Spring AOP(教科书式的教程)
目录
核心概念
通知类型
前置通知
环绕通知
异常通知
后置通知
返回通知
通知参数
通知顺序
实现Ordered接口
使用@Order注解
定义点切入
点切入代号
点切入表达式
组合点切入表达式
共享点切入表达式
同类共享
分离共享
完全共享
使用AOP功能
创建项目
创建目标对象
controller.HelloController
controller.UserController
使用五种通知类型
创建切面类
启动当前项目
访问控制器接口
测试异常返回后通知
测试其他点切入代号
AopTarget
Pointcuts
AOP(Aspect-oriented Programming,面向切面编程)是Spring框架的核心特性之一。
AOP允许在方法[之前、之后、之前和之后、抛出异常时、方法返回后]插入一段代码。
AOP使用了软件设计模式中的代理模式,插入代码的工作由AOP生成的代理对象完成。
核心概念
AOP中的几个重要的概念:
-
连接点(Join point):可以简单理解为被插入代码的方法(方法的执行时机)
-
切面(Aspect):通常指切面类,定义连接点的类
-
通知(Advise):在连接点中插入代码
-
点切入(Pointcut):用于匹配连接点的断言,通常指点切入表达式,就是符合一定规则的字符串
-
编织(Weaving):将切面和和其他应用程序类型或对象连接起来,这个是由AOP框架完成的,与我们程序员无关
-
目标对象(Target object):又叫做通知对象,指的是被插入代码的类的实例
-
AOP代理对象(AOP proxy):AOP框架创建的代理对象,用于实现通知的执行
通知类型
Spring AOP中包含了以下5种通知类型,对应不同的方法执行时机。
下文中会出现一些概念:
通知方法:使用AOP的通知注解的方法(比如@Before)
目标方法:指的就是连接点对应的方法,定义目标方法的类叫做目标对象。
前置通知
使用@Before注解定义前置通知。
@Before(value = "点切入表达式")
public void before() {
}前置通知是在连接点之前运行的通知,但不能阻止执行流进入连接点(除非抛出异常)。
“不能阻止执行流进入连接点”指的是在通知方法上通过return关键字返回一个值,并不能阻止目标方法的执行。
环绕通知
使用@Around注解定义环绕通知。
@Around(value = "点切入表达式")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("执行around()前...");
Object data = joinPoint.proceed(); // 执行点切入方法
System.out.println("方法的返回值:" + data);
System.out.println("执行around()后...");
return data;
}环绕通知是围绕连接点(在连接点之前和之后)运行的通知。
定义环绕通知的方法必须要定义一个ProceedingJoinPoint类型的参数,通过其proceeds()方法调用目标方法。
异常通知
通过@AfterThrowing注解定义抛出异常后通知。
定义抛出异常后通知时,可以通过@AfterThrowing注解的throwing属性绑定方法抛出的异常对象。
只需要参数名称和throwing属性的值保持一致即可完成绑定。
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "点切入表达式", throwing = "e")
public void afterThrowing(Exception e) {
// 访问方法抛出的异常对象e
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
System.out.println("执行afterThrowing()...");
}抛出异常后通知是在方法抛出异常退出时运行的通知,这个通知类似catch关键字的作用,只要方法运行时抛出了异常,就会执行这个通知的代码。
后置通知
通过@After注解定义抛出异常后通知。
后置通知又叫最终通知,无论连接点以何种方式退出(正常或特殊返回),都要运行通知。
@After(value = "点切入表达式")
public void after() {
System.out.println("执行after()...");
}这个通知类似finally关键字的作用,即使方法运行时因为抛出异常而退出,也会执行这个通知的代码。
返回通知
使用@AfterReturning注解定义方法返回后通知。
定义方法返回后通知时,可以通过@AfterReturning的returning属性将方法的返回值绑定到通知参数上。
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "点切入表达式", returning = "returnValue")
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue) {
// 访问方法的返回值returnValue
}在方法正常返回后运行的通知,如果方法运行过程中抛出了异常,这个通知不会被执行。
通知参数
所有通知类型的方法上都可以使用JoinPoint接口作为第一个参数。
环绕通知@Around的方法参数ProceedingJoinPoint就是JoinPoint接口的一个派生类。
JoinPoint这个接口中定义了几个常用的方法:
package org.aspectj.lang;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.SourceLocation;
public interface JoinPoint {
/**
* 获取连接点方法的参数
*/
Object[] getArgs();
/**
* 返回AOP代理对象
*/
Object getThis();
/**
* 获取目标对象
*/
Object getTarget();
/**
* 获取连接点方法的签名
* 通过方法签名Signature可以获取方法和它所在的类的信息
*/
Signature getSignature();
}通过Signature对象,可以获取目标对象的类的信息(类对象)
package cn.edu.sgu.www.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.Signature;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Arrays;
/**
* @author heyunlin
* @version 1.0
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class CustomAspect {
@Before(value = "execution(public * cn.edu.sgu.www.controller.*.*(..))")
