文件基础IO
参考上文中的进程控制中的进程替换,我们可以建议制作一个自己的命令行解释器,其原理如下。

1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<stdlib.h>
3 #include<assert.h>
4 #include<string.h>
5 #include<unistd.h>
6 #include<sys/types.h>
7 #include<sys/wait.h>
8
9 #define NUM 64
10 #define OP_NUM 64
11
12 char buff[NUM];
13 char* commande[OP_NUM];
14
15 int main(){
16 while(1){
17 printf("用户名@主机名 当前路径#");
18 //获取用户输入
W> 19 char* tmp = fgets(buff,sizeof(buff)-1,stdin);//fgets meet \n end,then add \0 on end
20 buff[strlen(buff)-1]=0;
21 assert(tmp);
22 //拆分命令
23 commande[0] = strtok(buff," ");
24 int i = 0;
W> 25 while(commande[++i]=strtok(NULL," "));
26 //fork execut
27 pid_t id = fork();
28 if(id == 0){
29 execvp(commande[0],commande);
30 exit(1);
31 }
32 int status = 0;
33 waitpid(id,&status,0 );
34 }
35 // for(int j = 0 ; j < i ; j++ ){
36 // printf("%s\n",commande[j]);
37 // }
38
39 return 0;
40 }
1.进程工作路径,内建命令
1.1问题引入
当在myshell进程中先输入pwd,再输入cd..,最后输入pwd时发现当前路径并没有改变。发生这个现象的原因是什么呢?
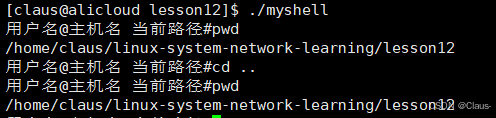
1.2 工作路径
当已经程序加载进内存时,其默认的工作路径就是当前路径,我们在/proc下可以看到进程的cwd,就是其工作路径,我们可以使用chdir改变进程的工作路径。

1.3问题解答
我们的shell在执行命令时是靠fork后的子进程进行执行的,当我们cd..后,改变的是子进程的工作目录,而父进程的工作目录并没有改变,所有使用pwd时未改变。
我们就可以改进我们的shell,使其支持cd..。其原理是不创建子进程,而是直接chdir,改变父进程的工作目录。
我们之前的echo实际上也是内建命令,例如echo $?只是在全局多了个变量存储上个子进程的退出码而已。
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<stdlib.h>
3 #include<assert.h>
4 #include<string.h>
5 #include<unistd.h>
6 #include<sys/types.h>
7 #include<sys/wait.h>
8 #include<unistd.h>
9
10 #define NUM 64
11 #define OP_NUM 64
12
13 char buff[NUM];
14 char* commande[OP_NUM];
15
16 int exit_sig = 0;
17 int exit_code = 0;
18
19 int main(){
20 while(1){
21 printf("用户名@主机名 当前路径#");
22 //获取用户输入
W> 23 char* tmp = fgets(buff,sizeof(buff)-1,stdin);//fgets meet \n end,then add \0 on end
24 buff[strlen(buff)-1]=0;
25 assert(tmp);
26 //拆分命令
27 commande[0] = strtok(buff," ");
28 int i = 0;
W> 29 while(commande[++i]=strtok(NULL," "));
30 //fork execut
31 if(strcmp(commande[0],"cd")==0){
32 chdir(commande[1]);
33 continue;
34 }
35 if(strcmp(commande[0],"echo")==0){
36 if(commande[1] != NULL &&strcmp(commande[1],"$?")==0){
37 printf("exit_sig is:%d,exit_code is:%d \n",exit_sig,exit_code);
38 }else if (commande[1] != NULL){
39 printf("%s\n",commande[1]);
40 }
41 continue;
42 }
43 pid_t id = fork();
44 if(id == 0){
45 execvp(commande[0],commande);
46 exit(1);
47 }
48 int status = 0;
49 waitpid(id,&status,0 );
50 exit_sig = status&0x7f;
51 exit_code = (status>>8)&0xff;
52 }
53 // for(int j = 0 ; j < i ; j++ ){
54 // printf("%s\n",commande[j]);
55 // }
56
57 return 0;
58 }
2.重谈文件
文件=文件内容+文件属性。对文件的操作实际上就是进程对文件内容和属性的操作。一个文件要被访问首先就要打开它。不同的语言有不同的库接口对文件操作,但是本质上都是对系统调用接口的封装。
2.1C语言库对文件的操作
2.1.1打开文件fopen

注意的是用w打开文件时,会默认清空文件信息。
2.1.2写入文件fwrite

1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<stdlib.h>
3
4 int main(){
5 FILE* fd = fopen("myfile","w");
6 if(fd == NULL){
7 perror("fopen");
8 exit(1);
9 }
10 char buff[]="claus is me\n";
11 fwrite(buff,sizeof(char),sizeof(buff)-1,fd);
12 fclose(fd);
13
14 return 0;
15 }
2.1.3读文件fread

1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<stdlib.h>
3 int main(){
4
5 FILE* fd = fopen("myfile","r");
6 if(fd == NULL ) exit(1);
7 char buff[64];
8 fread(buff,sizeof(char),sizeof(buff)-1,fd);
9
W> 10 printf(buff);
11 fclose(fd);
12 return 0;
13 }
2.1.4关闭文件fclose

