车载学习(6)——CAPL(1)一些基础知识
1.一些CAPL的知识
CAPL通讯访问编程语言(Commmunication Access Programming language)
CAPL的用途
- ECU的仿真实现(报文的收发、数据的处理)
- 实现总线日志纪录的控制
- 实现总线数据自动化分析
- 实现ECU功能的自动化测试
- 实现ECU报文发送周期的自动化测试
- 实现诊断测试的自动化
CAPL程序的运行机制 - 以“事件触发代码执行”的机制运行
- 在CANoe工程中,总线启动后,随着各种“事件”的发生而触发响应的代码
2.编辑工具
CAPL Browser
3.语法
类C语言。只专注不同。
3.1 数据类型
- 数值类型:整形、浮点型
- 整形:有符号(int (2byte),long(4byte),int 64(8byte)),无符号(byte,word(2byte),dword(4byte),gword(8byte))
- 浮点型:float,double
- 字符类型:char
3.2 新数据类型
3.2.1 报文类型
使用关键字message声明一个报文变量,当使用message声明报文变量时,默认变量是CAN报文变量。当有数据库支撑的时候,一个完整的声明应该包括Message ID或者Message name。
- 报文变量的声明:
- 报文变量的属性查看:
- 报文变量的属性配置:
- 报文的输出
On key 'a'
{// 报文的定义message 0x666 msg1;message DoorState msg2;message 0x30f msg3;message 200 msg4;message * msg5;// 报文属性的查看write("message id 0x%x\n",msg2.id);write("message name %s\n",msg2.name);write("message dlc: %d\n",msg2.dlc);
}On key 'b'
{message DoorState mess1;// 报文数据的赋值 // mess1.byte(0)= 0xC0; // 不建议// 信号赋值方式mess1.RightDoorState = 0; // 值赋值mess1.LeftDoorState = Opened; // 值表赋值mess1.LeftWindowPosition = 50; // 值赋值mess1.RightWindowPosition = 75;// 报文输出到总线output(mess1);
}
3.2.2 定时器
定时器变量会绑定自身的定时器事件处理函数,开启定时器,经过指定时间,执行处理函数代码。
- 秒定时器:Timer
- 毫秒定时器:msTimer
variables
{// 定时器变量声明msTimer t1;
}// 定时器处理函数
On timer t1
{write("进入定时函数");// 重置定时器setTimer(t1,3000);
}
On key '1'
{// 开启定时器setTimer(t1,3000);
}
4 运算符
类似C语言。
5.代码块
6.CAPL常用内置函数(详细描述查询CANoe手册F1)
1.输出到Write窗口
- Write——输出文本到write窗口的CAPL标签页
- void write(char format[], ...);
- setWriteDbgLevel——设置调试信息的输出等级(输出到System标签页)
void setWriteDbgLevel (unsigned int priority);
- writeDbglevel——输出调试信息到write窗口的System标签页只输出满足优先级的
long writeDbgLevel(unsigned int priority, char format1[], char format2[], ...);
- writeLineEx——设置输出窗口,并配置消息状态,输出信息。
void writeLineEx(long sink, dword severity, char format[], ...)
2.总线控制函数
- stop——停止总线上的测量,停止程序运行
3.日志(logging)相关函数
先对logging模块进行配置,CAPL触发日志纪录
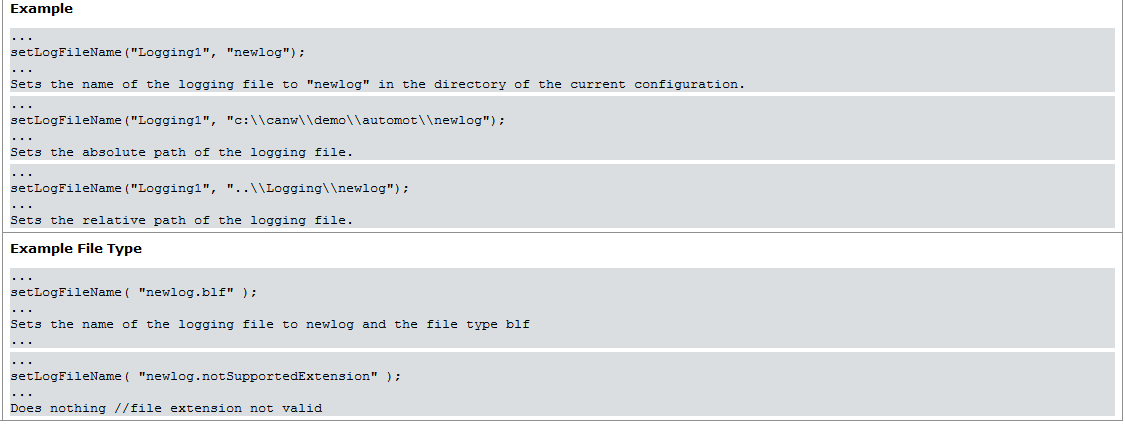
- setLogFilename——为对应日志模块设置日志文件的路径和名称
setLogFileName(char strLoggingBlockName[], char fileName[]);
- startLogging——启动日志模块的纪录
void startLogging();
void startLogging(char strLoggingBlockName[]);
void startLogging(char strLoggingBlockName[], long preTriggerTime);