public void before(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("方法的参数:" + Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
Signature signature = joinPoint.getSignature();
System.out.println(signature.getDeclaringType());
System.out.println("执行before()...");
}
}我们可以通过点切入代号args匹配参数名称,然后在通知方法的参数上声明参数的类型,这样我们就能获取到方法的参数。
@After("点切入表达式 && args(name,..)")
public void after(String name) {
// ...
}共享点切入的写法
@Pointcut("点切入表达式 && args(name,..)")
private void pointcut(String name) {}
@After(value = "pointcut(name)", argNames = "name")
public void after(String name) {
// ...
}通知顺序
当一个项目中有多个切面类时,如果一个方法被多个切面切入,可以自定义多个切面类的切入顺序。
实现Ordered接口
让切面类实现org.springframework.core.Ordered接口,重写getOrder()方法,返回一个数字。
指定的数字越小,越先被执行。
package cn.edu.sgu.www.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author heyunlin
* @version 1.0
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class CustomAspect implements Ordered {
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
}使用@Order注解
在切面类上使用@Order注解的value属性指定顺序;指定的数字越小,越先被执行。
package cn.edu.sgu.www.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author heyunlin
* @version 1.0
*/
@Order(value = 0)
@Aspect
@Component
public class CustomAspect {
}定义点切入
点切入代号
点切入代号(Pointcut Designators,PCD)是点切入表达式的一部分。
Spring AOP支持在点切入表达式中使用以下代号: 经测试@target和@within的作用是一样的。
| 点切入代号 | 代号说明 |
|---|---|
| execution | 用于匹配方法执行连接点。 |
| within | 限制匹配有特定类型的连接点(可以指定多个类型)。 |
| this | 限制匹配Spring AOP代理对象是指定类型的实例的连接点。 |
| target | 限制匹配目标对象是指定类型的实例的连接点。 |
| args | 限制匹配参数是指定类型的实例的连接点。 |
| bean | 限制匹配指定名称的Spring Bean的连接点(可以使用通配符) |
| 点切入代号 | 代号说明 |
|---|---|
| @args | 将匹配限制在实际传递参数的运行时类型具有给定类型注解的连接点。 |
| @target | 限制匹配到执行对象(方法)的类具有给定类型注解的连接点。 |
| @within | 将匹配限制在具有给定注解的类型中的连接点。 |
| @annotation | 将匹配限制在连接点的主题(连接点方法)具有给定注解的连接点。 |
有些代号需要组合使用,否则项目会让启动失败:args、@args、@target
点切入表达式
定义点切入需要指定点切入表达式,点切入表达式是用来表示一个或多个方法的模式匹配符,类似正则表达式。
点切入代号([访问修饰符] 返回值类型 类的全限定名.方法名(参数列表))点切入表达式中可以使用通配符:
| 通配符 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| * | 匹配任意一个包名、类名,访问修饰符不能用* |
| (*) | 匹配任意一个参数 |
| (..) | 匹配任意多个参数 |
组合点切入表达式
在定义点切入表达式时,可以使用&&、||和!来连接多个点切入表达式。
共享点切入表达式
点切入表达式可以通过方法指定,供其他通知使用。
同类共享
可以通过@Pointcut注解实现点切入表达式的共享。
@Pointcut("execution(public * cn.edu.sgu.www.controller.*.*(..))")
public void pointcut() {
}
@Before("pointcut()")
public void before() {
}分离共享
点切入甚至可以放在一个单独的类中
public class Pointcuts {
@Pointcut("execution(public * cn.edu.sgu.www.controller.*.*(..))")
