return;}// 删除头节点if (head.val == key) {head = head.next;return;}ListNode cur = findNodeOfKey(key);if (cur == null) {return;}ListNode del = cur.next;cur.next = del.next;}private ListNode findNodeOfKey(int key) {ListNode cur = head;while (cur.next != null) {if (cur.next.val == key) {return cur;}cur = cur.next;}return null;}注意:
找到 要删除的节点 的前一个节点
这一思路在单链表中很关键
10.删除所有key值节点

// 删除 所有key值 节点@Overridepublic void removeAllKey(int key) {if (head == null) {return;}ListNode prev = head;ListNode cur = head.next;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == key) {prev.next = cur.next;cur = cur.next;}else {prev = cur;cur = cur.next;}}if (head.val == key) {head = head.next;}}11.clear

@Overridepublic void clear() {ListNode cur = head;while (cur != null) {ListNode curNext = cur.next;cur.next = null;cur = curNext;}head = null;}注意:
此处最后 head 也要置空
3.练习
3.1 删除链表中等于给定值 val 的所有节点
203. 移除链表元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {if (head == null) {return head;}ListNode prev = head;ListNode cur = head.next;while (cur != null) {if (cur.val == val) {prev.next = cur.next;cur = cur.next;}else {prev = cur;cur = cur.next;}}if (head.val == val) {head = head.next;}return head;}
}203. 移除链表元素 - 力扣(LeetCode) 此处和 2.3 中的 10.删除所有key节点 一样
3.2 反转一个单链表
OJ链接
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {if(head == null) {return head;}ListNode cur = head.next;head.next = null;while(cur != null) {ListNode curNext = cur.next;cur.next = head;head = cur;cur = curNext;}return head;}
}3.3 给定一个带有头结点 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点
OJ链接

/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/class Solution {public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {if(head == null) {return null;}ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next.next;} return slow; }}注意:
做这些练习的时候,要考虑 空链表 的情况,也就是 head == null
3.4 输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点
OJ链接

/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public int kthToLast(ListNode head, int k) {if(head == null) {return -1;}ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;// fast 走 k - 1 步int count = 0; while(count != k - 1) {fast = fast.next;count++;}while(fast.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next;}return slow.val;}
}注意:
1. fast.next != null;
此处 fast 走到最后一个节点即可,不必走到 null
2.此处 k 值,不确定是否合法,一般题目中会设置范围,但是没设置的话就需要补充上k值合法性的校验
补充:验证 k 的合法性

/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public int kthToLast(ListNode head, int k) {if(head == null) {return -1;}if(k <= 0) {return -1;}ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;// fast 走 k - 1 步int count = 0; while(count != k - 1) {fast = fast.next;if(fast == null) {return -1;}count++;}while(fast.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next;}return slow.val;}
}3.5 将两个有序链表合并为一个新的有序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的
OJ链接

/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/class Solution {public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode list1, ListNode list2) {ListNode newHead = new ListNode();ListNode cur = newHead;while(list1 != null && list2 != null) {if(list1.val > list2.val) {cur.next = list2;list2 = list2.next;cur = cur.next;}else {cur.next = list1;list1 = list1.next;cur = cur.next;}}if(list1 != null) {cur.next = list1;}if(list2 != null) {cur.next = list2;}return newHead.next;}}3.6 编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前
OJ链接
import java.util.*;/*
public class ListNode {int val;ListNode next = null;ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}
}*/
public class Partition {public ListNode partition(ListNode pHead, int x) {ListNode cur = pHead;ListNode beforStart = null;ListNode beforEnd = null;ListNode afterStart = null;ListNode afterEnd = null;while(cur != null) {if(cur.val < x) {if(beforStart == null) {beforStart = cur;beforEnd = cur;}else {beforEnd.next = cur;beforEnd = beforEnd.next;}cur = cur.next;}else {if(afterStart == null) {afterStart = cur;afterEnd = cur;}else {afterEnd.next = cur;afterEnd = afterEnd.next;}cur = cur.next;} }if(beforStart == null) {return afterStart;}// 置空 afterEnd.nextif(afterStart != null) {afterEnd.next = null;}beforEnd.next = afterStart;return beforStart;}
}注意:
此处思路:是把 大于x 和 小于x 的值分为两个链表。
但是:注意特殊情况,比如大于x的链表为空 和 小于x的链表为空。
而且:要注意,在 小于x的链表不为空时, 置空 afterEnd.next
3.7 链表的回文结构
OJ链接

