算法篇(八)【递归】
一、了解递归
1. 什么是递归?
递归就是自己调用自己
递归的概念解释起来就短短的几句话,但是写起来总是无从下手 ,但是首先要相信,在学过了数据结构 -- 树 之后 , 其实就已经具备了一定的递归思想,接下来的就是强化了!
2. 为啥会用递归呀?
本质:在处理主问题的时候,需要解决子问题,两者的处理方式完全一致。
大事化小 , 且每个子问题,子问题的子问题的解决方案都一样 !
递 --> 递推 , 归 --> 回归 !递推到终点之后,回归!!!
3.从宏观的角度看代递归!
1) 不要在意递归的细节展开图 :写完代码之后不要纠结展开之后是什么样子
2)把递归函数当成一个黑盒 : 赋予这个黑盒一个任务
3)相信这个黑盒能够帮助我们完成任务
4.如何写好一个递归:
1) 找到相同的子问题 : 确定函数的功能以及函数头的设计
2) 只关心某一个子问题是如何解决的 : 函数体
3)不能继续拆分的子问题 : 递归出口
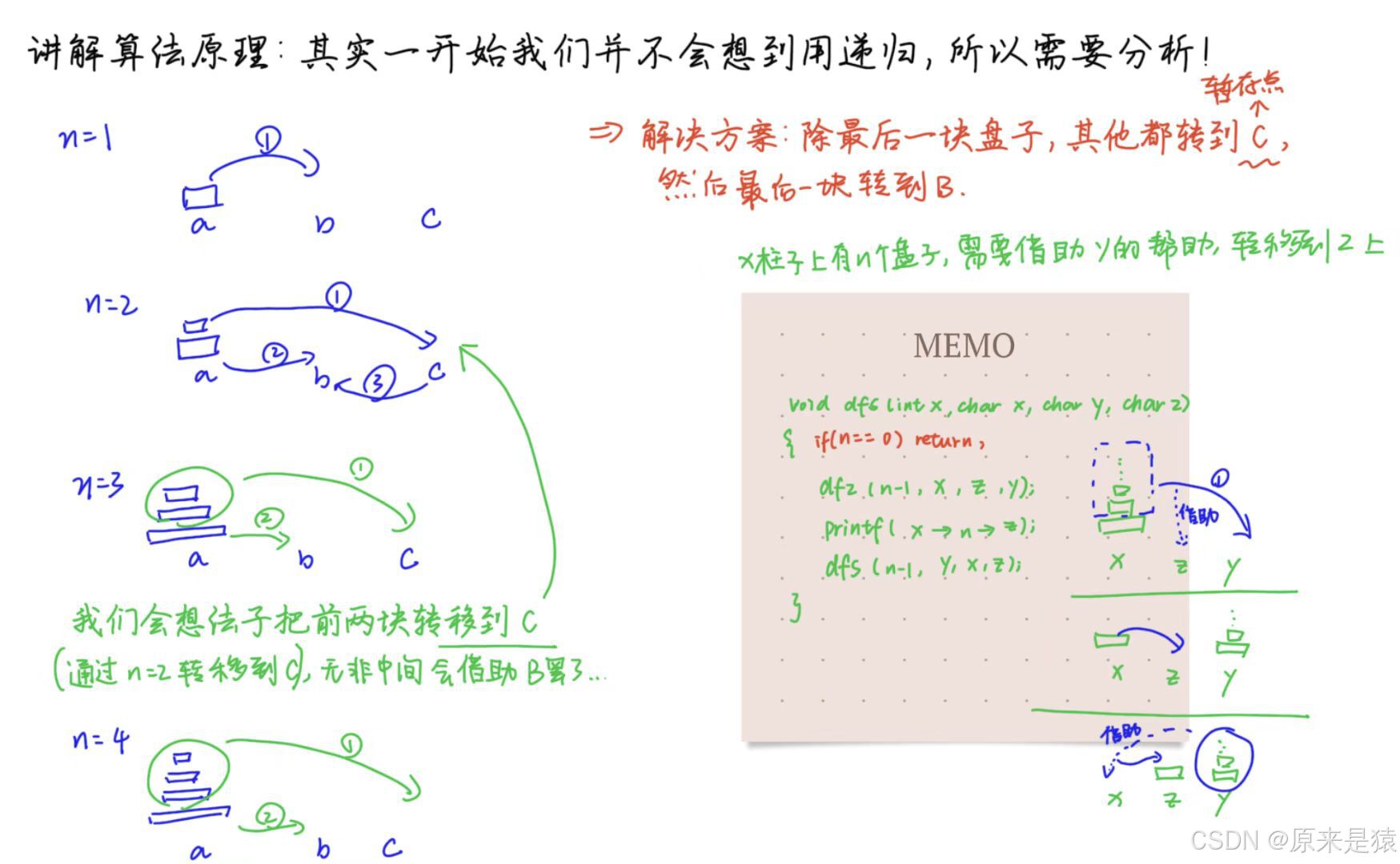
二、汉诺塔
信息学奥赛一本通(C++版)在线评测系统
具体的转移方法如果想理解的更加清楚,搜索引擎走起~