- stopLogging——停止日志模块的纪录
void stopLogging();void stopLogging(char strLoggingBlockName[]);void stopLogging(char strLoggingBlockName[], long postTriggerTime);

4,定时器相关函数
- setTimer —— 设置定时器,启动定时器
void setTimer(msTimer t, long duration); // form 1
void setTimer(timer t, long duration); // form 2
variables {msTimer t1;Timer t23;
}
on key F1 {setTimer(t1, 200); // set timer t1 to 200 ms
}
on key F2 {setTimer (t23, 2); // set timer t23 to 2 sec
}
on key F3 {setTimer (t23, 0, 1250*1000 ); // set timer t23 to 1.250 milliseconds
}
on timer t1 {write("F1 was pressed 200ms ago");
}
on timer t23 {write("F2 was pressed 2 sec ago or F3 1250000 nsec ago");
}
- cancelTimer—— 取消停止定时器
void cancelTimer(msTimer t);
void cancelTimer(timer t);
4 文件读写相关代码
以读取模式打开文件
dword openFileRead (char filename[], dword mode); // form 1
dword openFileRead (char filename[], dword mode, dword fileEncoding); // form 2
已写入模式打开文件
dword openFileWrite (char filename[], dword mode); // form 1
dword openFileWrite (char filename[], dword mode, dword fileEncoding); // form 2
从文件中读取字符串
long fileGetString (char buff[], long buffsize, dword fileHandle);
输出字符串到文件中
long fileGetString (char buff[], long buffsize, dword fileHandle);
关闭文件
long fileClose (dword fileHandle);
读写例子
variables
{
msTimer writeTimer;
long glbPeriod = 250;dword glbHandle = 0;
long glbValue;
}on Start
{
char buffer[64];
long ret;//
// Opens the file in ASCII mode for read access.
//
// To determine the absolute path, the search procedure will be used.
// The file must be located in the directory of the databases or the
// configuration directory.
//
glbHandle = OpenFileRead ("Data.Txt",0);if ( glbHandle!=0 )
{//// got to end of file ...//while ( fileGetString(buffer,elcount(buffer),glbHandle)!=0 ) {};//// Get the last parameters// (saved on disk after the end of the last measurement)//glbValue = atol (buffer);write ("Last value %d.",glbValue);fileClose (glbHandle);
}
else
{write ("File 'Data.Txt' was not opened for read access.");
}
//
// Open the file in ASCII mode for write access.
//
// The write path was not set using the function setWritePath(), so
// the configuration directory will be used instead. This is the
// default behavior.
//
glbHandle = OpenFileWrite ("Data.Txt",2);if ( glbHandle!=0 )
{setTimer (writeTimer,glbPeriod);
}
else
{write ("File 'Data.Txt' was not opened for write access.");
}
}on timer writeTimer
{
long randomValue;
char buffer [64];if ( glbHandle!=0 )
{randomValue = random (32767);snprintf (buffer,elcount(buffer)," %d \n",randomValue);filePutString (buffer, elcount(buffer),glbHandle);setTimer (writeTimer,glbPeriod);
}
else
{write ("Error, invalid file handle.");
}
}on StopMeasurement
{
fileClose (glbHandle);
}
6.数学函数
参考博主:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42957717

7.其他函数
- elCount——计算数组、字符串的长度
long elcount(...) // if used with arrays which are function parameters
dword elcount(...) // in all other cases
- getLocalTimeString——获取系统当前的时间字符串
void getLocalTime(long time[]);

- snprintf——将格式化的数据写入字符串。
long snprintf(char dest[], long len, char format[], ...);
7.常用事件
1on start :程序启动事件
2.on stopMeasureMent:
程序结束事件。
3.on key * :
按键事件。
// 函数中的this 当前键值。
on key * {
switch(this) {case 'a' : ... break;case F10: ... break;...
}
4.on message 事件:
- 当在总线上发现一个指定的报文出现时,触发该事件
- 每次总线探测到这个报文,就会触发一次。
- 该事件发生,this关键字可用,代表触发此次事件的报文数据。
5.on timer 定时器变量名:
定时时间到了触发一次。
6.On signal 信号名:
信号发生变换,触发事件
7.On signal_update 信号名 :
检测到信号更新(发送),一旦更新就触发一次。
8.访问信号的值
需要任意时刻访问信号的当前值。
语法 : $ 信号名、$ 报文名:: 信号名
// 访问物理值$EngineSpeed.phys // 访问实际值$EngineSpeed.raw