import java.util.*;/*
public class ListNode {int val;ListNode next = null;ListNode(int val) {this.val = val;}
}*/
public class PalindromeList {public boolean chkPalindrome(ListNode A) {if(A == null) {return true;}ListNode fast = A;ListNode slow = A;while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;}ListNode cur = slow.next;while(cur != null) {ListNode curNext = cur.next;cur.next = slow;slow = cur;cur =curNext;} while(A != slow) {if(A.val != slow.val) {return false;}// 偶数情况if(A.next == slow) {return true;}A = A.next;slow = slow.next;}return true;}
}注意:
1. 三步走:找中间节点,反转中间节点后的链表,比较前半部分和后半部分链表的val值
2. 偶数情况:
if(A.next == slow) {
return true;
}
3.8 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点
OJ链接

/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) {* val = x;* next = null;* }* }*/
public class Solution {public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {ListNode pLong = headA;ListNode pShort = headB;// 先求两个链表的长度int lenA = 0;int lenB = 0;while(pLong != null) {lenA++;pLong = pLong.next;}while(pShort != null) {lenB++;pShort = pShort.next;}pLong = headApShort = headB// 求差值int len = lenA - lenB;if(len < 0) {pLong = lenB;pShort = lenA;len = lenB - lenA;}// 走完上述两步 pLong 一定指向最长的链表 pShort 一定指向最短的链表// 接下来的操作 只需要操作 pLong 和 pShort 就行了// 让最长的链表走 len 步while(len != 0) {pLong = pLong.next;len--;}// 两个引用同时走 直到他们相遇while(pLong != pShort) {pLong = pLong.next;pShort = pShort.next;}if(pLong == null) {return null; // 不相交}return pLong;}
}注意:
1.主要思路就是:走两个链表长度的差值步
2. 此处注意还原 pLong 和 pShort ,因为算长度,他们的位置发生了改变,要还原,否则影响下面代码
pLong = headA
pShort = headB3.注意不相交的情况:
if(pLong == null) {
return null; // 不相交
}
3.9 给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环
OJ链接

/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) {* val = x;* next = null;* }* }*/
public class Solution {public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {if(head == null) {return false;}if(head.next == null) {return false;}ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;if(fast == slow) {return true;}}return false;}
}【思路】
快慢指针,即慢指针一次走一步,快指针一次走两步,两个指针从链表起始位置开始运行,如果链表带环则一定会在环中相遇,否则快指针率先走到链表的末尾。比如:陪女朋友到操作跑步减肥。
【扩展问题】
-
为什么快指针每次走两步,慢指针走一步可以?
假设链表带环,两个指针最后都会进入环,快指针先进环,慢指针后进环。当慢指针刚进环时,可能就和快
指针相遇了,最差情况下两个指针之间的距离刚好就是环的长度。此时,两个指针每移动一次,之间的距离就缩小一步,不会出现每次刚好是套圈的情况,因此:在慢指针走到一圈之前,快指针肯定是可以追上慢指针的,即相遇。
-
快指针一次走3步,走4步,...n步行吗?

注意:
1.链表为空,和只有一个节点的情况是不存在环的
if(head == null) {
return false;
}if(head.next == null) {
return false;
}2.快慢指针的步数问题:
快 2 慢 2:会相遇
快3 慢 1 :永不相遇
可见:并不是快指针比慢指针快就行,还得注意步数问题。
3.10 给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 NULL
OJ链接

/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) {* val = x;* next = null;* }* }*/
public class Solution {public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;if(head == null) {return null;}if(head.next == null) {return null;}while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {fast = fast.next.next;slow = slow.next;if(fast == slow) {break;}}if(fast == null || fast.next == null) {return null; // 没有环}slow = head;while(slow != fast) {fast = fast.next;slow = slow.next;}return slow;}
}【结论】
让一个指针从链表起始位置开始遍历链表,同时让一个指针从判环时相遇点的位置开始绕环运行,两个指针都是每次均走一步,最终肯定会在入口点的位置相遇。
【证明】

注意:
1.链表为空,和只有一个节点的情况是不存在环的
if(head == null) {
return false;
}if(head.next == null) {
return false;
}2.相遇时出循环:
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if(fast == slow) {
break;
}
}3.去除没有环的情况:
if(fast == null || fast.next == null) {
return null; // 没有环
}4.关键:让慢指针回到链表开头,然后慢指针与快指针以相同的速度走
slow = head;
while(slow != fast) {
fast = fast.next;
slow = slow.next;
}5.证明:此处最关键的是,fast的路程是slow路程的二倍,建立等式,计算,取极端情况 得出关系,写代码。