public void pointcut() { }
}然后在切面类中,指定点切入表达式时,在前面加上保存点切入的类的全限定名。
@Before("Pointcuts.pointcut()")
public void before() {
}如果切面类和定义点切入的类在同一个包下,可以不指定类的包名(如上代码)。
完全共享
当使用PCD组合符时,可以将每个点切入表达式都分开定义(这是使用AOP的最佳实践)。
public class Pointcuts {
@Pointcut("execution(public * cn.edu.sgu.www.controller.*.*(..))")
public void executionPointcut() { }
@Pointcut("args(String, ..)")
public void argsPointcut() { }
/**
* 完全分离点切入表达式
*/
@Pointcut(executionPointcut() && argsPointcut())
public void pointcut() { }
}使用AOP功能
创建项目
在Intellij IDEA中创建一个springboot项目springboot-aop
添加依赖
修改pom.xml文件,添加aspectj的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.6</version>
</dependency>或者添加Spring Boot整合AOP的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>完整的pom.xml文件的内容
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath />
</parent>
<groupId>cn.edu.sgu.www</groupId>
<artifactId>springboot-aop</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>springboot-aop</name>
<description>Spring Boot整合AOP案例项目</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.6</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>创建目标对象
创建两个控制器类,用来测试AOP。
两个控制器类除了类名和路径不一样,其他都没什么区别。
controller.HelloController
package cn.edu.sgu.www.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author heyunlin
* @version 1.0
*/
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "Hello World!";
}
@GetMapping("/greet")
public String greet(@RequestParam String name) {
return "Hello " + name + "!";
}
}controller.UserController
package cn.edu.sgu.www.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
/**
* @author heyunlin
* @version 1.0
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "Hello World!";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/greet", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String greet(@RequestParam String name) {
return "Hello " + name + "!";
}
}使用五种通知类型
创建切面类
创建切面类aop.CustomAspect来测试上面介绍的5种通知类型。
通过点切入表达式execution(public * cn.edu.sgu.www.controller.*.*(..))匹配cn.edu.sgu.www.controller包下的所有类的所有方法。
package cn.edu.sgu.www.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author heyunlin
* @version 1.0
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class CustomAspect {
@Before("execution(public * cn.edu.sgu.www.controller.*.*(..))")
public void before() {
System.out.println("执行before()...");
}
@Around("execution(public * cn.edu.sgu.www.controller.*.*(..))")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("执行around()前...");
Object data = joinPoint.proceed(); // 执行目标对象的方法
System.out.println("执行around()后...");
return data;
}
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "execution(public * cn.edu.sgu.www.controller.*.*(..))", throwing = "e")
public void afterThrowing(Exception e) {
// 访问方法抛出的异常对象e
System.out.println("异常提示信息:" + e.getMessage());
System.out.println("执行afterThrowing()...");
}
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "execution(public * cn.edu.sgu.www.controller.*.*(..))", returning = "returnValue")
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue) {
// 访问方法的返回值returnValue
System.out.println("方法的返回值:" + returnValue);
System.out.println("执行afterReturning()...");
}
@After("execution(public * cn.edu.sgu.www.controller.*.*(..))")