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int n;
char a,b,c;
//把x柱子上的n个盘子,借助 y 的帮助,转到z上
void dfs(int n,char x,char y ,char z)
{
if(n == 0)return;
dfs(n-1,x,z,y);
printf("%c->%d->%c\n",x,n,z);
dfs(n-1,y,x,z);
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> a >> b >> c;
dfs(n,a,c,b);
return 0;
}面试题 08.06. 汉诺塔问题 - 力扣(LeetCode)
同样的LeetCode也有相同的题:
class Solution {
public:
void hanota(vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b, vector<int>& c) {
dfs(a,b,c,a.size());
}
void dfs(vector<int>& a, vector<int>& b, vector<int>& c,int n)
{
if(n == 1)
{
c.push_back(a.back());
a.pop_back();
return;
}
dfs(a,c,b,n-1);
c.push_back(a.back());
a.pop_back();
dfs(b,a,c,n-1);
}
};题外话:如果这是一个笔试题 , 以下代码也是过的了的~
class Solution {
public:
void hanota(vector<int>& A, vector<int>& B, vector<int>& C) {
C = A;
}
};三、占卜DIY
P10457 占卜DIY - 洛谷

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 15;
int n = 13,m = 4;
int cnt[N];
int a[14][5];
void dfs(int x)
{
if(x == 13)return;
int t = a[x][cnt[x]];
cnt[x]--;
dfs(t);
}
int main()
{
//处理输入
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
cnt[i] = 4;
for(int j = 1;j <= m;j++)
{
char ch;cin >> ch;
if(ch >= '2' && ch <= '9')a[i][j] = ch -'0';
else if(ch == 'A')a[i][j] = 1;
else if(ch == 'J')a[i][j] = 11;
else if(ch == 'Q')a[i][j] = 12;
else if(ch == 'K')a[i][j] = 13;
else a[i][j] = 10;
}
}
//摸牌 - 递归处理
for(int i = 1;i<=m;i++)
{
dfs(a[n][i]);
}
int ret = 0;
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(cnt[i] == 0)ret++;
}
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}四、FBI 树
P1087 [NOIP 2004 普及组] FBI 树 - 洛谷

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 11;
int n;
int f[1<<N];
void dfs(int left,int right)
{
if(left > right) return;
//判断类型
char ret;
int sum = f[right] - f[left - 1];
if(sum == 0)ret = 'B';
else if(sum == right - left +1)ret = 'I';
else ret = 'F';
//划分区间
if(right == left)
{
cout << ret ;
return;
}
int mid = (left + right)/2;
dfs(left,mid);
dfs(mid+1,right);
cout << ret;
}
int main()
{
int n;cin >> n;
n = (1 << n);
for(int i = 1;i<=n;i++)
{
char ch;cin >> ch;
int t = 0;
if(ch == '1') t = 1;
f[i] = f[i-1] + t;
}
dfs(1,n);
return 0;
}五、能力提升题
5.1 合并两个有序链表
21. 合并两个有序链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)