2.1.5其他流输入输出
fgets(从流中获取)
具体将fgets就是读取一行字符(遇到\n),之后会在buff后加上\0,然后返回
fputs(放置在流中)

puts(放置数据到stdout中,会自动\n)

gets一般不使用,因为其有溢出的风险。
fprintf

sprintf

2.2linux系统对文件的操作
2.2.1打开文件open

值得注意的是,C语言对文件的操作是对系统调用接口的封装,因此C引用的返回的FILE*结构体中必然包含fd文件标识符返回值。
2.2.2写入文件write

2.2.3关闭文件close

例子:
1 #include<sys/types.h>
2 #include<sys/stat.h>
3 #include<fcntl.h>
4 #include<string.h>
5 #include<unistd.h>
6
7 const char* FILENAME = "text.txt";
8
9 int main(){
10 umask(0000);
11 int fd = open(FILENAME,O_WRONLY | O_CREAT,0666);
12 const char* buff = "hello claus 111";
13 write(fd,buff,strlen(buff)-1);
14 close(fd);
15
16 return 0;
17 }
2.2.4读文件read

1 #include<sys/types.h>
2 #include<sys/stat.h>
3 #include<fcntl.h>
4 #include<unistd.h>
5 #define MAXBUFF 1024
6 const char* FILENAME = "text.txt";
7 char buff[MAXBUFF]= {0};
8
9 int main(){
10 int fd = open(FILENAME,O_RDONLY);
11 ssize_t ret = read(fd,buff,MAXBUFF);
12 buff[ret] = 0;
12 write(1,buff,ret);
13 return 0;
14 }
值得注意的系统接口从fd读取数据到buffer后不会添加\0结尾,需要我们手动添加\0
2.3.对被打开文件的管理
一个进程可以打开多个文件,那么我们的系统中一定有大量被打开的文件,OS需要对其进行管理,管理的方法无非就是先描述再组织
2.3.1对文件的描述与组织
在linux系统中的进程pcb中存在着一个struct files_struct *files,指向files_struct结构体,其中包含着一个文件描述符表
struct file * fd_array[NR_OPEN_DEFAULT];这是一个结构体指针数组,元素对象指向file结构体,这是对某个具体的文件的描述,其中包含着文件的属性等信息。

文件描述符表中的数组下标对应的就是该文件的fd。
在C语言层面上,会默认打开三个接口stdin,stdout,stderro。其文件描述符对应的就是0,1,2.
这上个接口都是指向FILE*的指针,其中就包含有fd
1 #include<stdio.h>
2 #include<sys/types.h>
3 #include<sys/stat.h>
4 #include<fcntl.h>
5 #include<unistd.h>
6
7 int main(){
8 printf("fd of stdin:%d\n",stdin->_fileno);
9 printf("fd of stdout:%d\n",stdout->_fileno);
10 printf("fd of stderro:%d\n",stderr->_fileno);
11 return 0;
12 } 
2.3.2文件描述符fd的分配规则
文件描述符fd,按照从小到大依次安排。例如如果stdin被关闭,那么fd0空闲出来,那么新打开的文件分配的fd就会是0;
2.4重定向
我们就可以利用上面的操作干一些事情:例如我们可以先将fd0关闭,然后再打开一个文件,那么它就会被分配1这个文件标识符,但是其他接口任然会默认1号为stdout,向其输出数据,实际上是被新打开的文件接收,这也叫重定向。
所有重定向的本质是:上传的fd不变,只是改变fd所对应的struct file*结构体。
linux系统为我们提供了dup2接口

2.4.1输出重定向
1 #include<sys/types.h>
2 #include<sys/stat.h>
3 #include<fcntl.h>
4 #include<unistd.h>
5 #include<stdio.h>
6
7 int main(){
8
9 int fd = open("mytext",O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0666);
10
11 dup2(fd,1);
12
13 printf("this is text of dup2");
14
15 close(fd);
16
17
18 return 0;
19 }
~
如上的小demo代码就是输出重定向,将stdout重定向为fd,原本输出到stdout中的数据输出到了fd中。
2.4.2追加重定向
我们只需要将打开文件的方式变为O_APPEND,重复上述代码就是追加重定向
1 #include<sys/types.h>
2 #include<sys/stat.h>
3 #include<fcntl.h>
4 #include<unistd.h>
5 #include<stdio.h>
6
7 int main(){
8
9 int fd = open("mytext",O_WRONLY|O_APPEND);
10
11 dup2(fd,1);
12
13 printf("\nthis is append text of dup2\n");
14
15 close(fd);
16
17
18 return 0;
19 }
2.4.3输入重定向
输入重定向就是将文件的内容当做为stdin的内容输入给buffer。
1 #include<sys/types.h>
2 #include<sys/stat.h>
3 #include<fcntl.h>
4 #include<unistd.h>
5 #include<stdio.h>
6
7 int main(){
8 int fd = open("mytext",O_RDONLY);
9 dup2(fd,0);
10 char buffer[1024]={0};
11 while(1){
12 char* tmp = fgets(buffer,sizeof(buffer),stdin);
13 if(tmp==NULL) break;
14 printf("%s",buffer);
15 }
16 close(fd);
17 return 0;
18 }