public void after() {
System.out.println("执行after()...");
}
}启动当前项目
启动项目,此时项目的结构如下
访问控制器接口
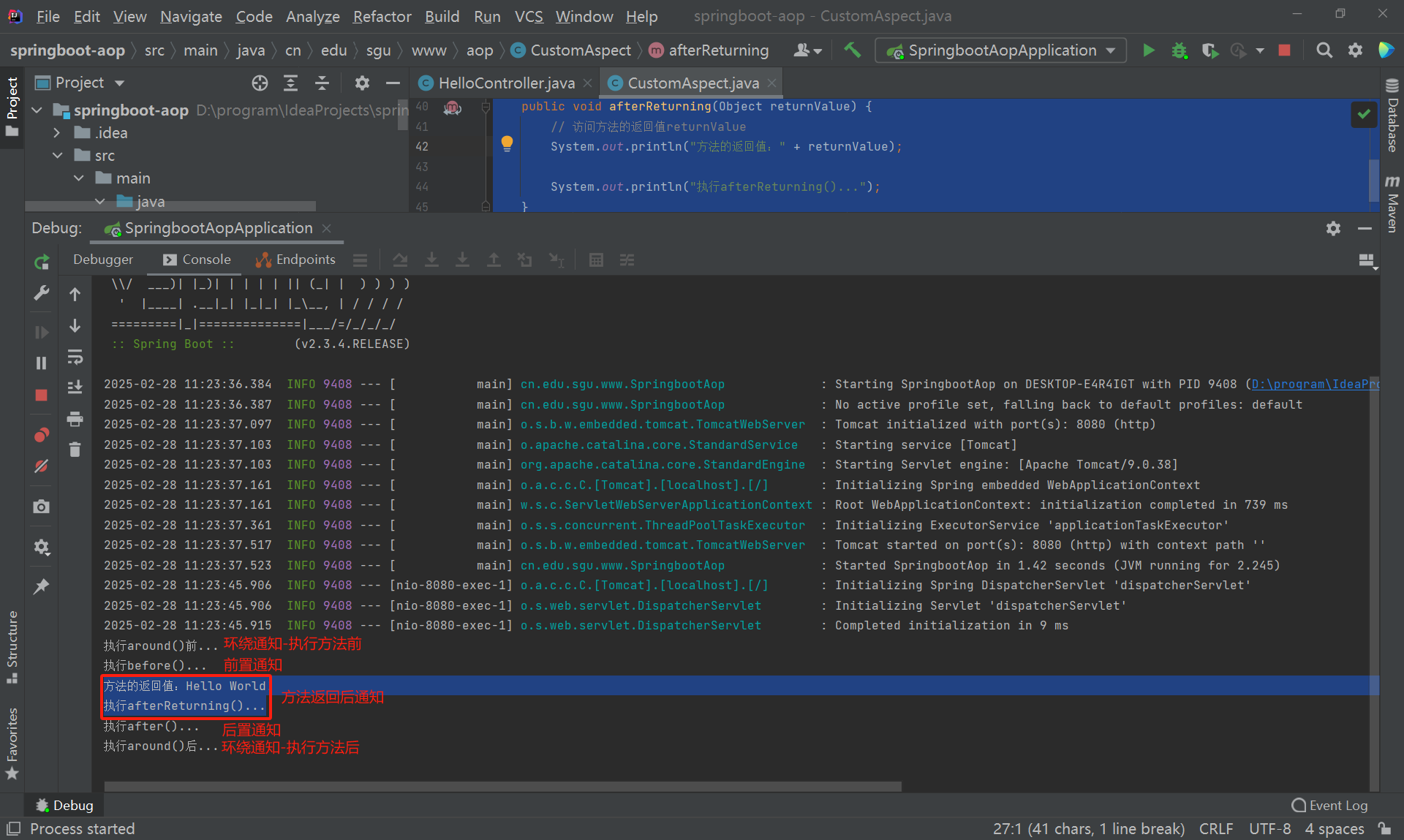
访问HelloController或UserController中的hello()方法。
localhost:8080/hello

然后在Intellij IDEA的控制台中,可以看到执行了所有(除了异常返回后)通知的代码。
测试异常返回后通知
修改HelloController的greet()方法,通过null对象调用方法主动产生一个空指针异常。
package cn.edu.sgu.www.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author heyunlin
* @version 1.0
*/
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "Hello World!";
}
@GetMapping("/greet")
public String greet(@RequestParam String name) throws InterruptedException {
// 主动产生NPE
Object obj = null;
obj.wait();
return "Hello " + name + "!";
}
}重启项目,访问HelloController的greet()方法。
localhost:8080/greet?name=Tom
可以看到浏览器给我们显示了500状态码,因为这个接口的方法运行时抛出了NullPointException。
并且我们没有通过try...catch...语句块处理异常。

通过控制台可以看到,已经执行了异常抛出时的通知。

将切面类的点切入表达式共享
package cn.edu.sgu.www.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* @author heyunlin
* @version 1.0
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class CustomAspect {
@Pointcut("execution(public * cn.edu.sgu.www.controller.*.*(..))")