/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode() : val(0), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(nullptr) {}
* ListNode(int x, ListNode *next) : val(x), next(next) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2)
{
if(l1 == nullptr) return l2;
if(l2 == nullptr) return l1;
if(l1->val <= l2->val)
{
l1->next = mergeTwoLists(l1->next,l2);
return l1;
}
else
{
l2->next = mergeTwoLists(l1,l2->next);
return l2;
}
}
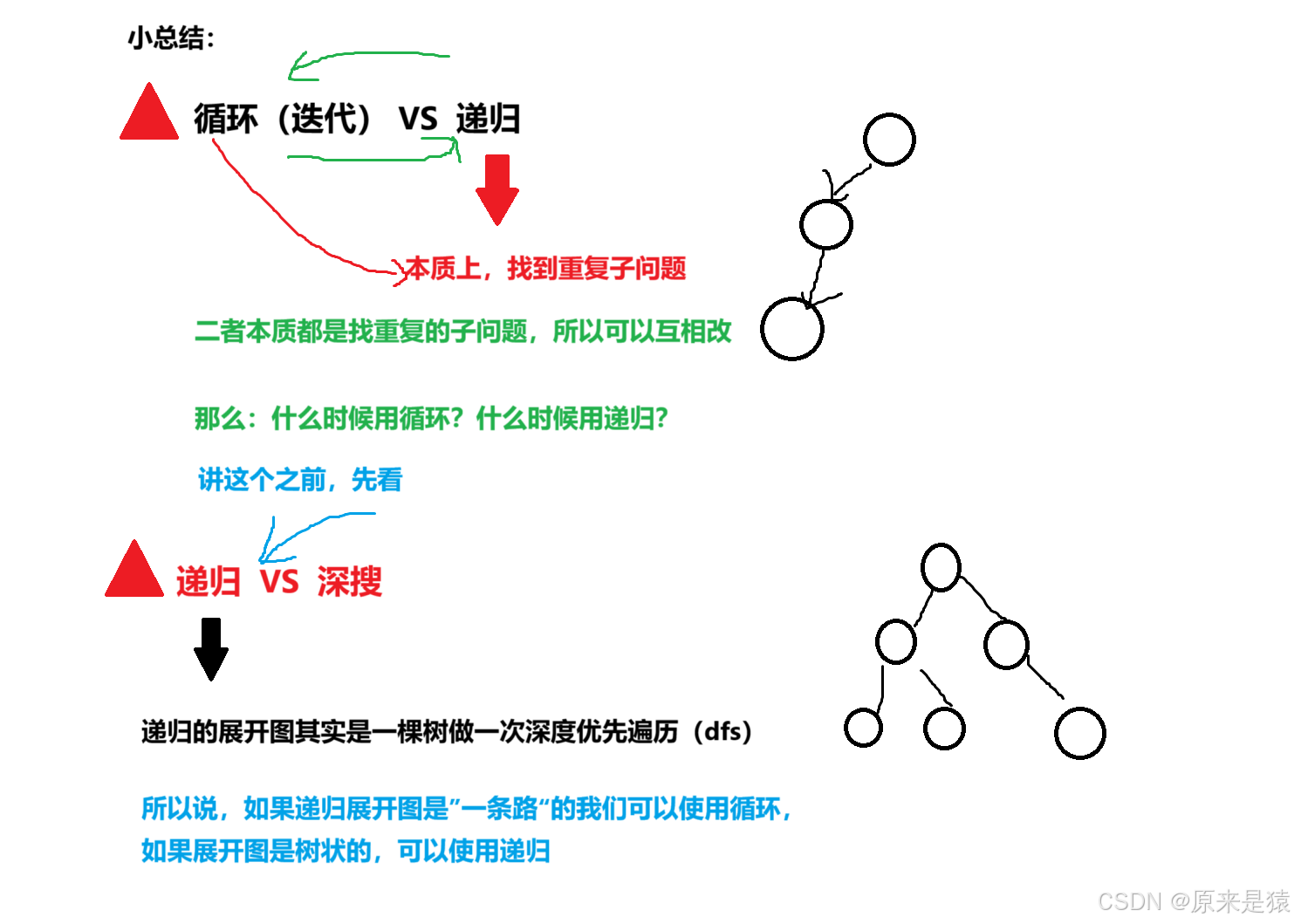
};5.2 递归VS循环 and 递归VS深搜
5.3 反转链表
206. 反转链表 - 力扣(LeetCode)
算法思路:
1)递归函数的含义:交给你一个链表的头指针,完成逆序之后,返回逆序后的头结点;
2)函数体:先把当前结点之后的链表逆序,逆序完之后,把当前结点添加到逆序后的链表即可;
3)递归出口:当前结点为空或者当前只有一个结点的时候,不用逆序,直接返回。


class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head)
{
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr) return head;
ListNode* newHead = reverseList(head->next);
head->next->next = head;
head->next = nullptr;
return newHead;
}
};
5.4 两两交换链表中的结点
24. 两两交换链表中的节点 - 力扣(LeetCode)

class Solution {
public:
ListNode* swapPairs(ListNode* head)
{
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)return head;
auto tmp = swapPairs(head->next->next);
auto ret = head->next;
head->next->next = head;
head->next = tmp;
return ret;
}
};5.5 Pow(x,n)
50. Pow(x, n) - 力扣(LeetCode)

class Solution {
public:
double myPow(double x, int n) {
return n < 0 ? 1.0/pow(x,-(long long)n):pow(x,n);
}
double pow(double x,int n)
{
if(n==0)return 1.0;
double tmp = pow(x,n/2);
return n%2==0 ? tmp*tmp : tmp*tmp*x;
}
};