public void pointcut() { }
@Before("pointcut()")
public void before() {
System.out.println("执行before()...");
}
@Around("pointcut()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("执行around()前...");
Object data = joinPoint.proceed(); // 执行目标对象的方法
System.out.println("执行around()后...");
return data;
}
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "pointcut()", throwing = "e")
public void afterThrowing(Exception e) {
// 访问方法抛出的异常对象e
System.out.println("异常提示信息:" + e.getMessage());
System.out.println("执行afterThrowing()...");
}
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "pointcut()", returning = "returnValue")
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue) {
// 访问方法的返回值returnValue
System.out.println("方法的返回值:" + returnValue);
System.out.println("执行afterReturning()...");
}
@After("pointcut()")
public void after() {
System.out.println("执行after()...");
}
}测试其他点切入代号
AopTarget
创建自定义注解类annotation.AopTarget,用于测试@开头的PCD
因为要在类、方法、方法的参数上使用@AopTarget注解,所以就指定可以在这个三个地方使用。
package cn.edu.sgu.www.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @author heyunlin
* @version 1.0
*/
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.PARAMETER})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface AopTarget {
}Pointcuts
创建aop.Pointcuts类保存所有点切入,用于测试所有点切入代号。
package cn.edu.sgu.www.aop;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
/**
* @author heyunlin
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Pointcuts {
@Pointcut("execution(public * cn.edu.sgu.www.controller.*.*(..))")
public void pointcut() { }
/**
* 匹配bean名称为helloController的类下所有方法(HelloController)
* bean代号中也可以可以使用通配符:
* bean(*)匹配所有bean
* bean(hello*)匹配所有bean名称以hello开头的所有bean
* bean(*Controller)匹配bean名称以Controller结尾的所有bean
*/
@Pointcut("bean(helloController)")
public void beanPointcut() { }
/**
* 匹配HelloController下的所有方法(AOP代理对象是HelloController类型)
*/
@Pointcut("this(cn.edu.sgu.www.controller.HelloController)")
public void thisPointcut() { }
/**
* 匹配HelloController下的所有方法(目标对象是HelloController类型)
*/
@Pointcut("target(cn.edu.sgu.www.controller.HelloController)")
public void targetPointcut() { }
/**
* 匹配通过组合符||连接的所有类下的所有方法
*/
@Pointcut("within(cn.edu.sgu.www.controller.HelloController || cn.edu.sgu.www.controller.UserController)")
public void withinPointcut() { }
/**
* 匹配只有一个String类型参数的方法
* args代号的断言中要使用类的全限定名,java.lang包下的类可以不指定包名
*/
@Pointcut("pointcut() && args(java.lang.String)")
public void argsPointcut() { }
/**
* 匹配参数的类型上使用了@AopTarget注解的所有方法
* 在HelloController/UserController类的greet方法的参数的类型上使用@AopTarget注解进行测试
*/
@Pointcut("pointcut() && @args(cn.edu.sgu.www.annotation.AopTarget)")
public void args_Pointcut() { }
/**
* 匹配使用了@AopTarget注解的所有类的所有方法
* 在HelloController/UserController类上使用@AopTarget注解进行测试
*/
@Pointcut("pointcut() && @within(cn.edu.sgu.www.annotation.AopTarget)")
public void within_Pointcut() { }
/**
* 匹配使用了@AopTarget注解的所有类的所有方法(同@within)
* 在HelloController/UserController类使用@AopTarget注解进行测试
*/
@Pointcut("pointcut() && @target(cn.edu.sgu.www.annotation.AopTarget)")
public void target_Pointcut() { }
/**
* 匹配使用了@AopTarget注解的所有方法
* 在HelloController/UserController类的方法上使用@AopTarget注解进行测试
*/
@Pointcut("pointcut() @annotation(cn.edu.sgu.www.annotation.AopTarget)")
public void annotation_Pointcut() { }
}具体测试的方法就是修改CustomAspect的pointcut方法上的点切入表达式为Pointcuts.方法名()

这样就可以轮流使用点切入类Pointcuts下的所有点切入表达式去匹配不同的连接点了~
文章代码已经上传到gitee,有需要的可以去下载~
Spring Boot整合AOP案例项目![]() https://gitee.com/muyu-chengfeng/springboot-aop.git
https://gitee.com/muyu-chengfeng/springboot-aop.git
创作不易,如果看完之后觉得文章对你有帮助,或者觉得博主写的很好,不要忘了点赞+收藏哦~
